Chapter 7 Critical Thinking Concepts
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
If lactose is the substrate, what enzyme breaks it down?
Lactase
Products formed from the breakdown of lactose
Glucose
Galactose
How would we measure the reaction rate (enzyme speed)
How fast Lactose (substrate) is converted into Glucose and Galactose (products)
When the enzyme concentration increases and the substrate concentration remains uncharged what happens to the reaction rate?
Increases
What happens when there is a high enzyme concentration
More active sites available to breakdown Lactose
Lactose is a _______
substrate
When the substrate concentration increases and the enzyme concentration remains constant, what happens to the reaction rate?
It levels off
Why does the reaction rate level off when the substrate concentration increases and the enzyme concentration remains constant?
the enzyme level reaches saturation
What does high heat do to the protein portion of an enzyme
Denature
The denaturing of the protein portion of an enzyme with ______ _____ can lead to cell death
High fevers (above 107F)
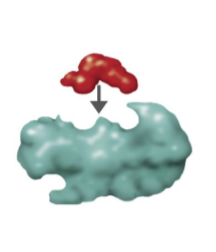
What type of inhibition?
No inhibition
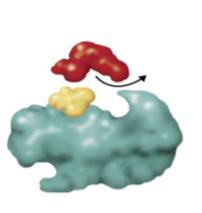
What type of inhibition?
Competitive
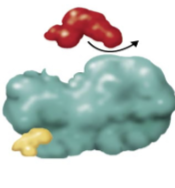
What type of inhibition
noncompetitive
Both substate and inhibitor compete for the ACTIVE SITE
Competitive inhibition
Active site is altered as an inhibitor is bonded to REGULATORY SITE. Thus it changes the active site and the substrate cannot bind to the active site
Noncompetitive
Where does the competitive inhibitor bind to?
Active site
When the inhibitor binds to the active site of an enzyme, what happens to the reaction rate?
Slows down
What can you add that takes away the effects of the reversible competitive inhibitor?
Increase the concentration of the substate
Statin drugs act as a ______ _____ for the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase
competitive
HMG-CoA reductase is an important enzyme for _______ production
cholesterol
If the statin drugs inhibit the enzyme needed to convert lipids into cholesterol, this will:
Lower the levels of LDL production in the liver → lower levels in the blood
Succinate + FAD → fumarate + FADH2
Is FAD oxidized or reduced during this reaction?
reduced (gains electrons)
Succinate + FAD → fumarate + FADH2
Name the substrate in this reaction
Succinate
Succinate + FAD → fumarate + FADH2
Suppose you add malate to this reaction, and very little fumarate form. Why would the product amount decrease?
Malate acts as an inhibitor
_________ are electron-transporting proteins in the ETC
Cytochromes
_____ is a coenzyme utilized by many enzymes during glycolysis, prep reaction, and Kreb’s cycle
NAD+
NAD+ is reduced to _____
NADH
_______ serves as an electron carrier, carrying the electrons from glycolysis, Krebs cycle and prep reaction to the cytochromes
NADH
If the cytochromes and NAD+ are inhibited the cell will not be able to
synthesize ATP
What diseases are caused by H. influenzae?
Bacterial meningitis
bacterial flu
bacterial pneumonia
Where does fermentation occur in a prokaryotic cell?
Cytoplasm
Fermentation: In some bacteria and yeast, pyruvate is reduced. Where did the electrons come from to reduce pyruvate? (That is, which molecule was oxidized so that pyruvate may be reduced?
NADH
In fermentation, how many NET ATP molecules form from substrate level ATP synthesis?
2 (glycolysis)
In fermentation, how many ATP molecules form from oxidative phosphorylation?
0 (fermentation does not involve ETC and chemiosmosis)
ABS syndrome is also known as gut fermentation syndrome. This rare condition makes you feel:
drunk (without drinking alcohol)
In ABS, you feel drunk when you body turns _______ into _______
carbohydrates
alcohol
In ABS your body makes “brews” _______ out of the _______ you eat.
alcohol (ethanol)
carbohydrates
ABS happens inside the gut or intestines and may be caused by too much ______ in the gut
yeast
Why did the physician prescribe a strict carbohydrate-free diet to the patient with ABS?
Carbohydrate is the only substrate that is converted to alcohol by fungi
The drug HIVID (ddC) and PABA are a ______ ________. It will compete for an active site as the _______ of the drug and the actual substrate is similar
competitive inhibitors
structure
All cells require _____ ______ for growth (PABA)
folic acid
Bacteria have to make folic acid using ______
PABA
Signs and Symptoms of Septicemia
Lethargy
Drowsy
LOW BP
LOW O2 Sat
HIGH FEVER
weak pulse
RAPID Heart rate
The clinical name for blood poisoning by bacteria
Septicemia (sepsis)
Sepsis triggers ______ throughout the body
inflammation
A ______ _____ test indicates poor organ function due to low oxygen availability
serum lactate
With low O2 availability, the body utilizes anaerobic modes to generate ATP which increase the levels of _____ _______
lactic acids
High levels of lactic acid can alter the blood pH leading to ______ _____
lactic acidosis
Treatment for sepsis
Early fluid resuscitation
Antibiotic therapy
Check levels of BP and perfusion (prevent further organ damage)