PSY1101 Exam 2023
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/232
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:04 PM on 4/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
233 Terms
1
New cards
The Scientific Method
1. Identify the problem
2. gather information
3. generate a hypothesis
4. design and conduct experiments
5. analyze data and formulate conclusions
6. restart process
2
New cards
Naturalistic observation
Observation as it happens without an attempt to manipulate or control the subjects environment
3
New cards
field experiment
experiment takes place in the real world
4
New cards
case study
in-depth analysis of a unique circumstance or individual.
5
New cards
hippocampus
plays a role in the transfer of memories to long term memory
6
New cards
entorhinal cortex
found in the temporal lobe and plays a role in behavior and memory.
7
New cards
procedural memories
memories that pertain to how something is done (i.e., riding a bike)
8
New cards
surveys
a method using questions to collect information on how people think or act. Quick way to collect lots of information.
9
New cards
sample
subset of a population
10
New cards
sampling error
a sample that deviates from a true representation of a population
11
New cards
bias
an unfair or unequal representation of a person or thing
12
New cards
response bias
the tendency for people to answer the questions the way they feel they are expected to answer
13
New cards
acquiescent response bias
the tendency for participants to agree or respond “yes” to all questions regardless of their actual opinions. (“yea-saying”)
14
New cards
socially desirable bias
participants respond to questions in ways that would be seen as notable by others (i.e., people wont openly admit to illegal acts)
15
New cards
illusory superiority
the tendency to describe our own behavior as better than average
16
New cards
The Tuskegee Syphilis Study
Study to follow the natural progression of syphilis. They infected African American men. Study lasted 40yrs and denied participants medical treatment even though there were advancements in the treatment of syphilis.
17
New cards
5 ethical principals of research
1. Beneficence and non-maleficence
2. Fidelity and Responsibility
3. Integrity
4. Justice
5. Respect for rights and dignity
18
New cards
beneficence
Principle states that research should strive to do good
19
New cards
Maleficence
Avoid creating experiments that can intentionally harm participants
20
New cards
Fidelity and Responsibility
The ethical principle of developing trusting relationships between researchers and participants
21
New cards
Integrity
An ethical principle that psychologists should engage in accurate, honest, and non-biased practices in the science, teaching, and practice of psychology.
22
New cards
Justice
An ethical principle in research where those people who participate in research should get the benefits of the research. (if they pass a drug then the test group should be the first to get it)
23
New cards
inclusion criteria
an attribute of participants that is necessary to be a part of a research study
24
New cards
exclusion criteria
an attribute of a person that would prevent them from participating in a research study
25
New cards
eligibility criteria
The combination of inclusion and exclusion criteria to create a set of characteristics shared by all participants that ensure that those participating will meaningfully address the research question.
26
New cards
Respect for rights and dignity
An ethical principle where the researchers should take measures to respect and protect participants rights, privacy, and welfare. Also includes confidentiality.
27
New cards
The IRB reviews research studies to make sure they’re ethical by confirming:
1. proposed study will use sound research design
2. risks are minimized
3. benefits outweigh the risks
4. can make informed consent and withdraw whenever
5. safeguards in place to protect the participants
6. all data collected will be confidential
28
New cards
correlation
a measure (denotes as r) that captures the direction and strength of a relationship between variables. Relationship is strong when points are clustered tightly together in a linear relationship.
29
New cards
positive correlation
When variables change in the same direction (i.e., one increases and the other does as well)
30
New cards
negative correlation
When variables are opposite (i.e., as one increases the other decreases).
31
New cards
zero correlation
two variables exhibit no apparent relationship
32
New cards
Correlation coefficient
A numerical representation of the strength of the relationship between variables (denoted as r). Ranges from -1 to +1 (sign indicates direction of correlation). A perfect positive is +1, no relationship is 0, and a perfect negative is -1)
33
New cards
extraneous/confounding variables
variables that are not the focus of the study but they influence the outcome if they are not controlled.
34
New cards
What is the best placebo?
a) a white pill is more effective than a blue pill
b) a needle is more effective than a capsule
c) a letter on a white pill is more effective than a capsule
d) a blue pill is more effective than a capsule
a) a white pill is more effective than a blue pill
b) a needle is more effective than a capsule
c) a letter on a white pill is more effective than a capsule
d) a blue pill is more effective than a capsule
b) a needle is more effective than a capsule
35
New cards
descriptive statistics
a collection of ways to describe the data in the simplest way, which involves quantitative values.
36
New cards
types of central tendency
mean (average), median (middle), and mode (most frequently reoccurring number)
37
New cards
What is a disadvantage of using the mean as central tendency?
It can be affected by outliers
38
New cards
neuron
cells that communicate with the brain to form thoughts and actions. Cell codes info through electrical signals.
39
New cards
glial cells
perform numerous support functions in the nervous system
40
New cards
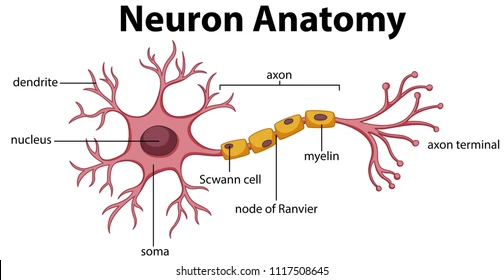
dendrites
extensions of the cell body membrane that branch out to communicate with other neurons
41
New cards
neurotransmitter
chemicals released from the end of an axon that acts as messages to other neurons and body parts. Chemicals bind to receptors
42
New cards
receptors (neurons)
proteins that are embedded in the cell body to receive chemical messages from neurotransmitters
43
New cards
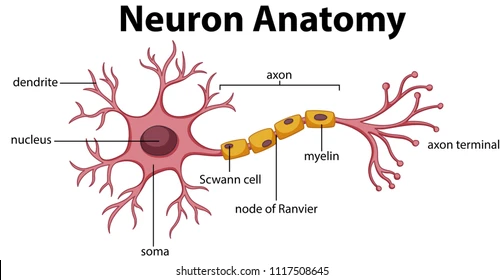
soma
The cell body of a neuron, contains the organelles and controls the metabolic processing for the cell
44
New cards
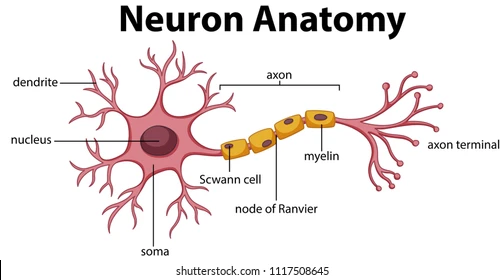
axon hillock
The intersection between the soma and the axon. This is where the axon begins.
45
New cards
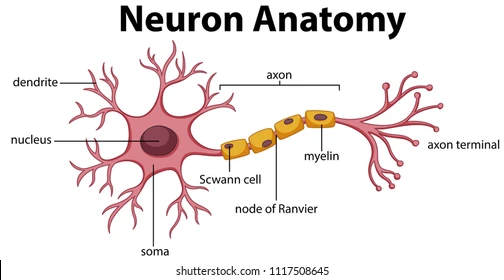
axon
a long, narrow, projection from the cell body
46
New cards
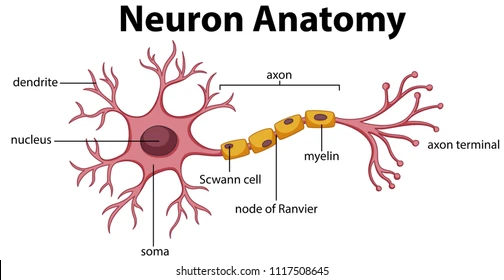
axon terminals
part of the axon that releases the neurotransmitter. Once the action potential reaches the axon terminal, it triggers the release of a neurotransmitter.
47
New cards
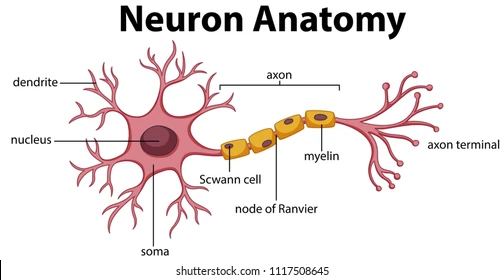
terminal buttons
the very edge of the axon terminal, where the neurotransmitter exits
48
New cards
vesicles
little bubbles at the terminal button that store neurotransmitter molecules.
49
New cards
presynaptic neuron
portion of the neuron that releases the neurotransmitter into the synapse
50
New cards
synaptic cleft
the space between the end of the neuron that releases a neurotransmitter (axon terminal) and the end of the receiving neuron (dendrite).
51
New cards
synapse
small fluid-filled gap between neurons into which neurotransmitters are released
52
New cards
postsynaptic receptor
the other side of the synapse. The neuron contains receptors ready to bind to the neurotransmitter released from the presynaptic neuron
53
New cards
myelin
a protein and fatty substance that wraps around the axon to PROTECT and INCREASE speed of action potentials
54
New cards
nodes of Ranvier
gaps in the myelin that allow ions to enter the axon
55
New cards
polarize cell state
\-70mV inside the cell. Polarization (-ve) and depolarization (+ve)
56
New cards
Steps to action potential in a neuron
1. small influx of Na+
2. triggering of voltage-sensitive Na+ channels
3. large influx of Na+
4. efflux of K+
57
New cards
oligodendrocytes
glial (helper) cells that wrap the myelin insulation around the axons in the CNS
58
New cards
Schwann cells
Glial (helper) cells that wrap the myelin insulation around the axons in the PNS
59
New cards
astrocytes
glial (helper) cells that help get nutrition to neurons and maintain the balance of ions inside and outside the neuron
60
New cards
microglia
Glial (helper) cells that clean debris and get rid of germs
61
New cards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
composed of the brain and the spinal cord
62
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
all the nerves outside the skull and vertebral column, as well as the specialized sensory endings (i.e., hair cells in the ear)
63
New cards
Somatic Nervous System
contains the neurons and nerves that control the muscles for voluntary movement and bring sensory info back to the brain from the body.
64
New cards
pons
a network of cells in the brain stem that regulate
* awareness/alertness
* sleep
* motor function
* awareness/alertness
* sleep
* motor function
65
New cards
What do the medulla and pons do?
* regulate basic life functions
* connect the PNS and CNS to regulate what we do and what we pay attention to
* connect the PNS and CNS to regulate what we do and what we pay attention to
66
New cards
Medulla
* lowest portion of the brain (transition between brain and spinal cord)
* Vital to support life; damage is fatal
\
* Vital to support life; damage is fatal
\
67
New cards
basal ganglia
Interconnected groups of neurons near the base of the brain that help us:
* learn movements
* coordinate movement patterns
* learn movements
* coordinate movement patterns
68
New cards
Parts of the basal ganglia
1) dorsal striatum
2) ventral striatum
3) globus pallidus
4) substantia nigra
2) ventral striatum
3) globus pallidus
4) substantia nigra
69
New cards
dorsal and ventral striatum
inputs to the basal ganglia come in
70
New cards
globus pallidus and substantia nigra
send out inhibitory outputs to the thalamus to help integrate sensory and motor information.
71
New cards
What disease is the basal ganglia associated with?
Parkinson’s disease (impaired movement)
72
New cards
cerebellum (“little brain”)
Two-lobed part of the brain posterior to the brain stem that helps:
* movement
* problem-solving
* movement
* problem-solving
73
New cards
What are the divisions of the cerebellum?
* spinocerebellar (helps match sensory input w/ motor plans to refine movement patterns)
* vestibulocerebellar (processes info form the inner ear to adjust balance)
* cerebrocerebellar (adjusts the timing and planning of movements)
* vestibulocerebellar (processes info form the inner ear to adjust balance)
* cerebrocerebellar (adjusts the timing and planning of movements)
74
New cards
thalamus
the body’s information relay station
75
New cards
temporal lobe
part of the cortex that assists with:
* forming memories
* processing sound input
located on the right side of the brain above the ear
\
* forming memories
* processing sound input
located on the right side of the brain above the ear
\
76
New cards
the corpus callosum
thick bundle of fibers that connects the two brain hemispheres and allows them to share info. All sensory info except for olfactory (smell) crosses to the other side of the brain.
77
New cards
split brain
cut the corpus callosum to treat seizures. Patients have trouble seeing an object in the left visual field and naming it. Visual info from the left is processed in the right visual cortex.
78
New cards
Three major endocrine control centers in the CNS
1) hypothalamus - secretes hormones and controls the pituitary gland
2) pineal gland - secretes melatonin to regulate the sleep cycle
3) pituitary gland - secretes hormones that affect sexual behavior, reproduction, circulatory function, hunger, and responses to aggression.
2) pineal gland - secretes melatonin to regulate the sleep cycle
3) pituitary gland - secretes hormones that affect sexual behavior, reproduction, circulatory function, hunger, and responses to aggression.
79
New cards
bottom-up processing
the processing of physical messages delivered to the senses.
80
New cards
top-down processing
combine incoming neural message with our own understanding of the world to interpret information in a way that has value
81
New cards
Principle of proximity
objects that are close to one another will be grouped together
82
New cards
The principle of similarity
objects that are physically similar to one another will be grouped together
83
New cards
The laws of Gestalt
Ways of organizing and understanding the world
84
New cards
principle of closure
people tend to perceive whole objects even when part of the information is missing
85
New cards
principle of good continuation
if lines cross each other or are interrupted, people tend to still see continuously flowing lines
86
New cards
principle of common fate
objects that are moving together will be grouped together (i.e., group of birds)
87
New cards
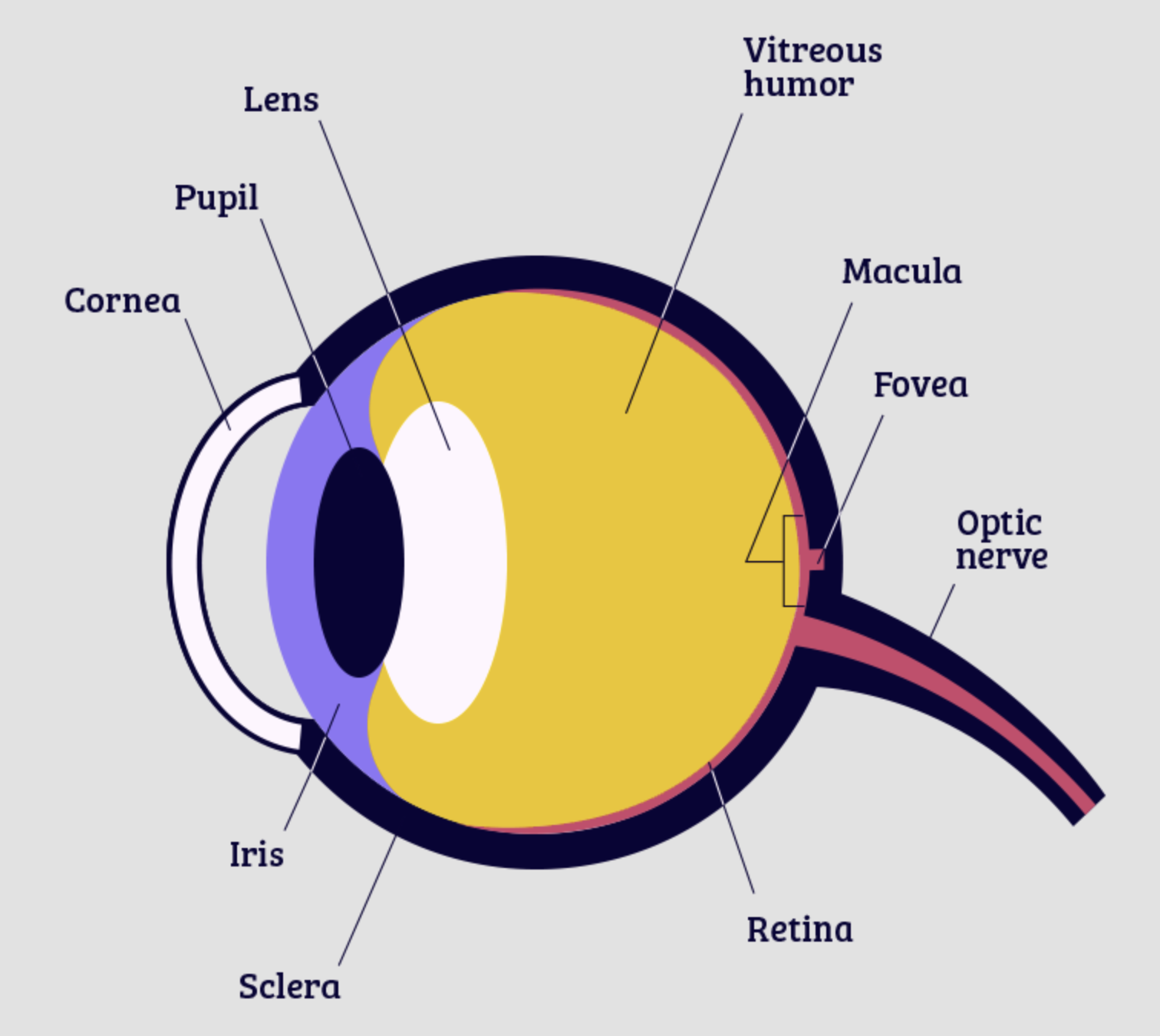
retina
Thin layer of tissues on the back of each eye that contains the photosensitive receptor cells
88
New cards
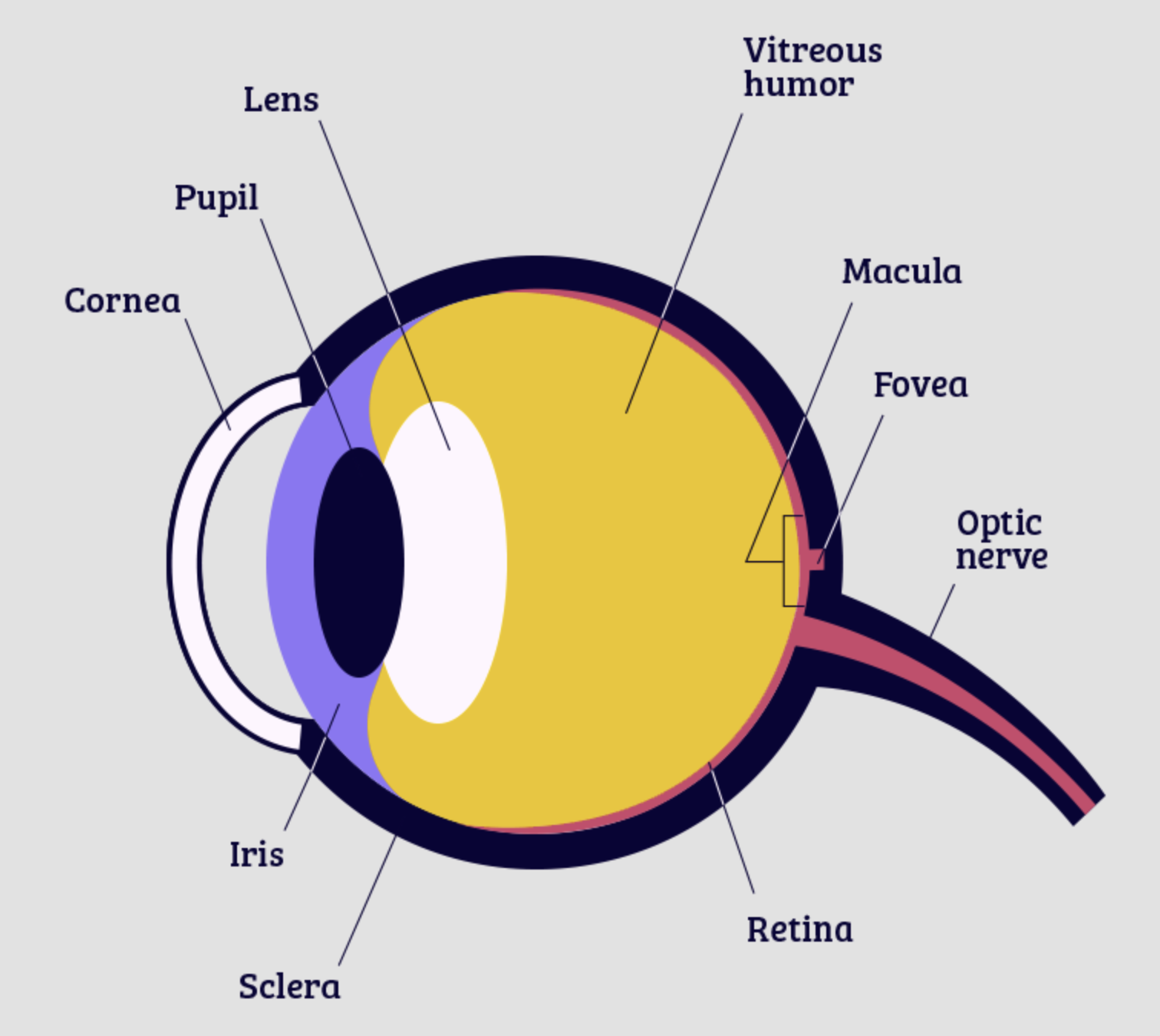
cornea
The transparent covering of the eye
89
New cards
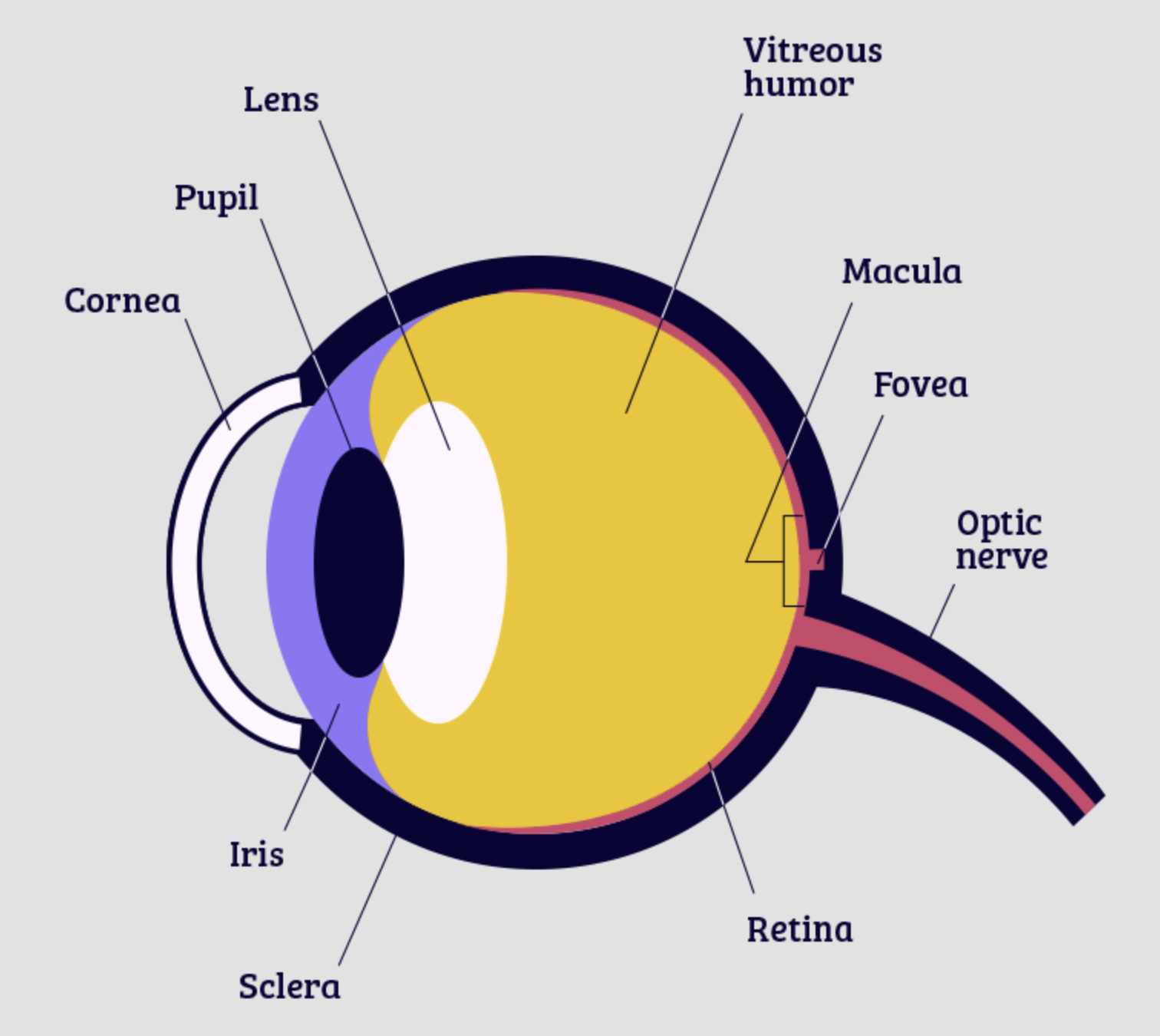
pupil
The hole in the center of the eye that allows light to enter
90
New cards
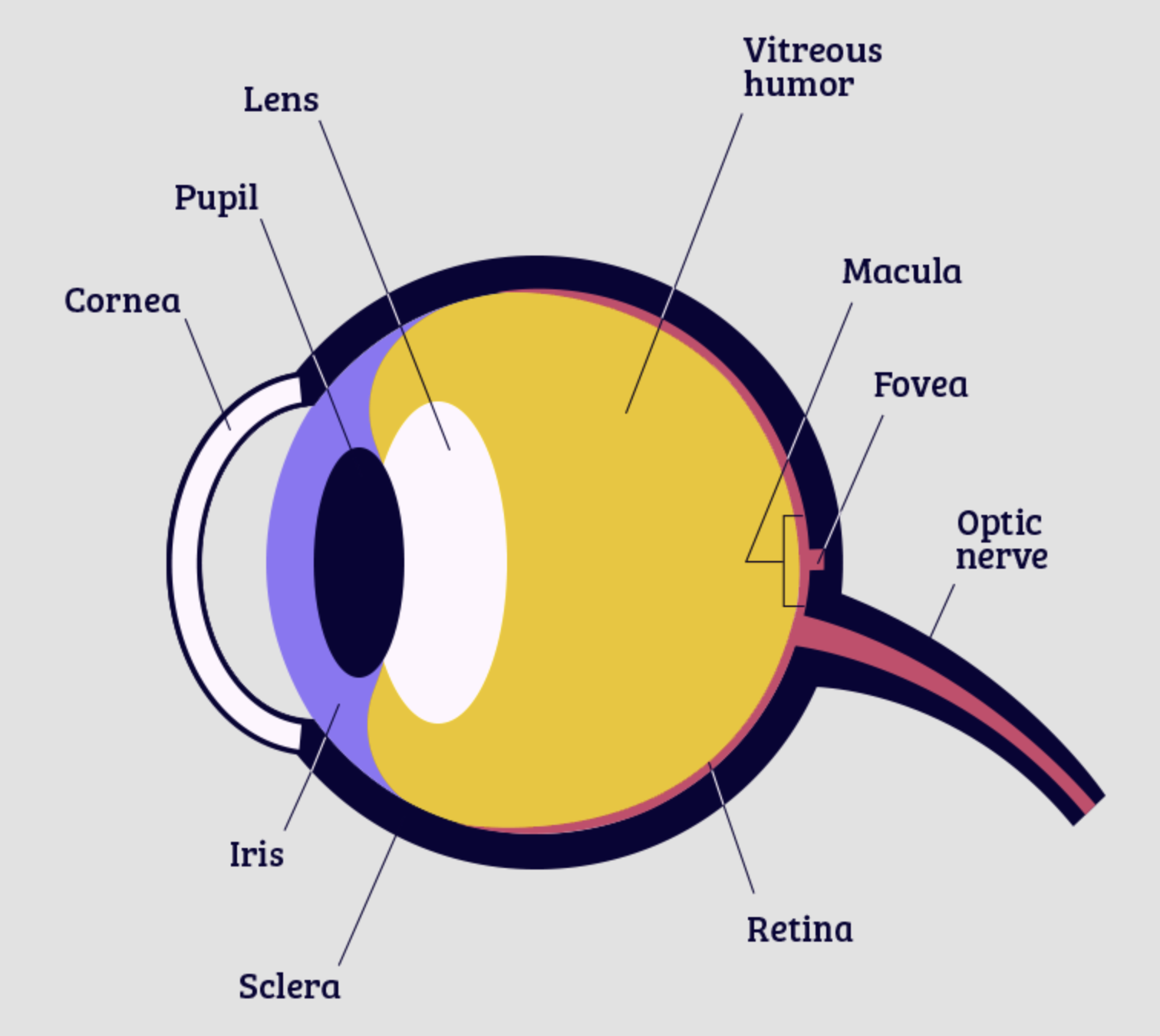
iris
The ring of pigmented tissues surrounding the pupil. Responsible for:
* controlling diameter and size of pupil
* controlling amount of light that reaches retina
* controlling diameter and size of pupil
* controlling amount of light that reaches retina
91
New cards
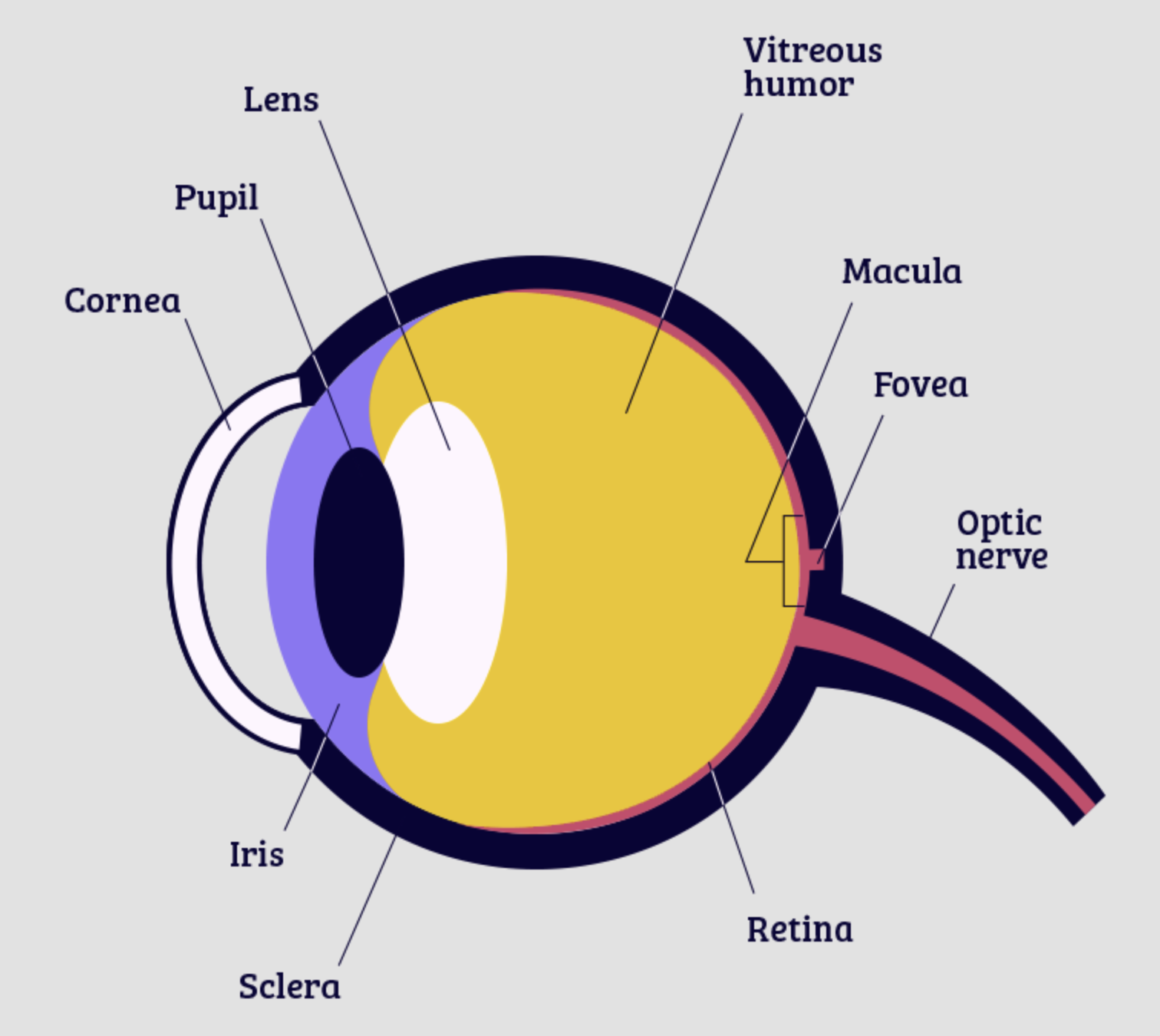
lens
A flexible piece of tissue located behind the pupil that focuses light on the retina
92
New cards
photoreceptors
Cells that are specifically sensitive to exposure t light. Located at the back of the eye
93
New cards
rods
kind of photoreceptor in the retina; typically most responsive to LOW levels of light
94
New cards
cones
type of photoreceptor in the retina that is responsive to BRIGHT light. Responsible for communicating info about acuity and color
95
New cards
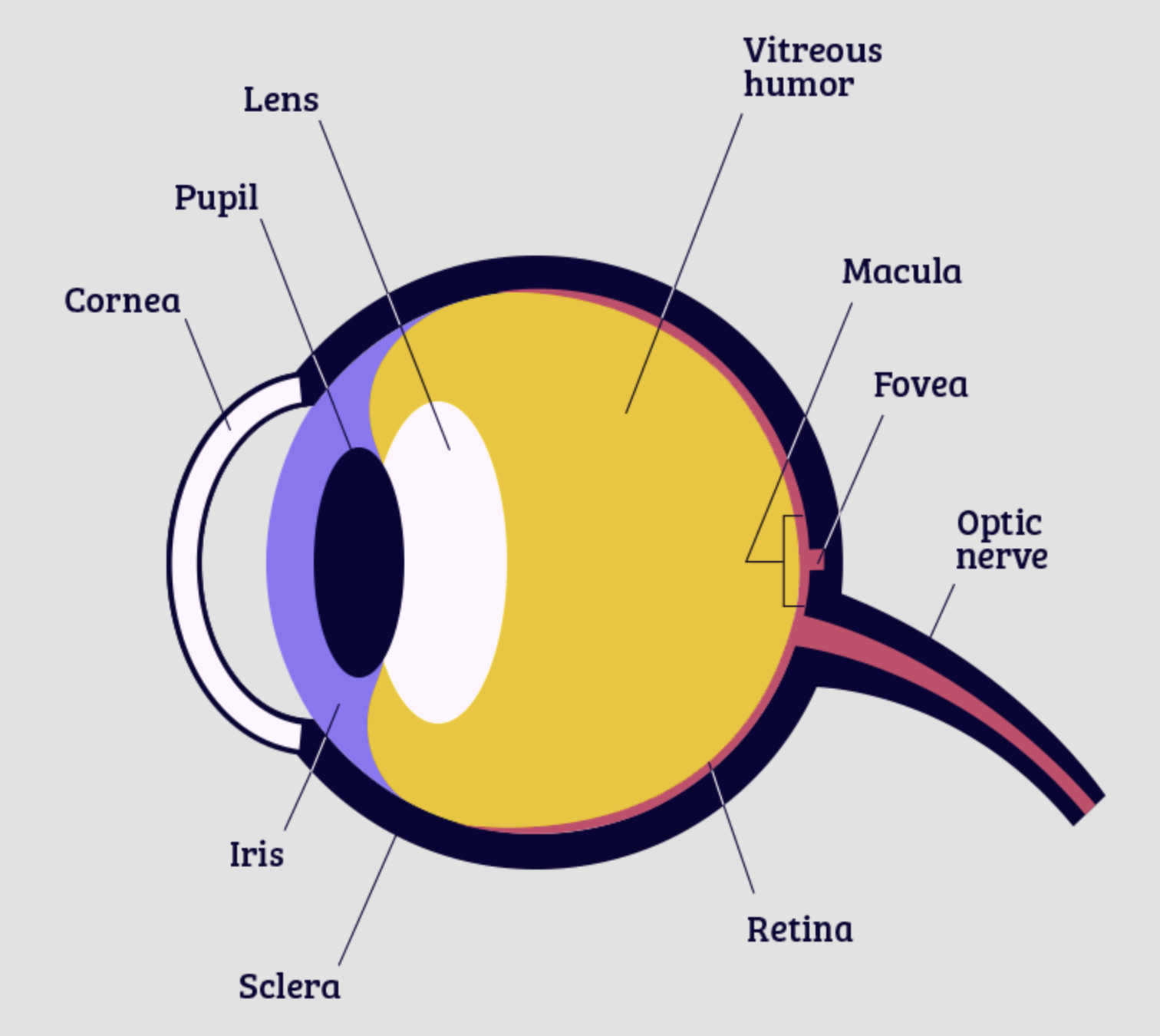
fovea
the portion of the retina directly behind the pupil. Contains a large concentration of CONES and no rods.
96
New cards
diffuse bipolar cells
part of the bipolar layer of the retina. These cells receive signals from rods and send messages to large ganglion cells
97
New cards
midget bipolar cells
Part of the bipolar layer of the retina. These cells receive signals from cones and send their messages to the small ganglion cells
98
New cards
pinna
the external part of the ear
99
New cards
tympanic membrane (eardrum)
transfers energy to the smallest bones of the body (ossicles)
100
New cards
ossicles
3 smallest bones of the body. Responsible for amplifying vibrations arriving at the eardrum and transmitting these signals to the oval window of the cochlea