3.8 Phenomenon of Godon. Equilibrium of periodontium
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is Ante’s Law?
Total periodontal membrane area of the abutment teeth must be equal or greater than that of the teeth to be replaced
simple terms - surface areas of abutment teeth should be equal to or greater than that of pontics
what is Wusrow (1919) talk about?
Each tooth can compensate double of normal physiological pressure
simple terms - each tooth can compensate for double the normal physiological pressure. This could relate to how teeth distribute force when chewing or how they adapt to changes in the oral environment.
what did Blabanov (1970) say?
they postulated the so called “functional-mechanical equilibrium of periodontium” concept
the periodontium of a tooth is in a condition of functional and mechanical equilibrium when the correlation between area of occlusal surface of tooth and area of its active root surface is constant.
what should the ratio of total occlusal surface to total periodontal surface not exceed to be at equilibrium?
2:1 ratio
why is the equilibrium between between total occlusal surface and periodontal surface important in dental restorations?
balance is crucial for stability and health of supporting structures in dental restorations
what does the total occlusal surface include?
mix of elements such as retainer’s occlusal surfaces and pontics ones
what is Balabanovs formulae?
2Fo/Fp = K
Fo = occlusal surface
Fp = root surface area.
K = functional equilibrium
what is physiologic tolerance?
refers to the periodontium to adapt to functional forces generated during activities such as chewing, speaking, and swallowing. The periodontal ligament plays a role in distributing and dissipating the occlusal forces.
what is loading limit?
Loading limits refers to the maximum forces the periodontium can tolerate without causing damage.
The periodontium has certain physiological limits which excessive forces can lead to physiological changes.
These changes include: alveolar bone bucking, bone loss, gingival recession, and even tooth loss.
what is Boyanovs concept for fixed prosthodontics?
Total occlusal surfaces of retainers and pontics should correlate to the summary area of the periodontal surface
in the range of: Fo/Fp->2Fo/Fp
Fo - occlusal surface
Fp - periodontal surface area
what should be taken into consideration when planning FPDs?
General biologic factors. Reactivity of patient (age, disease etc)
Local factors
Anatomic
Hard tissue (enamel and dentin)
Periodontium
Functional factors (horizontal forces)
what are important things to make sure when constructing the pontic?
occlusal surface of FPD should be considerate of the state of compensatory forces of periodontium, ensuring that the prosthetic design respects the natural biomechanical balance of the oral structure
Pontic must connect the abutments in the shortest way possible
profile of a pontic must accommodate the atrophic processes in the alveolar ridge, ensuring both phonetic and aesthetic functions.
Correct occluso-articulating relationship
what should be taken into account when constructing retainers?
full crown for better statics (FC help manage static forces by reinforcing the tooth structure and ensuring even distribution of pressure)
From aesthetic point of view and intact abutments the full crown is best but partial crowns should be a matter of choice
What is the constructional guidelines for retainers (and what is a requirement of partial retainers)?
REPRODUCE anatomically and functionally the abutment teeth, proper contact points with adjacent and opposing teeth and proper articulation
PROTECT exposed dentin from outer irritants and decay
MAINTAIN morphological integrity and functional state of periodontium
PARTIAL RETAINERS:
Max contact surface with 1 mm distance from the gingiva margin
what does static methods in Balabanov’s approach refer to?
Specific techniques used for the initial orientation of articulators. These techniques help establish the starting position of the articulator in relation to the patients anatomy
what is the classical principle of the static method in Boyanov initial orientation
The total sum of the coefficient of all members of the FPD, should be less or equal to the abutment teeth (same concept as stated by Ante’s Law dwww)
what is a coefficient in dnetistry?
Occlusal Force Distribution – Coefficients can be used to analyze how chewing forces are spread across teeth to maintain balance
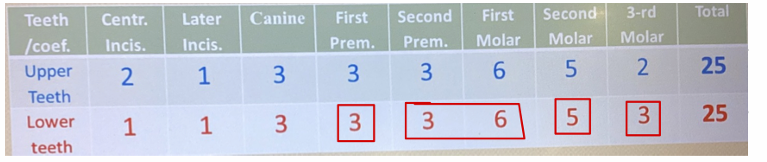
what is this and how is it used?
It is Boyanovs table
This table displays coefficient values for different types of teeth in the upper and lower jaws. Each tooth type—such as central incisors, lateral incisors, canines, premolars, and molars—has a specific coefficient that contributes to the total dental balance.
How It’s Used:
Dental Load Calculation – These coefficients might help dentists estimate how different teeth distribute chewing forces.
Occlusal Adjustments – Dentists may use these coefficients when making refinements to occlusion (bite alignment) for better static balance.
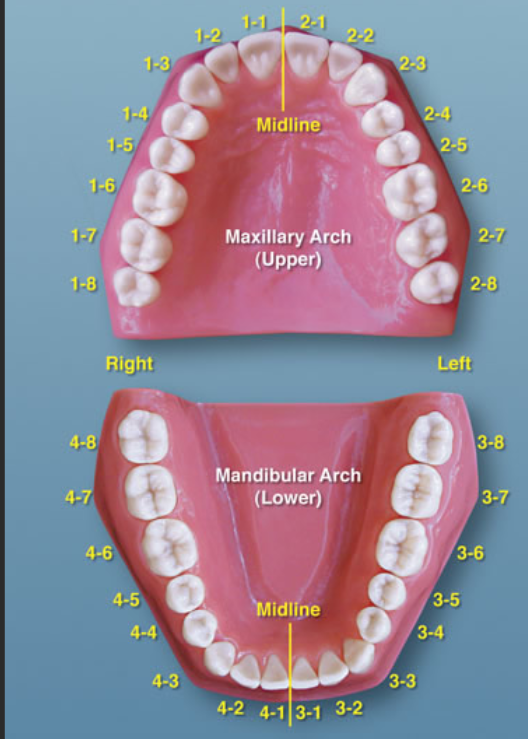
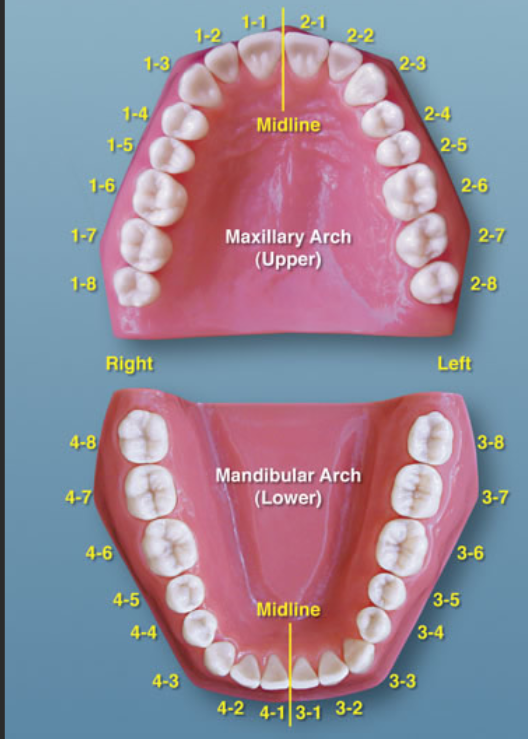
ISO teeth numbering system
ISO teeth numbering system
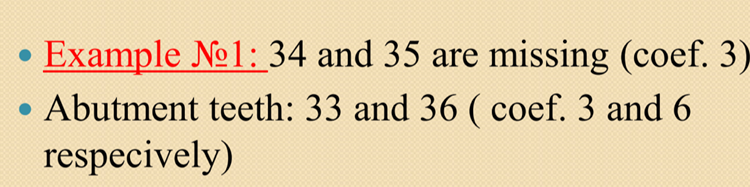
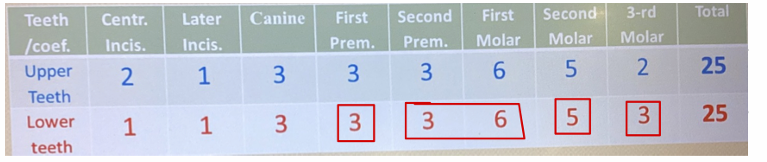
If this is the case then how much would the coefficient be for the total FPD and the coefficient of abutment teeth? Is the total coefficient of FPD less or equal to the abutments?
Total coefficient for FPD is less than abutments so this is good


If this is the case then how much would the coefficient be for the total FPD and the coefficient of abutment teeth? Is the total coefficient of FPD less or equal to the abutments?
Coefficient of abutments is lower which is bad this is fixed by adding one more abutment tooth (38) making total FPD 20 (3+3+6+5+3) and the abutment teeth total being 22 (3+5+3)

What are some solutions if the total coefficient of the FPD is higher than coefficient of abutement?
Reduce occlusal surface of the retainers and pontic by 50%
Adding other abutments with healthy periodontium
Reducing occlusal surface of pontic ONLY by 50% AND adding another abutment with healthy periodontium
What is Phenomenon of Godon simply?
Popov-Godon phenomenon refers to the changes that occur in the dentition after tooth loss
What is phenomenon of Godon entail (more detailed)?
When tooth is lost, structural integrity of dental arch is disturbed
Leads to realignment of teeth until new state of equilibrium is reached
Adjacent and opposing teeth of the edentulous space frequently move into it, especially those distal to the space
Instead of drifting bodily, tilting movement is more common
Teeth adjoining an edentulous space usually move but they do not always move
Clinically what occurs in Godon phenomenon?
During first month after tooth extraction, visible changes are noticed
Small threshold dimension occurs (minimum required space for proper fitting of restorations)
If there is no contact with antagonist by the drifting tooth (opposite teeth above or below the edentulous ridge for the missing tooth/teeth)
Opposite side tooth will continue its movement, leading to resorption of alveolar ridge (gradual loss of bone in jaw after a tooth extraction)
How is Godon Phenomenon diagnosed?
Through intraoral examination
How is Godon phenomenon treated?
Prosthetic treatment administered promptly (2-3 weeks after tooth extraction) has highly prophylactic effect)
prophylactic effect refers to preventative measures taken to maintain oral health and prevent dental issues
How is sanitation of oral cavity done in case of Godon phenomenon if there is contact with the antagonist?
Selective reduction of outgrown tooth with diamond burr and turbine in order to achieve a symmetrical curve of spee on both sides of dentition (in enamel only)
Tooth prep for casted crown if threshold is more than 1.5-2mm, or dentin exposed. Sometimes tooth devitalisation (root canal treatment) is preformed in greater reduction is needed
Tooth extraction
Splinting (block-crowns to prevent further overeruption of the antagonist
what is one of the main disadvantages of conventional fixed partial dentures?
removing of healthy enamel and dentin for abutment prep
what is a solution to remove the disadvantage of tooth prep of abutments required in conventional fixed partial denture?
Development of acid etching of enamel for improving retention of resin (Buonocore 1955)
Ibsen first described the attachment of an acrylic resin pontic to an unprepared tooth using a composite bonding resin
Extended wings over the abutement teeth
Electrochemical pit corroding technique
Use of silane coupling agents
What are the classifications of FPDs by term of differences in metal framework treatment technique ?
Rochette bridge
Maryland bridge
Cast mesh FPD
Virginia bridge
Selectively opened partial retainer
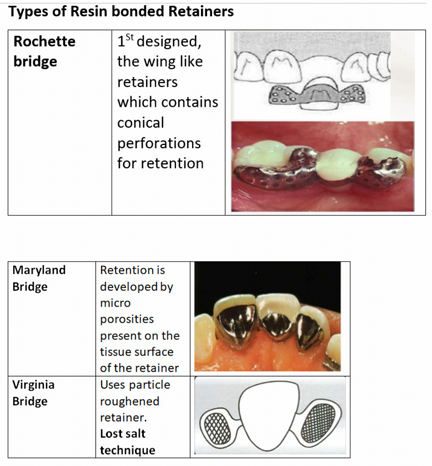
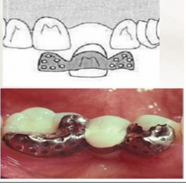
Rochette bridge
1st designed, the wing like retainers which contain conical perforations for retention
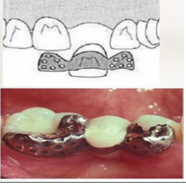
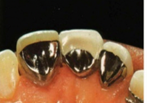
Maryland Bridge
Retention is developed by micro porosities present on the tissue surface of the retainer
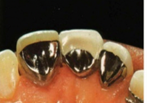
Virginia Bridge
Use particle roughened retainer.
Lost salt technique:
Salt Crystals as a Spacer – During the fabrication process, salt crystals are placed inside the denture base material.
Processing the Denture – The denture is cured and shaped around the salt.
Salt Removal – The denture is then soaked in water, dissolving the salt and leaving behind a hollow space.
Final Adjustments – The hollow denture is polished and refined for comfort and stability.
what are some advantages of FPD?
Low cost
no anaesthesia recquired
supragingival margins
minimal or no preparation needed
possible rebonding
time-saving
What are disadvantages of FPD?
irreversible
uncertain longevity
no space correction
no alignment correction
impossible temporisation
What are indications for having FPD?
caries free abutment teeth
incisor replacement
single posterior tooth replacement
splints
What does FPD teeoth prep entail?
Early used of acid-etched resin-bonded FPD recommeneded without any tooth prep (improve stability and longevity of construction) NB!
Framework is outlined on die inclduing contact points with antagonis NB!
Splint withstand approx 1mm away from gingival margin and incisal edge
Holes in wax pattern quite visible (spots of preliminary contacts with the antagonist that should be avoided)
Mechanical retention - vestivular surfaces of frontal teeth are absolutely intact (guarantees aetshtic look of bridge)
what is a splint?
splint refers to a structure that connects multiple teeth or abutments to improve stability, load distribution, and longevity of the prosthesis.
Splinting is often used when individual teeth may not provide sufficient support on their own
Why is resin bonded FPD recommended in long term provisional restorations?
Because of the reliability of the bond strength