Hormonal Contraception (Xavioer)
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
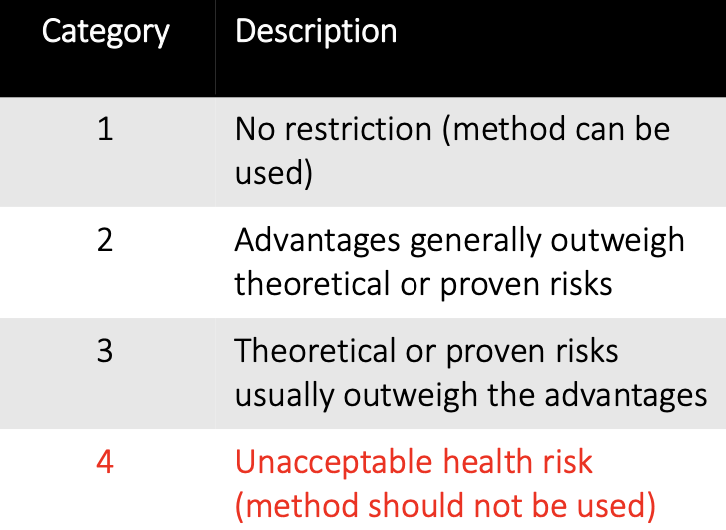
What are the USMEC risk categories?
See image
What are the 6 important contraindications for combined hormonal contraception (category 4)?
Breastfeeding and <21 days postpartum
Smoker >35 years old
Multiple risk factors for CVD
Current or history of DVT or PE
Major surgery with prolonged immobilization
Migraine headache with aura
How does estrogen in COCs prevent pregnancy?
By suppressing FSH and preventing ovulation
What is a monophasic COC?
A COC where hormone content stays the same throughout the cycle
What is a biphasic COC?
A COC where hormone content changes twice throughout the cycle, typically with an increase in progestin on day 11
What is a triphasic COC?
A COC where hormone content changes three times during the cycle
What is a multiphasic (extended cycle) COC?
A COC where hormone content changes four or more times throughout the cycle
What important counsleing point should you be aware of for Estetrol/drosperinone (Nextellis®)?
Nextellis may be less effective in females with a BMI ≥30 kg/m² in females with this BMI decreaseing effectiveness may be associated with increasing BMI
What is the Sunday-start method for starting combined oral contraceptives (COCs)?
Start active tablets on the first Sunday after menses begin, with backup non-hormonal contraception for the first 7 days
What is the first-day or same-day start method for COCs?
Take the first active tablet the same day that menses begin, with no backup contraception required
What is the quick-start method for starting COCs?
Start active tablets immediately, regardless of menstrual cycle day, and use backup contraception for the first 7 days
In the quick-start method for COCs, when should a woman expect her next menses?
After all active tablets have been taken and the hormone-free week begins
What should you do if you miss one COC pill or take it late?
Take the missed pill as soon as you remember, continue the rest as scheduled (even if taking two in one day). No backup contraception needed
If a patient misses one pill and remembers the next day, what should they do?
Take the missed pill as soon as they remember and continue with the rest of the pills as scheduled
What should you do if you miss two consecutive COC pills in week 1 or 2?
Take one missed pill as soon as you remember, discard the rest of the missed pills, continue the other pills as scheduled, and use backup contraception for 7 days
What should a patient do if they miss two pills in week 3 of their COC pack?
Take one missed pill as soon as they remember, discard the rest of the missed pills, finish remaining active pills, skip the placebo week, and start a new pack with backup contraception for 7 days
What is the MOA for transdermal contraceptive patches like Xulane?
Delivers norelgestromin 0.15 mg/day and ethinyl estradiol 35 mcg/day
Hormone passes into skin and metabolized by liver where norelgestromin is converted to norgestimate
What are the pros and cons for using a transdermal contraceptive patch?
Easier to use for women who do not like taking pills, not good option for women who have history/risk of VTE (delivers 60% more estrogen), less effective in women >90 kg
When should you start the transdermal patch if not using any prior hormonal contraceptive?
First day of menses, or the Sunday after. Use backup for 7 days
How do you start the transdermal patch when switching from another CHC
Apply on first day of withdrawal bleeding; no backup needed
What should you do if the patch falls off for less than 24 hours?
Reapply ASAP; no backup needed
What should you do if the patch falls off for 24+ hours?
Apply a new patch, start a new cycle, and use backup for 7 days
What should you do if the patch is detached or delayed in week 3?
Omit hormone-free week, start new patch cycle, and use backup if needed
What if you forget to apply a new patch after the hormone-free week?
Apply ASAP and use backup for 7 days
What if you forget to apply a patch during weeks 2 or 3, but it's been less than 48 hours?
Apply ASAP, adjust Patch Change Day; no backup needed
What if you forget to apply a patch during weeks 2 or 3 and it's been 48+ hours?
Apply new patch, start new 4-week cycle, use backup for 7 days
What if you forget to remove the patch during the hormone-free week?
Remove ASAP, start new cycle on the usual day; no backup needed
What if you go more than 7 days without wearing a patch?
Apply a new patch and use backup for 7 days
What hormones does the NuvaRing release?
Etonogestrel (0.12 mg/day) and ethinyl estradiol (0.015 mg/day)
How is the NuvaRing used?
Insert vaginally for 3 weeks; remove during the 4th week for withdrawal bleeding
Can you use a diaphragm with the NuvaRing?
No, diaphragms should not be used with the NuvaRing (think sponges)
What are common side effects of the NuvaRing?
Foreign body sensation, vaginal discomfort, and other vaginal symptoms
What are some pros and cons of the NuvaRing?
Pros: improved adherence. Cons: not suitable for women with vaginal irritation or discomfort with insertion
When should the NuvaRing be inserted?
On or before the 5th day of the menstrual cycle
How can insertion of the NuvaRing be made easier?
Stand and raise one leg, squat, or lie down; using a tampon applicator can also help
Does the exact position of the NuvaRing matter?
No, as long as there is good contact with the vaginal walls
Can the NuvaRing stay in place during intercourse and tampon use?
Yes, it can remain in place during both
What if the NuvaRing has been removed for more than 3 hours?
Reinsert ASAP and use backup contraception for 7 days
What if the NuvaRing is removed for more than 3 hours during the 3rd week?
Insert a new ring and start a new cycle
What is a side effect for too much estrogen and when there is not enough estrogen?
Too much: Bloating
Not enough: Breakthough bleeding early in cycle
What can be done if breakthrough bleeding occurs with contraceptives?
It often improves within 3 months; if persistent, consider increasing estrogen or progestin
How might contraceptives cause weight gain, and what can help?
Too much progestin may increase appetite (noncyclic), while too much estrogen can cause water retention (cyclic). Consider low-dose estrogen/progestin or drospirenon
What is recommended if headaches or migraines occur during the placebo week?
Consider lower estrogen or replace placebo with estrogen; try shorter placebo or extended cycle regimens
How can acne be managed with contraceptives?
Consider a progestin with lower androgenic properties or switch to a 3rd or 4th generation progestin
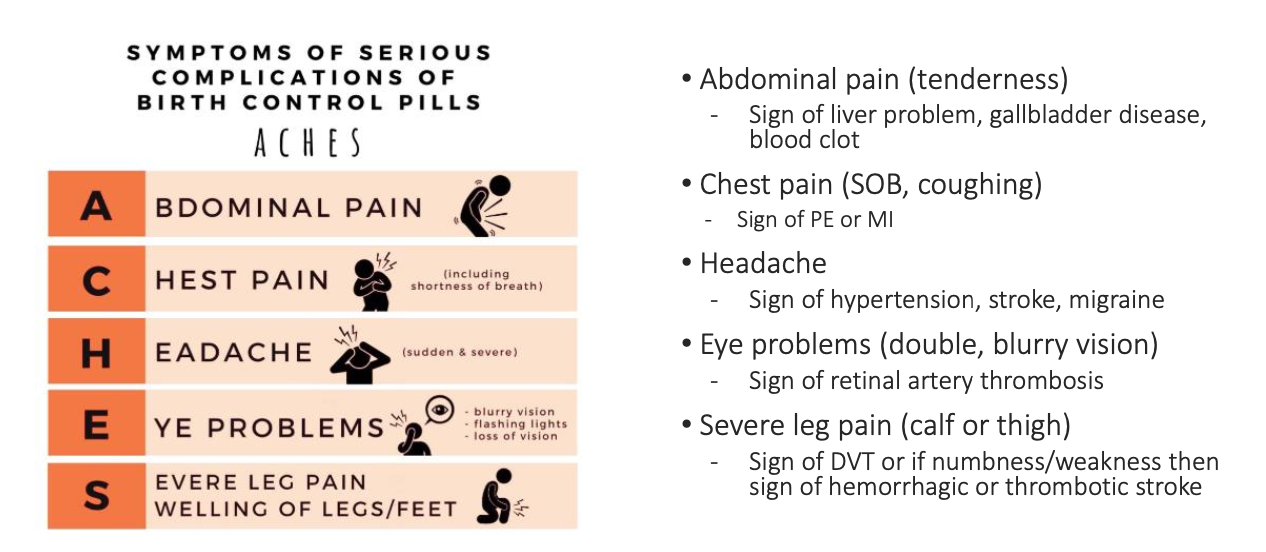
What are the serious adverse effects of CHCs?
See image
How do CYP enzymes affect Combined Oral Contraceptives (COCs)?
COCs undergo hepatic metabolism via CYP enzymes, with estrogens being substrates of CYP3A4
Which antibiotic has an important DDI with birth control and how do you manage it?
Recommend backup contraception for 7-28 days after rifampin d/c
What important counseling points should you consider for patients who are anticonvulsants?
Long term seizure disorder - switch product
What must you monitor for patients using drospirenone?
Monitor K+
What counseling point do you need to know for patients taking corticosteroids, theophylline, aspirin, APAP?
May need to reduce doses to prevent risks if use long-term
When should progestin-only contraceptives be avoided?
Avoid in individuals who may be pregnant, have known or suspected breast cancer, undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding, or acute liver disease
What are the common types of progestin in progestin-only pills (POP) by generation?
1st gen: norethindrone, 2nd gen: levonorgestrel, 3rd gen: norgestimate, norelgestromin, 4th gen: drospirenone
What is the advantage of higher-generation progestins?
Higher generations have lower androgenic side effects
What properties does drospirenone have?
Drospirenone has anti-androgenic and anti-mineralocorticoid properties
What symptoms can progestin-only pills help reduce?
They can reduce estrogen-related symptoms like migraines, cramping, and breast tenderness
When can a progestin-only pill (POP) be started postpartum?
For non-breastfeeding: as early as 1-4 weeks; for exclusive breastfeeding: 6 weeks after delivery; for partial breastfeeding: at least 3 weeks after delivery
When can a POP be started after an abortion or miscarriage?
POP can be started the day after an abortion or miscarriage
How does body weight affect POP effectiveness?
There is a slight increase in unintended pregnancy risk for women over 70 kg
When should the POP be taken for maximum effectiveness?
Take at the same time each day, starting on the first day of the menstrual period
What should be done if the first POP dose is not started on the first day of the menstrual period?
Use backup contraception for the first 48 hours
Does POP have placebo pills or breaks between packs?
No, there are no placebo pills or breaks between packs
What should you do if a POP dose is missed by less than 3 hours?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. No backup contraception is needed
What should you do if a POP dose is missed by more than 3 hours?
Take the missed dose as soon as possible and use backup contraception for the next 48 hours
What should you recommend if a POP dose is missed by over 3 hours and there was unprotected intercourse?
Consider emergency contraception
What should you do if 2 or more POP doses are missed?
Take the first missed dose as soon as you remember and the regularly scheduled dose (2 pills total). Take the second missed dose and regular dose the next day. Use backup contraception for 48 hours
How often is DMPA injected?
Every 3 months
How does DMPA work?
It reliably blocks ovulation within 24 hours of the dose
When can DMPA be initiated postpartum in lactating patients?
6 weeks postpartum
What are the pros and cons of DMPA?
Pros: Weight-independent efficacy, avoids first-pass metabolism. Cons: Delayed return to fertility, risk of bone density loss with prolonged use
What are two important counseling points regarding DMPA?
Amenorrhea can be concerning side effect
Short term bone loss can occur
When should the first DMPA injection be given?
Within 5 days of the start of menstruation
What should be done if DMPA is started more than 7 days after the start of the menstrual cycle?
Use backup contraception for the first 7 days
Is there a grace period for DMPA doses?
Yes, a 2-week grace period if a dose is delayed
What is the mechanism of action of a progestin IUD?
Contains levonorgestrel; prevents implantation, thickens cervical mucus, and inhibits sperm motility
Is there a non-hormonal IUD option?
Yes, the copper IUD, which does not contain hormones
What is a concerning cousneling point regarding IUDs?
Greatest risk of pelvic infection is within first 20 days following insertion of device
Progestin IUDs can be used for 3-5 years
What is the active ingredient in Nexplanon?
Etonogestrel, the active metabolite of desogestrel
How long is Nexplanon effective for contraception?
Up to 3 years
When can Nexplanon be used postpartum?
As early as 4 weeks postpartum, including in lactating women
When should Nexplanon be placed to avoid needing backup contraception?
Between days 1-5 of menses onset
What should a patient do if Nexplanon is placed after the 5th day from the onset of menses?
Use a backup contraceptive method for the first 7 days
Can Nexplanon be inserted while using other contraceptives like oral contraceptives, DMPA, or an IUD?
Yes, it can be placed anytime without regard to menses
What is the active ingredient commonly found in emergency contraception pills?
Levonorgestrel
Name common OTC emergency contraception products.
My Way, Plan B One-Step, Next Choice
What factors can reduce the efficacy of emergency contraception?
Time delay (over 120 hours), high BMI (>26), or vomiting within 1-2 hours after taking
What is recommended for emergency contraception if BMI is over 26?
Ulipristal acetate (Ella) or copper IUD
What should a patient do if they vomit within 1-2 hours of taking emergency contraception?
Take another dose and consider taking an antiemetic, such as meclizine or dimenhydrinate