Unit 1: Fluids - Pressure and Forces
1.5(2)Studied by 157 people
0%Unit 1 Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:51 PM on 4/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
1
New cards
Density
\________ is a positive scalar quantity.
2
New cards
Density
Mass per unit volume of a substance is defined as density.
3
New cards
Buoyancy
If a body is fully or partially immersed in a fluid, it experiences an upward force due to the fluid called buoyant force, and the phenomenon is called buoyancy.
4
New cards
The Volume Flow Rate
It is the volume of fluid that passes through a particular point per unit of time.
***f = Av***
* f = volumetric flow rate
* A = cross-sectional area
* v = flow velocity v
***f = Av***
* f = volumetric flow rate
* A = cross-sectional area
* v = flow velocity v
5
New cards
Bernoulli’s Effect
At comparable heights, the pressure is lower where the flow speed is greater.
6
New cards
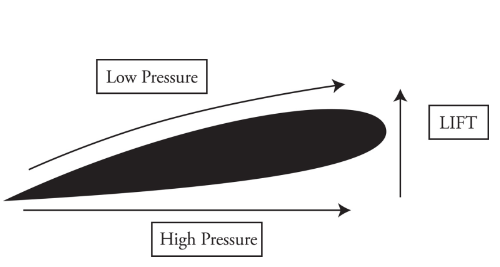
Air Flow
The air on the bottom has greater pressure and pushes up on the wing giving the airplane lift force
7
New cards
Pressure
Pressure is defined as the magnitude of the normal force acting per unit surface area.
P = F/A
* P is pressure
* F is force
* A is the area
P = F/A
* P is pressure
* F is force
* A is the area
8
New cards
Pressure units
Pascal (Pa) 1 Pa = 1 N/m^2
Practical units: atm, bar, torr
Practical units: atm, bar, torr
9
New cards
Hydrostatic pressure
It is the pressure due to the liquid.
10
New cards
Continuity equation
The density of the fluid is constant.
***A1V1 = A2V2***
* A1 and A2 (cross-sectional areas)
* V1 and V2 (flow velocities)
***A1V1 = A2V2***
* A1 and A2 (cross-sectional areas)
* V1 and V2 (flow velocities)
11
New cards
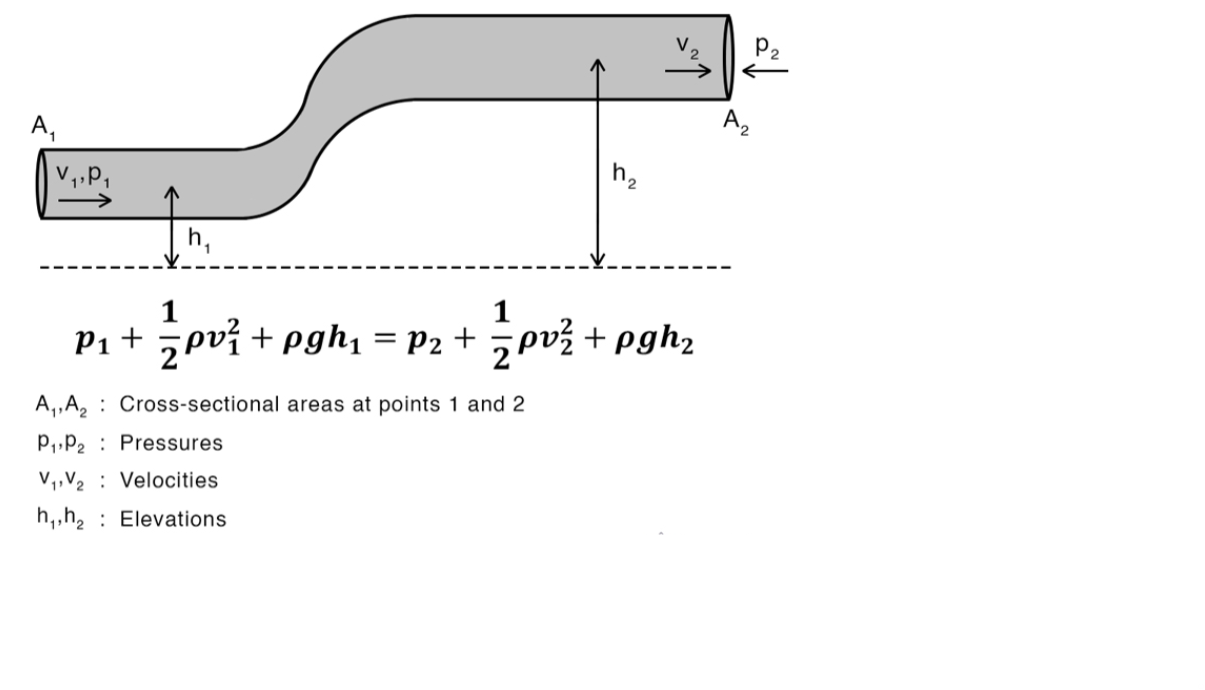
Bernoulli’s Equation (Conservation of energy in liquids)
* fluid is incompressible.
* fluid’s viscosity is negligible.
* fluid is streamlined.
* the equation is very similar to the conservation of energy with total mechanical energy.
* fluid’s viscosity is negligible.
* fluid is streamlined.
* the equation is very similar to the conservation of energy with total mechanical energy.