Chapter 4, Lesson 1: The Nucleic Acids
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 4, Lesson 1 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Johann Miescher
A Swiss biochemist who lived from 1844 to 1895; he studied the nuclei of white blood cells and coined the term nuclein - what we now call genes
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
A long, thread-like molecule with uniform diameter and varied length; it’s a polymer of nucleotides
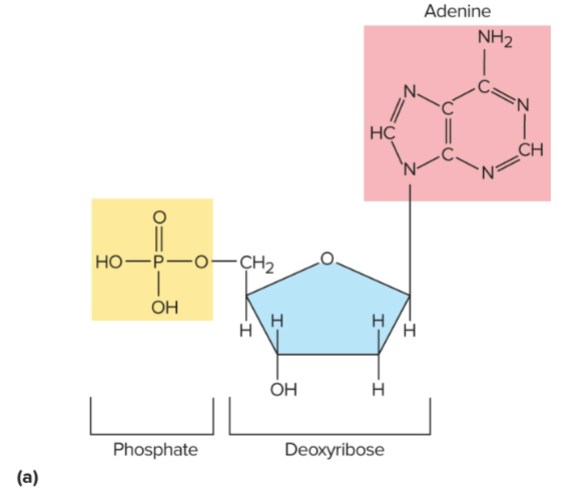
Nucleotide
A molecule made of a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base
Ribose
The sugar in nucleotides
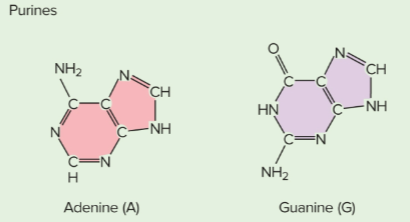
Purines
The adenine and guanine nitrogenous bases
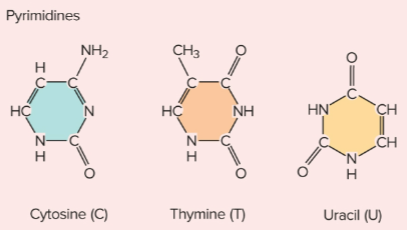
Pyrimidines
The cytosine, thymine, and uracil nitrogenous bases
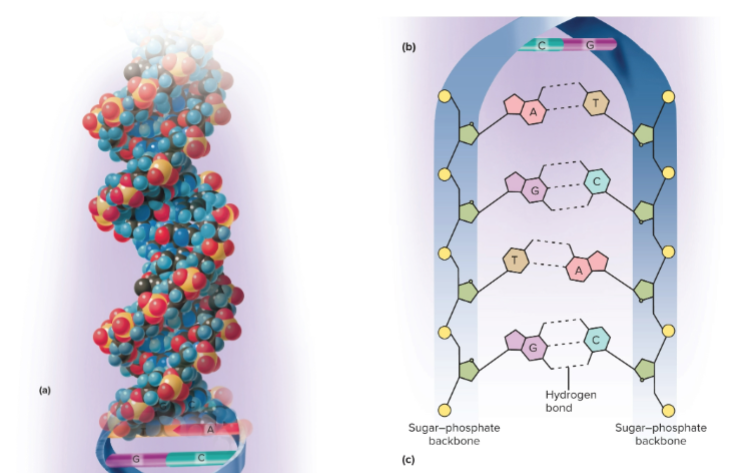
Double helix
The structure of a DNA molecule; resembles a spiral staircase with the ‘steps’ being the nitrogenous base pairs
Base pairing
How DNA is bonded using hydrogen bonds; A always pairs to T with 2 bonds and C always pairs to G with 3 bonds
Gene
Segment of DNA coding for the synthesis of a specific protein
Genome
All the genes of one person; humans have 20,000 but only 2% is human-specific while the other 98% is for chromosome structure and gene activity regulation
Chromatin
Fine filamentous DNA material complexed with proteins; may change movement in non-dividing cells according to genetic activity
Ribonucleic acids (RNAs)
Contain the sugar ribose; uracil takes the place of thymine in DNA and is smaller
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Sends the genetic code to ribosomes
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Carries out protein synthesis in enzymes
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Obtains amino acids for ribosomes according to mRNA