Microbiology in Wastewater Treatment Processes
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What microbe is responsible for typhoid fever?
Infection caused by Salmonella typhi.
What microbes are used for screening water samples for contamination?
Indicator microorganisms such as Coliforms are indicative of fecal contamination
Most Probable Number (MPN)
Statistical estimate of viable bacteria in samples based on serial dilution and growth in selective media eg EMB
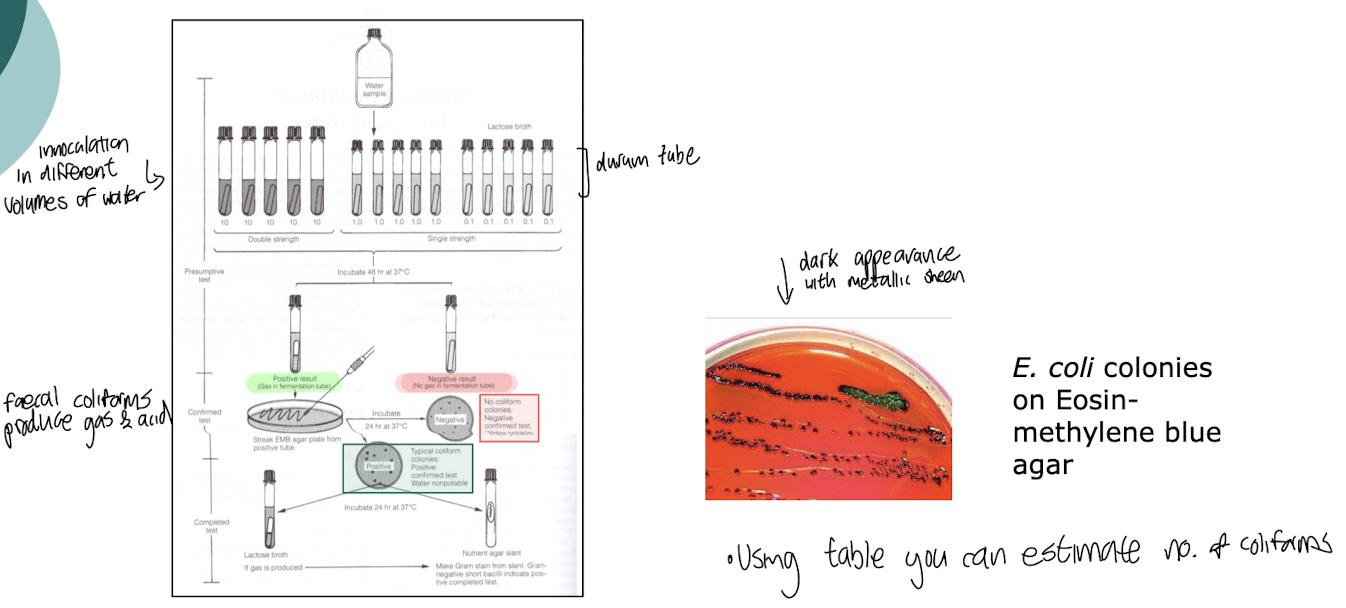
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
Amount of dissolved oxygen consumed by microorganisms to oxidize compounds, typically increased if wastewater contains harmful organic/inorganic compounds & pathogens
Domestic wastewater BOD
Typically around 200 BOD units.
What is the BOD of treated water?
< 5 BOD units
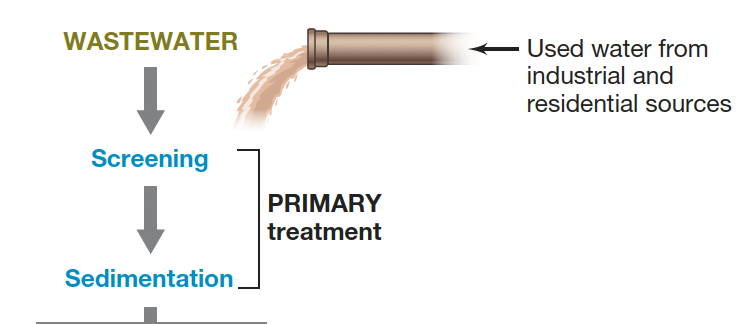
What is the primary treatment method in wastewater treatment?
Physical screening, removes solid/particulate matter through a series of grates
Effluent is allowed to settle for a few hours.
Solids settle to the bottom of the separation reservoir and the effluent is drawn off to be discharged or for further treatment
Level of BOD is still high and further treatment is needed to reduce BOD levels.
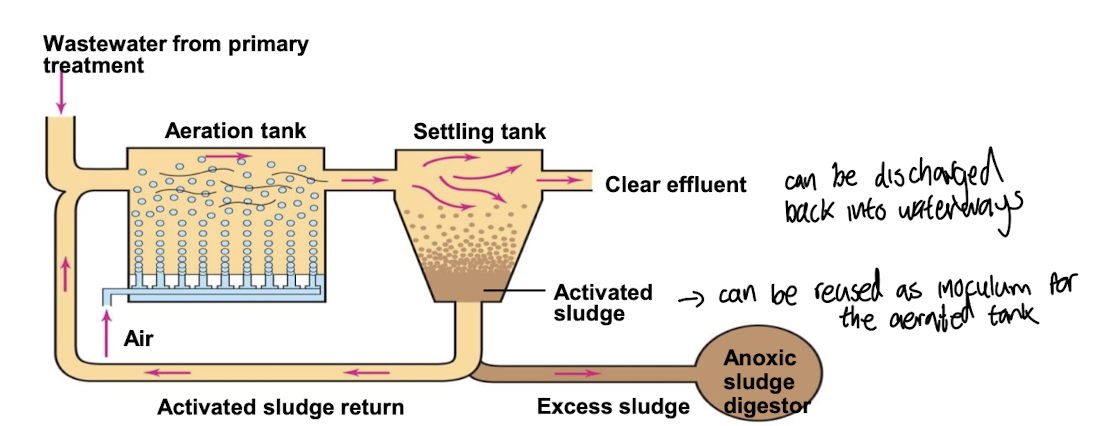
What is the secondary treatment method in wastewater treatment?
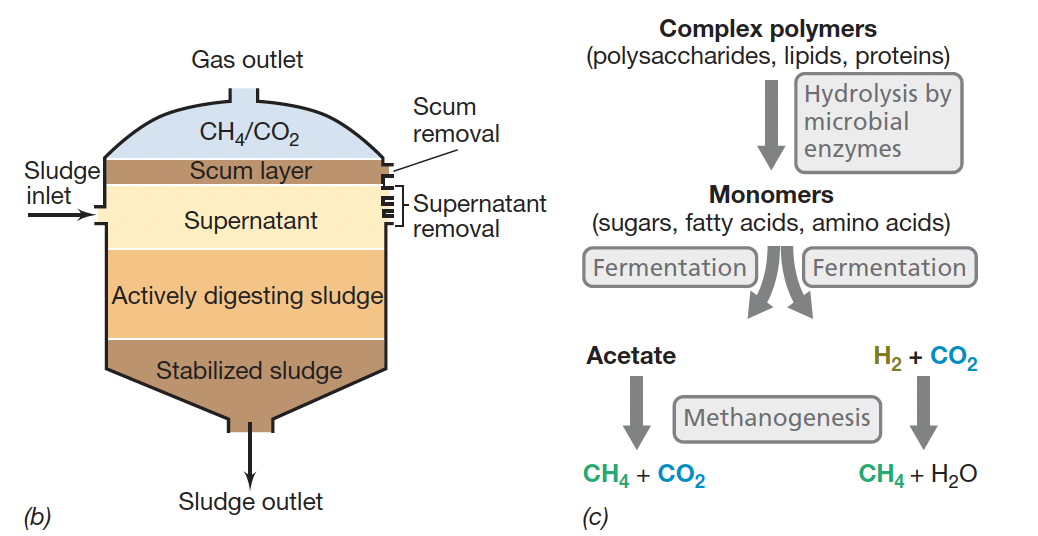
Anoxic treatment using bioreactors/sludge digesters
What type of material is treated in secondary treatment?
Insoluble material, e.g., cellulose
What types of enzymes do anaerobes produce during treatment?
Lipases, proteases, cellulases to digest suspended solids and large macromolecules into soluble components
What do anaerobes ferment during wastewater treatment?
Sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids
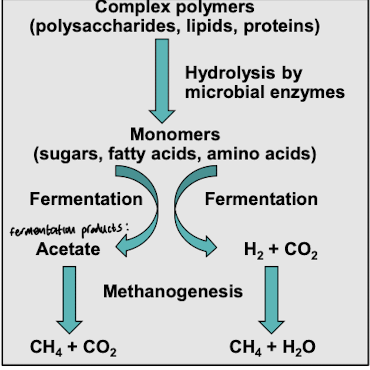
How can methane generated in wastewater treatment be used?
The CH4 is burned off or used as fuel to heat and power the wastewater treatment plant
Activated sludge
Microbial mass used in wastewater treatment process which is aerated in large tanks
Trickling filter
Aerobic treatment using sprayed wastewater on top of crushed rocks where organic material in the wastewater adsorbs to the rocks, and m/o grow on the large, exposed rock surfaces - forming a biofilm
The complete mineralization of OM to CO2, ammonia, nitrate, sulfate, and phosphate takes place in the extensive microbial biofilm that develops on the rocks.
what is the use of Zoogloea ramigera?
Slime-forming bacteria used in wastewater treatment
Helps in the formation of flocs
Enhances the settling properties of activated sludge.
Can be reused as inoculum
Tertiary treatment
Advanced treatment removing pathogens and inorganic compounds to make water more potable
Eg using chlorination, UV, ozone
Chlorination
Disinfection method using chlorine to kill pathogens.
what is the difference between anaerobes and aerobes in polyphosphate removal?
Anaerobes make polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) and release phosphate
Aerobes use the PHB and make polyphosphate
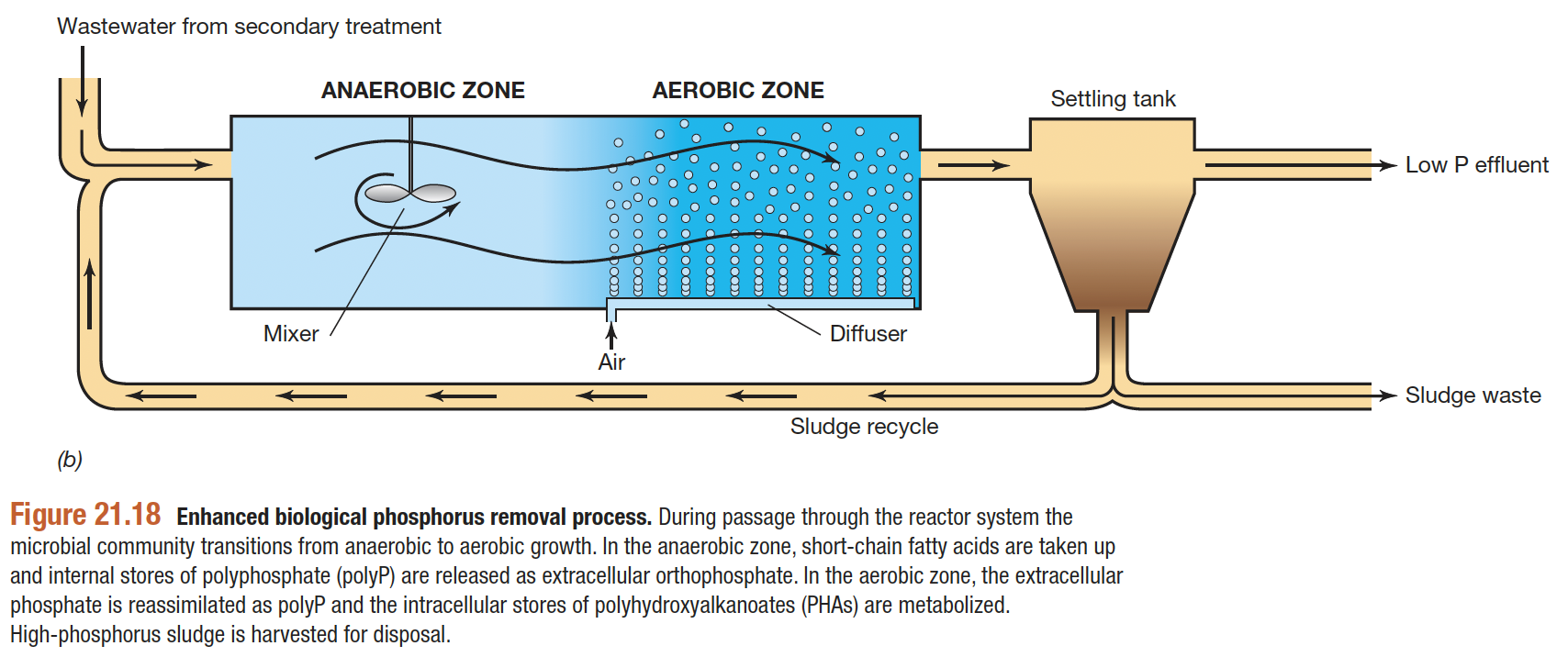
Accumulibacter phosphatis
Microbe involved in biological phosphate removal by accumulating polyphosphate in its cells
Has the correct conditions for enrichment in WWTP
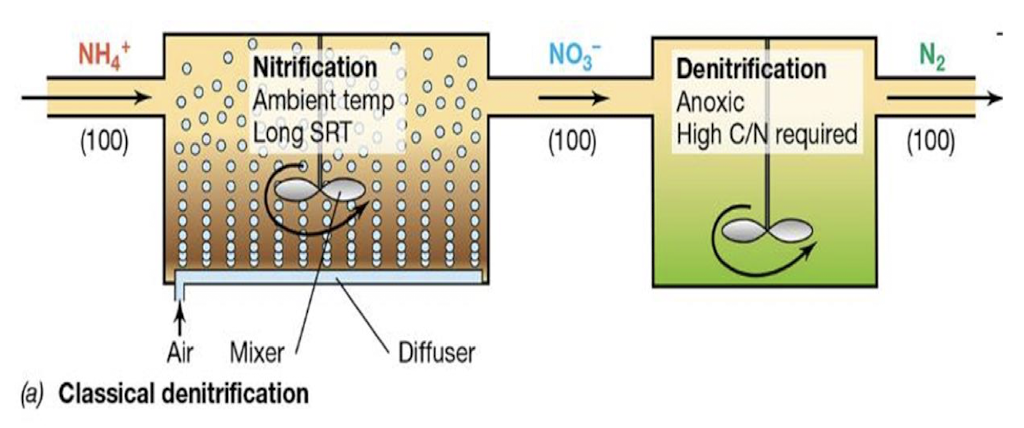
What is classic biological nitrogen removal?
(Denitrification) Process converting reactive ammonium NH4+ into gaseous nitrogen (N2), reducing nitrogen compounds in wastewater to improve water quality.
Anammox
Anaerobic ammonia oxidation converting ammonia to N2 by chemolithotrophs such as Nitrosommonas and Brocadia anammoxidans which uses nitrite as an e- acceptor + ammonia as an e- donor
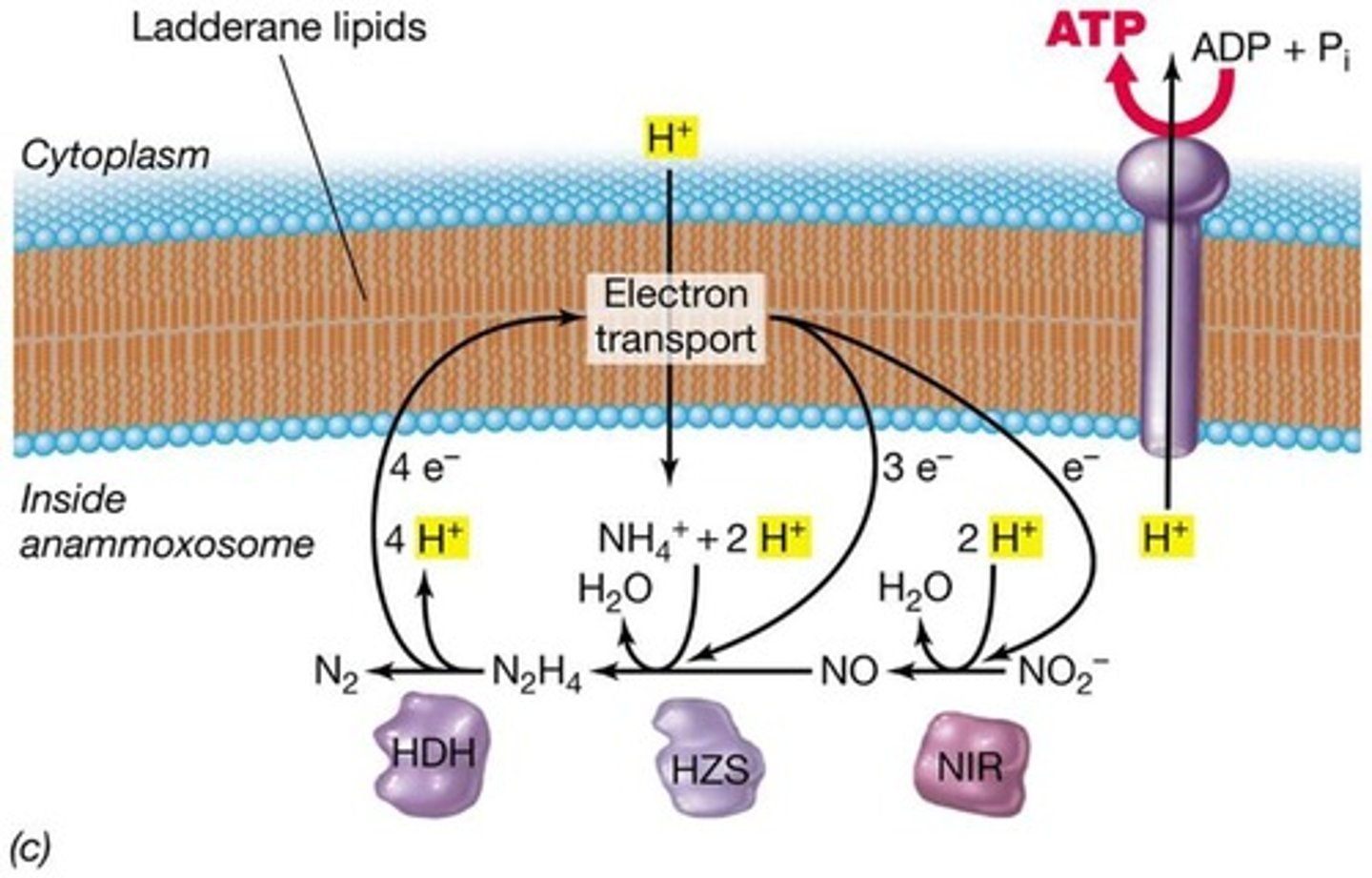
Brocadia anammoxidans
Microbe performing anammox using nitrite and ammonia.
Microbial source tracking
Using PCR to identify faecal contamination sources.
E.g. On beaches, where does the contamination come from Gull, dog, human
Can also be employed to monitor the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in WWTP
RT-qPCR
Monitor localised outbreaks - epidemiology outbreaks