epithelial tissue
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What is the purpose of epithelial tissue.
Covers and forms boundaries
What are the 2 main types of epithelial tissue ( by location)
Covering and lining epithelial
Glandular epithelial
What are the characteristics of epithelial tissue
Polarity
Specialized contacts
Supported by connective tissue
Avascular but innervated
Can regenerate
What are the functions of epithelial tissue
Protection
Absorption
Filtration
Excretion
Secretion
Sensory reception
Do epithelial cells have polarity
Yes
Describe the apical surface
Upper free, exposed to exterior
Smooth/slick
Most have microvilli to increase surface area
Some have cilia
Describe the basal surface
Lower and attached
Non cellular basal lamina
Glycoprotein and collagen fibers adjacent
Adhesive sheet
Selective filter
Scaffolding for cell migration in wound repair
What are specialized contacts of epithelial tissue
They bind adjacent cells together and form continuous sheets
Tight junctions aka impermeable junctions
Desmosomes aka anchoring junctions
what is epithelial tissue supported by
Connective tissue
where is the reticular lamina and what fibers does it have
Deep to basal lamina
Has network of collagen fibers
What is the basement membrane composed of
Basal lamina + reticular lamina
What does the basement membrane do
reinforces epithelial sheet
Defines epithelial boundary
Resists stretching and tearing
Does epithelial tissue have blood vessels
No! Avascular
How is epithelial tissue nourished
By diffusion from underlying connective tissue
Is epithelial tissue supplied by nerve fibers
Yes
What type of regeneration capacity does epithelial tissue have
High regeneration capacity
What is regeneration simulated by in epithelial tissue
The loss of apical-basal polarity and lateral contacts
Ex: friction or hostile substances
How do you replace lost cells in epithelial tissue
By cell division
What is glandular epithelial classified by
Exocrine or endocrine
Number of cells forming the gland ( unicellular/ multicellular )
Do endocrine glands have ducts?
No they are ductless
What do endocrine glands do?
Secrete hormones through lymph or blood to specific target organs
Do exocrine glands have ducts?
Yes
Name examples of exocrine glands
Mucus
Sweat
Oil
Salivary
Examples of unicellular exocrine glands
Mucus or goblet cells
Where are unicellular exocrine glands found
In epithelial linings
Intestinal & respiratory tract
Do all unicellular exocrine glands produce mucin
Yes
How to classify multicellular exocrine glands
By structure ( unbranched / branched)
And type of secretion ( merocrine, holocrine, apocrine )
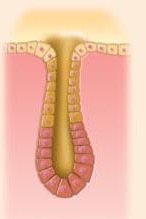
What type of multicellular exocrine glands produce is this
Simple tubular
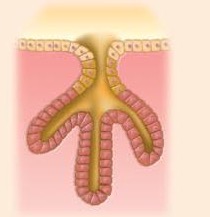
What type of multicellular exocrine glands produce is this
Simple branched tubular
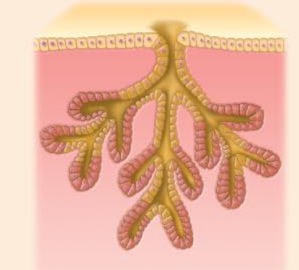
What type of multicellular exocrine glands produce is this
Compound tubular
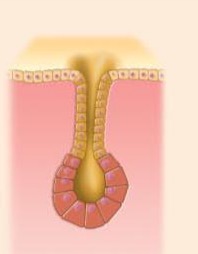
What type of multicellular exocrine glands produce is this
Simple alveolar

What type of multicellular exocrine glands produce is this
Simple branched alveolar
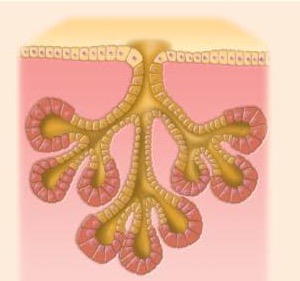
What type of multicellular exocrine glands produce is this
Compound alveolar
What is the most common type of secretion in multicellular exocrine glands
Merocrine glands
Where are Merocrine glands located
Sweat/Salivary glands, pancreas
What is the function of merocrine glands
Secrete produce by exocytosis
Where are Holocrine glands located
Sebaceous (oil) glands
What is the function of holocrine glands
Secretions accumulate and cell ruptures releasing secretions and dead cell fragments