UCM Animal Nutrition Quiz 2
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
low in oxygen, warm, moist
Why do microbes like the rumen?
volatile fatty acids
Microbes produce these to perform microbial digestion
Three examples:
1.Acetate
2. Propionate
3.Butyrate
Ruminants you for energy
Acetate, propionate, butyrate
Name examples of VFAs
starch
Besides microbial digestion digesting cellulose, hemicellulose, they digest….. , protein, and some lipids, which results in production of VFAs
Microbes digest protein from feedstuff
What is a source of protein for the ruminant?
They are carried out of the rumen with the digesta and are killed in the abomasum (true stomach). They are then digested in the duodenum and the amino acids from the digested protein from the them is absorbed in the jejunum and ileum to provide the protein for the ruminant.
papillae
how are VFAs abosrbed?
to regurgitate partially digested feed back to mouth for rumination
Main function of reticulum
Helps keep foreign objects from getting in GI tract
honey-comb lining
unknown
omasum function
abomasum
true stomach
functions to prepare feed bolus for digestion and absorption by mixing HCl and enzyme pepsin through muscular contractions
All types of digestion
Smooth muscle tissue
cecum
secondary area for microbial digestion in monogastrics and ruminants
VFAs are absorbed through cecum wall
similarites and differences between monogastric and ruminants
•The pancreas and gall bladder secrete enzymes, buffers and bile into the duodenum
•Protein and lipid digestion and absorption occurs in the small intestine
The small intestine is not the major site of carbohydrate digestion and absorption because the majority of carbohydrates have already been digested and absorbed as VFAs in the rumen.
undeveloped, nonfunctional rumen
At birth, the ruminant has ….
Milk goes from mouth, esophagus, and straight to the omasum and abomasum
reticular groove
structure that transports the milk straight to omasum
suckling reflex
The reticular groove forms in response to…
3.5 to 5
In cattle, the rumen is developed by … months of age
1 mo
In sheep/goats, the rumen is developed by … months of age
Increase, decrease
As animals nutritional needs change as they age, does the reticulum increase or decrease in size and does the abomasum increase or decrease?
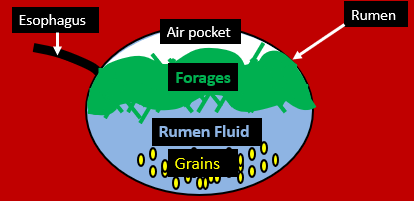
forages
what is lighter and stays on top to form a raft?
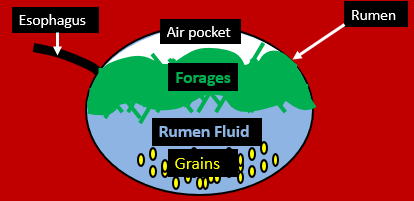
grains, rumen fluid
What sinks to the bottom? What fluid is in there?
mechanical digestion
The rumen is constantly undergoing …. through muscular contractions
Because they need to be killed in the stomach to be digested by protease
Why are microbes not a source of protein for hindgut fermentors?
chyme cant move back in the tract
yes
Do horse have molars and incisors top and bottom?
mastication
breaking down feed mechanically with saliva to moisten
upper molars are wider
What causes the issue that makes it hard for older horses to grind feed, since those molars do not meet evenly?
esophagus
transports feed bolus to stomach
horse can not vomit
small
Horses have a …. size stomach, which causes issues if they eat to much. If they eat too much, it can rupture
All three forms
Which types of digestion are in the stomach?
Killed by HCl or survive and live in cecum for microbial digestion
What happens to microbes in the stomach?
gallbladder
What do horses not have that ruminants do?
Do not consume high lipid diet, bile is continuously released from liver
Why do horses not need a gallbladder?
4 ft long, holds 8 gal
How long is horse’s cecum and how much does it hold?
cecum
Where is the site of microbial digestion for horses?
VFA
What are produced from microbial digestion and absorbed into the body from cecum and colon in a horse?
VFAs
What is main source of energy for a horse?
water absorption
Main purpose of large intestine
Abdominal pain in horse that can lead to death
What is colic?
Sharp turns in the large intestine can lead to compaction and blockage
What causes colic?
Use forages for energy through microbial digestion
similarities between hindgut fermenters and ruminants
R: primarily takes place in rumen, HGF: takes place in cecum
differences between hindgut fermenters and ruminants and microbial digestion
both have cecums
similarities between hindgut fermenters and monogastrics
one can utilizes forages while the other cant
differences between hindgut fermenters and monogastrics
pecking
What is chickens form of mechanical digestion for their mouth?
Used to break up food into smaller pieces
crop
In chickens, food enters the esophagus and then goes where?
Temporary storage where saliva softens feed
What is the purpose of the crop?
proventriculus
What is the true stomach in poultry?
proventriculus
Where is three forms of digestion occurring in poultry?
–Mechanical digestion through muscular contractions
–Chemical digestion through hydrochloric acid
Enzymatic digestion through pepsin
gizzard
Where is the main site of mechanical digestion chickens?
muscle contractions with grit
What is the purpose of the gizzard, which is why it has a tough lining?
Feed is ground by a mill
Why is the gizzard less important for chickens in modern day diet?
Chickens have two ceca, swine have one
Difference between poultry and swine
cloaca
This chamber is for digestion, urinary, and reproductive passages
vent
Where does the cloaca open externally to?
paste on feces
What is urine like in chickens?
Crop
Label E
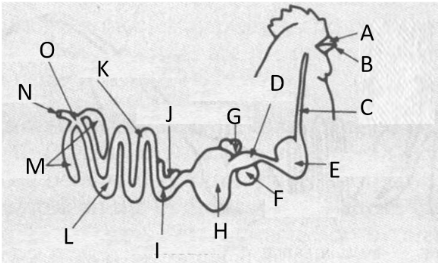
proventriculus
Label D
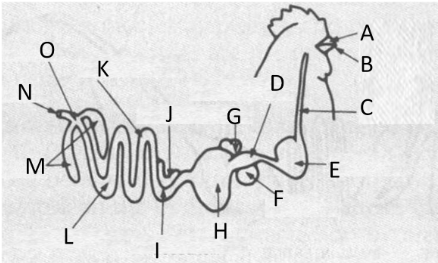
gizzard
Label H
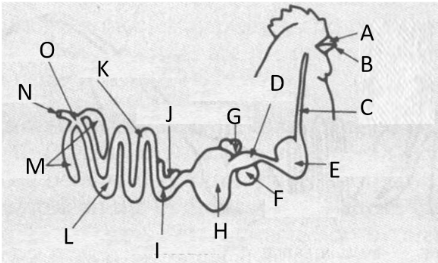
Cloaca
Label O
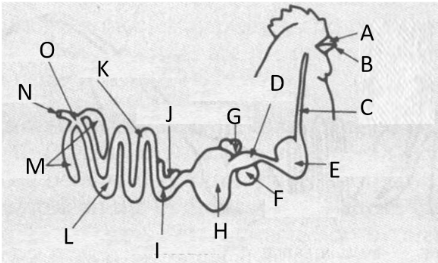
liver and spleen
Label G and F
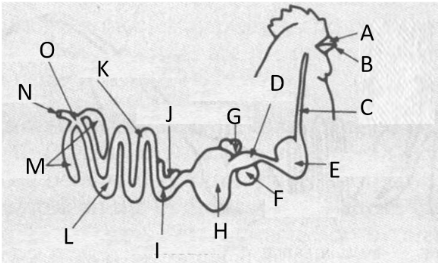
digestion in the body
Breaking feed particles into microscopic nutrient molecules (i.e. chemicals) by mechanical, chemical and enzymatic digestion
absorption into the body
Absorbing the microscopic nutrient molecules (i.e. chemicals) into the blood stream from the GI tract
metabolism by the body
Using the microscopic nutrient molecules (i.e. chemicals) in the body’s cells.
Nitrogen
Difference between carbohydrates and protein (element)
muscle, bones, hair, conn. tissue
How does the body use protein in structural ways?
enzymes, hormones, antibodies
How does the body use protein in physiological ways?
starving animal will begin to break down muscle
How does the body use protein in source of energy ways?
specific group of AAs that are connected together by a long chain
What is protein?
polypeptide chain
what is a long chain of AAs?
specific sequence of AAs
Each protein has what?
folds into specific 3D shape
The specific sequence of AAs determines what in the protein?
which is key for protein or enzyme to work correctly in the body
amino, carboxylic acid, side groups
What are AAs made of?
NH2
Amino group
COOH
Carboxylic acid group
peptide bond
How are the amino acids (AAs) connected to form protein?
H2O released
protein that catalyze chemical rxn
What is an enzyme?
10
How many are essential AAs that animal needs to consume?
essential AAs that are present in the lowest amount in the diet
What does limiting AAs mean?
lysine, methionine, threonine
What are the examples of limiting AAs?
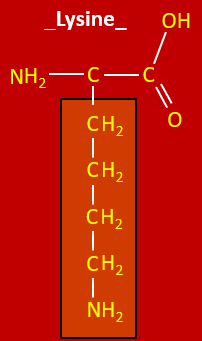
Draw lysine
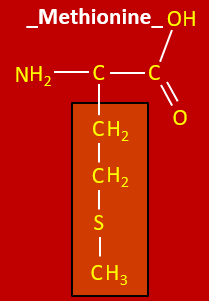
Draw methionine
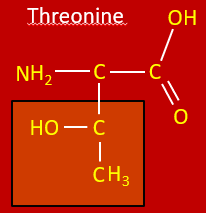
Draw threonine
lysine
What is the most limiting AAs in swine?
arginine
What is the most limiting AAs in cattle in high grain diet?
methionine
What is the most limiting AAs in cattle in high forage diet?
methionine
What is the most limiting AAs in poultry?
they are found in the lowest amount in plants or feedstuffs, thus lowest amount consumed in diet
Why are lysine, methionine and threonine usually the most limiting AAs in farm animal diets?
which is why these AAs are supplemented in most diets
limiting AAs
When proteins are being built, it stops as soon as…. is not present in the cell
animal’s body can make them
Non essential AAs are what?
requirement of essential and limiting AAs
What does the term ‘protein requirement’ refer to for farm animal diets?
microbes are a source of protein for ruminant, but not for monogastrics and HGF
How is protein requirement different for ruminants, monogastrics, and hindgut fermenters?
microbes make all 20 AAs for microbes own protein needs, microbes get broken down in stomach, the duodenum absorbs
Explain protein requirement for ruminants?????
difficult to estimate how much protein the animal will receive
What is difficult about microbes being a source of protein for ruminants?
diet must contain all essential and limiting AAs
Explain protein requirement for monogastrics and hindgut fermenters
quality and quantity of protein is very important
easily digestibility protein that contains essential AAs required
What is meant by protein quality?
high temperature
What can cause damage to protein quality?
animal protein
Which one is considered more protein quality plant or animal sources?
meat bone meal, expensive
Examples of animal protein sources and one draw back from it
protease enzyme
What accomplishes protein digestion in monogastrics and hindgut fermenters?
breaks it down into individual AAs
pepsin
What is the protease that is released from stomach into stomach?
trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase
What is the protease that is released from pancreas into duodenum? They cut long protein chains into short polypeptide chains
aminopeptidase, dipeptidase
What is the protease that is released by villi and act on surface of villi? They cut short polypeptide chains into individual AAs