Unit 3 - Cell Energy
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Metabolism
All the combined chemical reactions of an organism. Manages the material and energy resources of the cell
Catabolic Pathway
The release of energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler compounds. An example includes digestion
Anabolic Pathway
consume energy to build complicated molecules from simpler ones. An example is linking together amino acids to form muscle protein(monomers to polymers)
Energy
The capacity to do work
Kinetic energy
the energy of moving objects
chemical potential energy
The energy stored in the chemical bonds of molecules.
electrical potential energy
the energy available when you have an electrical gradient across a semipermeable membrane
Thermodynamics
study of energy transformations that occur in matter.
1st law of thermodynamics
states that the energy of the universe is constant and that energy can be transferred an transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
2nd law of thermodynamics
every energy transfer increases entropy, or the amount of heat loss/disorder or randomness
Free Energy
usable energy available for an organism to do work (ΔG)
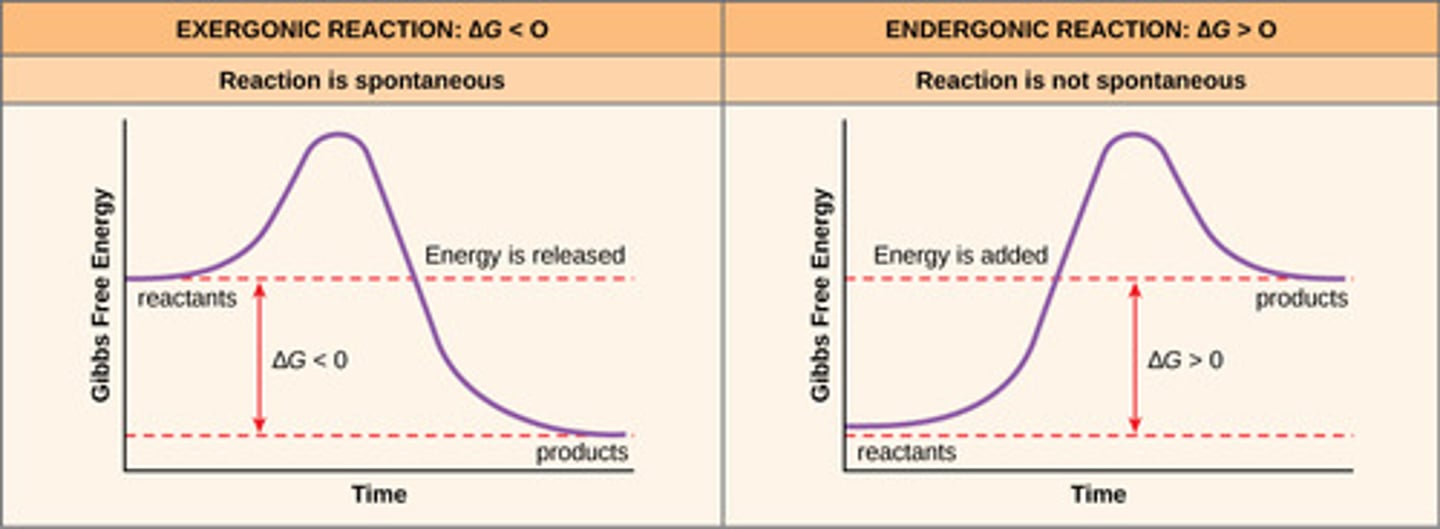
Exergonic Reaction
chemical reaction that releases free energy
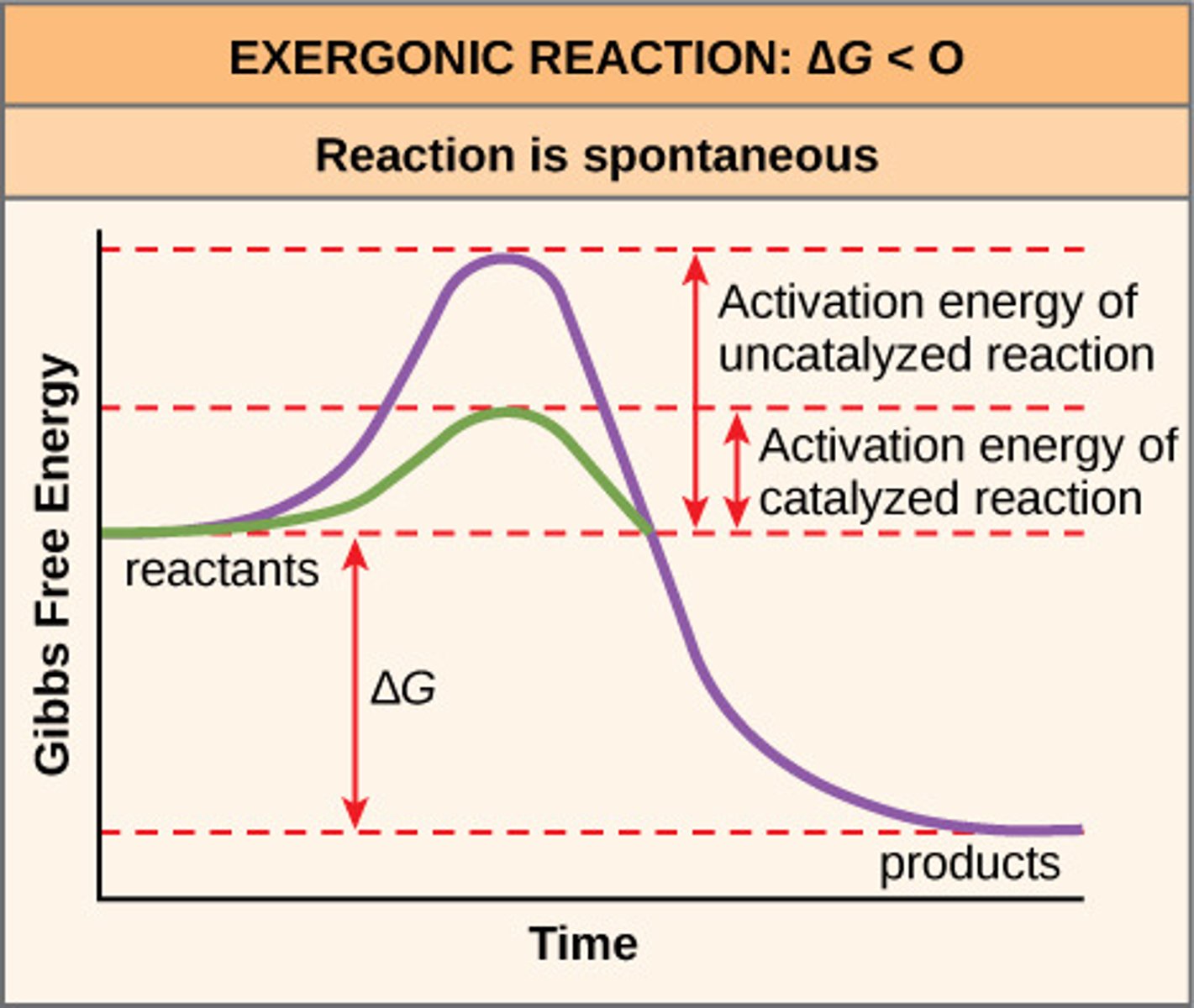
Endergonic Reaction
chemical reaction that absorbs free energy; that is they require the investment of free energy
Energy Coupling
Using an exergonic reaction to power an endergonic reaction
ATP
Adenine Triphosphate. They are molecules that deliver immediately available energy to run cellular processes(mitosis, active transport, etc.) Most biological energy consuming processes have an ATPase attached.
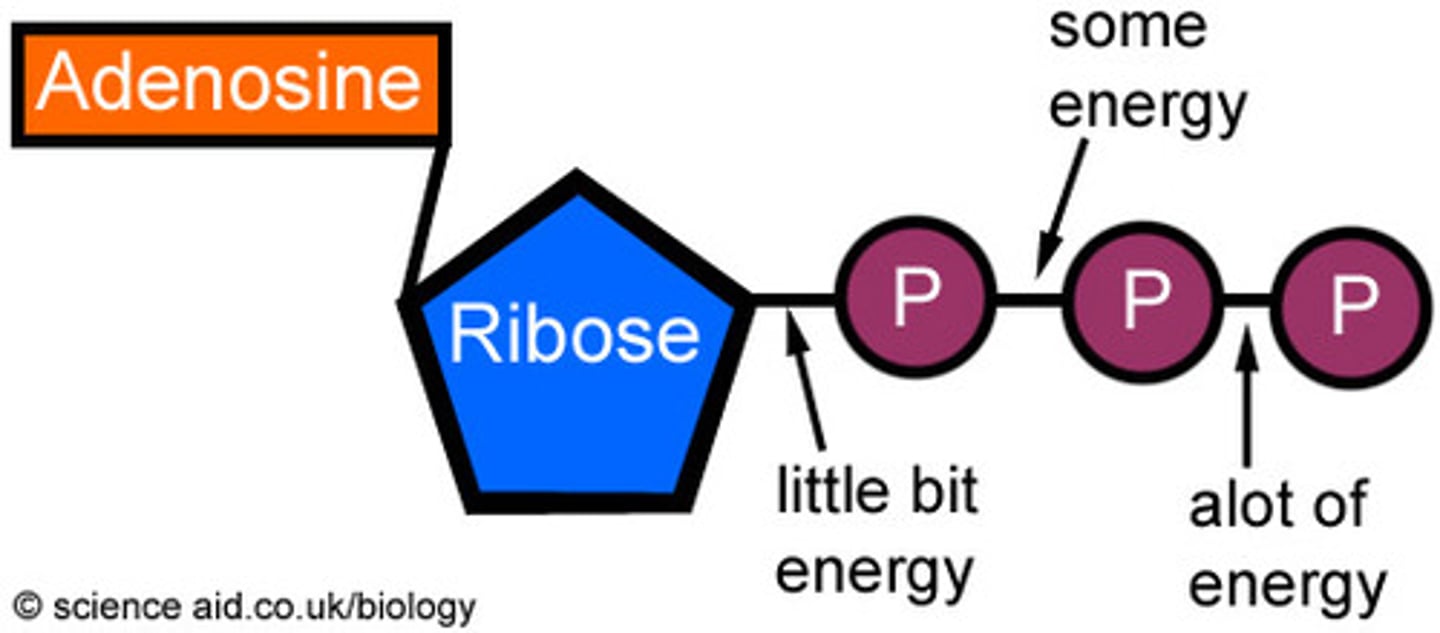
Phosphates
Phosphate groups are negatively charged. They are often added (phosphorylation) or removed (dephosphorylation) to manipulate free energy in a living system.
ATPase
An enzyme (protein) that catabolizes ATP into ADP and phosphate.
ATP synthase
An enzyme (protein) that anabolizes ATP using the flow of H+ ions to bind ADP and a phosphate group together.
Feedback Inhibition
When the end products of long metabolic pathways become allosteric inhibitors . Increases the efficiency of the pathway by turning it off when the end product accumulates in the cell
fermentation (anaerobic respiration)
The partial degradation of sugars that occur without the use of oxygen
Aerobic Respiration
the most prevalent and efficient catabolic pathway in which oxygen is consumed as a reactant along with organic fuel(most commonly glucose but other foods are sources)
Redox Reactions
Oxidation and reduction reactions (LEO says GER) coupled to transfer electrons (energy) in a chemical reaction.
Reduction
Reactants gain of one or more electrons (energy). They typically lose O and add H. [GER]
Oxidation
the loss of one or more electrons (energy) from a reactant. They typically lose H and gain O. [LEO]
NAD+ and NADH
NAD+ is a derivative of the B vitamin Niacin. It gains two electrons plus the stabilizing hydrogen ion to form NADH(it is reduced, therefore has gained energy)
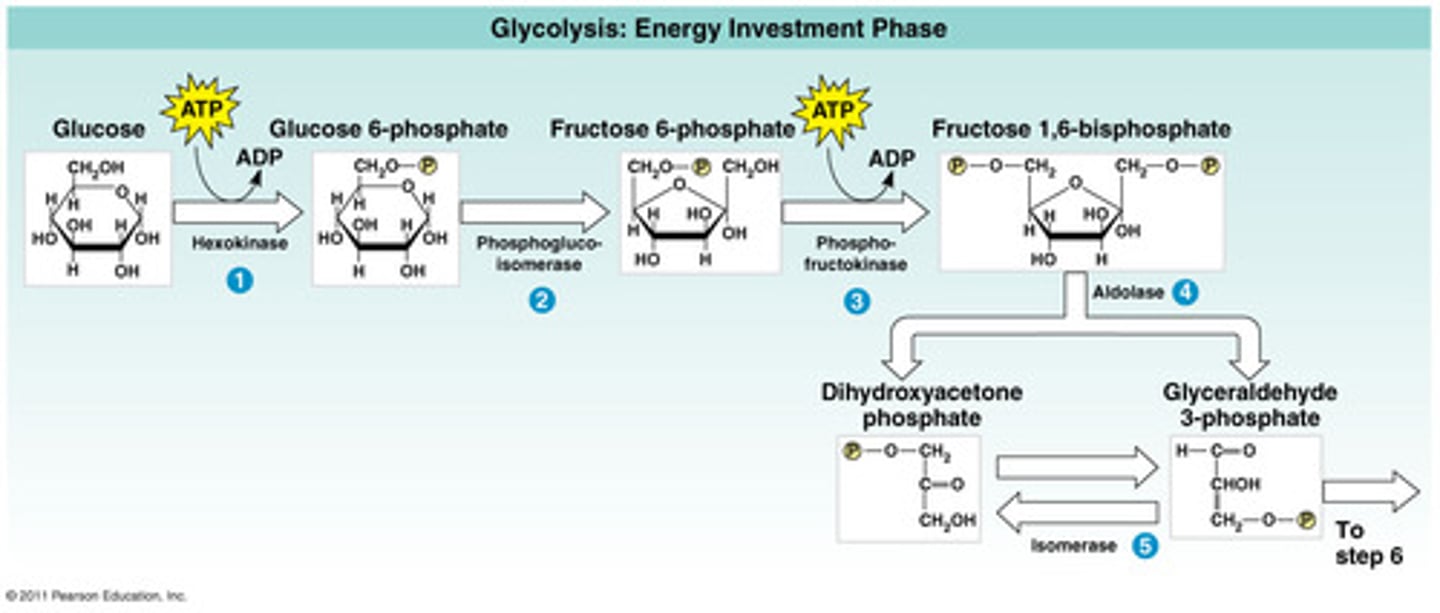
Glycolysis
Location is the cytoplasm/cytosol.
Needs 2 ATP to make glucose more reactive
Enzyme reactions produce 4 ATP through substrate level phosphorylation
Glucose(six Carbon) is converted to two pyruvate(3 carbons each)
Products:2 net ATP and 2 NADH
No oxygen is needed
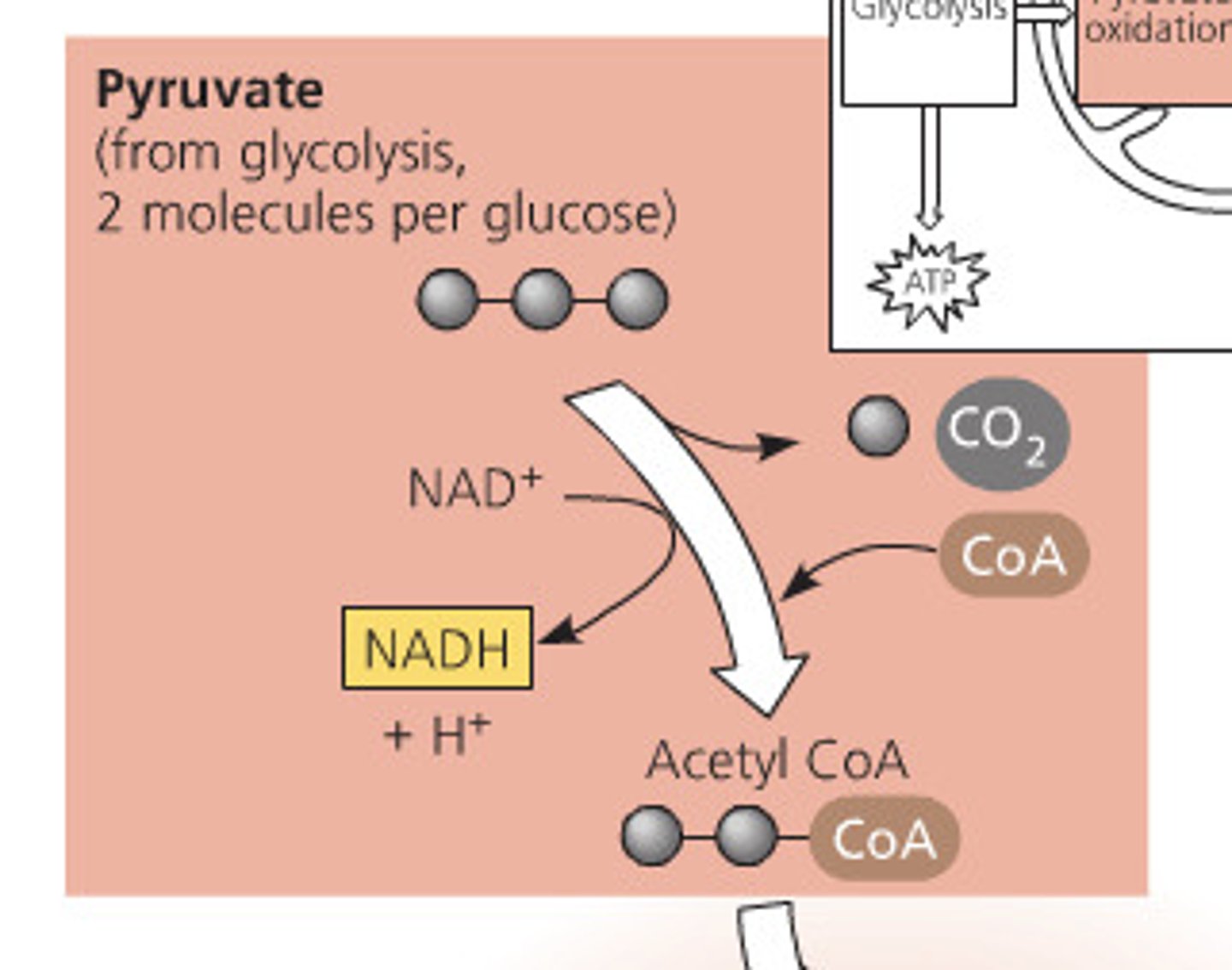
Oxidation of Pyruvate
A transport protein moves pyruvate from the cytosol into the matrix of the mitochondria
Carbon is removed in the form of CO2, electrons are stripped from the pyruvate to form 2 NADH, and coenzyme A joins with the remaining two carbons
2 acetyl are produced per glucose molecule
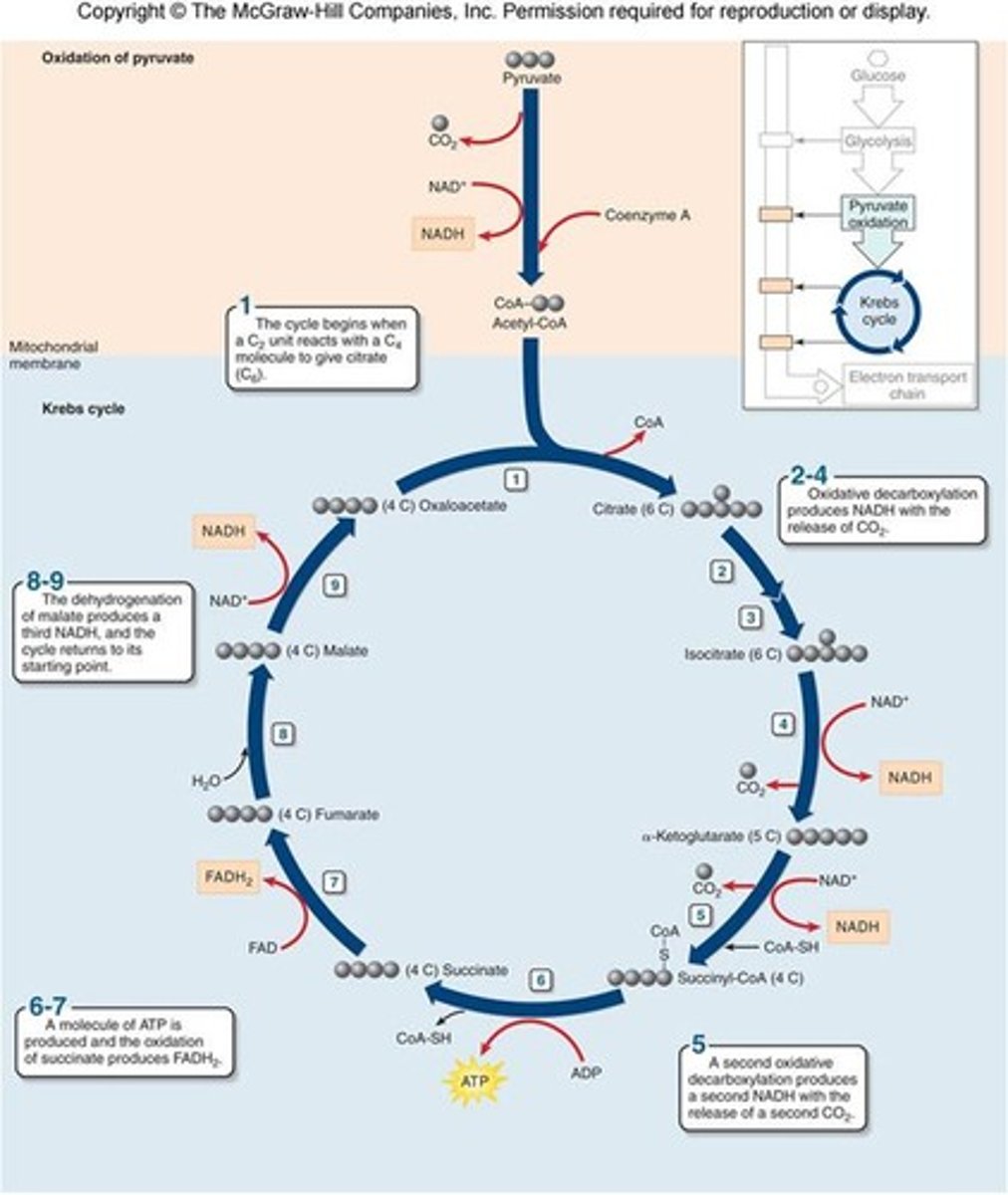
Krebs/Citric Acid Cycle
location: mitochondrial matrix
2 cycles each:
removes CoA from acetyl
release 2 carbon as CO2
production of 1 ATP through substrate level phosphorylation
production of 3 NADH
production of 1 FADH2
overall products are: 4 CO2, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, and 2 ATP
Electron Transport Chain
In the inner membrane of the mitochondria
powered by electrons from NADH and FADH2.
O2 is the final electron acceptor.
The loss of energy through the electrons causes the proton gradient.
At the end, the electrons combine with 2 hydrogen ions and oxygen to form water.
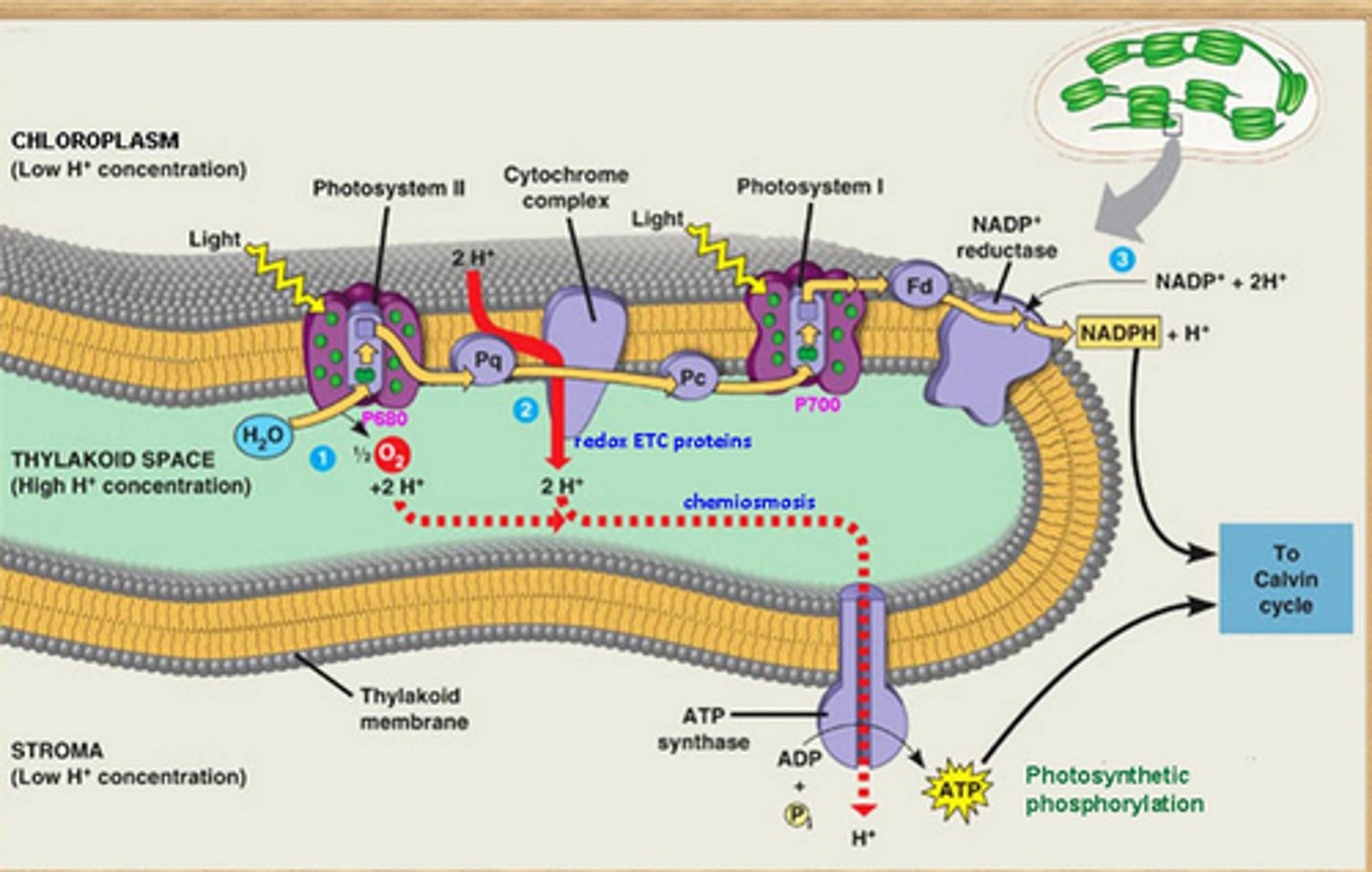
Proton gradient
Electrical potential energy created by the electron transport chain (ETC) during Oxidative phosphorylation and the Light Dependent Reactions (LDR).
FAD+ and FADH2
a B vitamin coenzyme that is an electron acceptor in the citric acid cycle as well as an electron donor in the ETC
Oxidative Phosphorylation
oxygen is used to convert ADP into ATP via two processes: ETC and Chemiosmosis.
Chemiosmosis
energy coupling that uses energy from the H+ ion gradient to drive cellular work, which in this case is ATP synthesis
Anaerobic Respiration
Produce ATP and recycle NAD+ without consuming oxygen (fermentation).
Fermentation
the recycling of NAD+ under anaerobic conditions
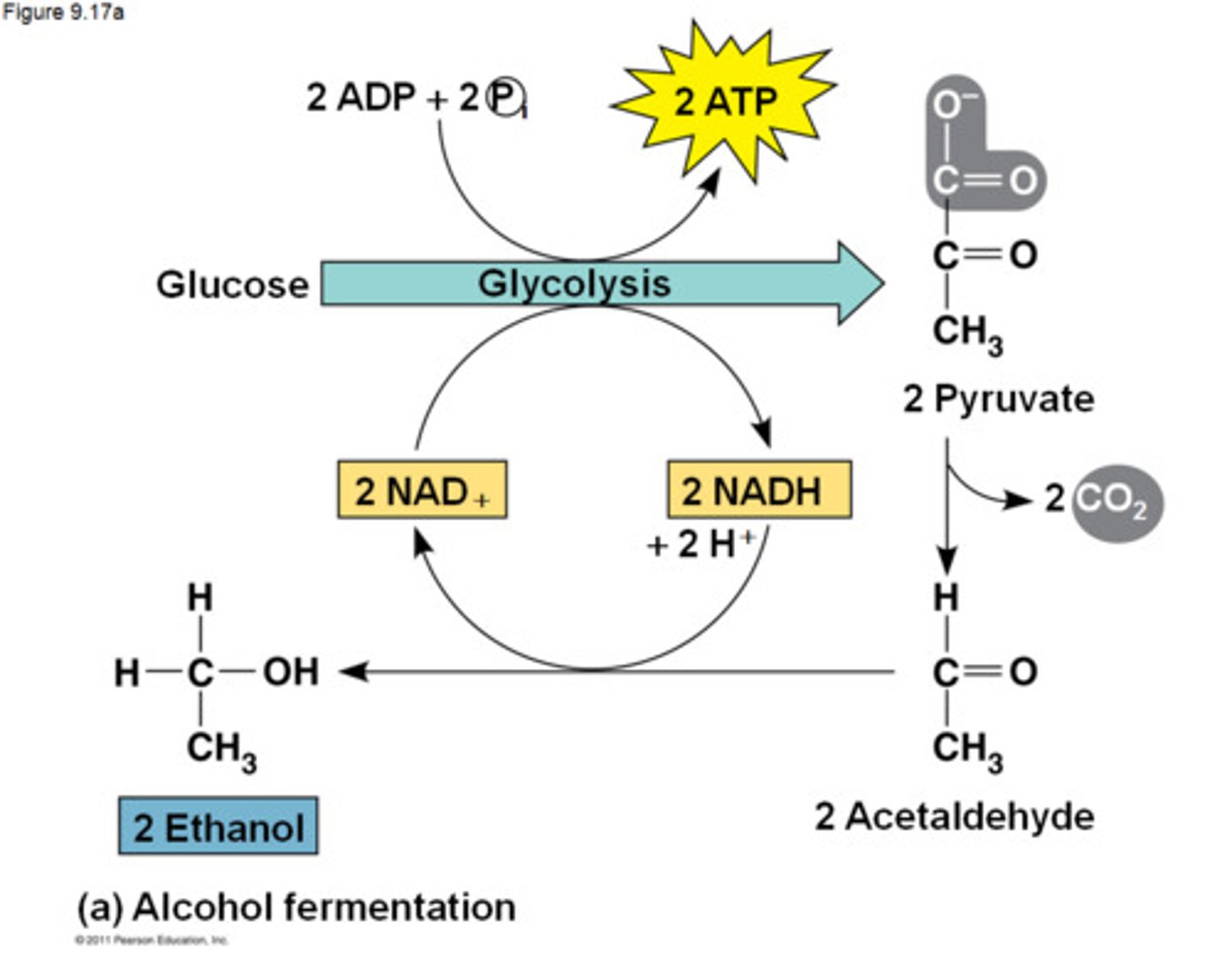
Alcohol Fermentation
pyruvate is converted to ethanol, releasing CO2 and oxidizing NADH in the process to create more NAD+
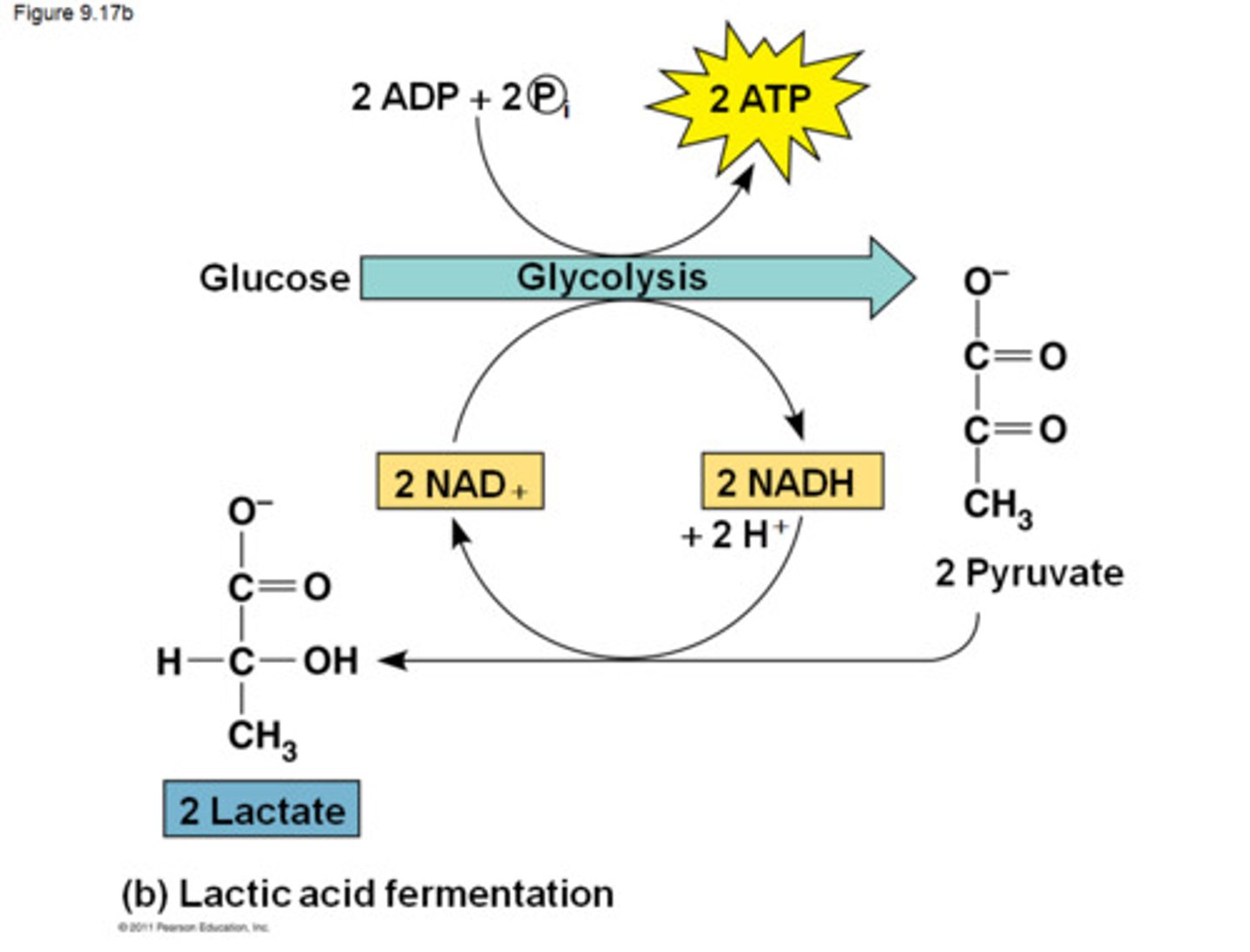
Lactic Acid Fermentation
pyruvate is converted to lactate and oxidizing NADH in the process to create more NAD+
facultative anaerobes
can make ATP via cellular respiration if oxygen is present or fermentation if oxygen is not present
Obligate Aerobe
Organisms that require oxygen for cellular respiration to survive.
Chloroplast
They are the organelle of photosynthesis
Stroma-plasma of the chloroplast (location of Calvin Cycle)
Thylakoids-pigment filled membranes (location of light dependent reactions)
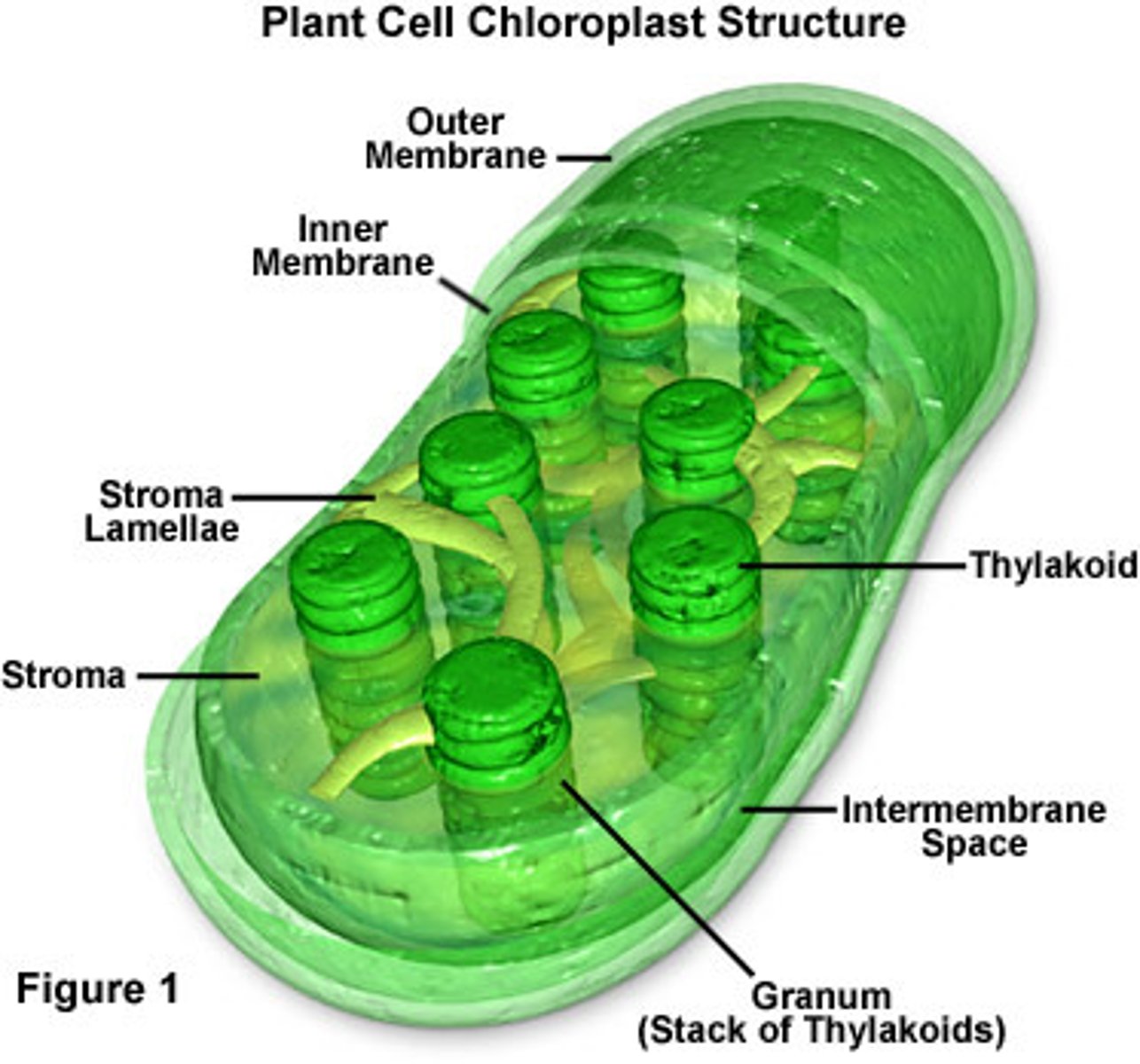
Chlorophyll
located in the thylakoid membranes and is the light absorbing pigment that drives photosynthesis and gives plants their green color
Stomata
tiny pores, usually on the lower epidermis of the leaf;
gas exchange happens here (CO2 in; O2 and H2O out)
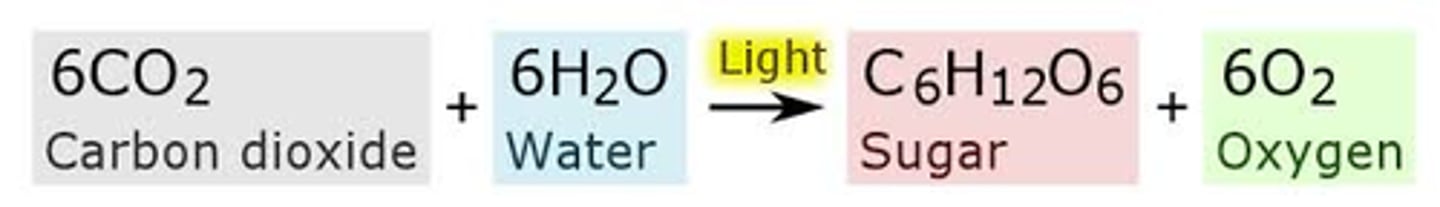
Photosynthesis Reaction Formula
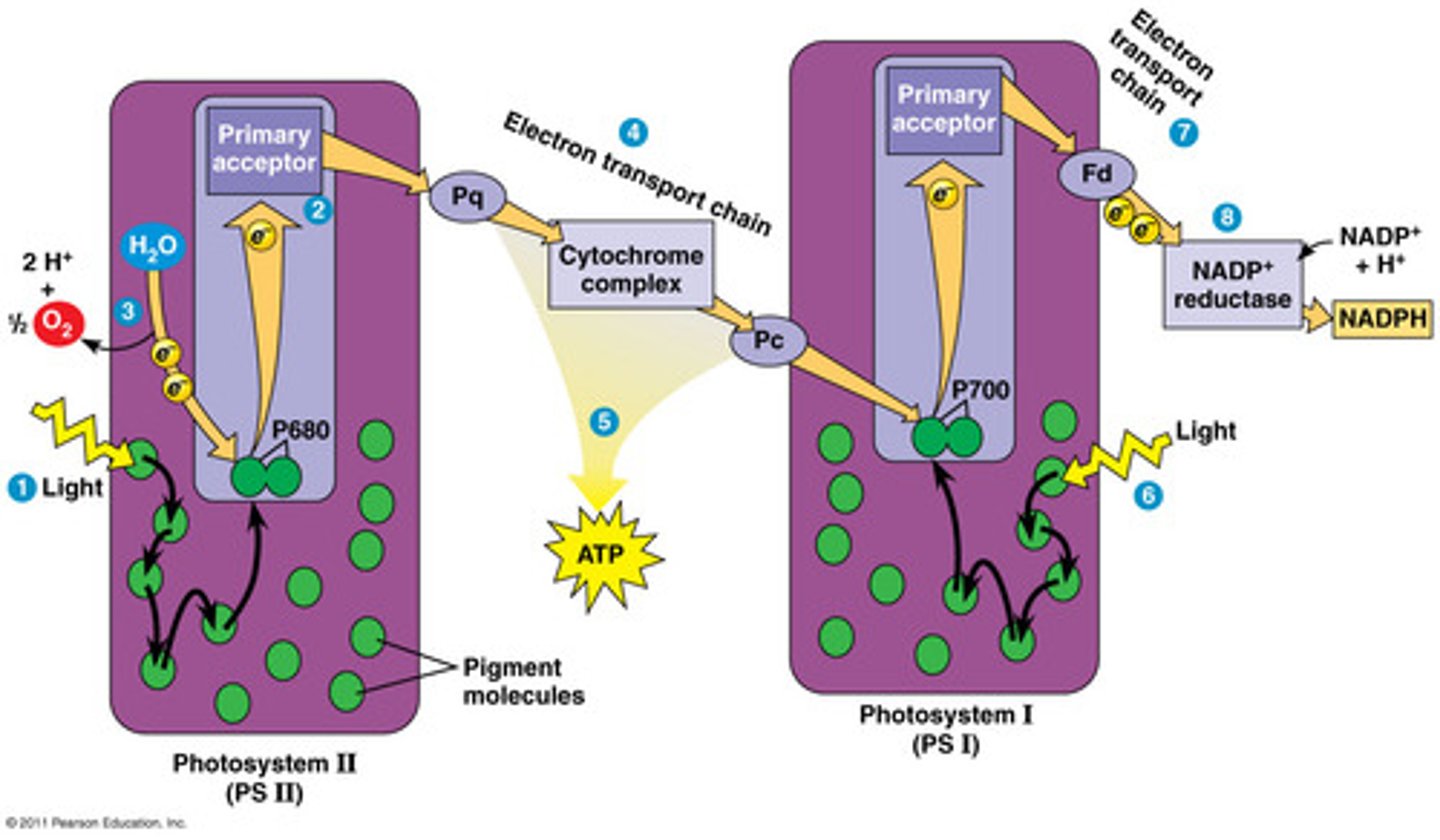
Light Dependent Reactions
occur in and around the thylakoid membrane;
stores chemical energy in the form of NADPH, and ATP;
oxygen gas is the waste product
Carbon Fixation
when CO2 from the air is incorporated into organic molecules
Photons
discrete particles of light, which is electromagnetic energy
Pigments
substances that absorb light
Absorption Spectrum
a graph plotting a pigment's light absorption versus wavelength
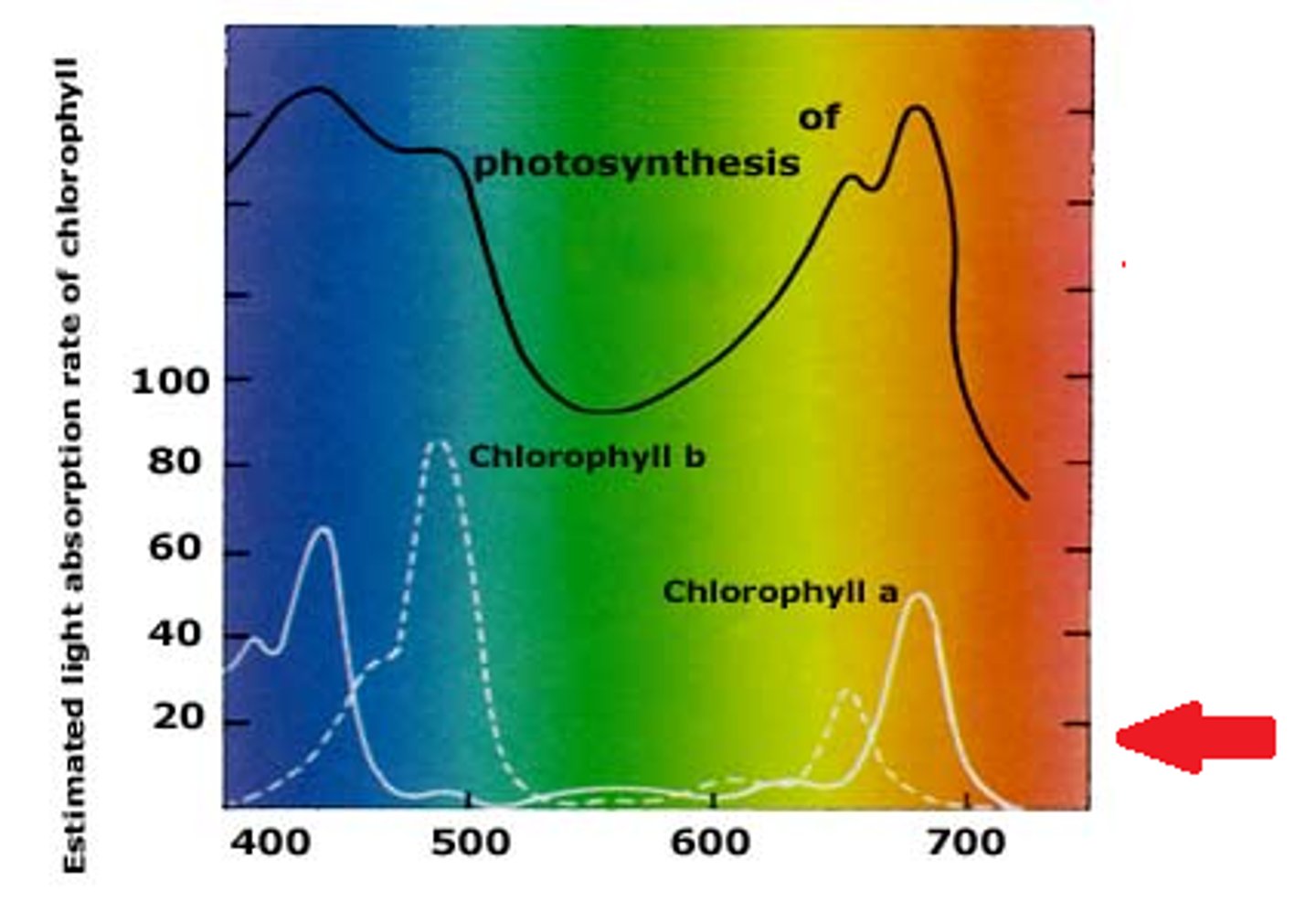
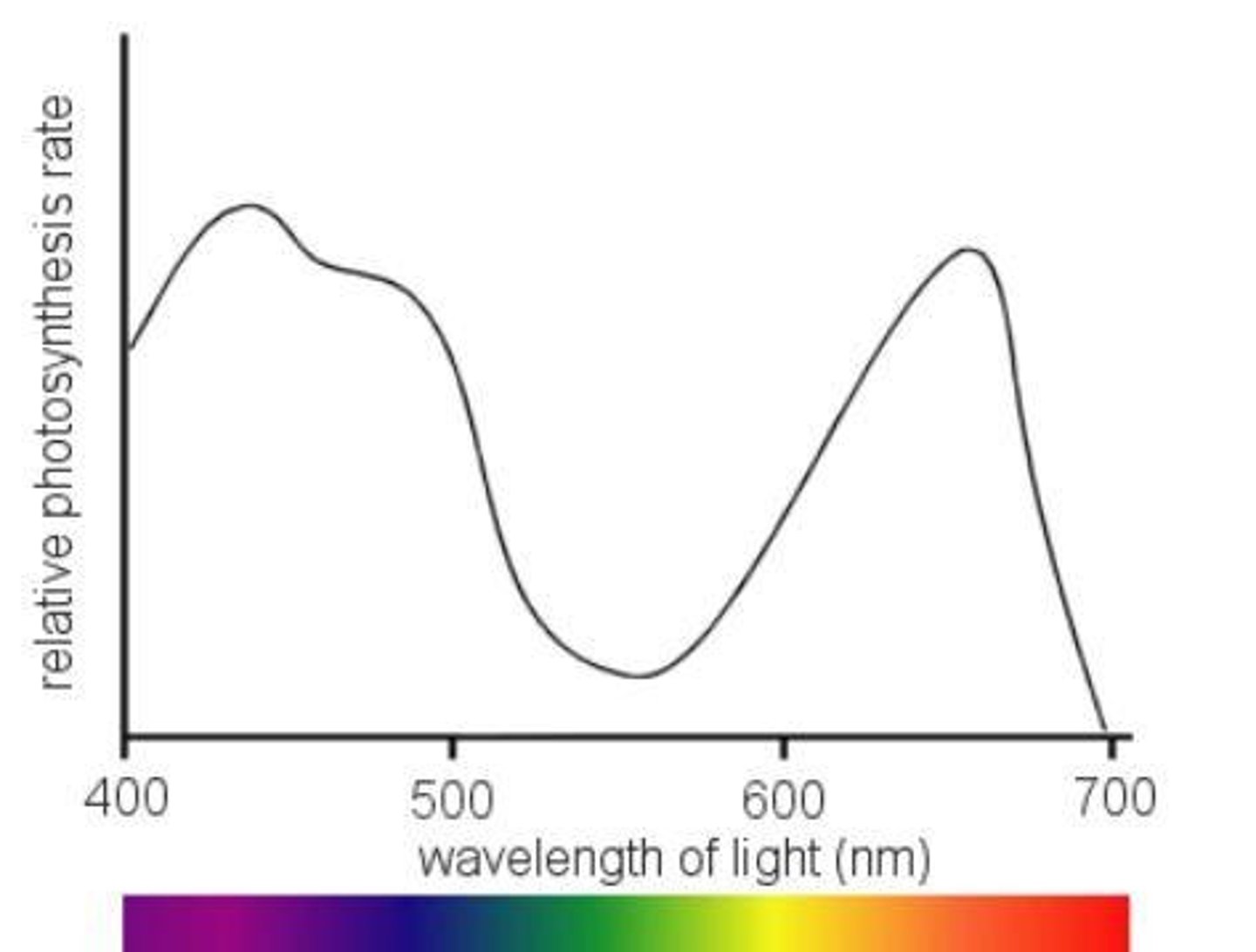
Action Spectrum
graphs the effectiveness of different wavelengths of light in driving the process of photosynthesis
Photosystem II (P680)
Photosystem II (aka P680) is the first photosystem in the light dependent reactions; it provides e- to the electron transport chain and hydrolyzes H2O for the e- and H+
Photosystem 1 (P700)
Photosystem I (aka P700) is the second photosystem in the light dependent reactions; it provides e- to NADP+ in linear e- flow OR e- to the electron transport chain for cyclical e- flow.
Linear(noncyclic) electron flow
Produces an electrochemical gradient in the first electron transport chain (ETC) and NADPH in the final ETC.
PS2 --> ETC1 --> PS1 --> ETC2 --> NADPH
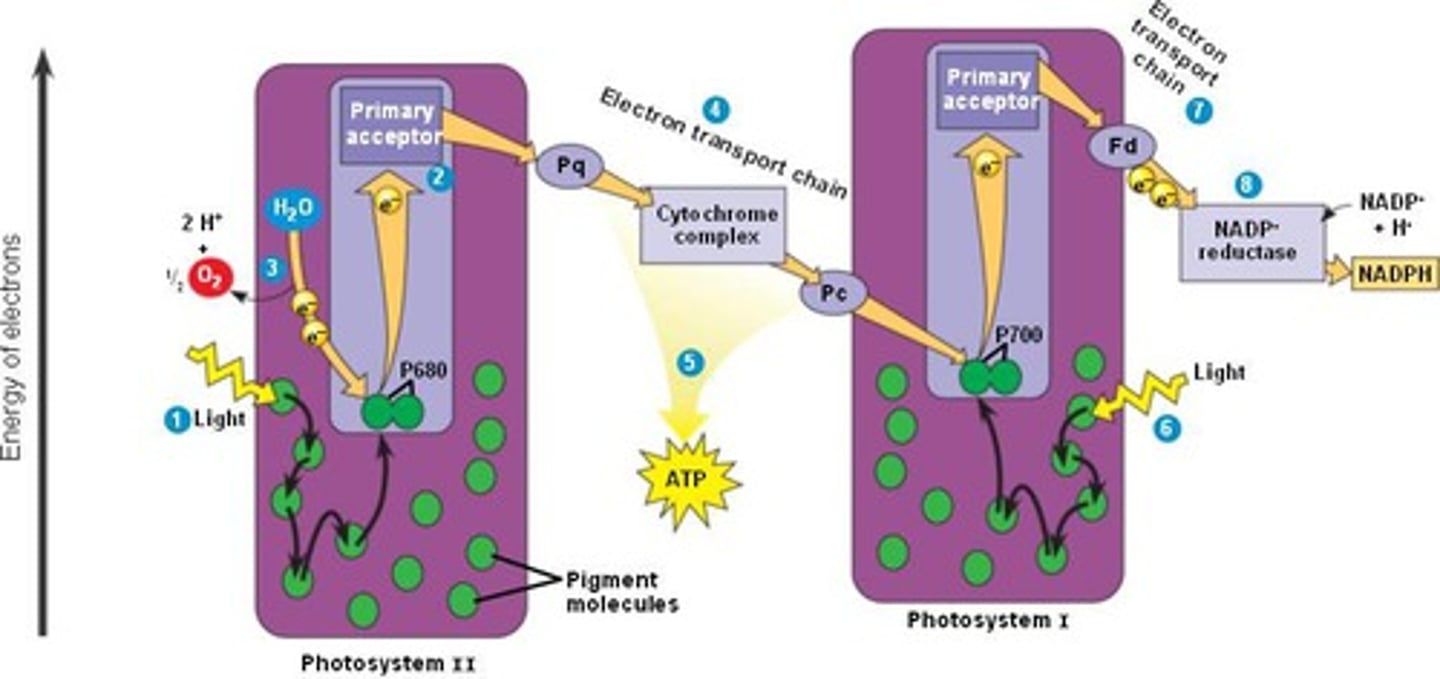
cyclic electron flow
Produces an electrochemical gradient in the first electron transport chain (ETC) over and over and over again.
PS2 --> ETC1 --> PS1 --> ETC1 --> PS1 --> ETC1 --> ...
Chemiosmosis in Chloroplasts
uses the electrochemical gradient across the thylakoid membrane (created by the ETC), to power ATP synthase to phosphorylate ADP into ATP
Calvin Cycle
Makes sugar from CO2 in three stages:
1. Carbon Fixation
2. Reduction
3. Regeneration of RuBP
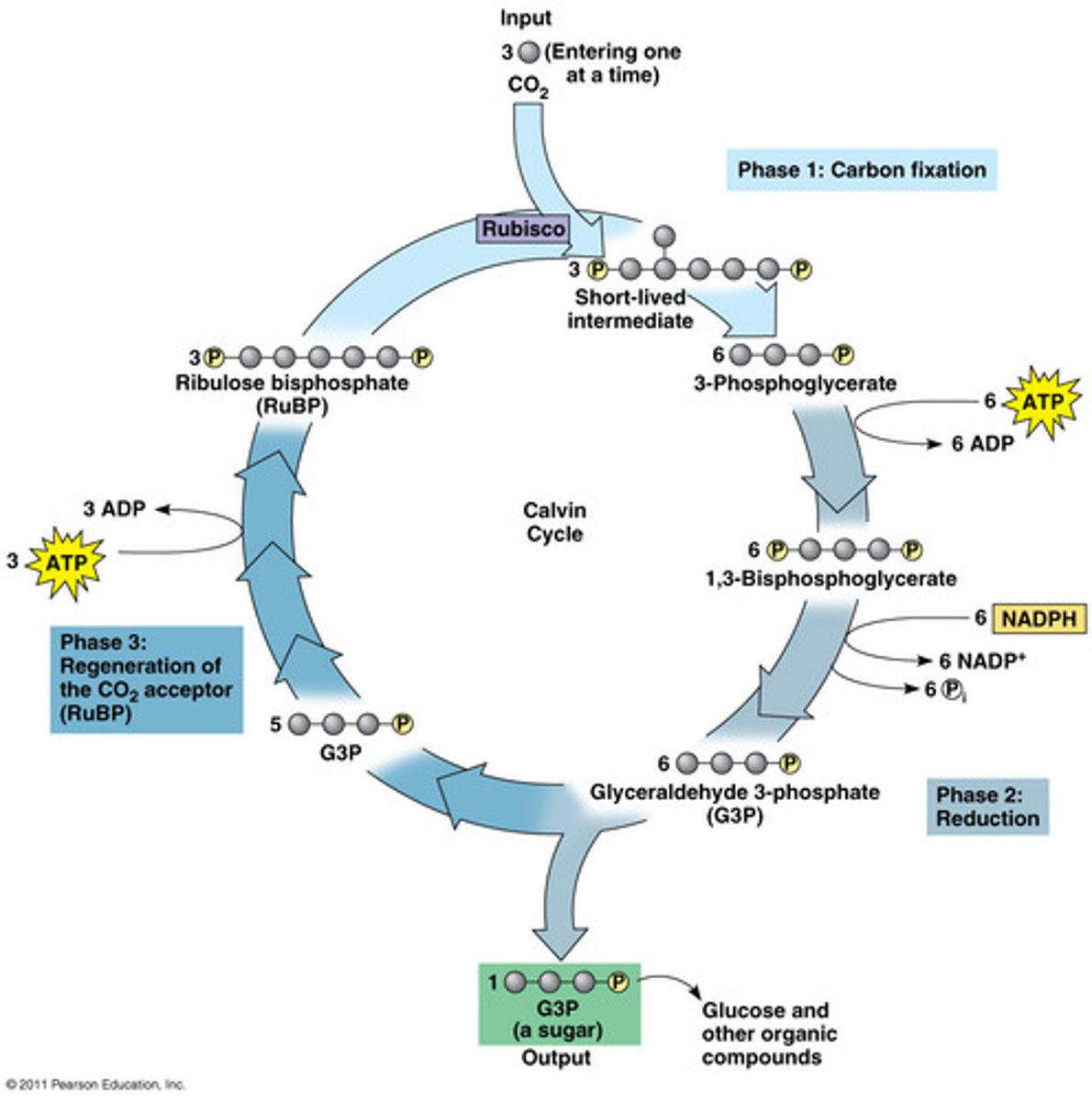
Carbon Fixation (Calvin Cycle)
Rubisco attaches CO2 to RuBP.
RuBP
ribulose biphosphate;
in the calvin cycle these are attached to CO2 molecules
Rubisco
an enzyme is supposed to fix CO2 to RuBP;
sometimes it fixes O2 to RuBP (photorespiration), this is bad for the plant
Reduction (Calvin Cycle)
ATP AND NADPH are used to convert molecules into pre sugars (G3P)
G3P
the product of reduction (Calvin Cycle) that are the building blocks of all sugars
Regeneration (Calvin Cycle)
New RuBPs are generated from the remaining G3P's.
Impact of Hot Dry Days on Photosynthesis
On hot days, plants close their stomata to conserve water; this means no CO2 uptake and no O2 release; this leads to an increase in photorespiration
Photorespiration
rubisco will bind to O2 instead of CO2 to RuBP; this is a highly inefficient energy consuming process.
C4 photosynthesis
mesophyll cells perform the light reactions, while bundle sheath cells perform the calvin cycle; this reduces the rate of photorespiration
CAM Photosynthesis
crassulacean acid metabolism;
stomata are closed during the day and light dependent reactions occur; at night, the stomata open and CO2 is fixed into malate, which is the carbon source for the Calvin Cycle
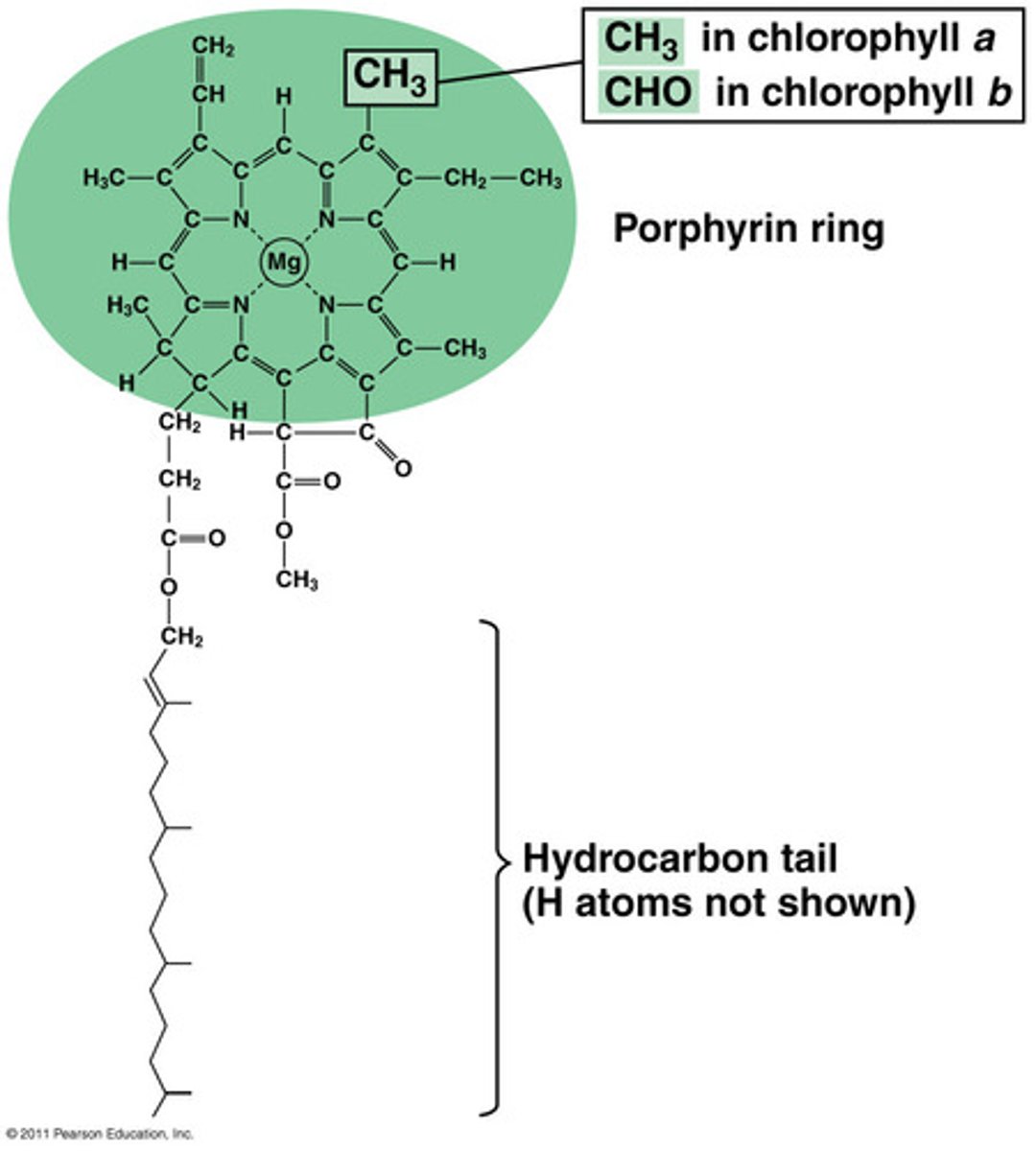
Structure of Chlorophyll
magnesium center
has a hydrocarbon tail to make it lipophilic for membrane attachment
Leaf Structure
photosynthesis takes place in the mesophyll cells; stomata are small pores for gas exchange; the epidermis is the outer protective layer (sometimes there is a waxy cuticle layer too); veins transport reactants to the leaf, and products out of the leaf
Paper Chromatography
technique for separating and identifying pigments from cell extracts
solvents move up by capillary action
Rf Values
ratio of the movement of the pigment(B) over the migration of the solvent(F)