Arthropods (Exam 1)
1/167
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1 of Parasitology is the Arthropods. Blue text is testable material, black text is general info or potential extra credit
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
168 Terms
Parasite
A smaller organism that lives on or in, and at the expense of a larger organism (a host)
Ectoparasite
A parasite that lives on the external surface of a host
Endoparasite
A parasite that lives within the body of a host
Ectoparasites cause an____
Infestation
Endoparasites cause an____
Infection
Obligate parasite
Parasites that always require a host
Facultative parasite
Parasites that only parasitize if given the opportunity
What is the prepatent period?
Time after infection before detection of the parasite
Definitive (final) Host
The host in which the parasite adult or sexual reproduction occurs
Paratenic host
Host in which No additional parasite development occurs
Intermediate host
A host required for larval development
Arthropods
Group of organisms encompassing insects, spiders, and crustaceans, that often have segmented bodies, jointed appendages
Insecta: include what, and physical description
Class of Arthropods that Include Flies, Fleas, Lice, Bugs
Segmented bodies with head, thorax and abdomen, 6 legs and up to 4 wings
Arachnida: Includes what and physical description
Class of Arthropods that includes Ticks and Mites
Fused Head, thorax and abdomen, have 8 legs as adults and 6 in larval stages
No wings

Name this insect (Scientific and Common names)
Arthropods > Insecta > Trichoptera (caddisflies)
Description: flies with 4 wings, short mouthparts, aquatic larvae in fresh water
Trichoptera (Caddisflies) are vectors of what disease?
Potomac Horse Fever
What is the causative agent of Potomac Horse Fever?
The bacterium Neorickettsia risticii in trematodes within Trichoptera (Caddisflies)
How do horses acquire Potomac Horse Fever?
Ingestion of Trichoptera (Caddisflies) in drinking water
Clinical Signs of Potomac Horse Fever
Acute enterocolitis, Abortion, laminitis
Treatment and Prevention of Potomac Horse Fever
Oxytetracycline, Turn off barn lights at night
Diptera
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies)
Flies with 2 functional Wings
Includes Nematocera, Brachycera, Cyclorrhapha

Name this Fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Nematocera
small delicate flies with long many segmented antennae (beads on a string appearance.
Females suck blood, males ingest nectar, aquatic larval forms
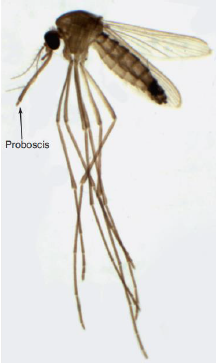
Name this Fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Nematocera > Culicidae (mosquitoes)
Includes Culex and Anopheles genus
Long segmented antennae, elongated proboscis, eggs laid in water, aquatic air-breathing larvae, free swimming pupae
Females require blood proteins for ovary maturation
Autogeny
Process by which females can undergo ovarian maturation without a bloodmeal
Culicidae (Mosquitoes) are vectors for what diseases?
Dirofilaria immitis (heartworm), Plasmodium (malaria) via Anopheles mosquitoes, West Nile Virus, Dengue fever, Equine encephalitides, Rabbit myxomatosis
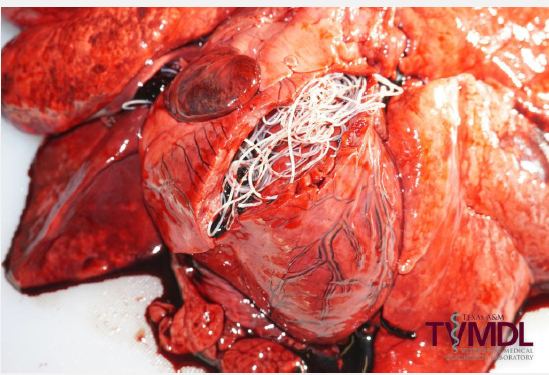
What disease is this and what is it caused by?
This is Heartworm caused by the nematode/roundworm Dirofilaria immitis and vectored by Culicidae (Mosquitoes)

Name this Fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Nematocera > Simulidae (blackflies)
Small stout bodied black, gray or yellowish-brown flies with short antennae and short mouthparts
Breed in running water, larvae cling to surfaces with posterior hooks or anterior prolegs
How do Simulidae (Blackflies) feed?
Vicious biters: feed by lacerating tissues and making a blood pool
Diseases caused or vectored by Simulidae (Blackflies)
Hypersensitivity (dermatitis, pruritus, edema, blisters) due to bites
Vectors for Leucocytozoon in birds, Onchocerca in cattle, dogs and humans which is the causative agent of River Blindness in humans in Africa
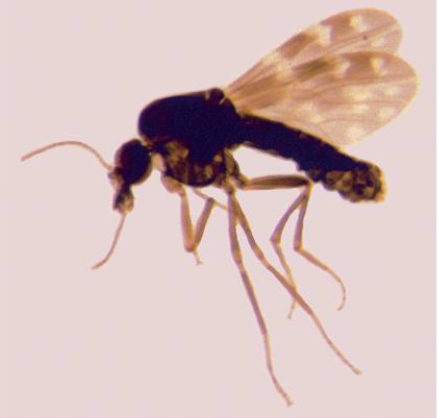

Name this fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Nematocera > Ceratopogonidae (midges)
Tiny <2mm flies, long slender antennae, short mouth parts, mottled wings, adults are nocturnal, females are bloodsuckers
Culicoides spp. and clinical disease
Genus of biting midges in Ceratopogonidae family Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Nematocera > Ceratopogonidae (midges) > Culicoides
Have very painful bites (like cigarette ash burns)
Can cause allergic dermatitis “Queensland Itch” in horses due to hypersensitvity reaction

Name this disease and the causative agent
African horse sickness, caused by an Orbivirus. Transmitted primarily by Culicoides biting midges
Ceratopogonidae (midges) vectors of what diseases?
Orbiviruses: Bluetongue, African Horse Sickness
Onchocerca in horses and cattle, Dipetalonema in humans, Hepatocystis in primates, Haemaproteus and Leukocytozoon in birds

Name this fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Nematocera > Psychodidae (phlebotomine sandflies)
small dull colored flies with long antennae
Wing veins radiate in straight lines
Phlebotomus in Old World
Lutzomyia in New World
Tropical distribution
What diseases does Psychodidae (Phleotomine sandflies) vector?
Pappataci fever virus, Bartonella bacilliformis in people
Leishmania spp.
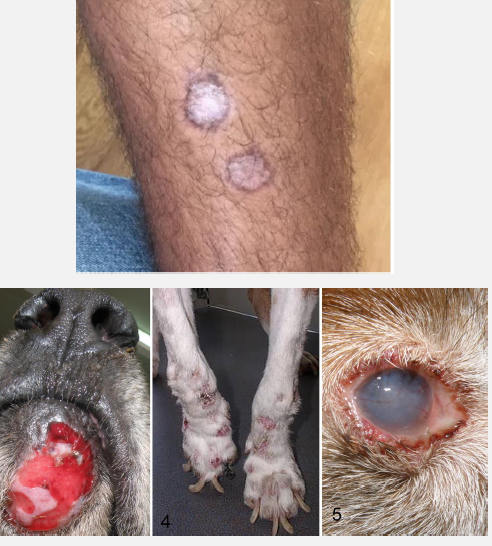
What disease is this? What are the clinical signs?
Cutaneous and visceral forms of Leishmania spp. (a protozoan parasite that circulates in macrophages). Causes dermal lesions, lymphadenomegaly, splenomegaly, ocular disease, onychogryposis (nail abnormalities)
Vertical transmission possible
Methods of Fly Control for Caddisflies, Mosquitoes, Blackflies, Midges, Sandflies
Caddisflies: Cover water sources
Mosquitoes: Dinetofuran + pyrethroids (permethrin) (topical), isoxazolines (afoxolaner)
Blackflies: Smoke repels flies, chemical repellents (pyrethroids), petroleum jelly, fly masks
Midges: Insect repellents
Sandflies: Deltamethrin collars, spot-on pyrethroids (permethrin) + imidacloprid, isoxazolines (afoxolaner, fluralaner)

Pyrethroids
Drugs ending in -thrin (tetramethrin, permethrin, deltamethrin)
Synthetic substances based on molecular structure of natural insecticidal compounds from chrysanthemum flower
Available as shampoos, spot-ons, pour-ons, pastes, ear tags, collars, dusts, foggers, insect-repellent cloths, household sprays
Pyrethroids mechanism of action
Paralyze and kill arthropods by binding and disrupting voltage gated sodium and GABA channels, disrupting neurotransmission
More effective at lower temperatures so more effective in insects than warm-blooded mammals
Pyrethroid toxicity
Toxic to fish
Cats are highly sensitive to permethrin = causes hyperexcitability, depression, ataxia, vomiting, anorexia, tremors, convulsions
Practice question: What is the causative agent of Potomac Horse Fever, vectored by Trichopteran caddisflies?
Answer = Neorickettsia risticii
Practice Question: Which of the following is the vector for onchocerciasis, the causative agent of river blindness in people?
Answer = Simulidae
Practice Question: A bite from which of the following can result in a host hypersensitivity reaction known as Queensland Itch?
Answer = Culicoides (Ceratopogonidae) midges
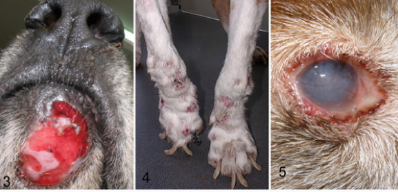
Practice Question: A dog with the following lesions was likely bitten by which fly?
Answer = Phlebotomine sandflies
Practice Question: Which of the following is true regarding pyrethroids such as permethrin?
Answer = They are highly toxic to fish
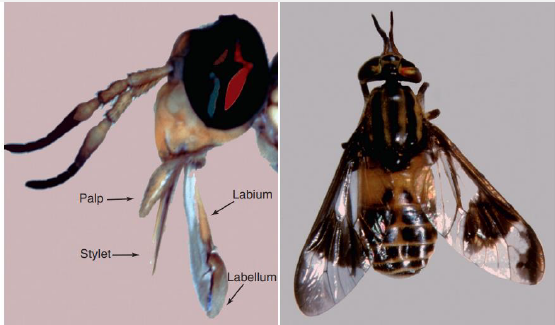
Name this fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Brachycera (tabanids)
Stout bodied, up to hummingbird sized with stout three-segmented antennae
Females require bloodmeal, males feed on nectar, sap, aphid feces, eggs laid in masses over water
Feed through laceration and blood pooling, attacks are painful
Brachycera (tabanids) vectors of
Anthrax, tularemia, anaplasmosis, Equine infectipouos anemia virus, Trypanosoma evansi (surra disease), Trypanosoma theileri (nonpathogenic), Elaeophora schneideri

Class of Diptera (flies) this fly belongs to
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Cyclorrhapha
Family including Muscidae, Glossinidae, Hippoboscidae, Sarcophagidae, Calliphoridae, Oestridae
Three-segmented antennae with frond-like structure on end (arista), Mouthparts adapted to feeding habits
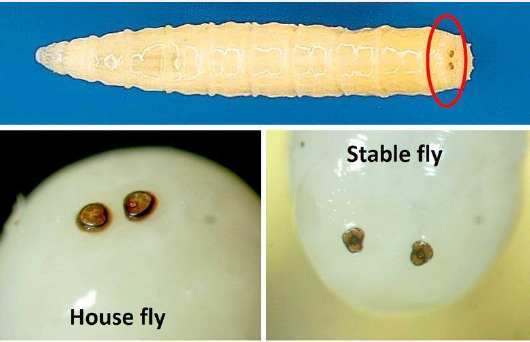
Larval forms of Cyclorrhapha: What is the name of the circled part, and the specific names for Muscids, Oestrids
Circled part are Spiracles (breathing organs)
Muscids, Sarcophagids, Calliphorids = Maggots
Oestrids = Bots
Myiasis
Parasitism by fly larvae
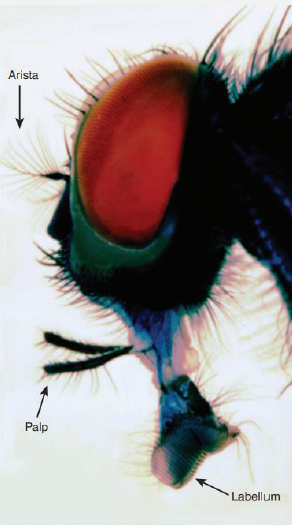
Name this fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Cyclorrhapha > Muscidae > Musca (filth flies)
Musca domestica (house fly) and Musca autumnalis (face fly)
Retractable proboscis with terminal spongy organs (labella)
Eggs laid in manure or decaying matter, feed on secretions around eyes, nostrils, mouth, and blood around wounds
M. autumnalis overwinters in buildings, but stays out of buildings in the summer
Musca domestica can vector____
parasitic nematodes (Draschia, Habronema)
Musca autumnalis can vector____
Thelazia (eyeworm) and Moraxella bovis, which causes infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis (pinkeye)

Name this fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Cyclorrhapha > Muscidae > Stomoxys (stable flies)
Stomoxys calcitrans stable fly
Long, pointed proboscis, palps shorter than proboscis
Eggs laid in decaying organic material (hay, lawn clippings, manure)
Both sexes feed on blood
Painful bite interrupts animal feeding
Stomxys (stable Flies) vector of____
parasitic nematode Habronema microstoma

Name this Fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Cyclorrhapha > Muscidae > Haematobia (horn flies)
Haematobia irritans
Small fly with short proboscis, palps same length as proboscis
Bite cattle and suck blood
Active during warmer months
Eggs laid in cow manure, hatch to adults within 6 days, eggs develop to new egg-laying adults withing 2 weeks
can irritate cattle, leading to decreased production
vector for nematode parasite Stephanofilaria stilesi

Name this fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Cyclorrhapha > Glossinidae (tse tses)
Localized to Africa
Long feather-like arista, Hatchet shape venation on wings, palps same length as proboscis
Larvae develop within mother feeding on uterine fluids
Bloodmeals required for larval development
Glossinidae (tse tses) vector for____
Protozoal parasite Trypanosoma brucei
Trypanosoma brucei causes what disease?
African sleeping sickness in humans, nagana in livestock

Name this fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Cyclorrhapha > Hippoboscidae (keds)
Dorsoventrally flattened, often wingless, piercing mouthparts, antennae embedded in head
Larvae develop within mother feeding on uterine fluids
Melophagus ovinus
Sheep Ked (Hippoboscidae)
Entire life cycle completed on sheep
Can vector Trypanosoma melophagium (nonpathogenic)
Hippobosca equinus
horse ked
Lipoptena cervi
deer ked
Hippobosca longipennis
Can vector nematode parasite Acanthocheilonema dracunculoides
Fly Control for Cyclorrhapha
Removal of breeding sites:
Musca – garbage and feces, Spraying environment with insecticides like organophosphates (tetrachlorvinphos, dichlorvos, coumaphos), pyrethroids
Stomoxys – contaminated hay (with feces and urine), Pyrethroids, organophosphates (coumaphos, dichlorvos, chlorpyrifos, tetrachlorvinphos, phosmet)
Haematobia – animal feces, Ear tags impregnated with pyrethroids (fenvalerate), some resistance to many insecticides (including permethrin and fenvalerate), Feed-through organophosphates
Brachycera: Difficult to repel, chemical repellents
Glossina (tse tses): Eradication efforts involve release of sterile males
Hippobosca (keds): Organophosphate (coumaphos) dips or sprays, ivermectin
Organophosphates
Things ending in –phos or –vos (dichlorvos, tetrachlorvinphos, coumaphos)
Available in fumigants, resin strips, sprays, dips, powders, collars, ear tags
Organophosphates Mechanism of Action
Act via irreversible binding and inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
Buildup of acetylcholine in synapse leads to constant stimulation
Organophosphate Toxicity and reversals
Toxicity in animals results in salivation, lacrimation, urination, and defecation (SLUD), convulsions, fasciculations
Atropine can be used to block overstimulation of Ach receptors
2-PAM (pralidoxime) can reverse effects by reactivating organophosphate-inhibited AChE
Practice Question: Which of the following is a distinguishing morphologic feature of tabanids?
Answer = stout, three segmented antenna
Practice Question: Which of the following is not considered a cyclorrhaphan fly?
Answer = Tabanids
Practice Question: Which of the following is a correct definition of myiasis?
Answer = Parasitism by fly larvae
Practice Question: Which of the following is transmitted by the tse tse fly (glossina)?
Answer = Trypanosoma brucei
Practice Question: Which of the following is an antidote to reverse the effects of organophosphate toxicosis?
Answer = Pralidoxime (2-Pam)

Name this Fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Cyclorrhapha > Sarcophagidae (flesh flies)
Large adults with longitudinal stripes on thorax and checkered abdomen
Large maggots with sunken spiracles
Can be facultative parasites, with maggots resulting in myiasis in wounded or wet skin
Two obligate parastite species Wohlfahrtia vigil and Cistudinomyia cistudinis

Name this fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Cyclorrhapha > Calliphoridae (blow flies)
Metallic blue, green, copper, or black adults
“Blow” eggs or larvae on meat
Spiracles lie flush with face of larva
Most are scavengers or facultative parasites
Attracted to wet skin, wounds, necrotic tissue
Affect incapacitated animals, including sheep, dogs, cattle, and rabbits
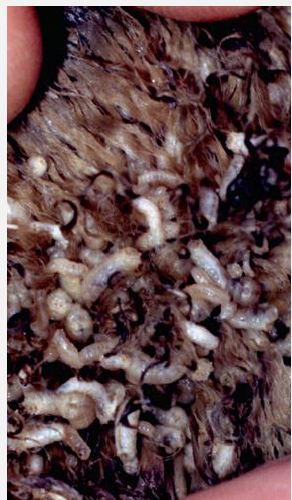
What is this condition? Treatment and prevention?
Wool strike in sheep (myiasis)
Developing larvae feed on scales and exudate on skin surface, and penetrate tissues
Affects areas stained by urine or feces (perineum, prepuce), or areas wet from rain (flanks, withers, ventral neck)
Fleece rot (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and lumpy wool (Dermatophilus congolensis) predispose to wool strike
Toxins absorbed from myiasis can lead to death
Treatment: Organophosphate (coumaphos) spray or dip, cyromazine (insect growth regulator)
Prevention: Clip wool around prepuce, tail docking
Mules’ operation: Removal of redundant skin folds

What Calliphoridae larvae is this?
Cochliomyia hominivorax: Obligate parasite
=American screwworm
Pigmented tracheal trunks in last 3-4 segments
Cause primary myiasis (feed on living tissue) vs. secondary myiasis (feed on dead flesh)
Eggs laid on fresh, uninfected wounds, maggots feed on living flesh and bone
Reportable
Method of fly control for Cochliomyia hominivorax?
Release of sterile males at the Panama Canal Border
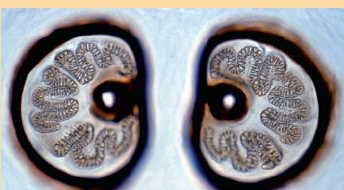
This spiracle belongs to which fly larvae?
Musca
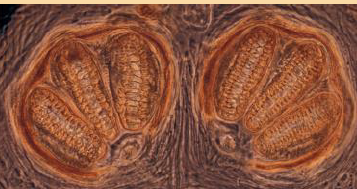
This spiracle belongs to which fly larvae?
Calliphoridae
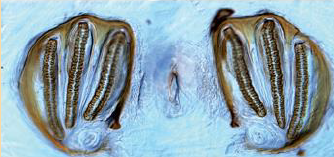
This spiracle belongs to which fly larvae?
Sarcophagidae
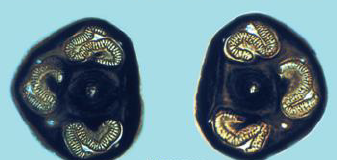
This spiracle belongs to which fly larvae?
Stomoxys
Oestridae (Botflies)
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Cyclorrhapha > Oestridae (botflies)
Typically host-specific, site-specific parasites in larval stage (bots)

Name this Fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Cyclorrhapha > Oestridae (botflies) > Oestrus ovis
Sheep nasal botfly
Stout, grayish-brown adults, covered with short hairs
Active in bright sun
Females deposit larvae in sheep nostrils
Larvae develop in mucosa of nasal cavity then frontal sinus, sneezed out and pupate = Heavy infection causes sneezing and nasal discharge
Treatment: macrocyclic lactones (ivermectin, eprinomectin)

Name this Fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Cyclorrhapha > Oestridae (botflies) > Hypoderma (Heelflies, Gadflies)
Hypoderma bovis and Hypoderma lineatum
Cattle often react to flies presence by becoming excited and galloping off
Adults oviposit on hairs of leg
Larvae burrow through skin and migrate through body
Hypoderma lineatum accumulate in what?
The esophagus
Hypoderma bovis accumulate in what?
The Spinal Cord
What are Warbles?
Lumps on dorsum of cattle caused by third-stage Hypoderma spp. larvae
Warbles can be removed by injecting 3% hydrogen peroxide into breathing hole
Treatment for Hypoderma spp. (Heelflies, Gadflies)?
Macrocyclic Lactones
Organophosphate treatment can cause host-parasite reactions (bloat, salivation, ataxia, posterior paralysis), Due to toxins elaborated by dying larvae. Counteract with phenylbutazone pre-treatment or adrenaline

Name this fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Cyclorrhapha > Oestridae (botflies) > Gasterophilus
Adult resembles bumblebee
Curved ovipositor beneath abdomen
Eggs deposited on horse hairs, depending on species:
G. nasalis: Intermandibular space
G. hemorrhoidalis: Lip hairs
G. intestinalis: Forelegs and shoulder
First-stage larvae tunnel into tongue and between molars
Second stage larvae in interdental pockets, root of tongue, and stomach wall
Larvae pass out into feces and pupate in soil
Where are third stage larvae of Gasterophilus nasalis located?
Ampulla of duodenum of horses
Where are third stage larvae of Gasterophilus hemorrhoidalis located?
Duodenum and rectum of horses
Where are third stage larvae of Gasterophilus intestinalis located?
Nonglandular stomach near margo plicatus
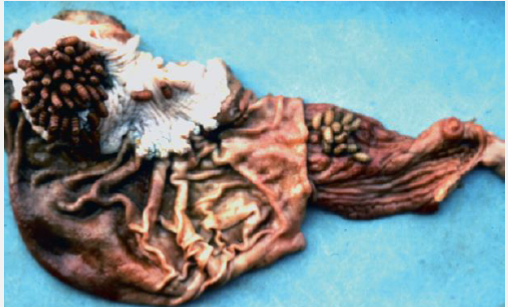
This is a picture of what species of fly bots infection? Is it pathogenic? Treatment?
Gasterophilus spp., considered largely nonpathogenic
Macrocyclic lactones

Name this fly
Arthropods > Insecta > Diptera (flies) > Cyclorrhapha > Oestridae (botflies) > Cuterebra
Obligate arthropod parasite of rodents and lagomorphs
Adult rarely seen

Name this bot
Third-stage larva large, dark-brown to black, with stout black spines
Commonly in northeastern U.S. around late summer to early fall
How are cuterebra bots acquired?
From rodent and rabbit burrows
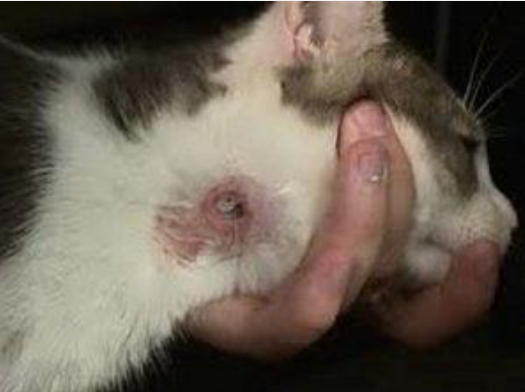
This is a ____ bot in a cat. Where can these bots migrate to?
Cuterebra: Bots found in cervical subcutaneous connective tissue
Can aberrantly migrate to ocular, nasal, oral regions, and brain
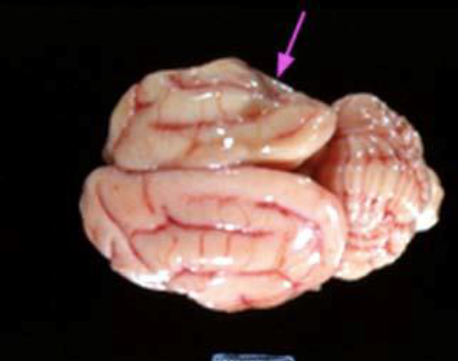
What disease is this? What is the causative agent?
Feline ischemic encephalopathy (FIE): Thrombosis of middle cerebral artery due to migration of Cuterebra or toxin secretion, causing Ischemic necrosis, degeneration of superficial layers of cerebral cortex and parenchymal destruction
Treatment and prevention of Cuterebra
Treatment: Manual removal, Topical imidacloprid or fipronil, Macrocyclic lactone (ivermectin) for CNS lesions, Diphenhydramine and dexamethasone added
Prevention: prevent outdoor activities in summer/fall, Insecticides (fipronil, imidacloprid) may be protective