Pediatric Growth and Development: Vaccines and Feeding
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
size, function, safety, screening
Well Child Visits: Components
-Growth and development screening
Growth = increase in ____
Development = increase in _________ physically and intellectually
-Physical exam
-Nutrition
-Behavior
-________
-Anticipatory guidance
-Counseling, education
-Other __________ tests
-Immunizations
predictable, wide, social, 3-5, 2, 9, annually
Well Child Visits
-Main Principles of Development
Proceeds along a _________ pathway
“Normal” development has a _____ range
Physical, ______, and environmental factors can affect development and health
Child’s developmental level affects how you perform H&P
-AAP Well Child Visit Recommendations → newborn, __-__ days, 1/_/4/6/_/12/15/18 months, 2 year, 2.5 year, 3 year, then _________
Hep B
What is the only vaccine given at birth?
2 months
What age should a child receive their Hep B, rotavirus, DTap, HIB, IPV, PCV13 or 20?
Oh 2 Be DR HIP
4 months
What age should a child receive their rotavirus, DTaP, HIB, IPV, PCV13 or 20?
Do it 4 DR. HIP
Influenza
What vaccine can start at 6 months? Need 2 doses the first time and then 1 dose annually
12 months
When can the infant get the MMR, varicella, and HepA vaccine?
1 Very MAD HIPster
RSV, 8
___ monoclonal antibody for all infants < _ months entering RSV season
4-6 years
When should the infant get their second dose of MMR and varicella?
Very DIM Between 4-6 PM
11-12 years
How old should the patient be when they receive their first Tdap and meningococcal vaccines?
16
When should the patient get their second dose of meningococcal vaccine?
11-12, 9
The HPV vaccine should be given the patient at age ___-___ years, but it can be started as early as _ years old
-9-14 year old children can get a 2 dose series 6-12 months apart
-15 and older need 3 dose series at 0, 1-2 mo, 6 mo apart
weight, 2, age, BMI, WHO, premature
Growth Charts
-Measurements → height, _________, and head circumference (usually stop at _ years old)
-Growth Chart → measure weight for ___, height for age, head circumference for age, weight for height, and ___
____ chart for birth to two years old, CDC for 2+
Separate charts for boys and girls
-Special growth charts for ____________ infants
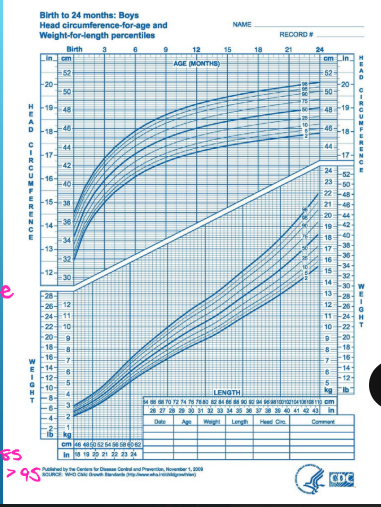
weight, height, increasing, height, tumor, sutures
Abnormal Growth Patterns
-Inadequate caloric intake → _______ percentile falls first, followed by ______ then HC
-Hypothyroidism → ____________ weight but falling _______ percentile
-Large HC → familial megalocephaly, hydrocephalus, brain ______
-Small HC → premature closure of __________
-Pay attention to sudden, extreme, or persistent declines in growth
lose, 2, 6, triple, 20-30, 15-20
Rules of Thumb for Growth: Weight
-Newborns can _____ 5-10% of birthweight
Should be back up to birthweight within _ weeks
-Double birthweight by _ months
-_______ birthweight by 1 year
-Gain approximately ___-___g/day for the first 3-4 months and ___-___ g/day for the rest of the first year
20, 30, double, 35
Rules of Thumb for Growth: Height and Head Circumference
-Height
__ inch is the average length at birth
__ inch is the average length at 1 year
_________ birth length by 4 years
-Head Circumference
__ cm average at birth
Increases by 1cm/month for first 6-12 months
nutrition, D, protein, sugar, 3-4, antibodies, infections, allergic, loss, bleeding, PPD
Normal Infant Nutrition: Benefits of Breastfeeding
-Provides optimal ___________ → only lacks vitamin _
Colostrum → thick, yellowish fluid; high in ________, low in ______, contains other beneficial compounds
Milk comes in around __-__ days after birth
-Loaded with mom’s __________ → protects or helps child fight off __________
-Decrease other health issues like ______ diseases, DM, leukemia, and SIDS
-Benefits mom → helps with weight ____, reduces uterine __________ after delivery by speeding up uterine involution, and reduces development of ___, HTN, DM
hand, opening, tongue, crying
Hunger Cues
-Putting ______ in mouth
-Rooting
-_________ mouth and sticking ________ out
-Fussiness/_________
2, 2, 4, 8, demand, 10, 1, 8
Feeding: Formula vs Breastfed Infant
-Formula Fed
Newborn - _ months → 2 oz every _ hrs
2-4 months → _ oz every 3-4 hours
4-6 months → 4-6 oz every 3-4 hours
6-12 months → _ oz every 4-5 hours
-Breastfed Infant
Fed on ________
Feeds every 1.5-2 hours at first
Feeds 8-12x/day
__ minutes on each breast
-Rule of thumb → amount of formula they drink increases on average by _ oz/month before leveling off at _oz
voiding, gain, 6-8, 4, varies
Feeding: Adequacy of Milk Intake
-Assessed by ________ and stooling patterns and weight _____
__-__ wet diapers/day
Breastfed infant → loose, yellow, seedy stools _x/day
Formula fed infant → stooling _______
4-6, 2-3, allergies, 4
Feeding: Introduction of Solids
-Around __-__ months
-Baby cereal (rice, oatmeal, barley)
-One food every __-__ days
Do this to not support nutrition but to help get the baby used to solids
-Identify food _________/intolerances
-About _oz of solids at each meal (2-3x/day)
1, 4, 8, 6, 1, whole, fat, 24
Feeding: Juice, Honey, Cow’s Milk
-Juice
Should wait until _ year old
100% juice, no sugar added
No more than _oz/day until 3 years old
Older children can have no more than _ oz/day
Can introduce sippy cup with water at _ months
-Honey
After _ year old due to risk of infant botulism
-Cow’s Milk
After 1 year
2% or _____ milk until 2 y/o then ___ free or 1%
No more than __ oz/day