2015 L6 Case 5 Car Crash Guy
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Hypovolemic Shock
A condition resulting from a sudden decrease in blood volume leading to severe drop in blood pressure and insufficient blood supply to organs.
Restoring Haemodynamic Stability
Pro-coagulant drugs e.g. transexamic acid
Saline
RBC
FFP
Packed Red Blood Cells (PRBC)
Blood product consisting of red blood cells with most plasma removed; used for transfusions.
40g of haemoglobin
RBC suspended in anticoagulant/nutrient solution (acid citrate dextrose)
patients may have special requirements
CMV (cytomegavirus) for babies
irradiated to prevent TA-GvHD
antigen negative
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
A serious disorder in which the proteins that control blood clotting become overactive, leading to excessive clotting and bleeding.
Tranexamic Acid
A medication that inhibits plasminogen activation and prevents the breakdown of blood clots.
antifibrinolytic agent
fibrin clot broken by plasmin
plasmin = the active form of plasminogen - usually activated alongside coagulation cascade, also a serine protease
prevents conversion of plasminogen and plasmin
synthetic lysine analogue
irreversibly binds to 5 lysine receptors on plasminogen
Blood Stats
Humans with a body weight of 60kg usually have around 4 to 5L of blood
RBC transfusion rec if > 30% of blood volume is lost or haemoglobin < 80g/L
History of Blood Transfusions
1818: first human-human transfusion by James Blundell
1901: Karl Landsteiner demonstrates main blood groups
Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)
Plasma that has been frozen and stored; contains coagulation factors necessary for blood clotting.
single donor (250-300ml) and frozen within 6hrs
contains plasma with all normal proteins e.g. fibrinogen, FVIII, other coagulation factors and antibodies
Stored at -30 degrees, shelf life of 2 yrs
Thawed in controlled environment, can be stored ↑ to 24hrs at 4 degrees
Coomb's Test aka Crossmatch Procedure
A test used to determine if the patient's body has alloantibodies against transfused blood cells.
recipient serum obtained containing antibodies
donor blood sample added to tube with serum
recipient’s antibodies target donor’s RBCs form antibody-antigen complexes
anti-human antibodies e.g. Coomb’s antibodies added
POSITIVE RESULT = agglutination of RBC occurs because human antibodies are attached to RBC
Rhesus Factor
An antigen found on the surface of red blood cells; significant in blood transfusion compatibility.
Discovery by Karl Landsteiner in 1937
Second major group of proteins found on cell surface
ABO Blood Group
Each blood group has different proteins/antigens on their surface
ABO locus located on Chr9, contains 7 exons
ABO gene encodes for glycotransferase
Main alleles for ABO locus: A, B, O
Saline Infusion
A common procedure in emergency care to increase blood volume and raise blood pressure without carrying oxygen.
Blood Group O
O allele due to frameshift mutation in exon 6 > loss of enzymatic activity
Lacks A or B antigens
Expresses H antigen, the precursor for all other antigens
Blood Group A
A allele of ABO locus encodes for glycosyltransferase
Bonds α-N-acetylgalactosamine onto the H surface
Blood Group B
B allele of ABO locus encodes for a glycotransferase
Binds α-D-galactose to H antigen
Blood Group AB
Heterozygotes for A and B allele produce AB blood
Consists of both antigens, often in in various quantities
RhDCE
Rh system consists of 50 antigens, but most important are D, C, c, E, e
5 antigens are products of the RHD and RHCE genes
RhD most clinically significant
Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction
A serious and potentially life-threatening response to transfusion, caused by the recipient's immune system attacking the transfused red blood cells.
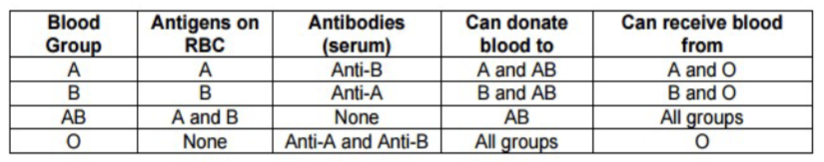
Lansteiner’s Law
Whenever an antigen is not present on red cells, the corresponding antibody will be found in the plasma
If you have A, you have anti-B antibodies in plasma
If you have B, you have anti-A antibodies in plasma
If you have O, you will have both anti-A and anti-B in your plasma
If you are blood group AB you will have no anti-A or anti-B
Safe Transfusions
Cell Salvage
A technique to collect and reinfuse a patient's own blood lost during surgery.
Antigen
A substance that induces an immune response, especially the production of antibodies.
Antibody
A protein produced by the immune system to recognize and neutralize foreign substances such as pathogens or incompatible blood.
Transfusion Labs
Ensures availability for transfusions, investigates
patient blood group
if patient has reactive antibodies
Ensures blood is safe, either by electronic issue and crossmatch
electronic issue = Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) determined
crossmatch = to detect the presence of antibodies in the recipient against the red blood cells of the donor, preventing hemolytic anaemia
Finding Blood Groups
Lab tests = antibody-antigen reactions
Pt RBC (no plasma) incubated with specific antibodies (anti-A and anti-B) - if agglutination occurs, reaction is positive
if pt is Type A, they’d have positive reaction with anti-A
Pt plasma (no cells) incubated with known antigens (A or B cells) - reverse group
pt with Type A would have anti-B antibodies in their plasma, positive agglutination would occur against B cells
O neg as a universal donor
potentially 600 diff antigens on RBC that can cause response
giving pt O neg without testing for other antigens only done in emergencies
its possible that pt who has never been transfused may have an antibody against one of these by chance
multiple transfused patients risk developing of antibody
Crush Syndrome
A condition that can occur after a major crush injury, leading to muscle and tissue damage, potential renal failure, and electrolyte imbalance.
Compartment Syndrome
A serious condition that occurs when there is increased pressure within a muscle compartment, leading to reduced blood flow, nerve damage, and muscle necrosis.
Antibody Screening
test for blood compatibility against 600 antigens
patient plasma incubated with cells of known antigen makeup
agglutination against cell = antibody present in plasma that has reacted against antigen
Electronic Issue
prior to blood transfusion, individual must submit 2 samples for blood grouping and antibody screening
if blood group is confirmed and antibody screen is negative, computer will issue comptable units to pt
Acute Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction
Occurs when the immune system attacks transfused red blood cells, resulting in their destruction. This reaction is typically caused by ABO incompatibility.
other causes of widespread haemolysis of RBC can be caused by the presence of very rare antigens thats never tested
free haemoglobin then causes renal damage (nephrotoxicity, glomeruli destruction > haematuria
hepatoxicity, Fe in haem can produce ROS which damage liver
rampant coagulation aka DIC
fragmented RBC = damage-associated molecular patterns, causes immune response (fever)
FFP Complications
Fluid overload: when FFP administered at large volumes > heart failure/pulmonary edema esp in patients with preexisting cardiac conditions
Immunosuppression: FFP may contain antibodies that suppress pt’s immune response
nvCJD from donors with infected with prion responsible
Viral infection e.g. HepB, HepC and HIV
Haemolysis if incompatibility or if FFP improperly handled FFP C
Methylene Blue Treatment of FFP
nvCJD is a prion disease
treatment for everyone before 1996 who is susceptible
when exposed to UV, meth blue will produce ROS aka free radicals that can denature prions
Cryoprecipitate
Made by freezing donor plasma in blast freezer then thawing at 4 degrees, causing plasma proteins e.g. VIII and fibrinogen to precipitate out - removal of more water from cryo
Plasma transferred to another bag and precipitate is refrozen and stored at 30 degrees
Prevents fluid overload as there is less water
Good for pt with trauma so they have coagulation factors for clotting