NSG 3107: Neuromuscular or Muscular Dysfunction
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Cerebral palsy (CP)
Group of nonprogressive disorders of movement caused by lesion in various motor centers of developing brain; abnormal muscle tone and coordination; difficulty walking, feeding, swallowing, articulation of speech

Prenatal brain abnormalities, chorioamnionitis in utero, prematurity, hypoxic brain injury, severe hypoglycemia
What are some causes of cerebral palsy?
True
True or false? Cerebral palsy is the most common permanent motor disability of childhood
Spastic CP
Most common clinical type of CP; pyramidal; upper motor neuron muscle weakness; increased stretch reflexes, increased muscle tone, weakness
Dyskinetic CP
Extrapyramidal; involuntary irregular jerking movements; slow, twisting movements that usually involve trunk, neck, facial muscles; pharyngeal, laryngeal, oral muscles cause drooling
Ataxic CP
Extrapyramidal; wide-based gait, rapid & repetitive movements performed poorly, disintegration of movements of upper extremities when child reaches for objects
Mixed CP
Combination of spastic and dyskinetic CP
Diplegia
Classification of spastic CP
All extremities affected; lower more than upper
Quadriplegia
Classification of spastic CP
All 4 extremities involved; legs & trunk, mount, pharynx, tongue
triplegia
Classification of spastic CP
Three limbs involved
Monoplegia
Classification of spastic CP
One limb involved
Hemiplegia
Classification of spastic CP
Motor dysfunction on one side of body; upper extremity more affected than lower
Early signs of CP
Early hand preference (before 18 months), delayed/absent achievement of motor development, persistent primitive reflexes
False
True or false? Cerebral palsy is linked to intellectual impairment
Neural tube defects
Abnormalities that derive from the embryonic neural tube; largest group of congenital anomalies
Cranioschisis
Skull defect through which various tissues protrude
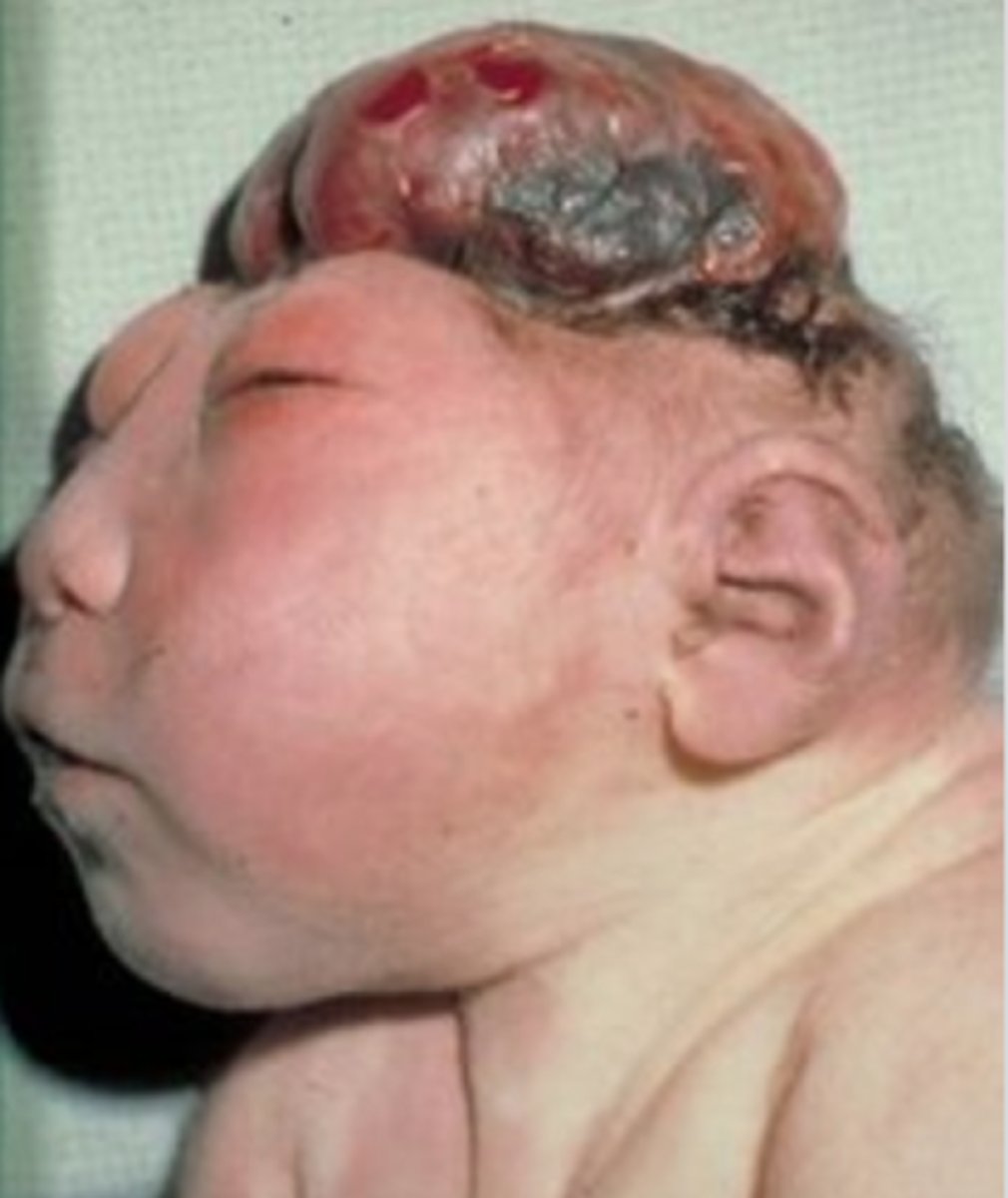
Exencephaly
Brain is totally exposed or extruded through an associated skull defect; fetus usually aborted
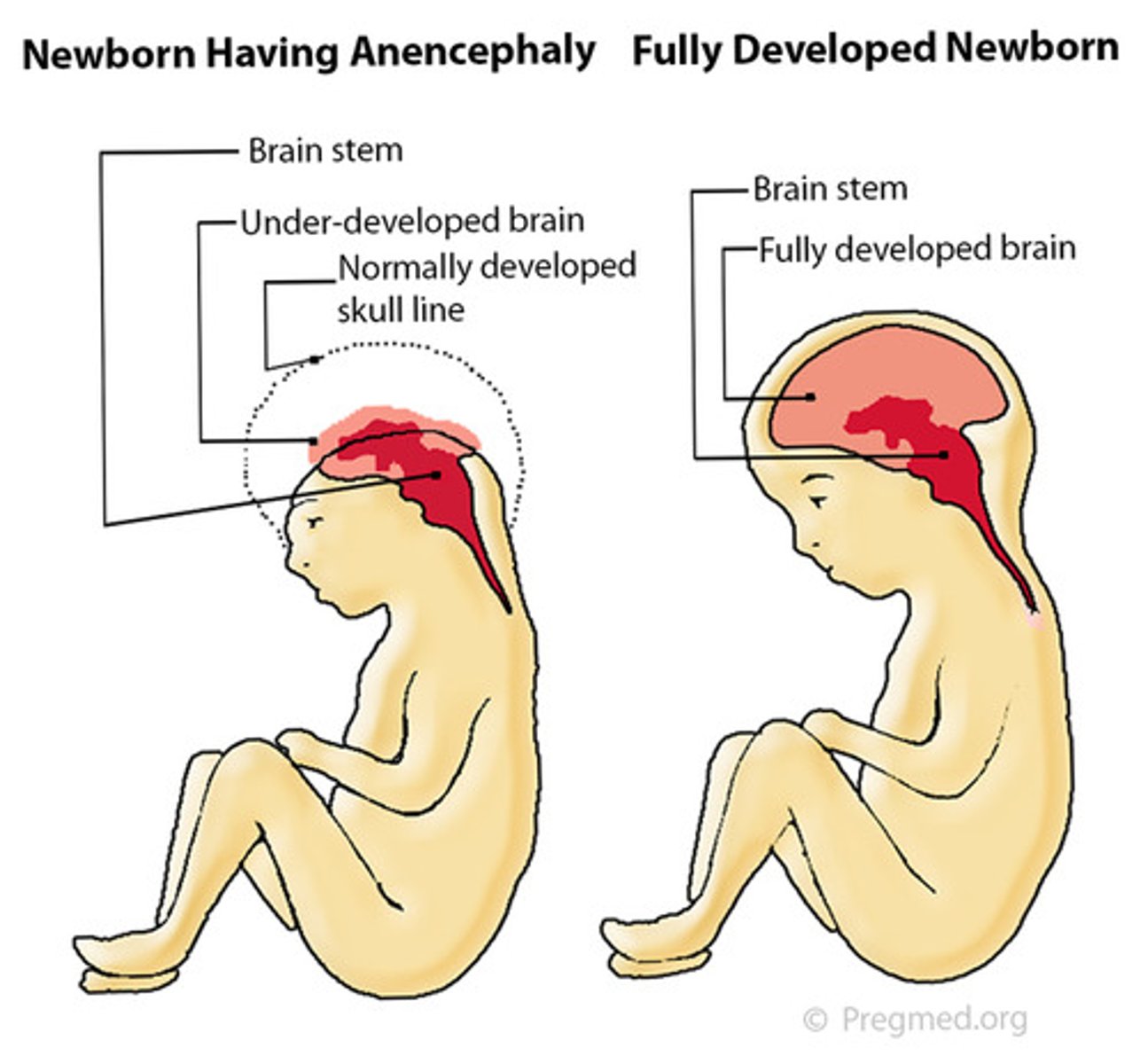
Anencephaly
If fetus with exencephaly survives, there is degeneration of the brain to a spongiform mass with no bony covering; incompatible with life usually beyond a few days
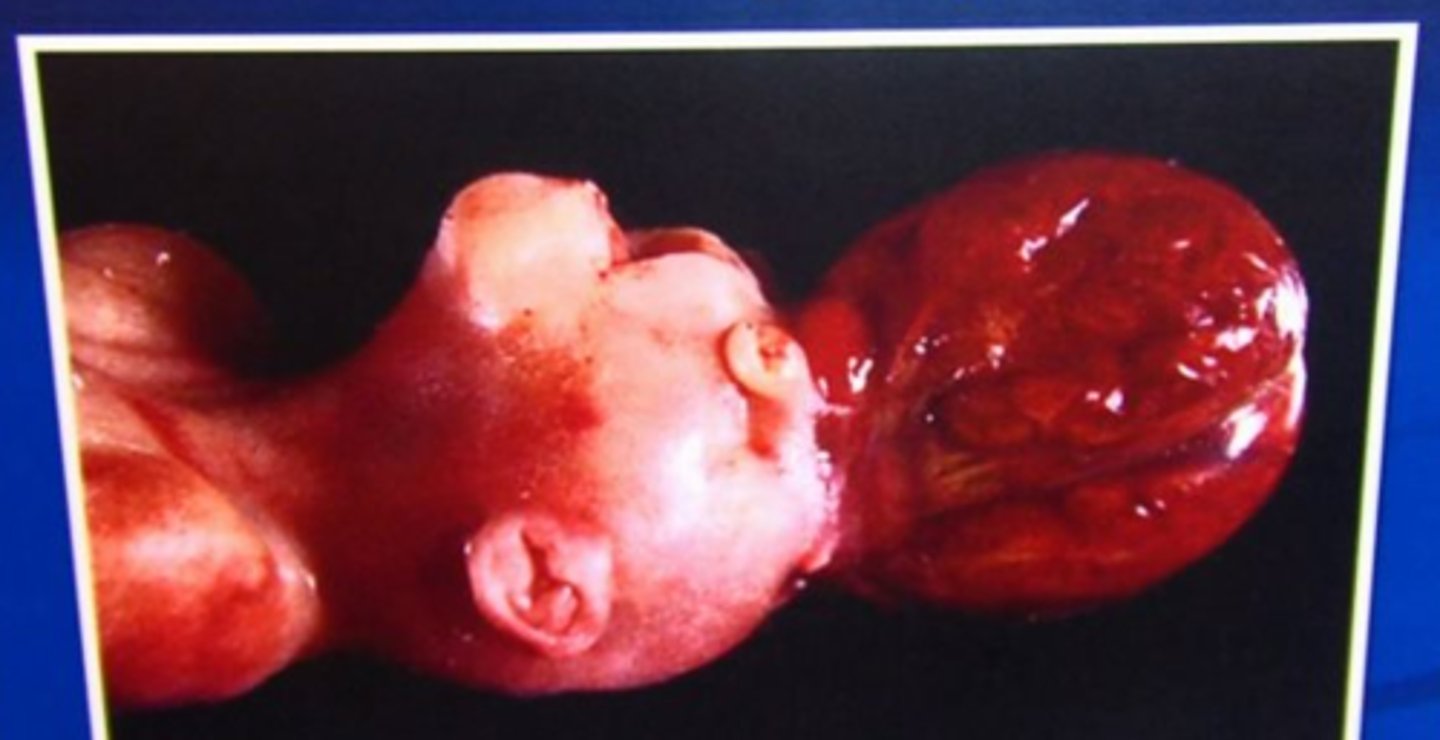
Encephalocele
Herniation of brain and meninges through defect in the skull producing a fluid-filled sac
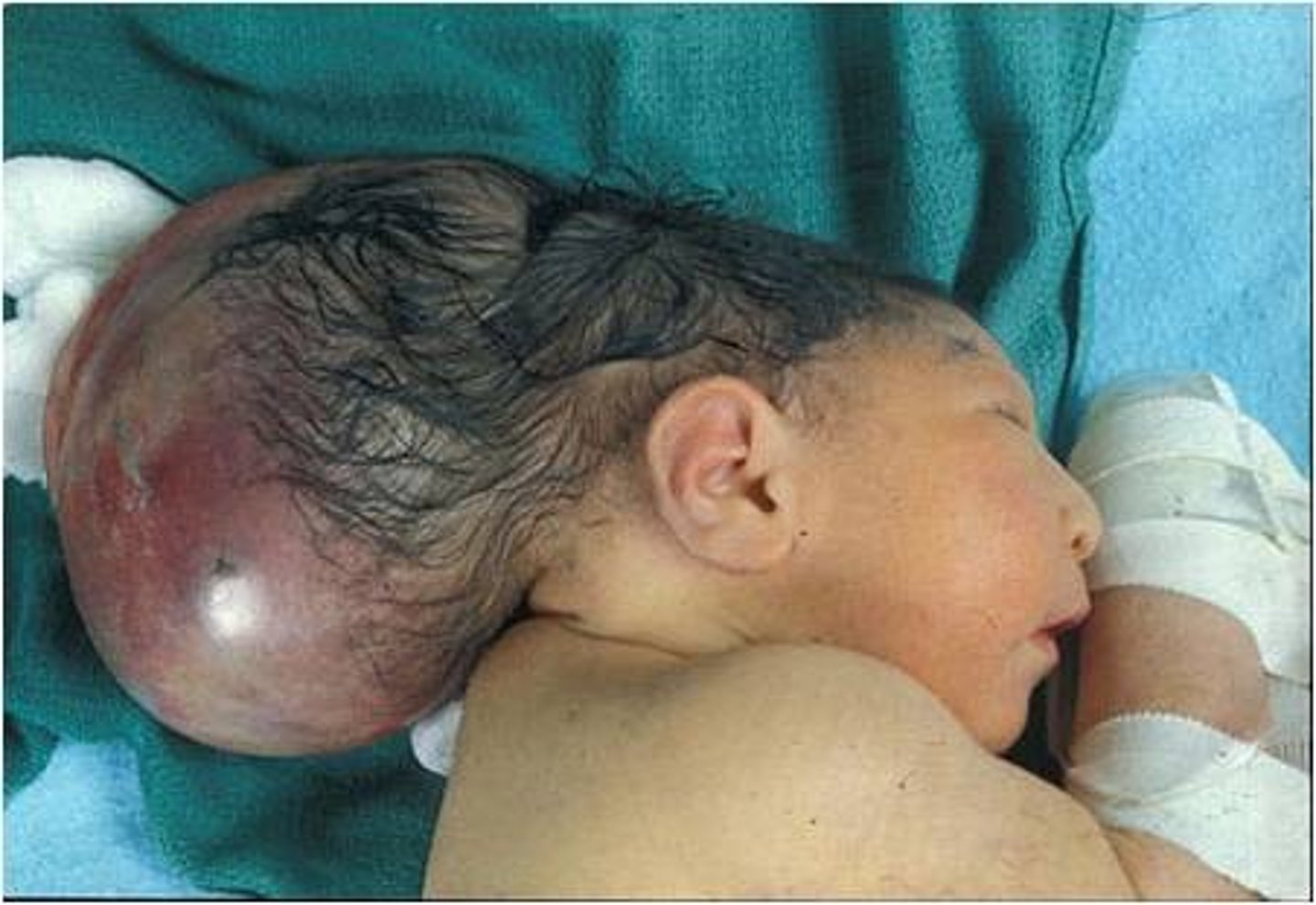
Spina bifida
Aka rachischisis; fissure in spinal column that leaves meninges and spinal cord exposed
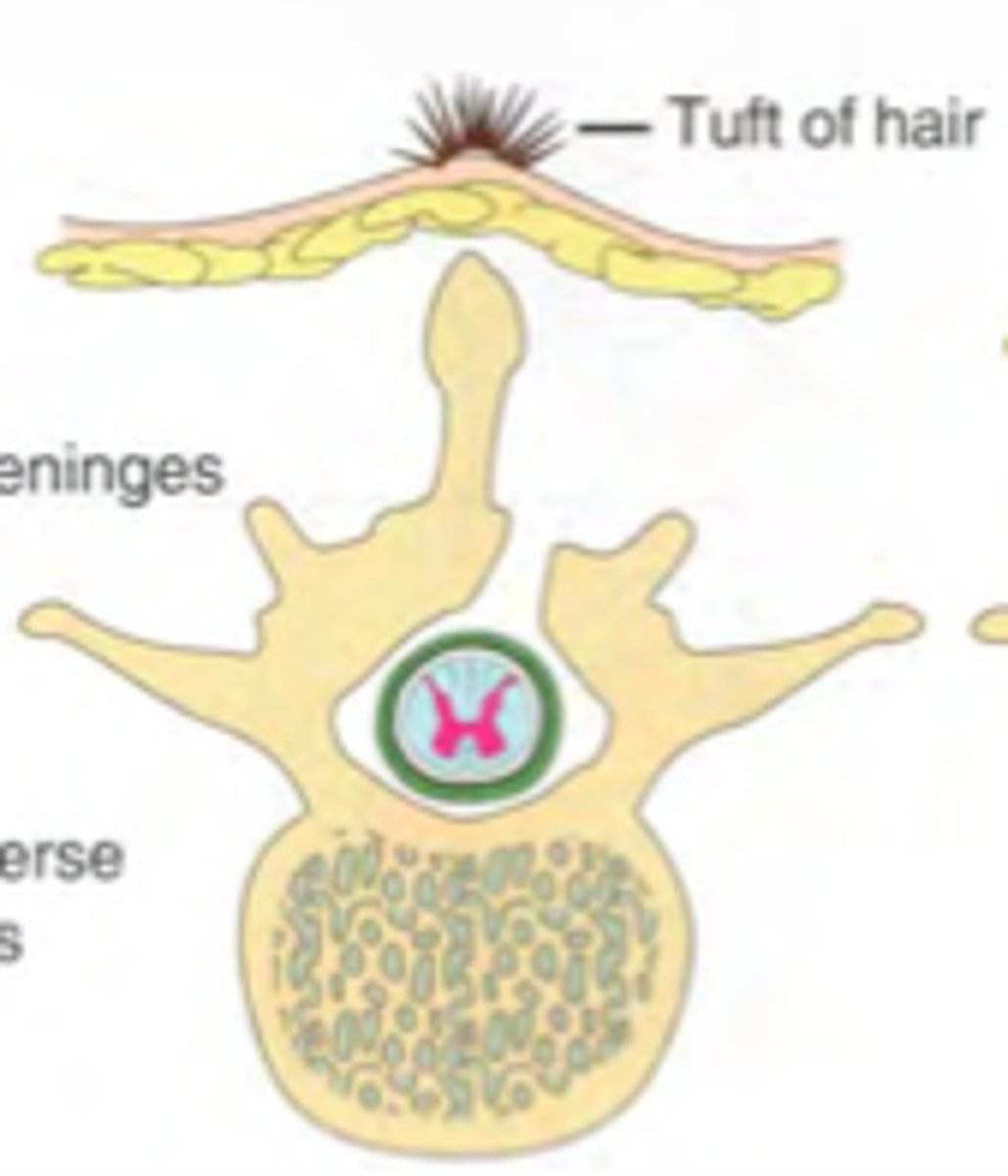
Spina bifida occulta
Type of spina bifida which is not visible externally and is seen as a dimple on the sacrum; also can manifest as port-wine angiomatous nevus, tufts of dark hair, soft, subcutaneous lipomas
Spina bifida cystica
Type of spina bifida that is visible; external sac-like protrusion; presents a meningocele or myelomeningocele
Meningocele
Type of spina bifida cystica; hernial protrusion of saclike cyst of meninges filled with spinal fluid
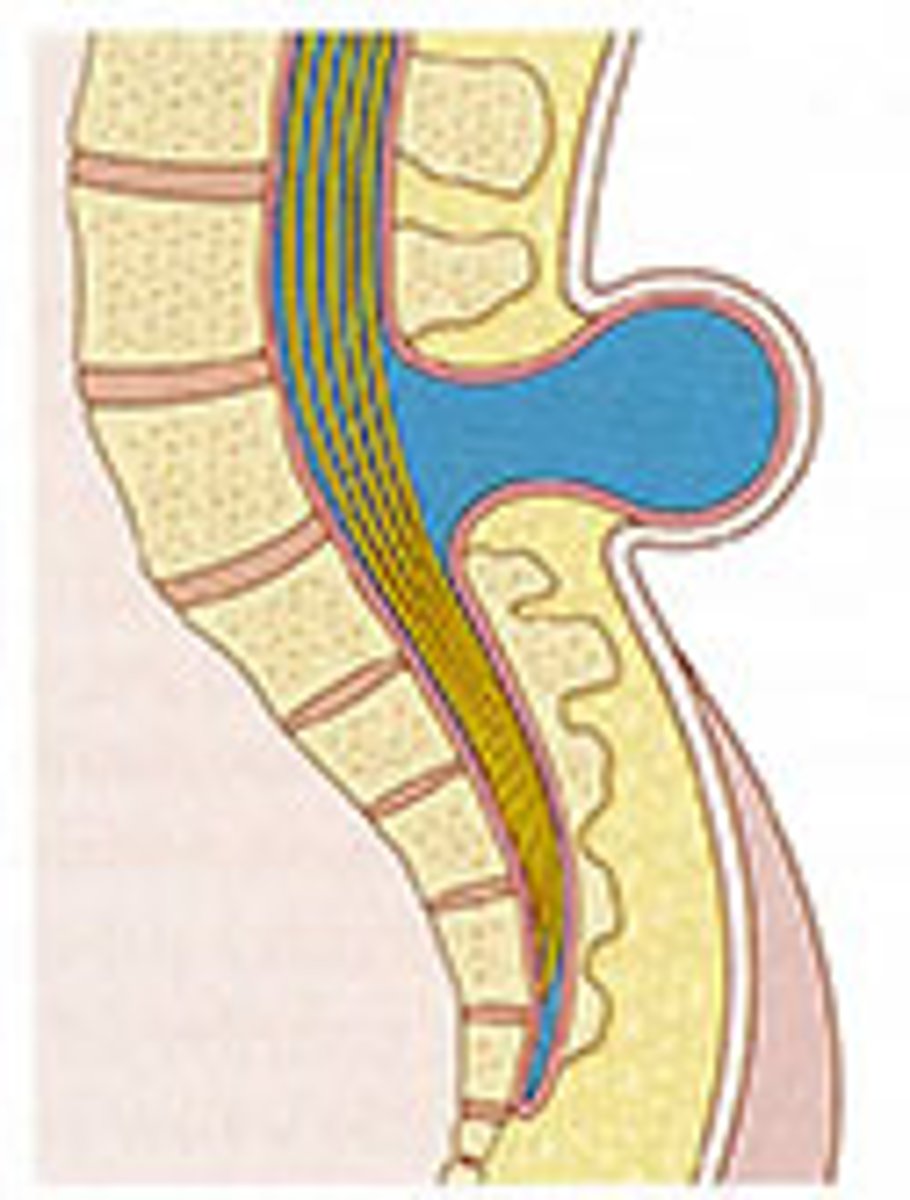
True
True or false? Meningocele is not associated with neurological deficit, which occurs in varying, often serious, degrees in myelomeningocele
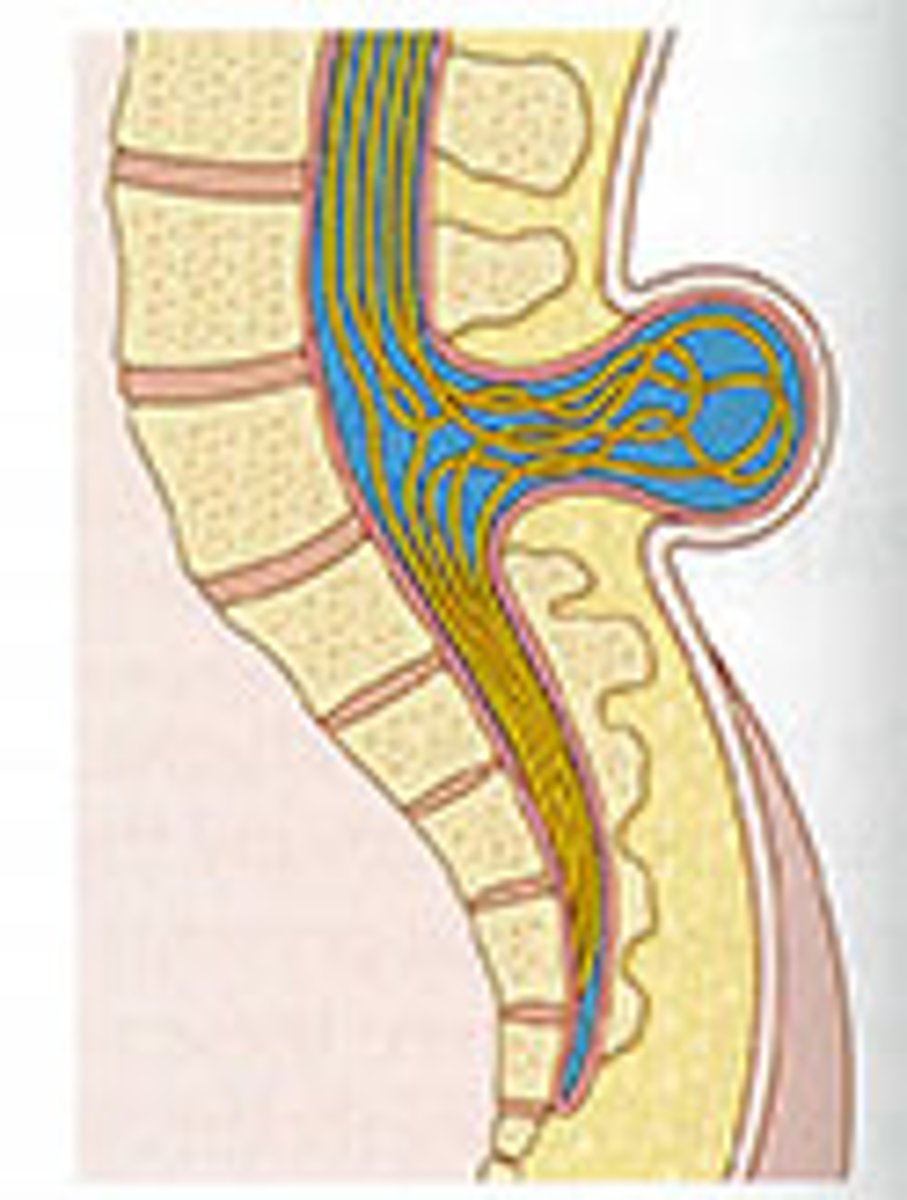
Myelomeningocele
Type of spina bifida cystica; hernial protrusion of saclike cyst containing meninges, spinal fluid, and portion of spinal cord with its nerves; various degrees of neurological deficit
False (can occur anywhere along spinal column)
True or false? Myelomeningoceles occur only at the base of the spine
0.4 mg
How many milligrams of folic acid should the pregnant person be instructed to take per day (she does not have a history of fetuses with neural tube defects)?
3 months
How many months preconception should folic acid supplementation begin?
Foods rich in folic acid
Dark leafy greens, legumes, asparagus, citrus, nuts, seeds, eggs, liver
Latex
Children with SB are a high risk of developing a ______ allergy
Banana, avocado, kiwi, chestnuts
Foods that children with latex allergies can have cross-reactions with
Muscular dystrophies
Group of muscular diseases in children; all forms have a genetic origin with gradual degeneration of muscle fibers, progressive weakness, and wasting of skeletal muscles
True
True or false? All forms of muscular dystrophy are characterized by increasing disability and deformity with loss of strength
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
Most severe and most common type of muscular dystrophy; absence of structural protein dystrophin found in muscle fiber membranes = progressive muscle degeneration and weakness; muscle cells go through cycles of deterioration and regeneration until the repair capacity is no longer sufficient and the fibers undergo irreversible degradation and are replaced by fat and connective tissue
X-linked recessive; 1/3 are fresh mutations
What kind of inheritance pattern does DMD follow?
Clinical manifestations of DMD
Waddling gait, frequent falls, Gower's sign, lordosis, enlarged muscles, profound atrophy in later stages, cognitive impairment, complications
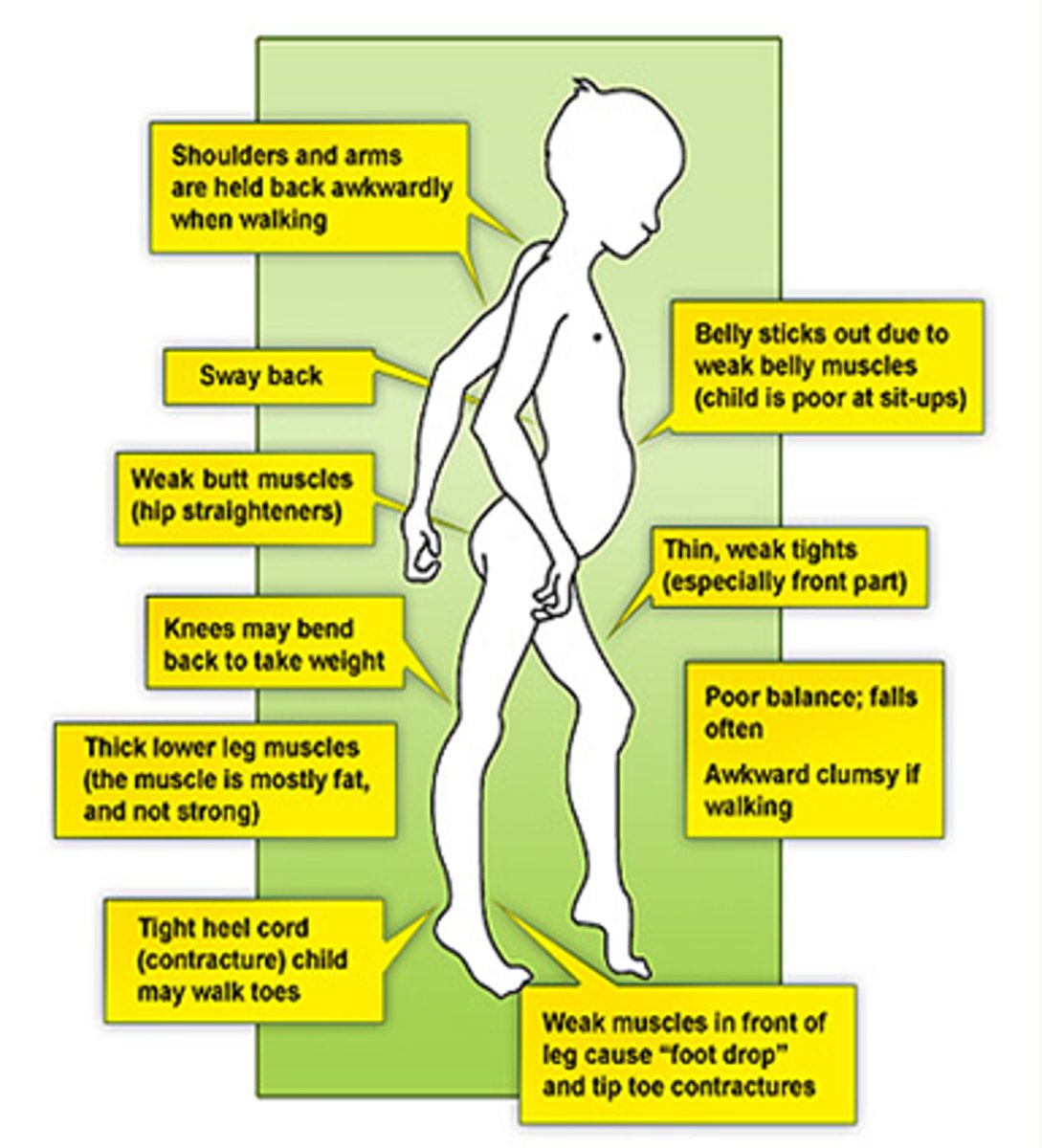
Gower's sign
When asked to get up from sitting on floor, child will move hands on legs as though crawling up to the thighs and then assume a standing position
Pseudohypertrophy
Seen in DMD, muscles in calves, thighs, upper arms become enlarged from fatty infiltration and feel unusually firm/woody/rubbery
Maintain function in unaffected muscles for as long as possible
What is the primary goal of DMD management?