Bio exam 1
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Why cell biology is important
it helps us understand how cells function and interact, leading to advancements in medicine, genetics, and biotechnology. It provides insights into diseases, drug development, and organ transplantation.
Scientific method
A way of learning about the world through observation and experimentation
observe: watching or measuring
data: record observation
experiment: a well controlled test
Why science matters in todays society
drives innovation, solves problems, and improves our lives. It helps us understand the world around us, Science provides evidence-based information, guiding policy decisions and shaping public understanding.
control group
a group separated from the rest of the experiment
independent variable
variable controlled by the scientist
dependent variable
variable measured by the researcher
boring water stimulates…
evaporation in primordial ocean
A mixture of water vapor, gasses, and electrical discharge stimulates…
lightening
Abstract
a brief overview
Introduction
background
Materials and methods
how experiment was preformed
results
description of data, analyses, figures, and tables
Discussion
interpret results, refine hypotheses
References
research and other information cited in the paper
Nature of atoms
Matter has mass and occupies space
all matter is made up of …
atomic structure
made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons
Electrons
Negatively charged particles located in orbitals
cation
more positively charged particles then negative
anion
more negatively charged particles than positive
neutrons
atoms that have the same number of protons and electrons
Redox
when electrons are transferred from one atom to another during a chemical reaction
oxidation
loss of an electron
Reduction
gain of an electron
hydrogen bonds
formed when slightly negative oxygen on one water molecule Is attracted to the slightly hydrogen molecule of another water molecule
Cohesion
polarity of water allows water molecules to be attracted to one another
Water is a good solvent
water dissolves polar molecules and ions
Water organizes non polar molecules
water causes hydrophobic(water fearing) molecules to aggregate or assume specific shapes
Properties of water
water is a good solvent
water organizes non ploar molecules
water can form ions
ph
measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution
acids and bases
Release H+ ions, lower pH, taste sour, turn blue litmus paper red.
Release OH- ions, raise pH, taste bitter, turn red litmus paper blue.
pH Scale: Measures acidity/basicity, ranges from 0 (acidic) to 14 (basic), 7 is neutral.
Neutralization: Reaction between acid and base, forms water and a salt.
buffers
substance that resists ph changes by releasing or absorbing hydrogen ions
Carbonic acid and bicarbonate
key buffer in human blood
hydrocarbons
Organic compounds made up of only hydrogen and carbon atoms.
polymer
built by linking monomers
monomers
small, similar chemical subunits
dehydration synthesis
formation of large molecules by removing water
monomers are joined to polymers
hydrolisis
breakdown of large molecules by adding water
polymers are broken down to monomers
carbohydrates
Molecules with a 1:2:1 ration of carbon hydrogen and oxygen
good energy storage molecules
Monosaccharide
Simpliest carbohydrate
6 sugars play important roles
Structural isomer
compound with the same formula but different atom arrangement
stereo isomer
each of 2 or more compounds differing only in spatial arrangement of their atoms
Disaccharide
2 monosaccharides linked together by dehydration synthesis
used for sugar transport or energy storage
polysaccharides
long chains of monosaccharides linked together by dehydration synthesis
Energy storage form polysaccharides
plants use starch
animals use glycogen
cellulose
plants use this for structural support
chitin
arthropods and fungi use this for structural support
lipids
non polar hydrophobic organic molecule that is insoluble in water but dissolves readily in nonploar solvents
ex: fats, oils, steroids, phospholipids
polar molecule
A molecule with a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end, due to an uneven distribution of electrons.
non polar molecule
A molecule with an equal distribution of charge, resulting in no positive or negative poles.
triglycerides
composed of 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids
saturated fats
no double bonds between carbon atoms
unsaturated fats
1 or more double bonds
trans fat
produced industrally
phospholipids
a molecules with 2 fatty acids and a modified phosphate group attached to a glycerol background
Micelles
lipid molecules orient with polar(hydrophilic) head toward water andnonpolar (hydrophobic) tails away fromwater
Phospholipid bilayer
more complicated structure where two layers form
hydrophilic
head points outward
hydrophobic
tails point inward towards each other
Proteins
composed of 1 or more long, unbranched chain
each chain is a polypeptide
Amino acid
monomer
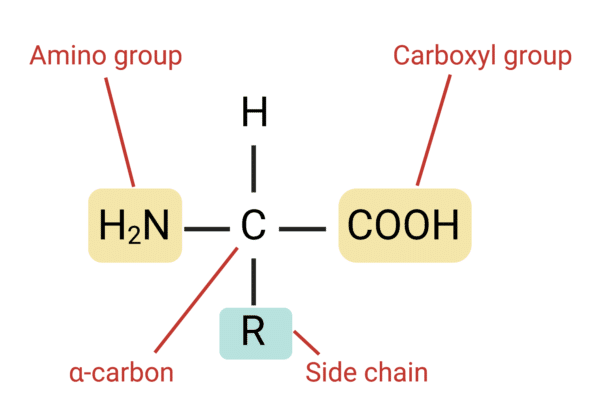
types of amino acids
histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine
peptide bond
formed through dehydration synthesis
Primary structure
sequence of amino acids
secondary structure
interaction of groups in the peptide backbone
tertiary structure
final folded shape of a globular protein
Quaternary structure
arrangement of individual chains in a protein with 2 or more polypeptide chains
motifs
common elements of secondary structures seen in many polypeptides
useful in determining function of unknown proteins
domains
Functional units within a larger structure
perform different parts of the protein’s function
chaperones
Once thought newly made proteins folded spontaneously
help protein fold correctly
Nucleic acids
polymer
nucleotide
basic building block of RNA and DNA (Nucleic Acids)
nucleotide structure
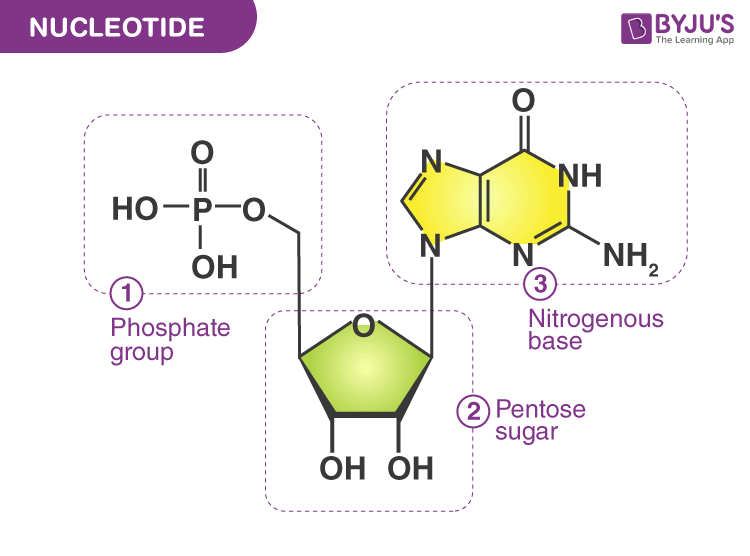
DNA
Encodes information for amino acidsequence of proteins
RNA
similar to DNA except– Contains ribose instead of deoxyribose– Contains uracil instead of thymine
Prokaryotic cell
Simplest organisms
Lack a membrane-bound nucleus
DNA is present in the nucleoid
Cell wall outside of plasma membrane
Do contain ribosomes (not membrane-bound organelles)
Domains are bacteria and Archaea
cell theory
All organisms are composed of cells
2. Cells are the smallest living things
3. Cells arise only from pre-existing cells
All cells today represent a continuous line of descent from the first living cells
What kills bacteria
Antibiotics
Bacteria cell wall
Protect cell, maintain shape, prevent uptake/ loss of water
composed of peptidoglycan
Gram postiive
Darker
Gram negative
lighter
Eukaryotic cells
Possess a membrane-bound nucleus
Hallmark is compartmentalization achieved through use of membrane-bound organelles and endomembrane system
Possess a cytoskeleton for support and to maintain cellular structure
Organelles
Small structures within cells that perform specific functions. Examples include the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum.
Nucleus
Where DNA is stored
Nucleous
region where ribosomal RNA synthesis takes place
Chromatin
DNA + Protein
Ribosomes
Cell’s protein synthesis machinery
Found in all cell types in all 3 domains
mRNA
Transcript
rRNA
protein complex
tRNA
carry amino acids
rRNA
Structural
Mitochondria
Found in all types of eukaryotic cells
Bound by membranes
Outer membrane
Intermembrane space
Inner membrane has cristae
Matrix
On the surface of the inner membrane, and also embedded within it, are proteins that carry out oxidative metabolism
Have their own DNA
chloroplasts
Organelles present in cells of plants andsome other eukaryotes
Contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis
Surrounded by 2 membranes
Thylakoids are membranous sacs within the inner membrane
– Grana are stacks of thylakoids
Have their own DNA
Endosymbiosisbiosis
the theory that organelles were created by prokaryotic cells being engulfed and becoming apart of another cell