English midterm
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
culture
shared belief, values, custom and symbols of a large group of people
Examples of culture
customs are practices like weddings, birthday parties and death
broad concepts (not limited to nations, race, religion or ethnic groups)
co-culture
presence of many different cultures (i.e Mexican culture and American culture) existing side by side
co-culture characteristics
usually attached outside of mainstream culture
culture practices inside a mainstream culture (sit under an umbrella of main culture)
communication
without communication there’s no identity, since we share our identities with each other.
Identity
it is impossible for one person only to have an identity no other person has, because identities are cultural (shared)
communication is symbolic, language is a code
in order to understand language, you have to decode the symbolic code
symbol
anything that stands or represents something else
verbal communication
words spoken or written
nonverbal communication
not spoken, involve use of symbols, gestures, facial expressions, visual representation of belonging, etc
communication is a process
has no definitive beginning or end
a constant flow of actions with consequences
communication is transactional
channels of communication carrying messages in two directions at the same time
model of communication
communication is contextual
relational and cultural context
relational communication
provides information about level of intimacy and / or balance of power and socially constructed rules
Cultural communication
provides another layer of information determining meaning and consequences of communication
family culture, regional culture, religious culture, racial / ethnic culture, professional culture, national culture, etc.
global community
people and nations of the world are connected by modern technology and are interdependent economically, socially, and politically
peaceful coexistence
interacting with individuals of another culture peacefully without discrimination
negative peace
the absence of violence & conflict between two groups of people
example: ceasefire
positive peace
success in no conflict remaining, eradicating structural and cultural violence
pure peace
there has never been a conflict in the first place
peacemaking
stopping and eradicating the conflict
ie: negotiating the ceasefire
peacekeeping
constant intervention to make sure people don’t go back to conflict thus preventing recurrence
peacebuilding
efforts to continue to grow peace between groups, so we can achieve positive peace
structural violence
comes from some kind of structure, sociopolitical and economical and produce or permit various forms of human suffering
cultural violence
prejudice beliefs about other cultural groups, manifests in feeling of indifference and discriminatory practices that deprive individuals of human rights
xenophobia
fear and hatred of anything foreign
ethnocentrism
ethnocentric belief of one culture being the center of everything, feeling their culture to be superior to other cultures
Deardorff model level 1: Requisite Attitudes
Respect (various cultures n diversity)
Openness (to intercultural learning)
Curiosity and Discovery (tolerating ambiguity and discovery)
Deardorff model level 2: Knowledge and Comprehension
Cultural self awareness
Deep understanding and knowledge of culture
cultural specific knowledge
Sociolinguistic Awareness
Deardorff model level 3: Skills
Listen
Observe
Interpret
Analyze
Evaluate
Relate
Deardorff model level 4: Desired internal outcome
Adaptability (to different communication styles)
flexibility (selecting and using appropriate communication styles)
ethnorelative view
empathy
Deardorff model level 5: Desired External Outcome
behaving and communicating effectively based on one’s intercultural knowledge, skills, and attitudes
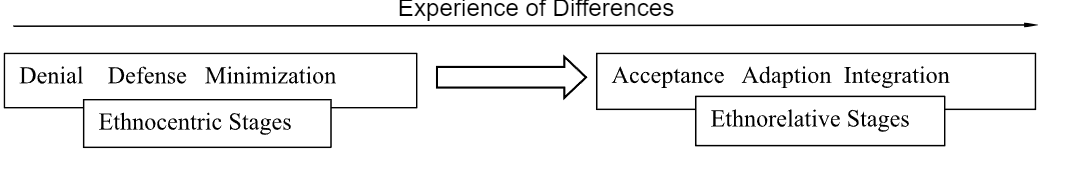
Milton Bennett’s stage model of intercultural sensitivity
Ethnocentric
Denial stage 🡪 fail to acknowledge existence of cultural differences
Defense stage 🡪 acknowledge cultural differences as threatening
Minimization stage 🡪 trivialize cultural differences and put little significance on differences
Ethnorelative
Acceptance stage 🡪 understand and respect cultural differences
Adaption stage 🡪 develop intercultural communication skills
Integration stage 🡪 multicultural view
intercultural communication competence
some people are more able communicators than other people
better ability through experiences with other cultures
most people can learn and be trained to improve those skills
competent communication should at least include two outcomes
it should be appropriate
it should be effective
cultural frame of reference
influences how we interpret and value appropriateness, as well as effectiveness of someone’s communication behavior
what we know about another culture influences our judgement
fossilizing
staying in one stage (f.e. denial stage) and not moving on
conflict transformation
changing conflict, proactive means of bringing the conflict participants together
social justice
belief in fair treatment and equal access to valued resources for all in multicultural society
social capital
beneficial interactions between people, participation to bring social justice
prejudice
negative attitudes towards a group or members of a group
certain attitude against another culture, ethnicity and / or race
ethnocentricity
ingroup
a group to whom you belong and anyone else is perceived as belonging to group
natural impulse to favor ingroups (which we belong) over outgroups (which we don’t belong)
Gordon Allport intergroup contact theory
four conditions for optimal intergroup contact to avoid prejudice: equal group status within the situation, common goals, intergroup cooperation and authority support
implicit prejudice
association and knee jerk reactions we have in response to other cultures that is usually hidden
explicit prejudice
open negative attitudes and hostile behavior towards other cultures
openly voiced or shown attitude against other cultures
harder and more resistant to change
stereotyping
apply a behavior to a group of people and assume everyone practices this application
orientalizing
idea that some cultural practice is placed higher in judgement because it’s exotic and therefore more beautiful or more interesting
automatic stereotyping
spontaneity
efficiency
uncontrollability
unconsciousness
social identity theory
group affiliations satisfy fundamental need for positive self esteem
outgroup homogeneity bias
exaggerate similarities, use stereotypes, and overlook individual differences among outgroup members compared to ingroup members
ultimate attribution error
we are more likely to attribute bad behaviors of ingroup members to things beyond their control
compared to outgroup member (attribute bad behavior within their control)