A&P - unit 3 HW questions
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapters 8,9,10 homework questions and their answers
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
which term refers to a place where two or more bones come together?
articulation
a joint has no joint cavity and exhibits little or no movement would be classified as a _____ joint.
fibrous
cartilaginous joints
unite two bones by means of fibrocartilage or hyaline cartilage
synovial joints are different from both fibrous and cartilaginous joints because synovial joints
are enclosed by a joint capsule
synovial fluid
decreases friction between bones
articular cartilage
covers the ends of bones in synovial joints
the function of a bursa is to
provide a fluid-filled cushion that reduces friction
articular cartilage provides
a smooth surface where bones meet
the joint capsule is a
double layer of tissue that encloses a joint
bowing the head is an example of _______
flexion
rotating the forearm so that the palm faces posteriorly is called _____
pronation
rotating the forearm so that the palm faces anteriorly is called _____
supination
bending your elbow decreases the angle at the joint is _____
flexion
which of the following pairs of terms are opposite?
abduction - extension
inversion - retraction
plantar flexion - dorsiflexion
pronation - rotation
elevation - protraction
plantar flexion - dorsiflexion
the opposite of depression is _____
elevation
the opposite of supination is ______
pronation
the opposite of extension is ______
flexion
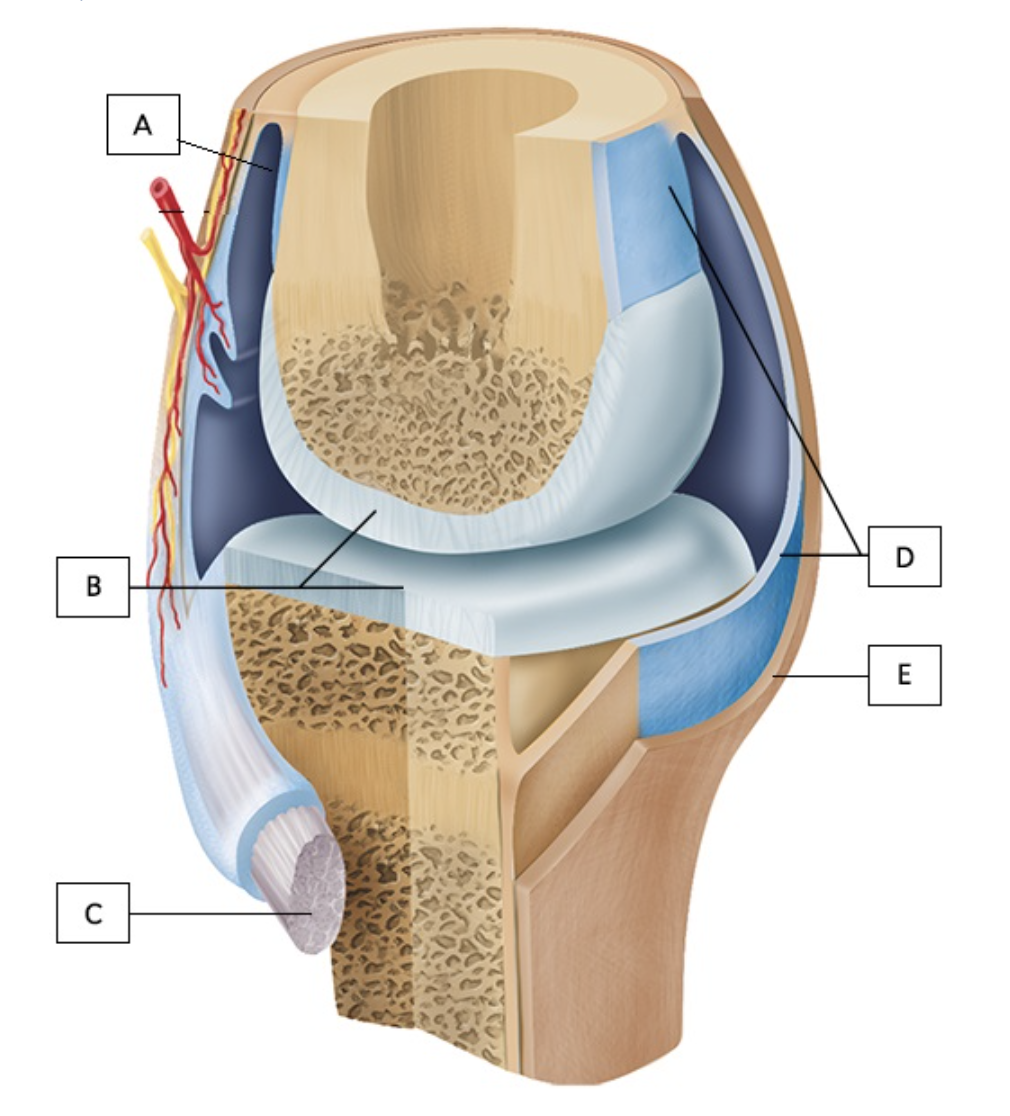
what does structure “B” represent on the diagram?
articular cartilage
joints joined together by hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage would be classified as ___ joints.
cartilaginous
while standing, looking up at the stars requires _______
hyperextension of the neck
the capacity of a muscle cell to shorten forcefully is known as
contractility
skeletal muscle fibers
possess striations
epimysium
surrounds individual muscles
myosin is also known as the
thick myofilament
which of the following is composed of myosin molecules?
thick myofilaments
I bands
Z disks
sarcolemma
tropomyosin
thick myofilaments
the active sites to which cross-bridges attach are found on the
actin myofilaments
a sarcomere extends from
one z disk to an adjacent z disk
which of the following is mismatched?
I band - contains only actin
M line - middle of the H zone
Z disk - structure between adjacent sarcomeres
myosin filament - thin myofilaments
actin myofilaments - thin myofilaments
myosin myofilaments - thin myofilaments
a sarcomere is the
structural and functional unit of the skeletal muscle fiber
the sarcolemma is the
plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
channels that open or close in respect to changes in the electrical charge or voltage across the plasma membrane are called
voltage-gated ions channels
depolarization of the plasma membrane occurs when there is a rapid influx (inflow) of
sodium ions (Na+)
synaptic vessels in the neuromuscular junction contain
acetylcholine
t tubules
conduct action potentials deeps into the muscle fiber
the sarcoplasmic reticulum
stores Ca2+
a sustained muscle contraction is known as ____
tetanus
what is the power stroke?
the movement of myosin head while attached to actin myofilament
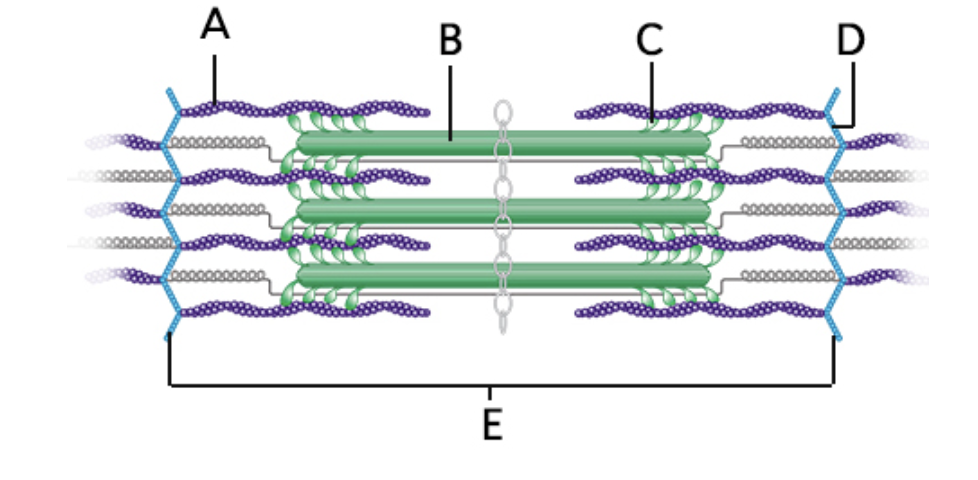
what does “A” represent on the diagram?
actin myofilament
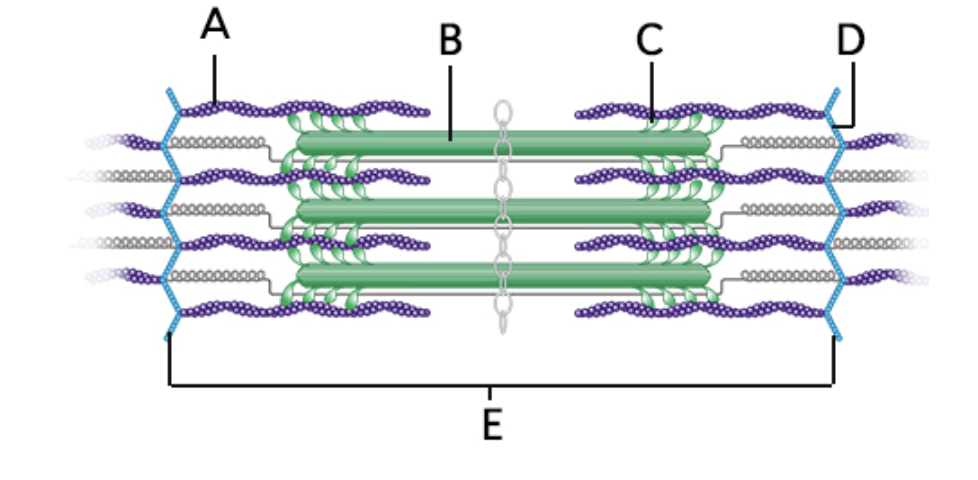
what does “B” represent on the diagram?
myosin myofilament
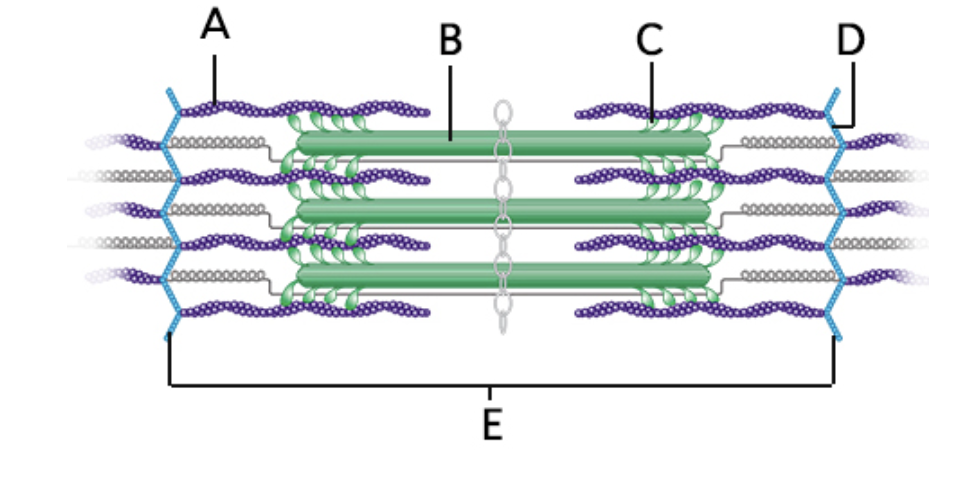
what does “C” represent on the diagram?
cross-bridge
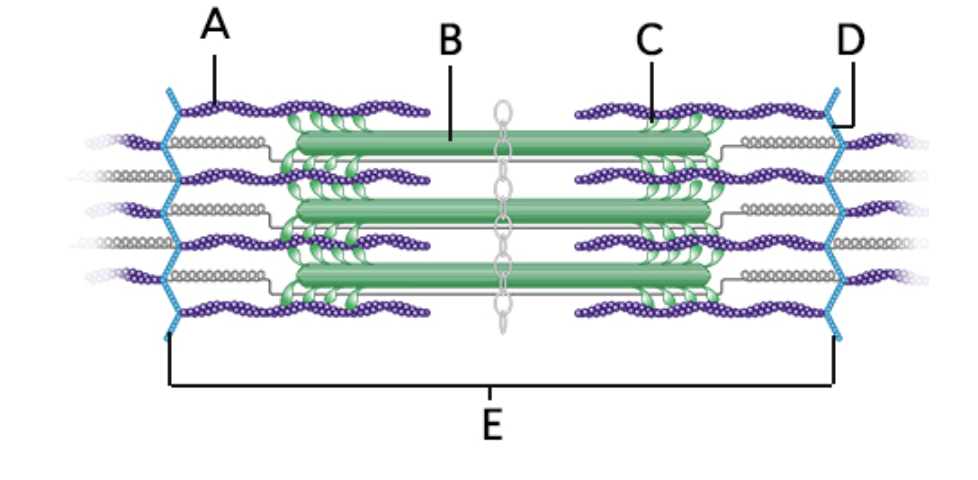
what does “D” represent on the diagram?
z disk
what does “E” represent on the diagram?
sarcomere
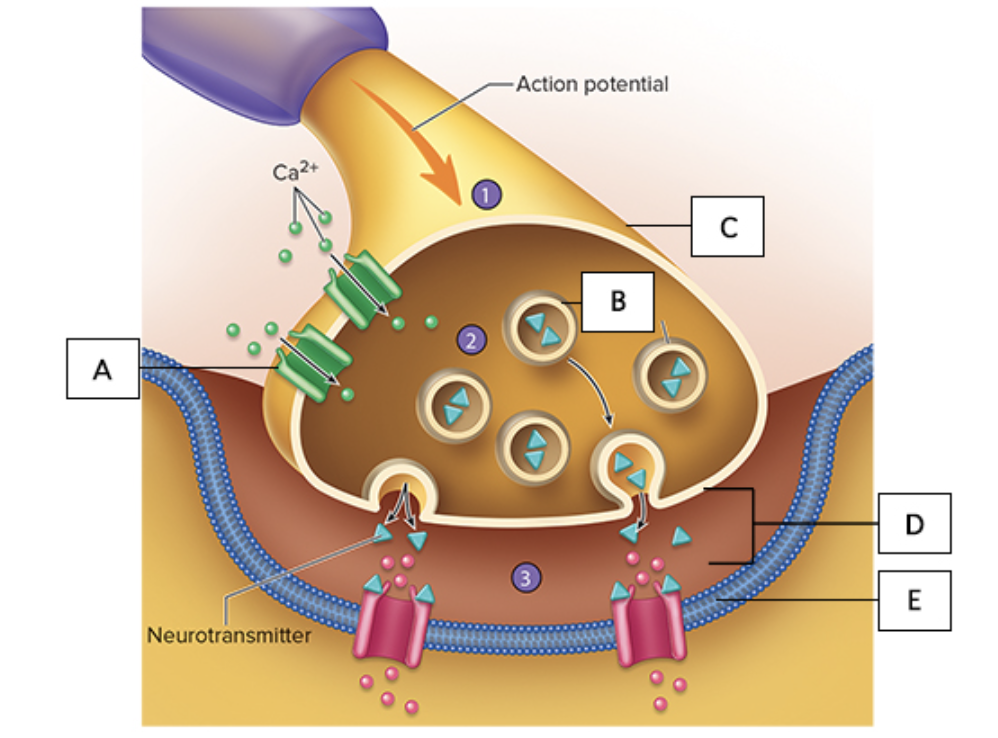
the figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction, what does “B” represent?
synaptic vesicles
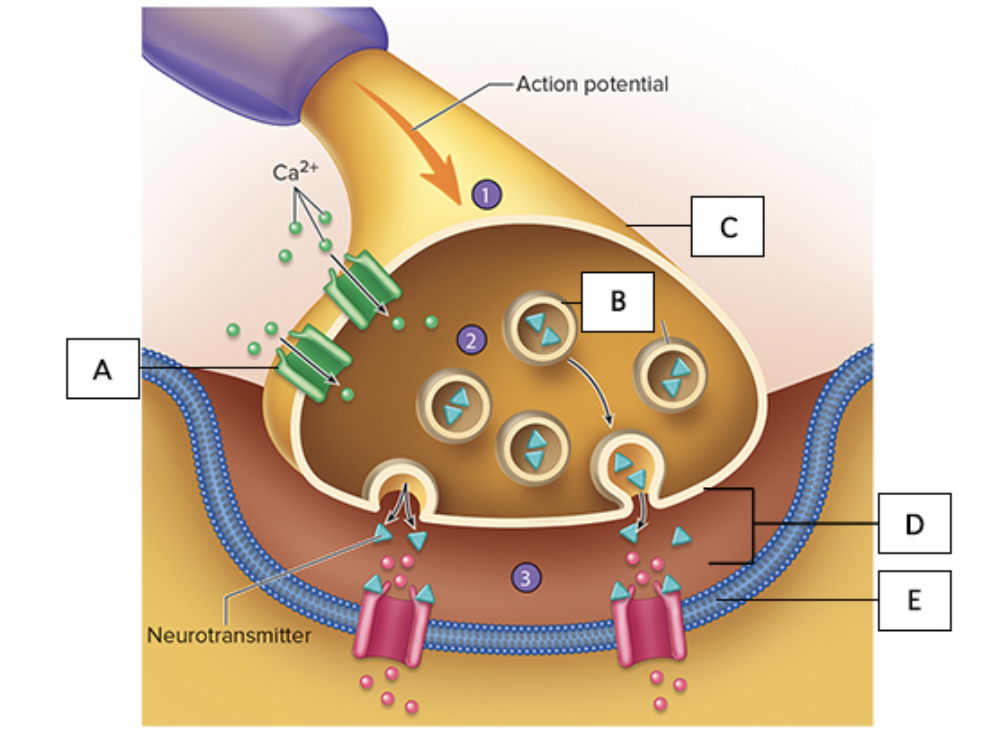
the figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction, what does “D” represent?
synaptic cleft
the origin is
the stationary end of the muscle
the prime mover is
the muscle that does most of the movement
an antagonist is
a muscle working in opposition to another muscle
when a skeletal muscle contracts to cause a given movement, the more moveable end of attachment of the muscle is called its ______
insertion

circular
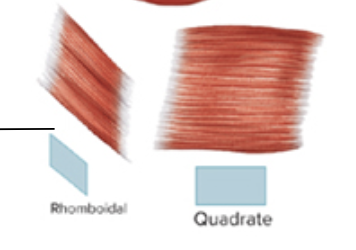
parallel

convergent
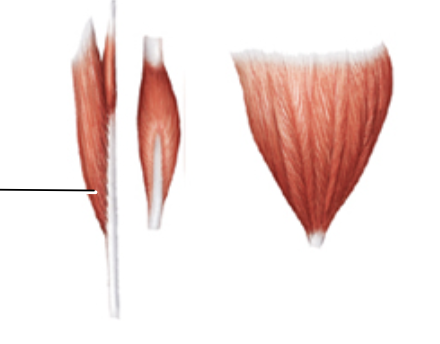
pennate
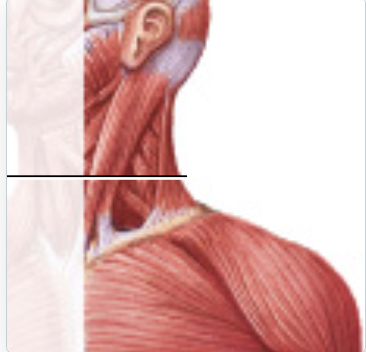
trapezius
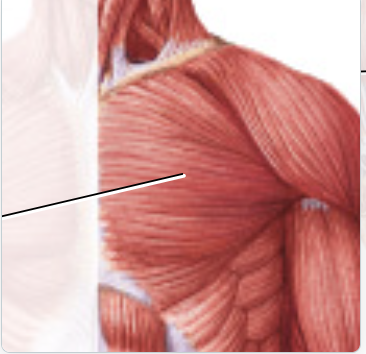
pectoralis major
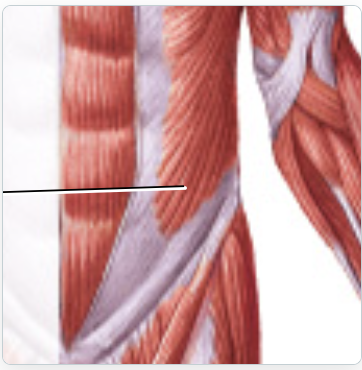
external abdominal oblique
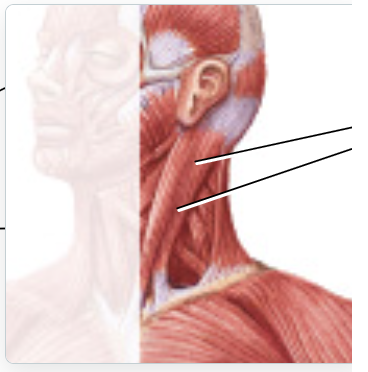
sternocleidomastoid
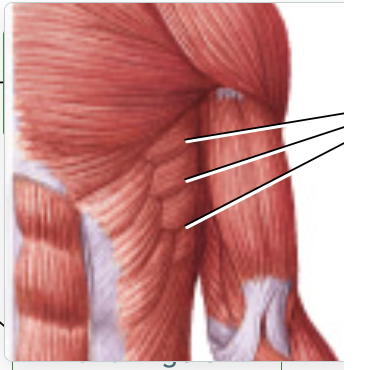
serratus anterior
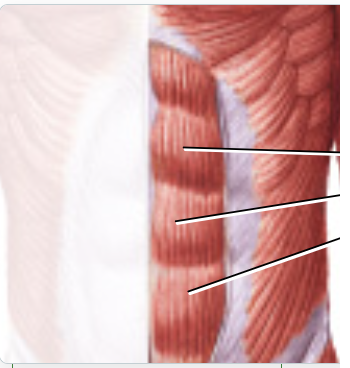
rectus abdominis
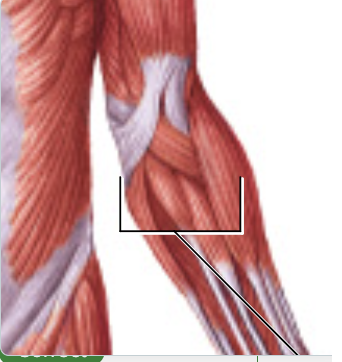
flexors of the wrist and fingers
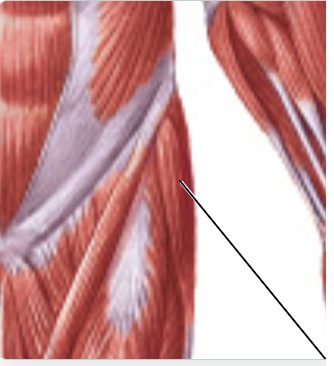
tensor fasciae latae
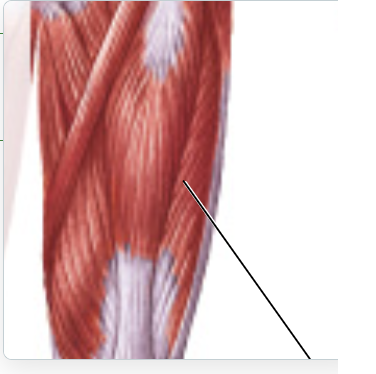
vastus lateralis
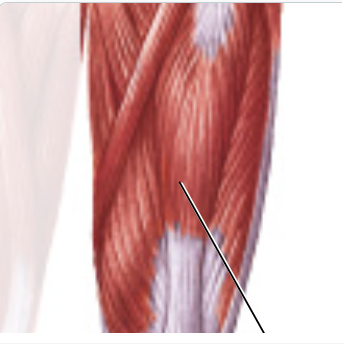
rectus femoris
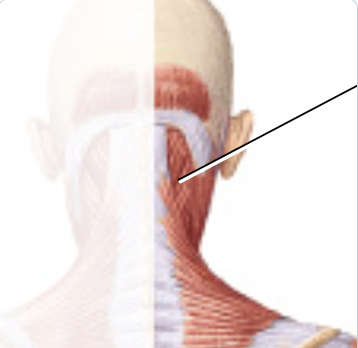
splenius capitis
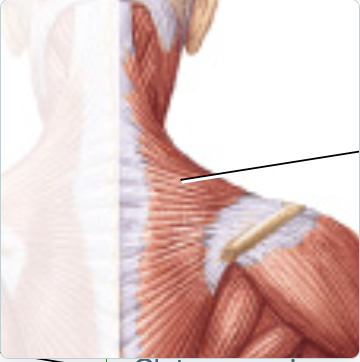
trapezius
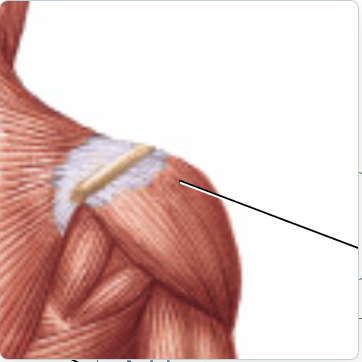
deltoid
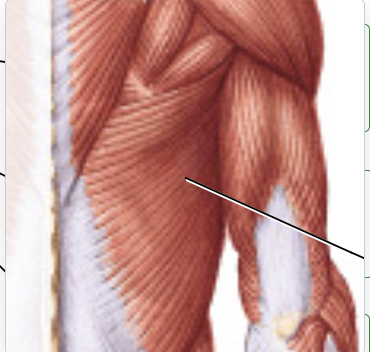
latissimus dorsi
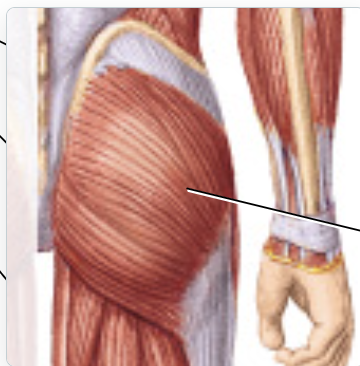
gluteus maximus
adductor magnus
iliotibial tract
gracilis
gastrocnemius
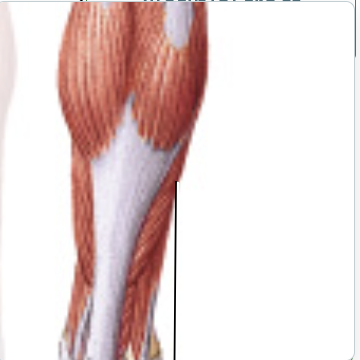
soleus
the brachioradialis is named for its ______
origin and insertion
of the following muscles of the head, which one wraps around the orbits?
nasalis
obticularis oris
masseter
orbicularis oculi
temporalis
orbicularis oculi
when an intramuscular injection is given in the anterior aspect of the thigh, injection is in the _____
rectus femoris
pectoralis major
named for location and size
gluteus minimus
named for location and size
triceps brachii
named for location and number of heads
rectus femoris
named for orientation of fasciculi and location
the fixed end of a muscle
origin
the mobile end of a muscle
insertion
a muscle that accomplishes a certain movement
agonist
a muscle that opposes a muscle that accomplishes a certain movement
antagonist
members of a group of muscles working together to produce a movement
synergist
muscles that hold one bone in a place relative to the body while a usually more
fixator
one muscle of a group working together that plays the major role in accomplishing the movement
prime mover