CH. 1: BASIC INFORMATION
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
kinesiology
the study of movement through the application of anatomy, physiology, physics, and mechanics
biomechanics
mechanical principles that relate directly to the human body
kinematics
the branch of mechanics describing the movement of a body without consideration of the forces or torque producing that movement (time, space, and mass aspects of a moving system)
fundamental position
same as anatomical, except that the palms face the sides of the body
What are the two components of biomechanics?
kinematics and kinetics
osteokinematics
the movement of bones in space around a joint axis
arthrokinematics
the movement of bone surfaces during joint movement (ex. roll and glide)
kinetics
the branch of mechanics describing how forces and torques affect the body (forces causing movement)
anatomical position
the human body standing in the upright position with palms facing forward
medial
location or position toward the midline
lateral
location or position farther/away from the midline
anterior
front of the body or a position closer to the front
posterior
back of the body or a position closer to the back
distal
away from trunk
proximal
toward the trunk
superior
location of a body part above another or the upper surface of an organ or a structure
inferior
a body part below another or the lower surface of an organ or a structure
cranial
a position or structure closer to the head
caudal
a position or structure closer to the feet
supine
the anterior surface of the body faces upward and the posterior surface of the body is in contact with a supporting surface
prone
the anterior surface of the body faces downward in contact with a supporting surface and the posterior surface of the body faces upward
bilateral
two or both sides
contralateral
opposite side
ipsilateral
same side
What body segment(s) is/are part of the upper extremity?
arm, forearm, and hand
What body segment(s) is/are part of the lower extremity?
thigh, leg, and foot
What body segment(s) is/are part of the trunk?
thorax (chest) and abdomen
What body segment(s) is/are part of the neck?
cervical vertebrae
What body segment(s) is/are part of the head?
cranium
kinetic chain
a series of connected rigid links which in the human body are the segments of the extremities
What are the two kinetic chains?
closed kinetic chain and open kinetic chain
closed kinetic chain
the proximal segment is free to move, while the distal segment is fixed
open kinetic chain
the distal segment is free to move, while the proximal segment is fixed
sagittal plane
a plane cutting the body into left and right parts
What movement(s) is/are associated with the sagittal plane?
flexion and extension
mid-sagittal plane
a plane cutting the body with equal left and right parts
front plane
a plane cutting the body into anterior and posterior parts
What movement(s) is/are associated with the frontal plane?
abduction and adduction
horizontal plane / transverse plane
a plane cutting the body into superior and inferior parts (goes through horizontal of the body)
What movement(s) is/are associated with the horizontal / transverse plane?
rotation occurs within this plane
sagittal axis
a line that passes through a joint from anterior to posterior
What movement(s) is/are associated with the sagittal axis?
abduction and adduction
frontal axis
a line that passes through a joint from side to side
What movement(s) is/are associated with the frontal axis?
flexion and extension
vertical axis
a line that passes through a joint from superior to inferior
What movement(s) is/are associated with the vertical axis?
rotation occurs
Osteokinematic movements
movement of bones around a joint through a range of motion (ROM) and can be performed as active or passive movements
Active ROM
– also known as AROM
– muscles contract to move joints through ROM
– ex: to bend your elbow, you need to contract your biceps while relaxing your triceps OR lifting your arms above your head to stretch the muscles happens within your AROM
Passive ROM
– also known as PROM
– muscles are not contracting and an external force moves a joint through its ROM
– ex: a massage or a PT
Flexion
movement of one limb segment on another about a joint axis, bring 2 anterior limb segment surfaces toward each other
Extension
movement of one limb segment on another about a joint axis, moving the anterior limb segment surfaces away from each other
Hyperextension
extension of a joint beyond its ROM
Adbuction
movement away from the midline of the body
Adduction
movement towards the midline of the body
Radial deviation
hand moves laterally or toward the radial/thumb side of hand
Ulnar deviation
hand moves medially or toward the ulnar/pinky finger side of hand
Lateral flexion
when the trunk bends to the side, moving the shoulder toward the same hip side
Medial rotation
anterior surface of a limb segment turns toward midline of body
Lateral rotation
anterior surface of a limb turns away from midline of body
Circumduction
producing a circular, cone-shaped pattern in which the distal segments move through larger arcs of movement than proximal (arm circles)
Inverison
moving the ankle so the sole of foot faces medially
Eversion
moving the ankle so the sole of foot faces laterally
Opposition
movement of thumb faces the pads of other 4 fingers
Reposition
movement that returns thumb to anatomical position
Range of motion (ROM)
– the amount of movement a joint can move in any of its possible directions and measured by a goniometer
– the anatomical position is the starting position for the measurement of joint ROM
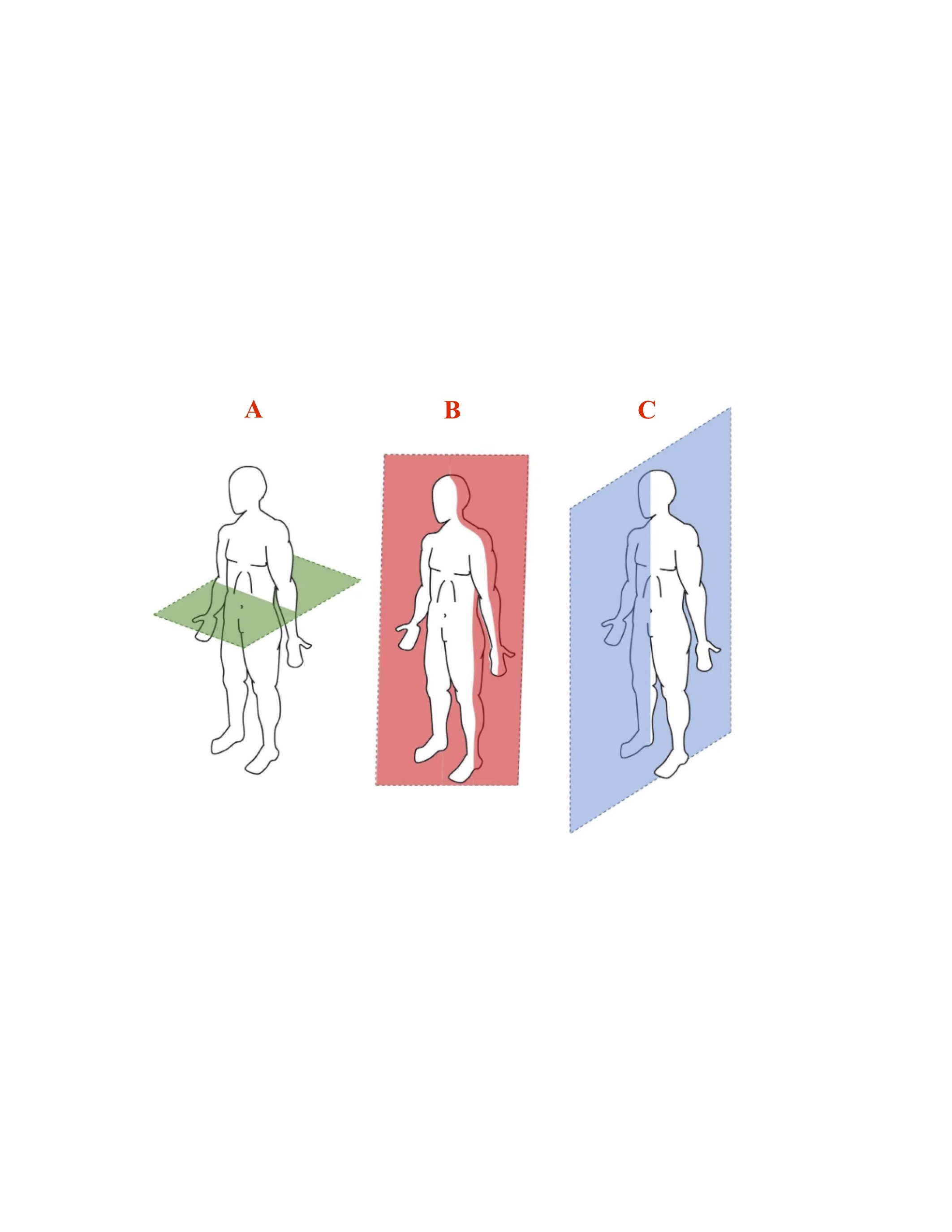
Label correct planes:
A: Transverse
B: Frontal
C: Sagittal
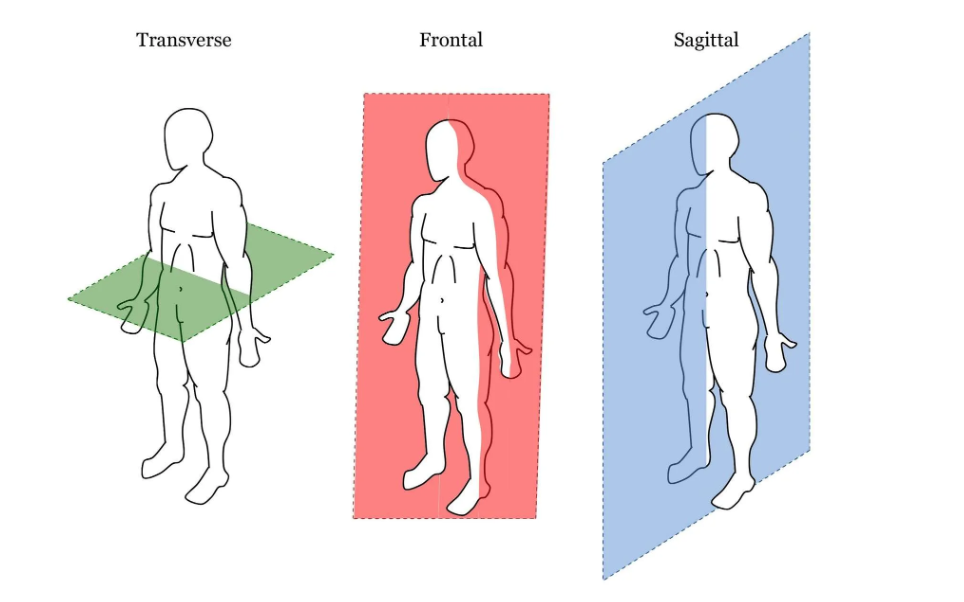
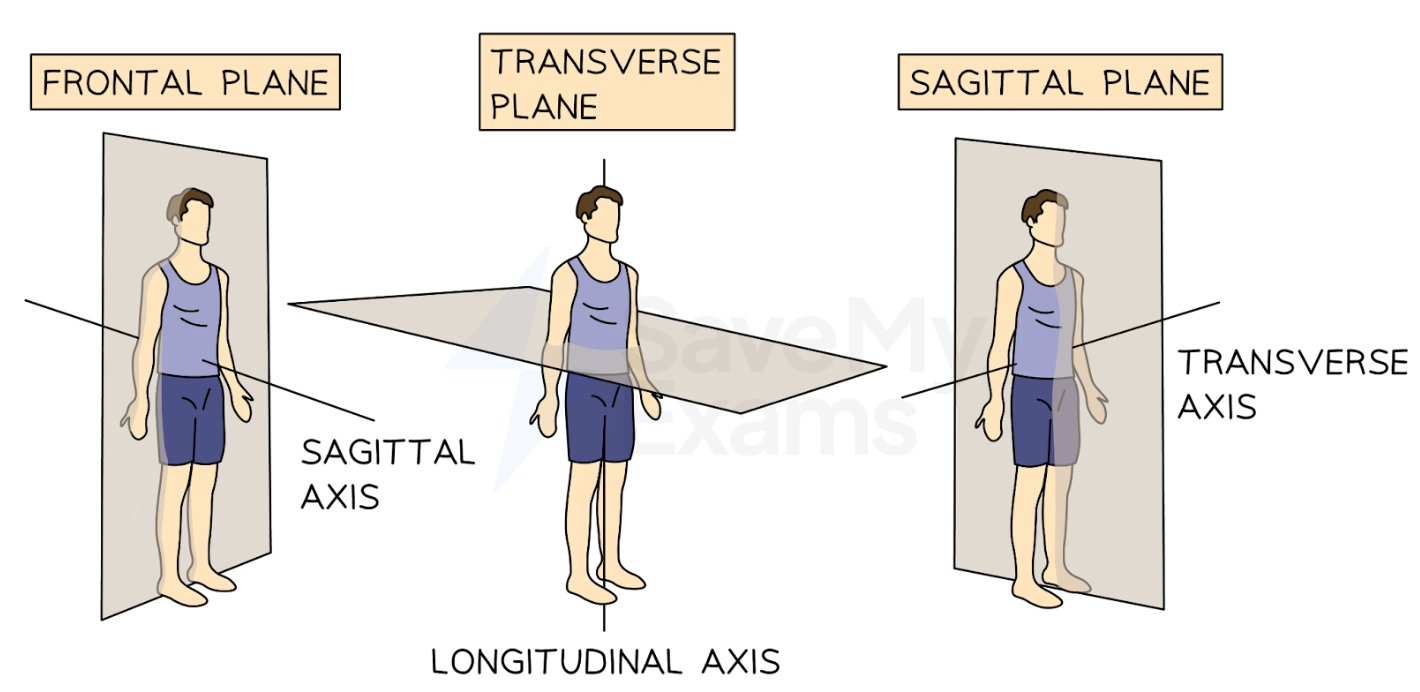
Study planes and axes
Superficial
towards the outside
Deep
towards internal
What type of kinetic chain is going from sitting to standing up?
closed kinetic chain
What type of kinetic chain is doing a pull-up?
closed kinetic chain
What type of kinetic chain is knee extension?
open kinetic chain
What type of kinetic chain is going from standing to sitting down?
open kinetic chain
What type of kinetic chain is drinking a glass of water?
open kinetic chain
How many degrees of freedom does a uniaxial joint have?
1 degree of freedom
How many degrees of freedom does a biaxial joint have?
2 degrees of freedom
How many degrees of freedom does a triaxial joint have?
3 degrees of freedom
How many degrees of freedom does your knees have? And what are the movements?
2 degrees of freedom; flexion–extension and rotation
How many degrees of freedom does your hips have? And what are the movements?
3 degrees of freedom; flexion–extension, abduction–adduction, and internal–external rotation
How many degrees of freedom does your ankles have? And what are the movements?
3 degrees of freedom; plantar flexion–dorsiflexion, abduction–adduction, and eversion–inversion
linear motion (translatory)
everything moves the same distance, same direction, at the same time
rectilinear motion
movement in a straight line in the same distance, same direction, at the same time
curvilinear motion
movement in a curved path in the same distance, same direction, at the same time
angular motion (rotatory)
movement of an object around a fixed point
palmar flexion
at the wrist
plantar flexion
at the ankle
functional observation
enables us to observe a client completing a functional activity and allows us to decide, based on this observation, whether a range of motion assessment, gross manual muscle testing (MMT) or isolated MMT is required
clinical reasoning
thinking as a therapist and using your clinic/patient time wisely
goniometry
measurement of the degree of motion that are available at a specific joint
goniometer
instrument to measure joint motion which has a body (contains a fulcrum) and 2 arms (stationary arm and moveable arm)
Is goniometry a formal assessment?
No, it is a functional observation
How is a goniometer used?
axis or fulcrum is placed over the axis of motion
stationary arm stays fixed and aligned with the plan of motion being measured
moveable arm is aligned, but will then follow the arc of movement
What is the order of goniometry?
observation/screening
PROM
AROM → observe for compensation
placement of goniometer → measured in degrees and reported with a beginning and an end measurement (majority begin at 0 degrees)
When should you NOT perform goniometry?
if patient has a dislocated joint and/or diagnosed with myositis ossificans (calcification of a muscle)
Precautions of using goniometry
Infection or inflammatory conditions
Recent surgical procedure
Unhealed fracture
Marked osteoporosis
Carcinoma of the bone or any fragile bone condition
Significant hypermobility
Significant pain
Hemophilia
Hematoma
Acute muscular injury
What are the categories for ROM?
functional observation and goniometry
What are the categories for strength?
functional observation and gross manual muscle testing
gross manual muscle testing
testing muscle groups as a whole versus individual muscles which includes testing of grades poor to normal (2–5)
isolated manual muscle testing
third category of specific muscle testing within a muscle group and tests for grade trace to normal (1–5)
Explain the testing positions
against gravity → body part being moved perpendicular to the ground
gravity eliminated → body part moved parallel to the floor
stabilization → necessary for both gravity and gravity eliminated, applied manually by the therapist, used to avoid any compensation from other muscles, and therapist placed hand just porximal to the joint being tested