Human Anatomy and Physiology: Chapter 1 pearson
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
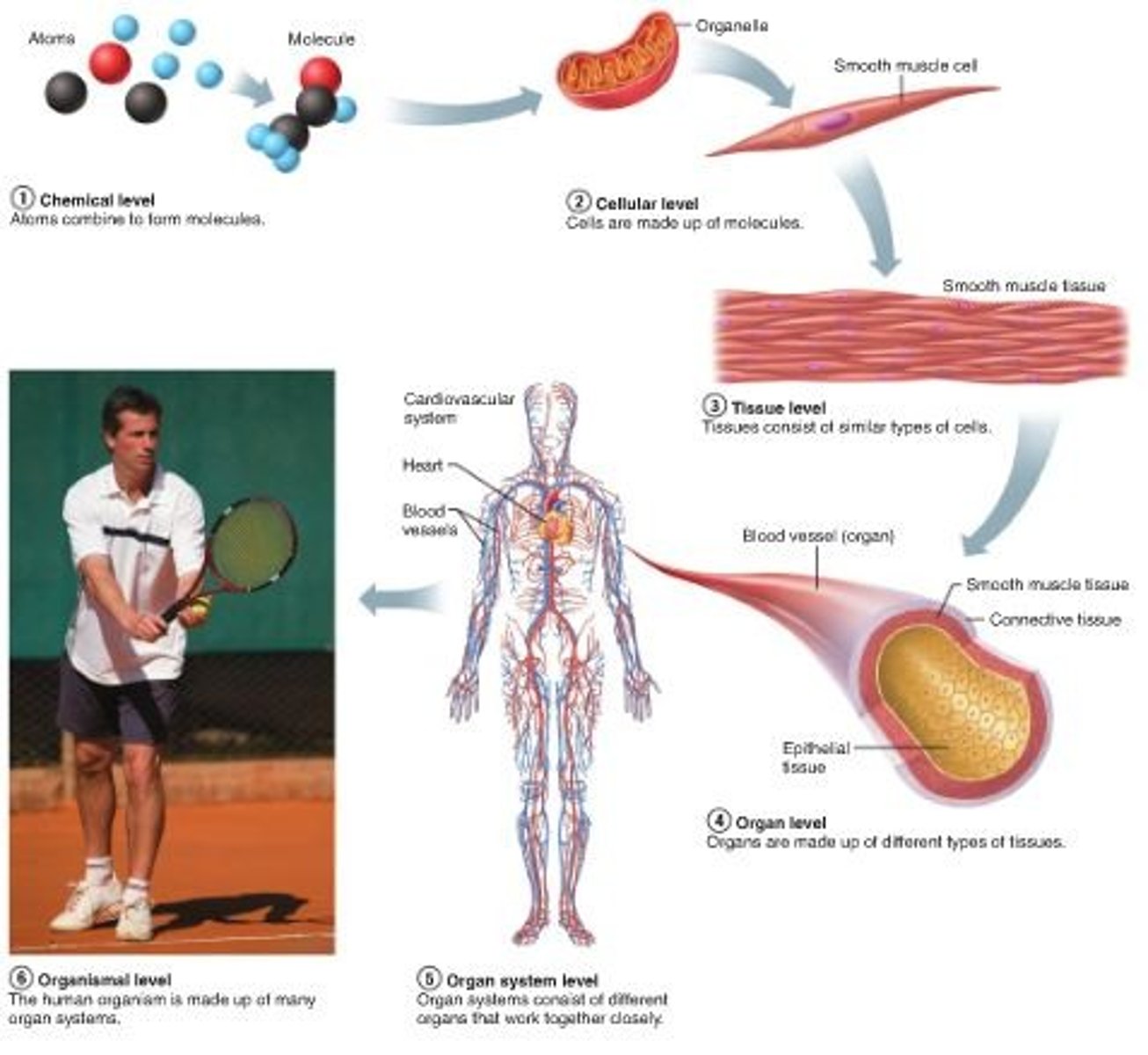
Levels of organization
Chemical (atom & molecule), Cellular, Tissue, Organ, Organ System, Organism
Anatomy
studies the structure of the body
Physiology
studies the function of the body parts

Cells
smallest unit of living things
Tissues
a group of similar cells that have a common function
Organ
structure composed of at least 2 tissue types that performs a specific function for the body.
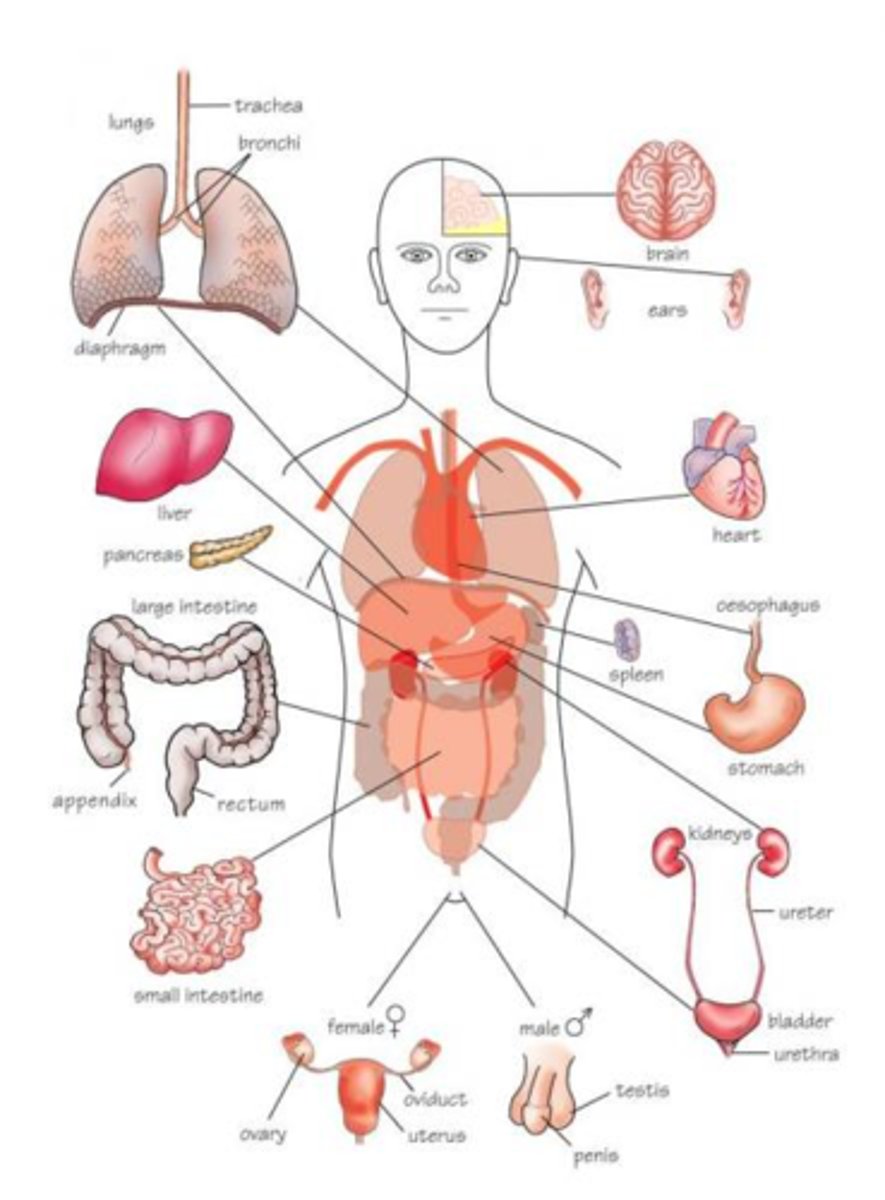
necessary life functions
1. maintaining boundaries
2. movement
3. responsiveness
4. growth
5. digestion
6. excretion reproduction
7. metabolism
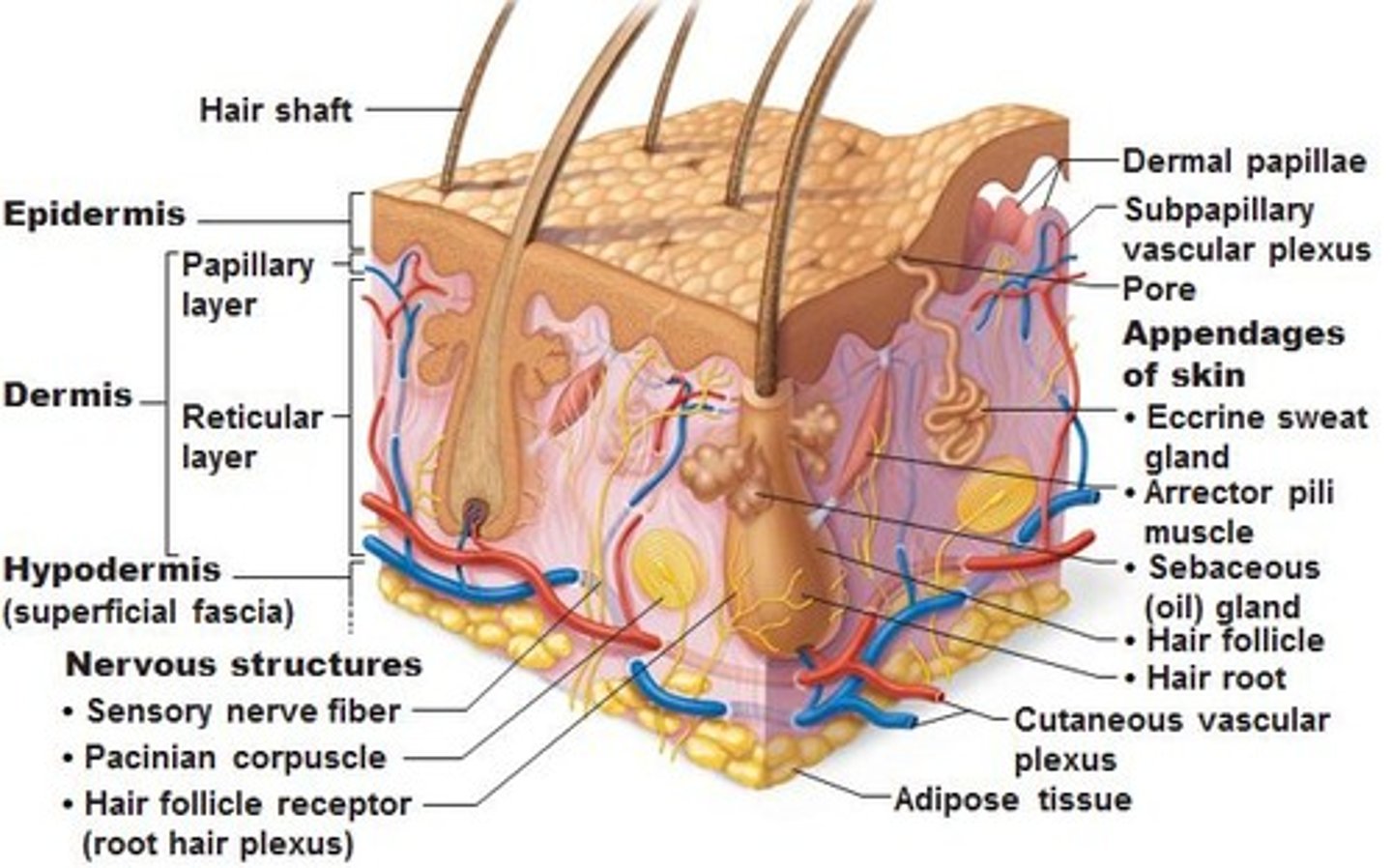
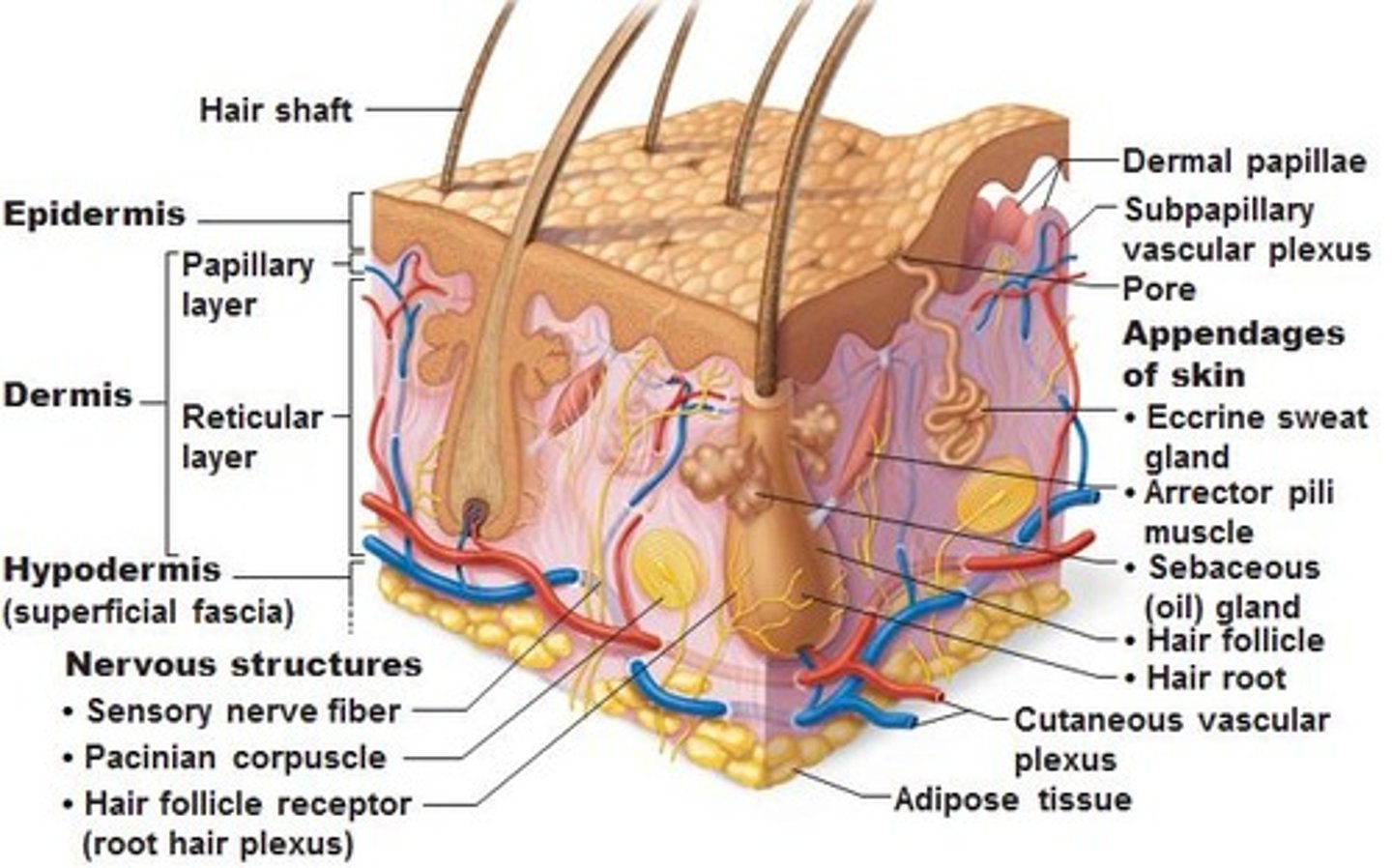
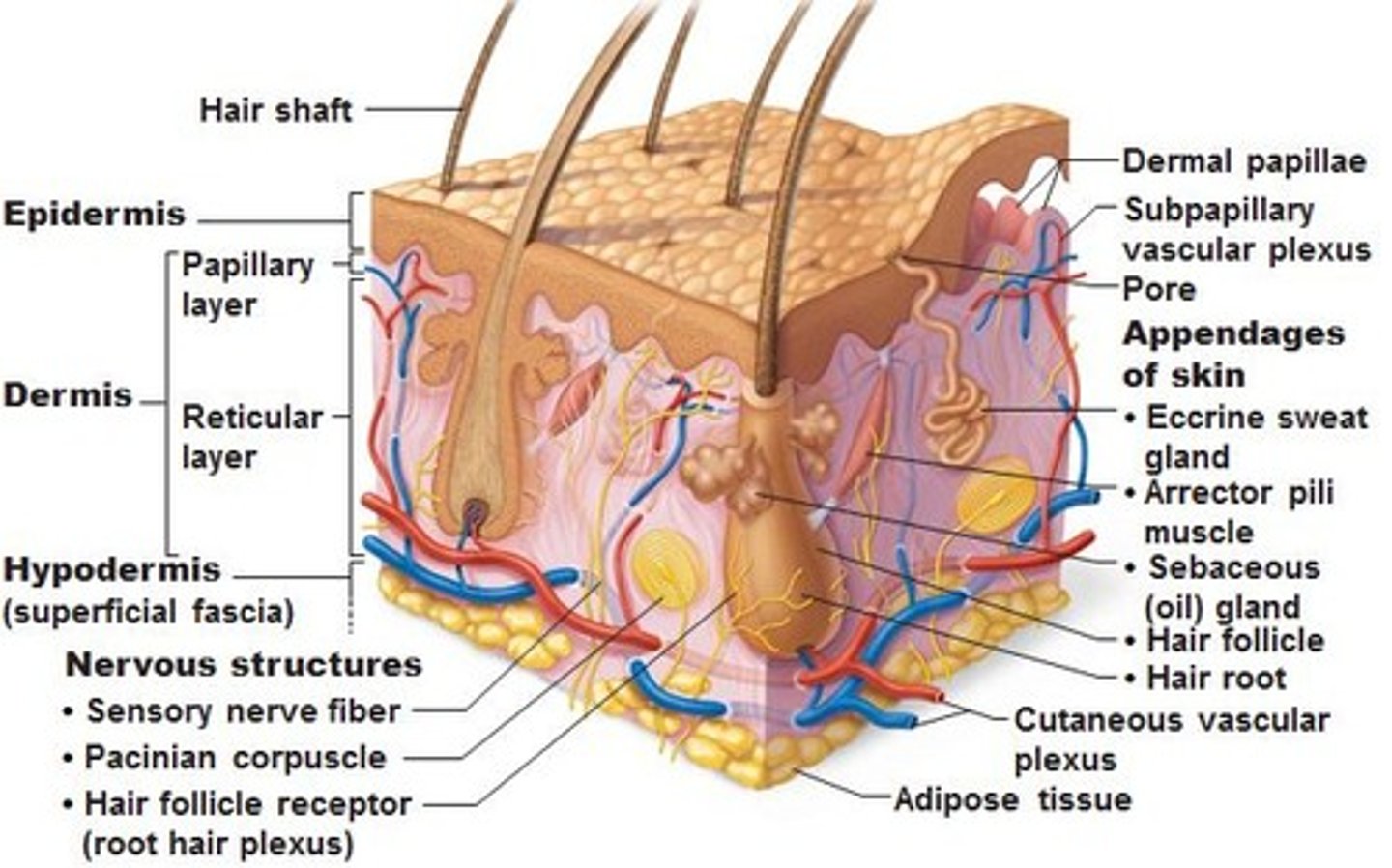
The Integumentary System
Protects against environmental hazards; Controls temperature
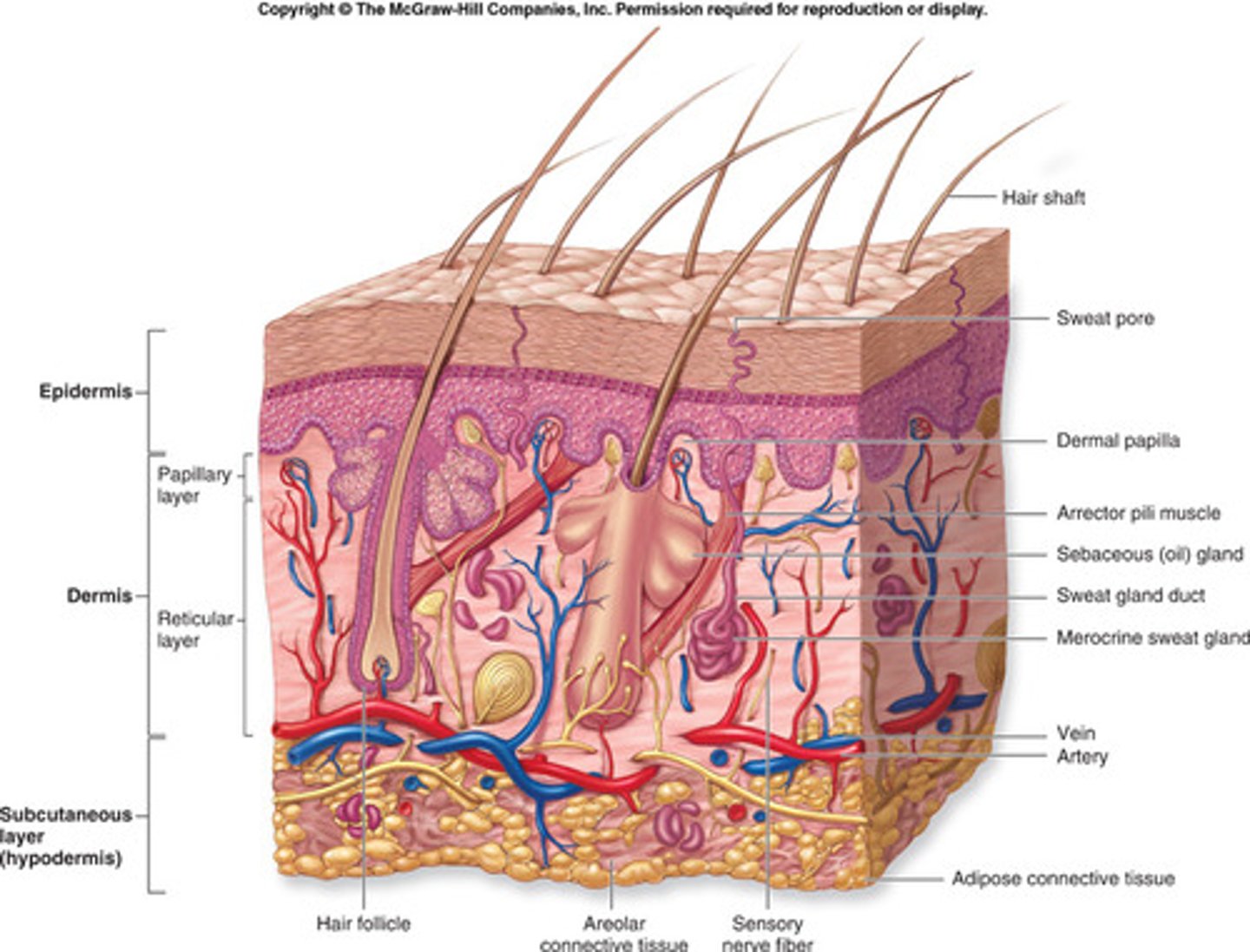
Skin: (Cutaneous membrane)
Dermis
1. Nourishes epidermis
2. Provides strength
3. Contains glands
Skin: (Cutaneous membrane)
Epidermis
1. Covers surface
2. Protects deeper tissue
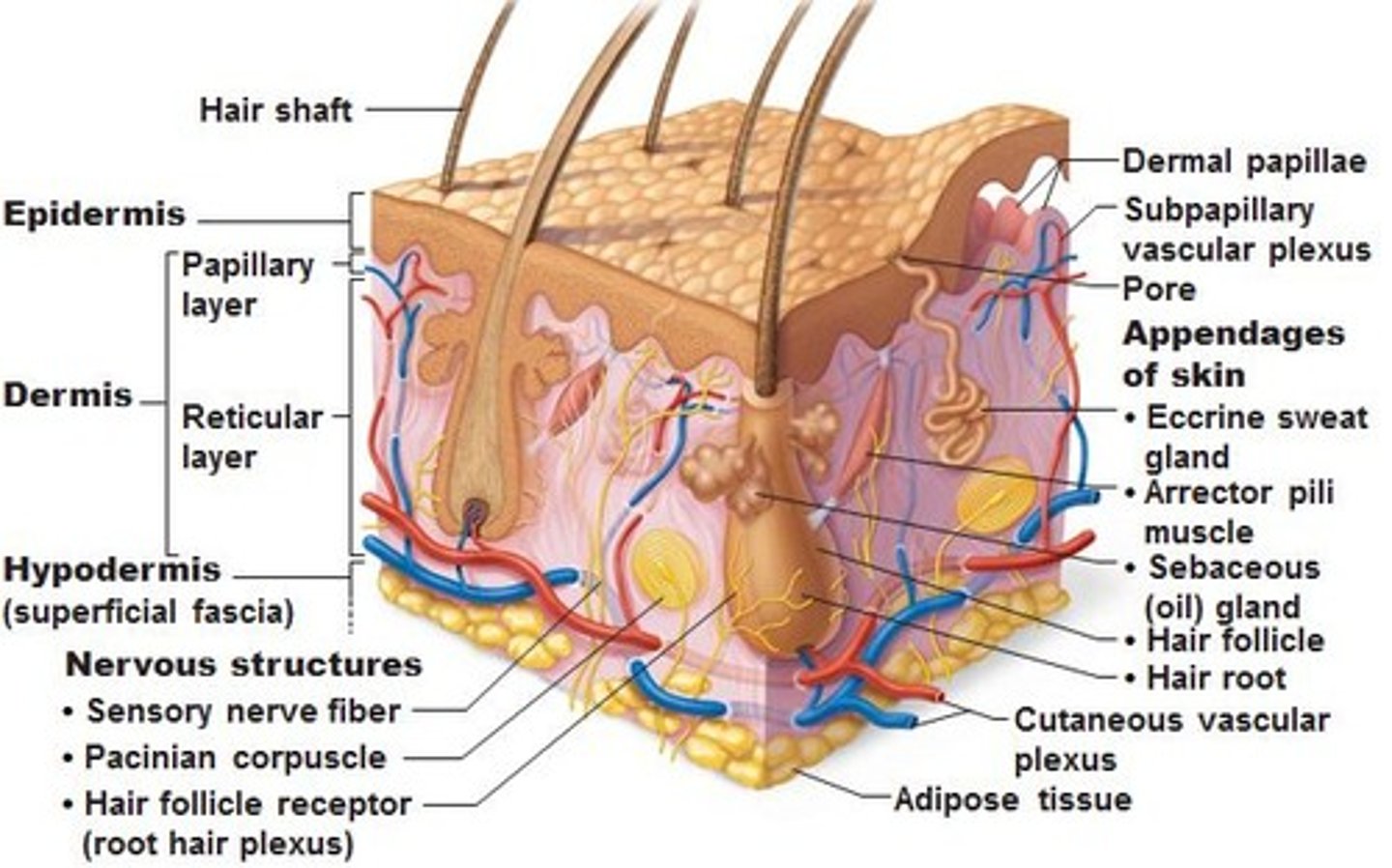
Hair Follicles:
1. Produce Hair
innervation (supply nerves to) provide sensation
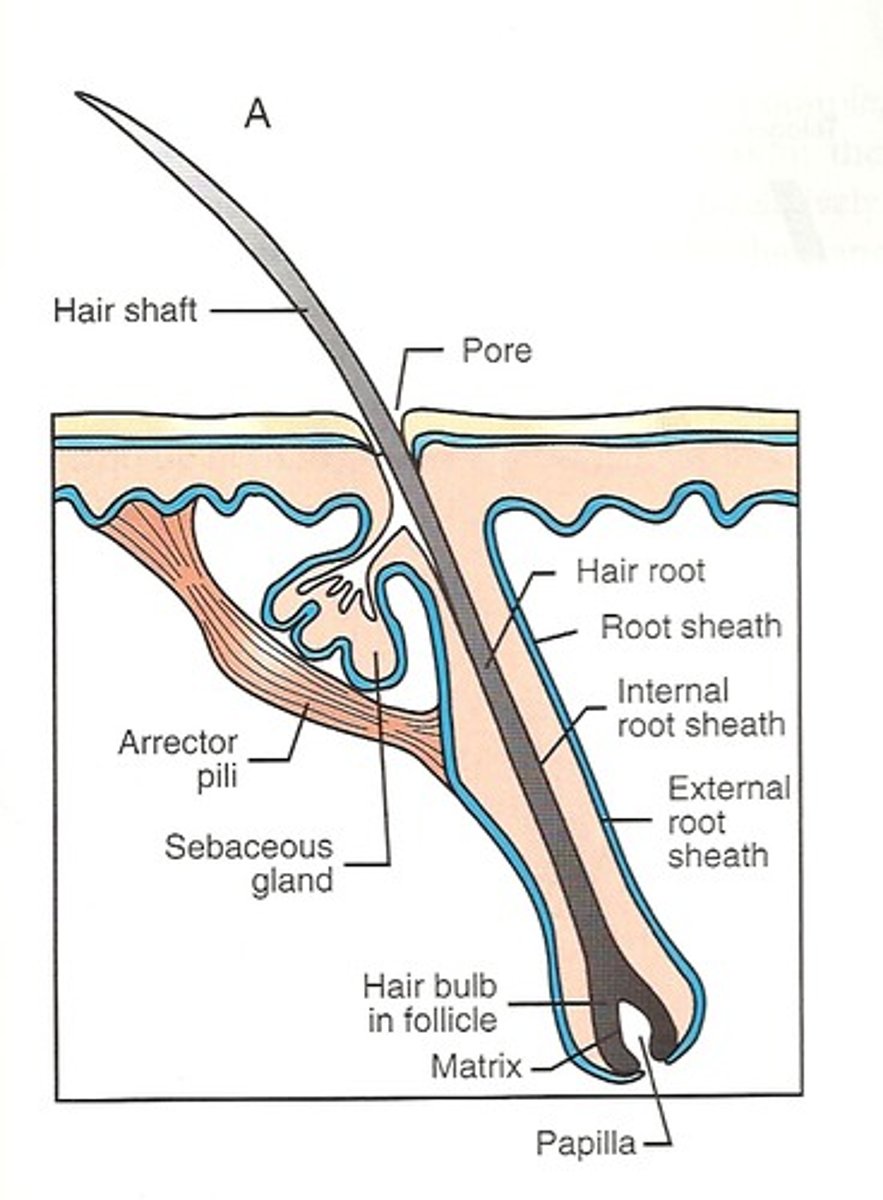
Hair Follicles:
Hairs:
1. Produce hair
2. innervation provides sensation
3 Provides protection for the head
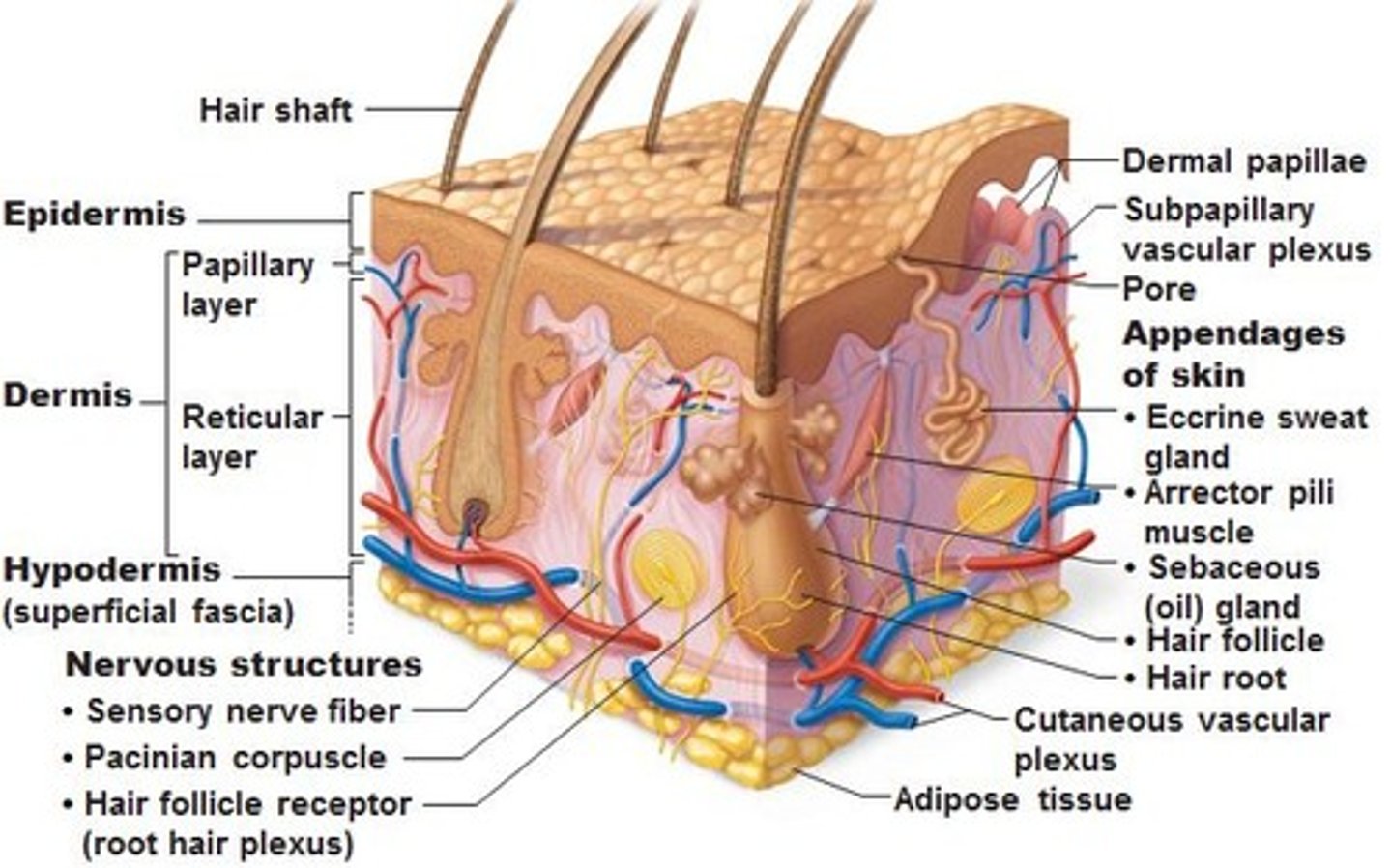
Hair Follicles:
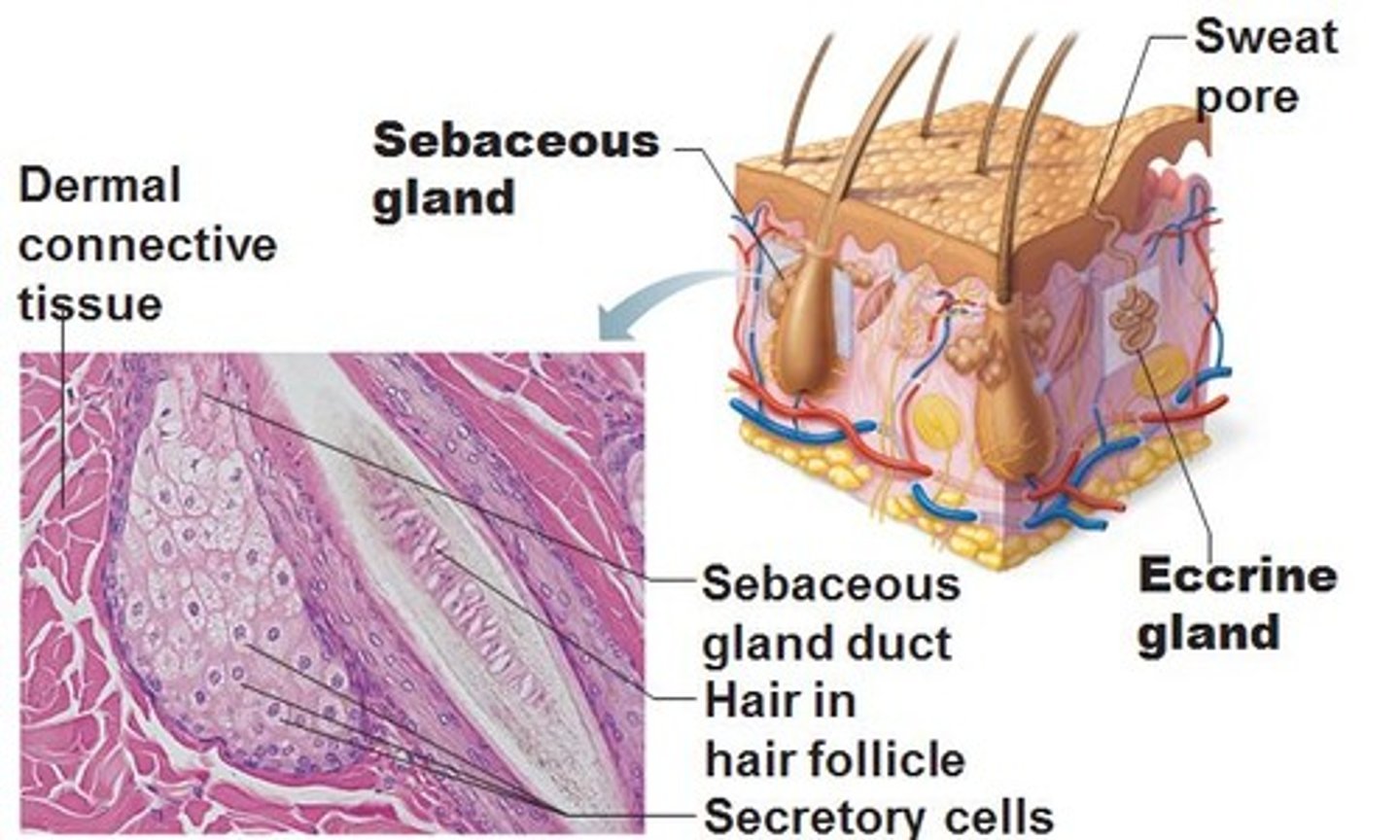
Sebaceous gland
Secretes lipid coating that lubricated hair shaft & epidermis
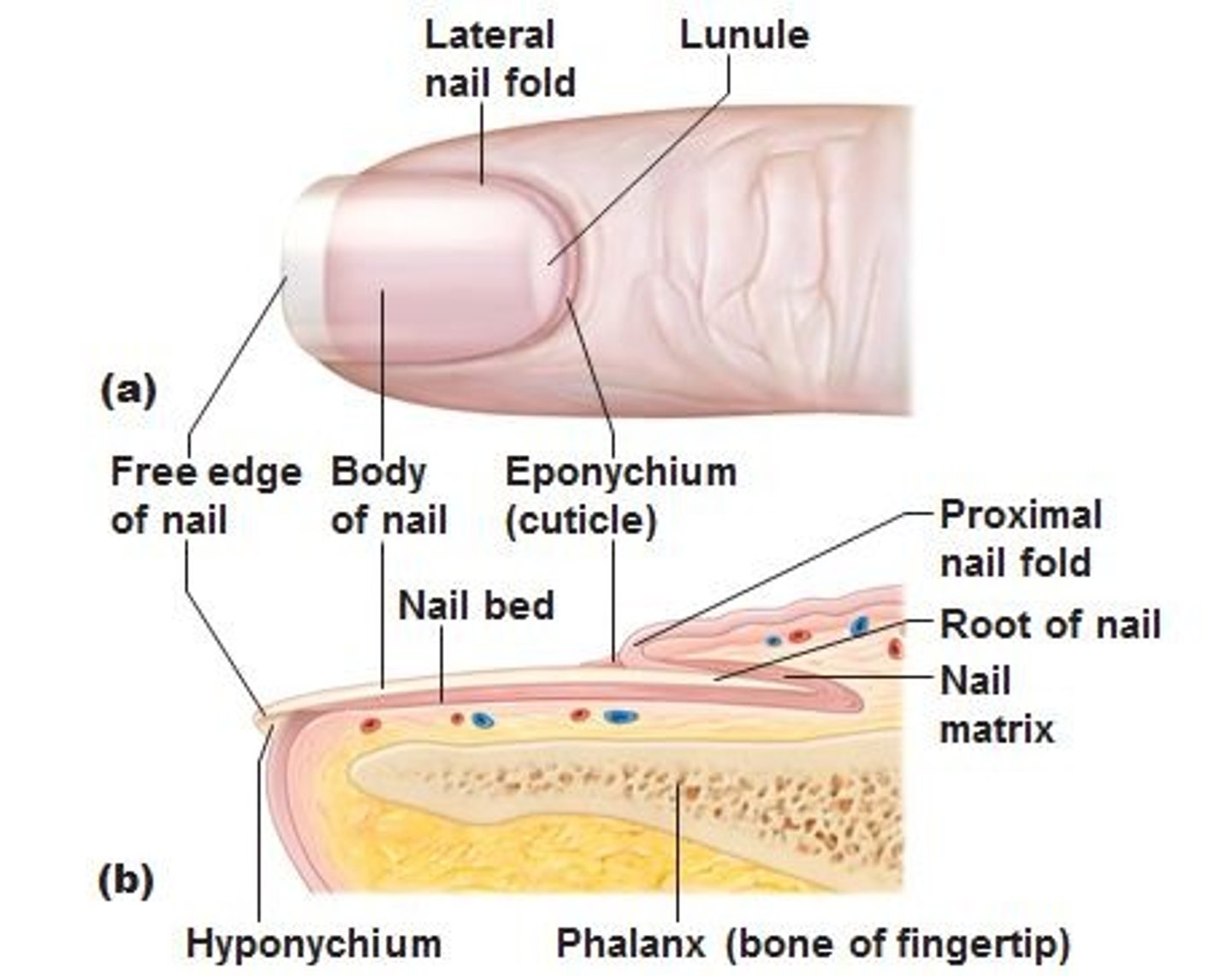
Nails:
Protect and stiffen distal tips of digits
Sensory receptors
Provided sensation of touch, pressure, temperature, and pain
Subcutaneous Layer
Stores lipids; attaches skin to deeper structure
Skeletal System
system composed of bones and joints, supports and protects tissues; stores minerals; forms blood cells
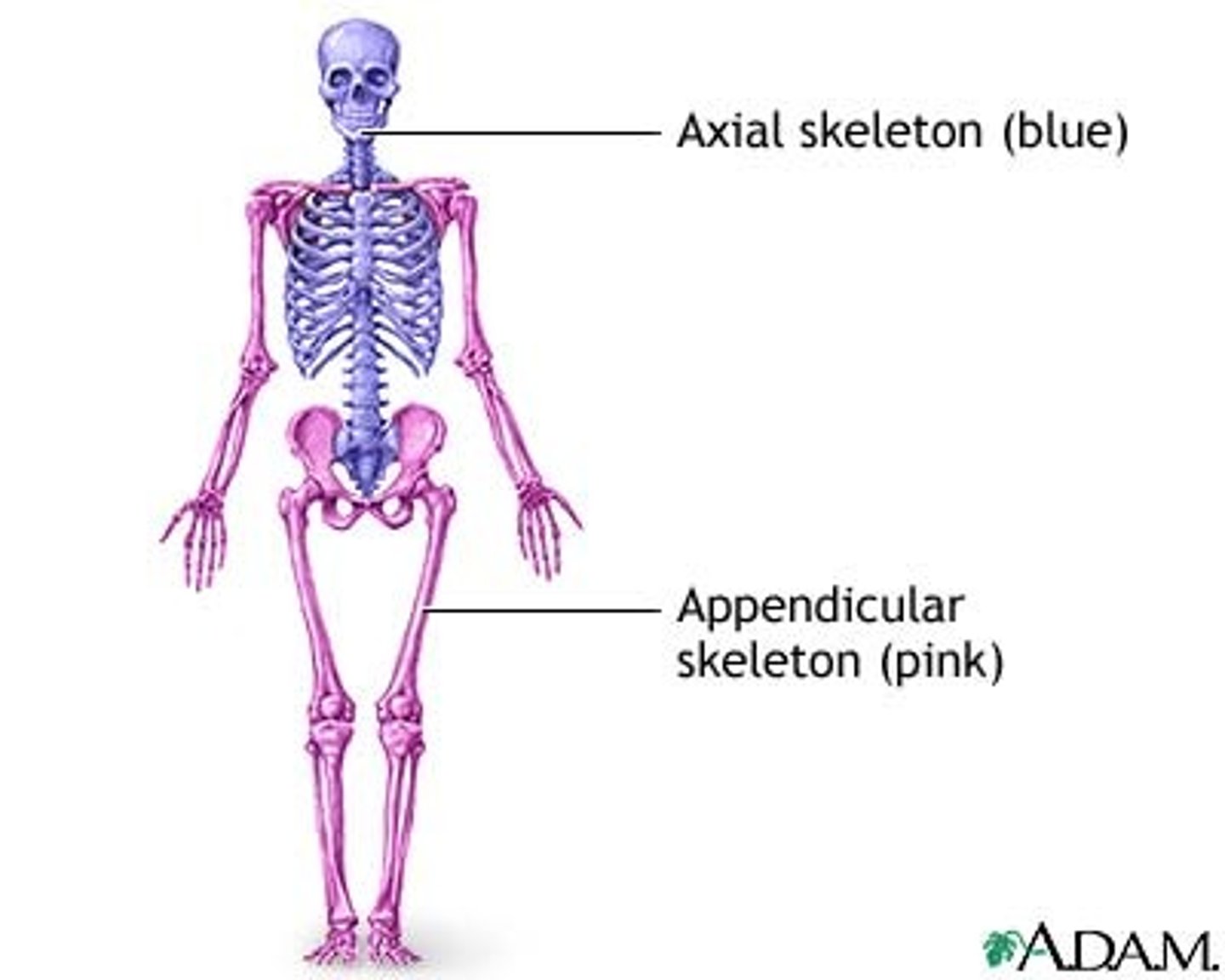
Bones, Cartilages, & Joints
Supports & protects soft tissue; bones store minerals
Axial Skeleton
Protects brain, spinal cord, sense organs, & soft tissues of thoracic cavity
supports body weight over lower limbs
(Skull, Sternum, ribs, vertebrae, Sacrum)
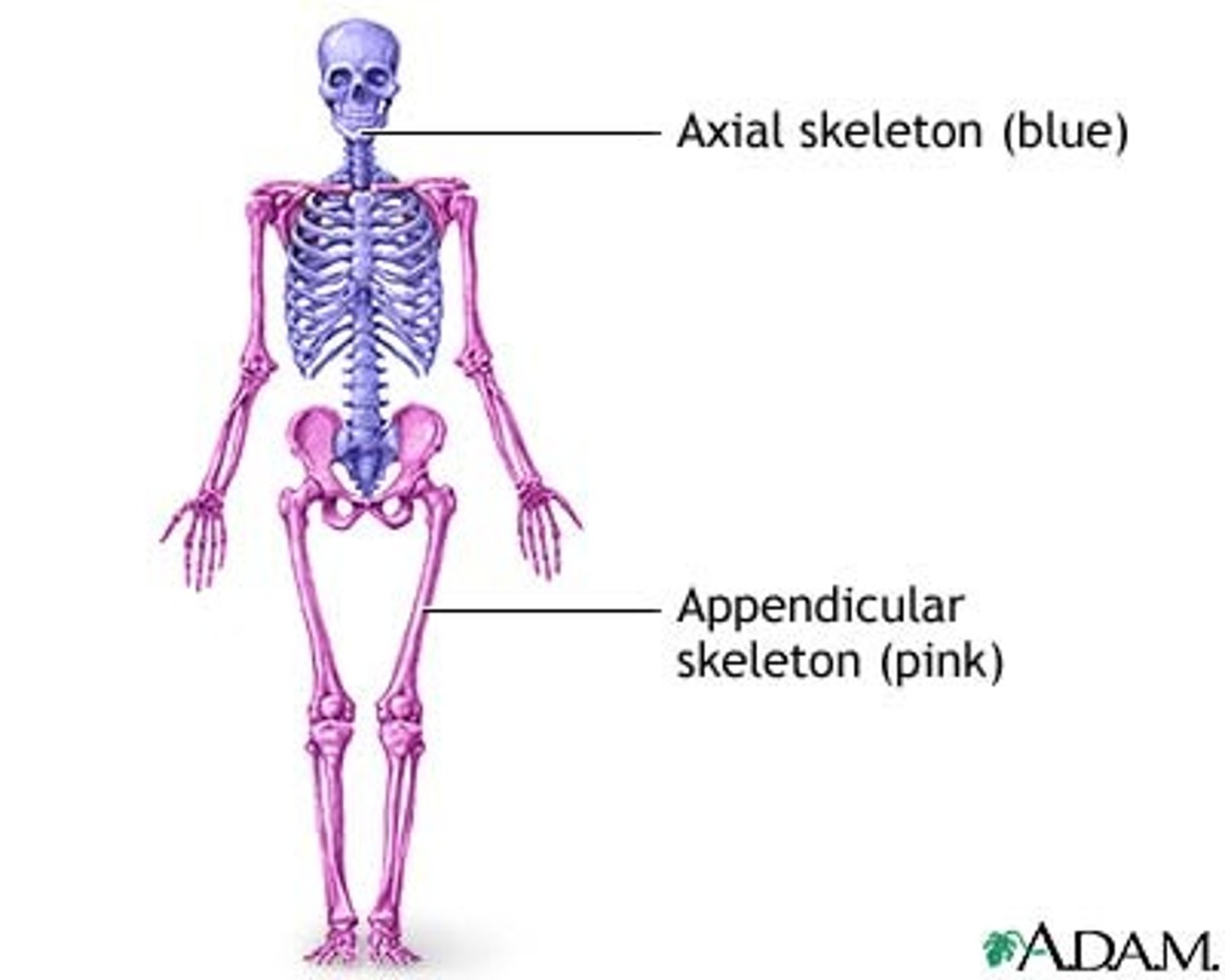
Appendicular Skeleton
Provides internal support & positioning of limbs
supports & moves the axial skeleton
(Pectoral gridle, Upper limb, & lower limb)
Muscular System
system composed of skeletal muscles and allows for movements and manipulation of the environment
nervous system
composed of spinal cord, brain and nerves. control system of the body and responds to changes by activating muscles and glands
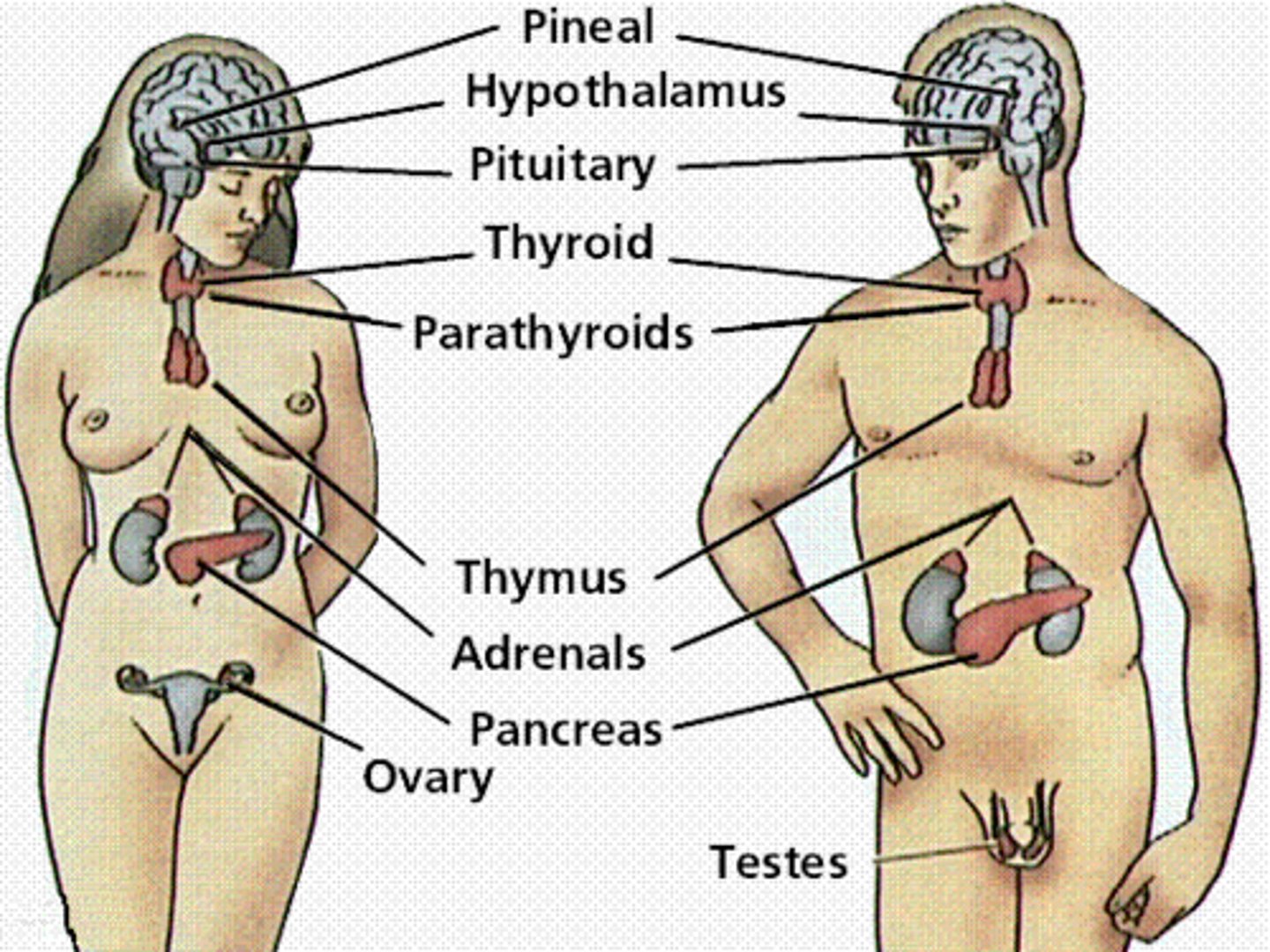
endocrine system
Composed of glands that regulate the processes such as growth and reproduction.
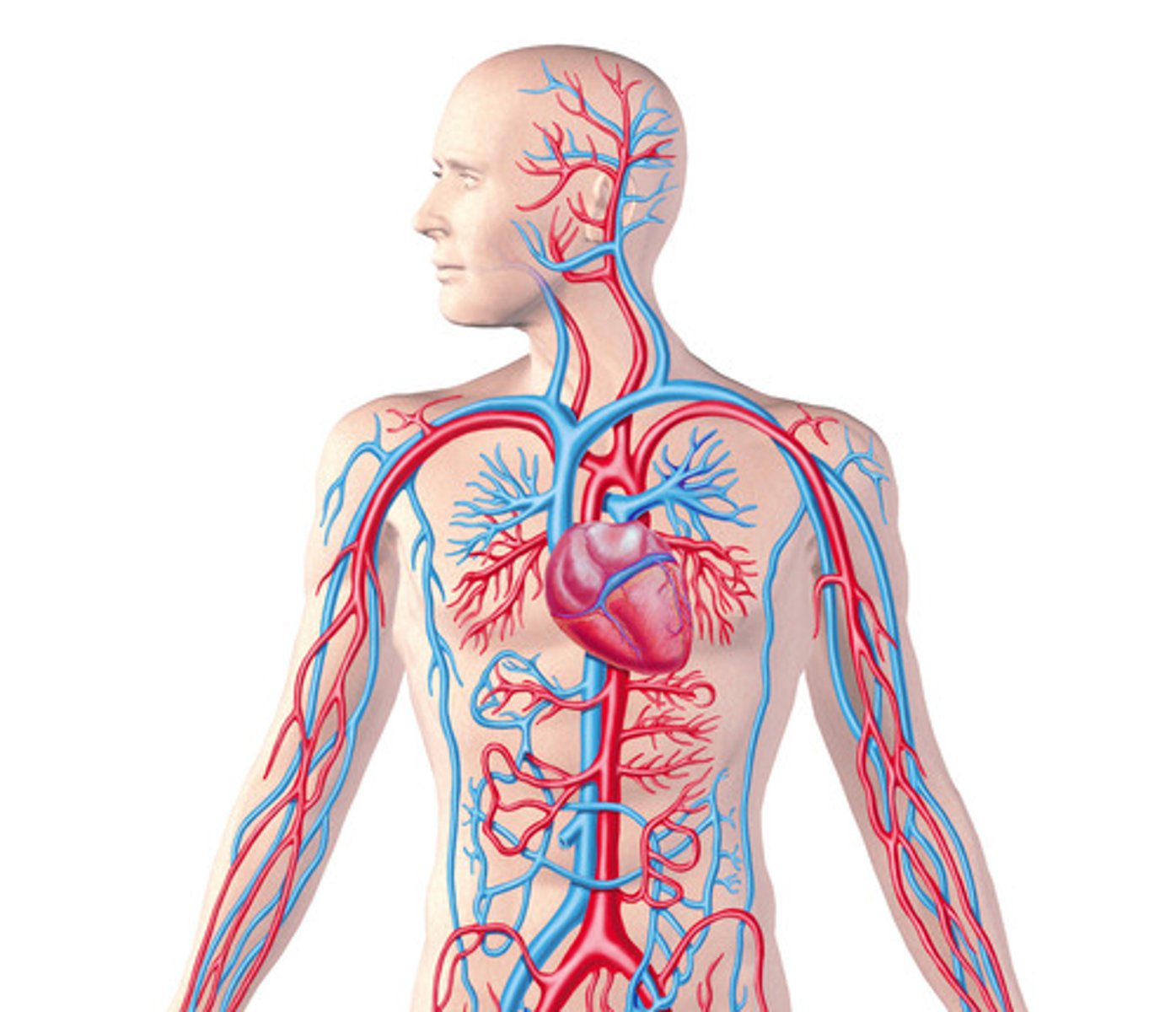
cardiovascular system
composed of heart and blood vessels, transports blood which carries oxygen, CO2, nutrients and waste.
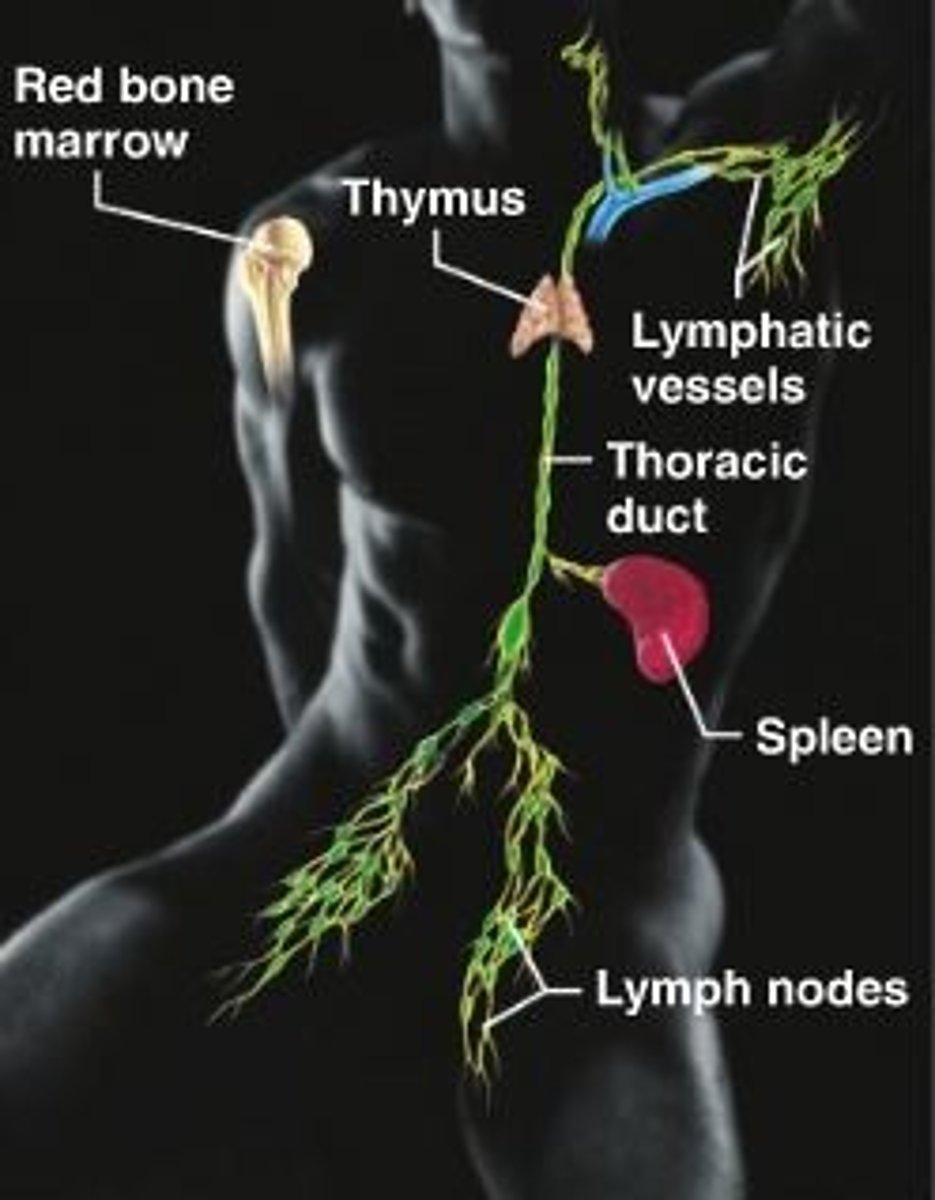
lymphatic system
composed of red bone marrow, nodes, spleen, vessles and thoracic duct, which disposes debris in the lymphatic stream.
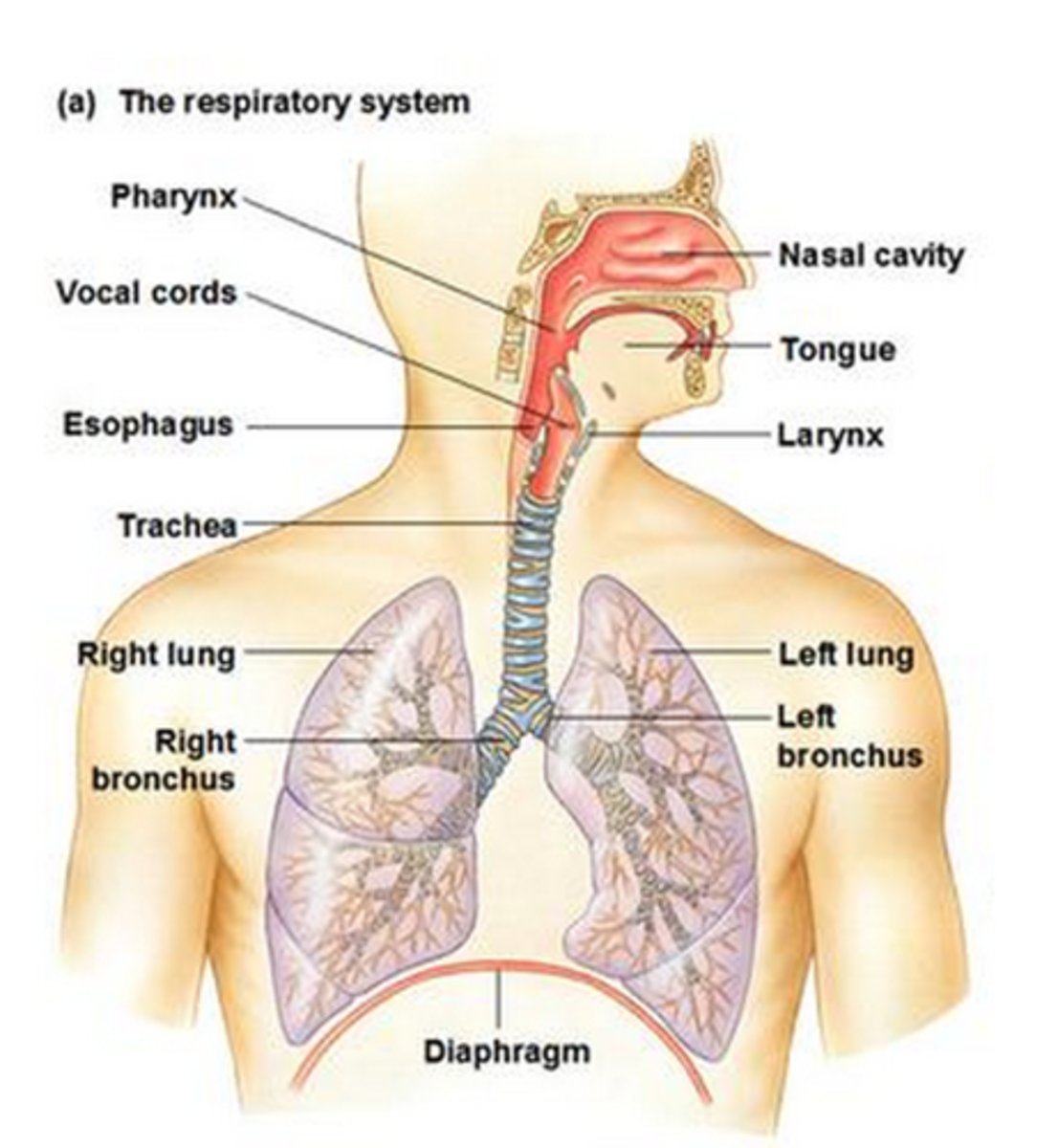
respiratory system
composed of nasal cavity, pharynx, larnx, trachea, broncus and lungs, keeps blood supplied with O2 and removes CO2
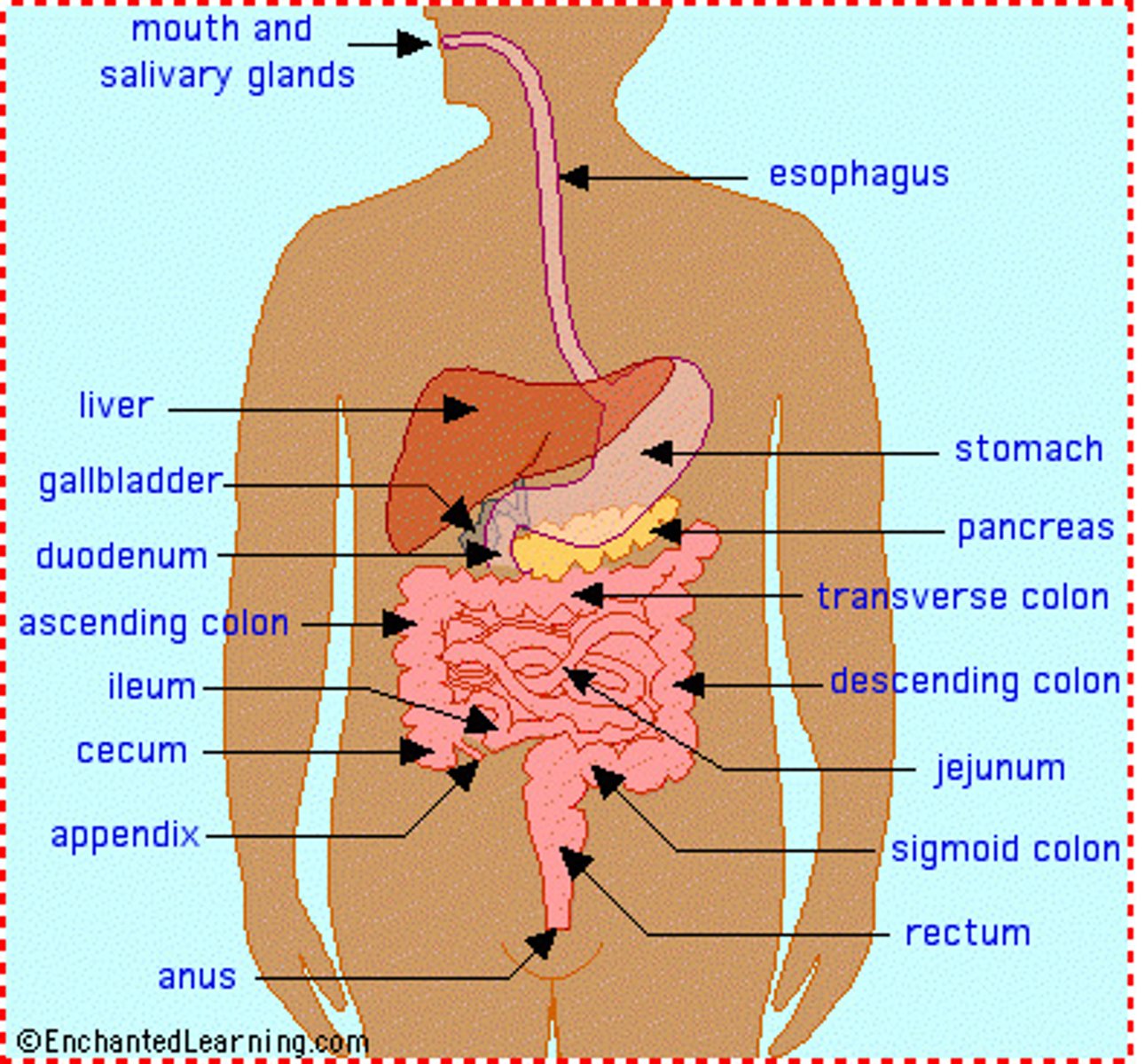
digestive system
Composed of oral cavity, esophogus, liver, stomach, intestines and rectum. breaks down food and absorbs nutrients
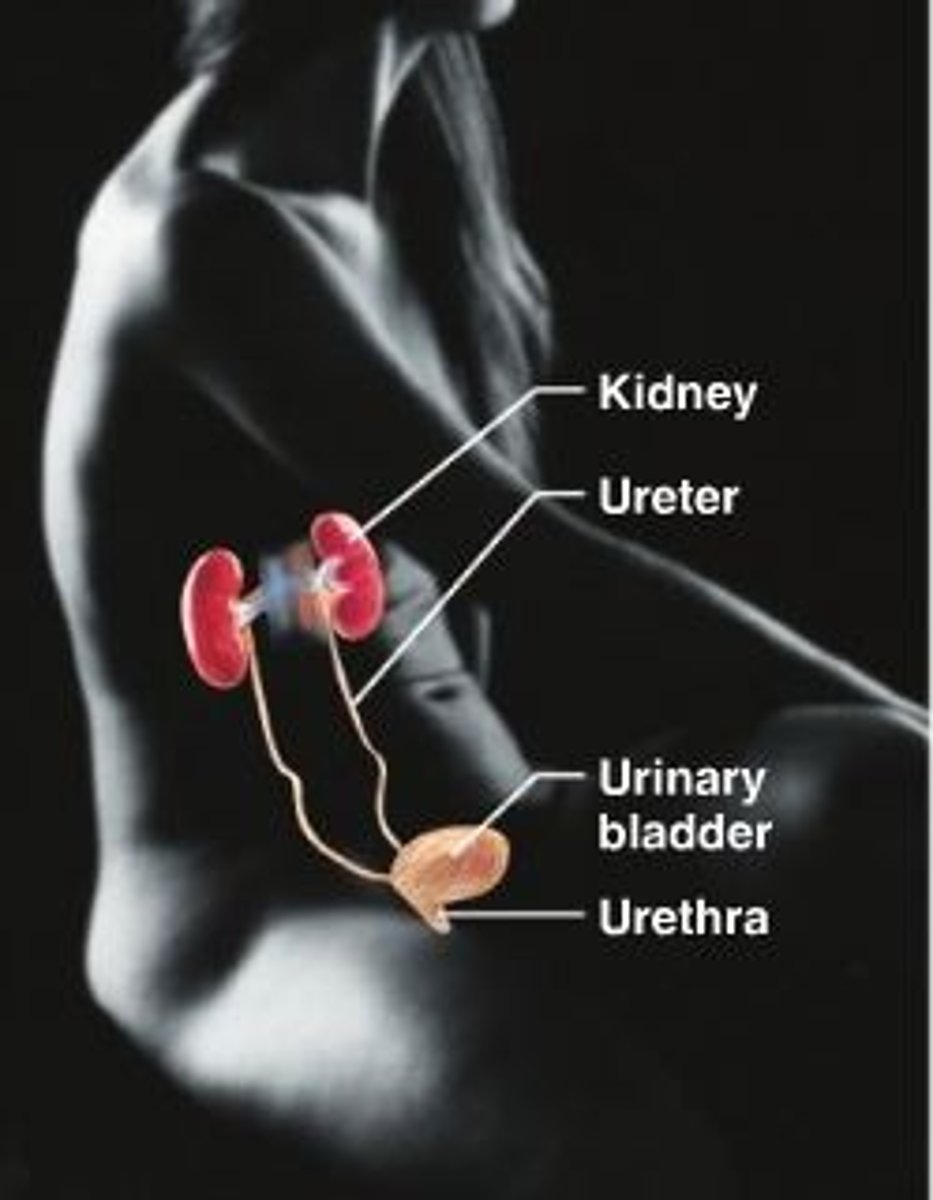
urinary system
Composed of kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra, rids the body of acid-based wastes.
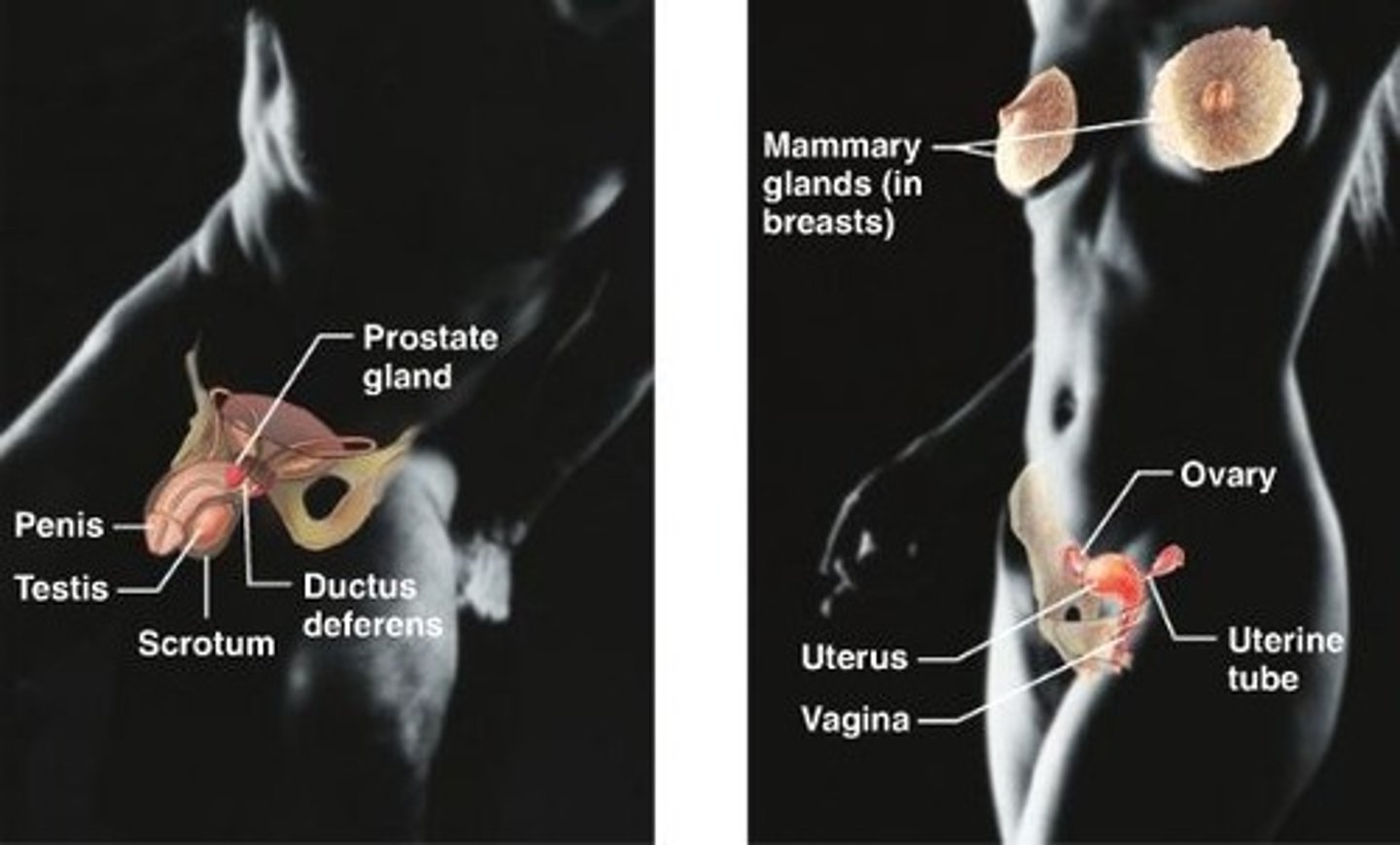
reproductive system
System that functions in producing offspring
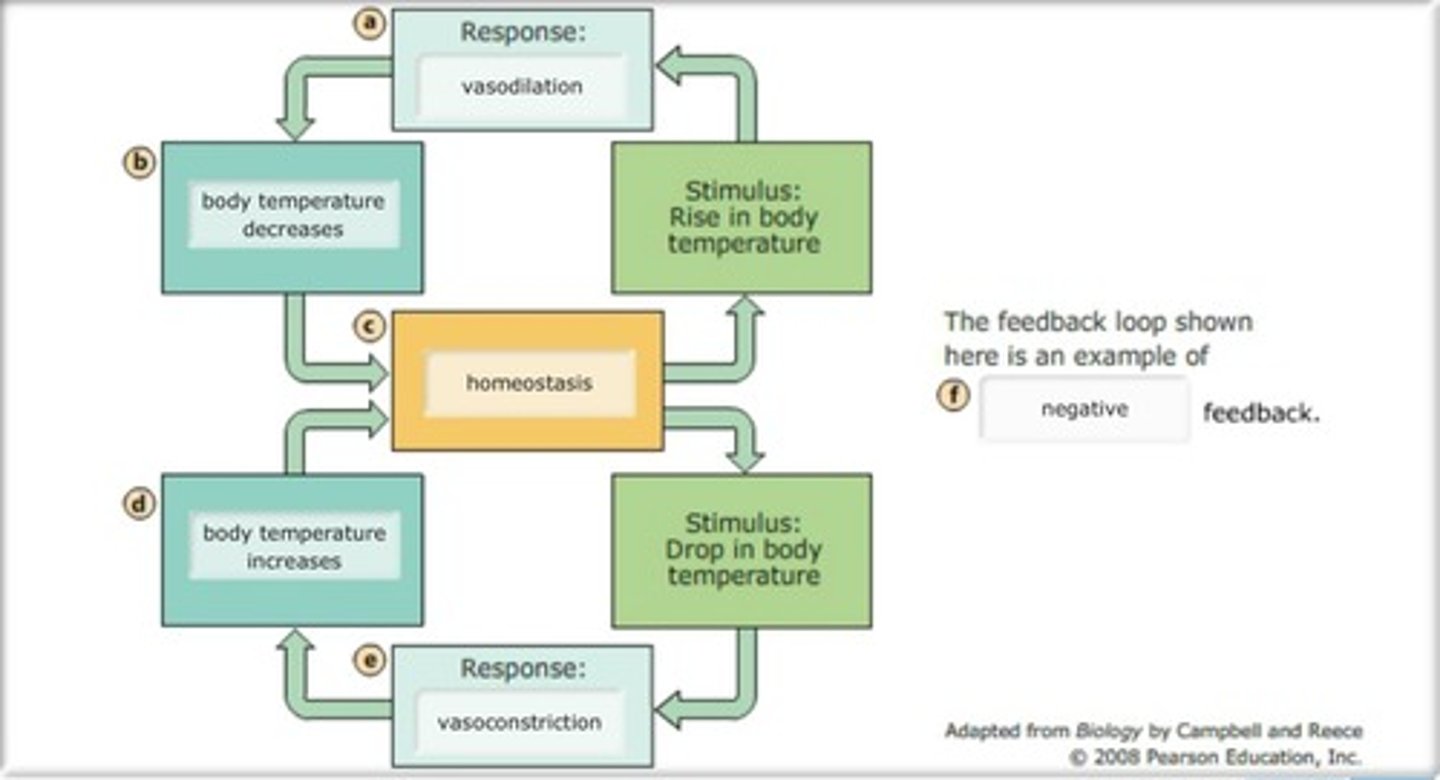
homeostasis
the ability to maintain an internal balance even when outside world changes. dynamic state of equilibrium
receptor, control center, effector
3 main parts of homeostatic control
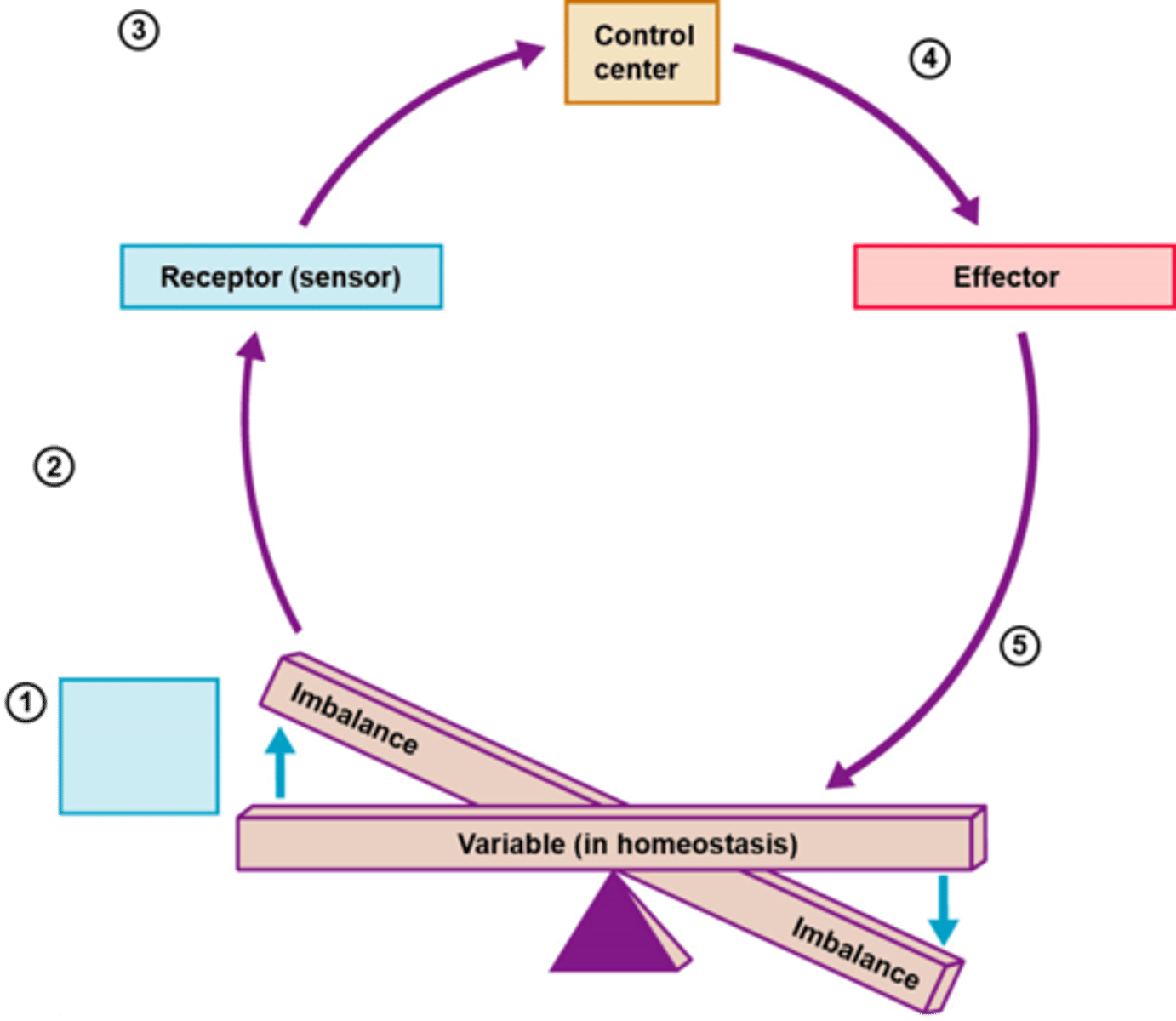
receptor
sensor that monitors changes and sends information in an afferent path to control center in negative feedback
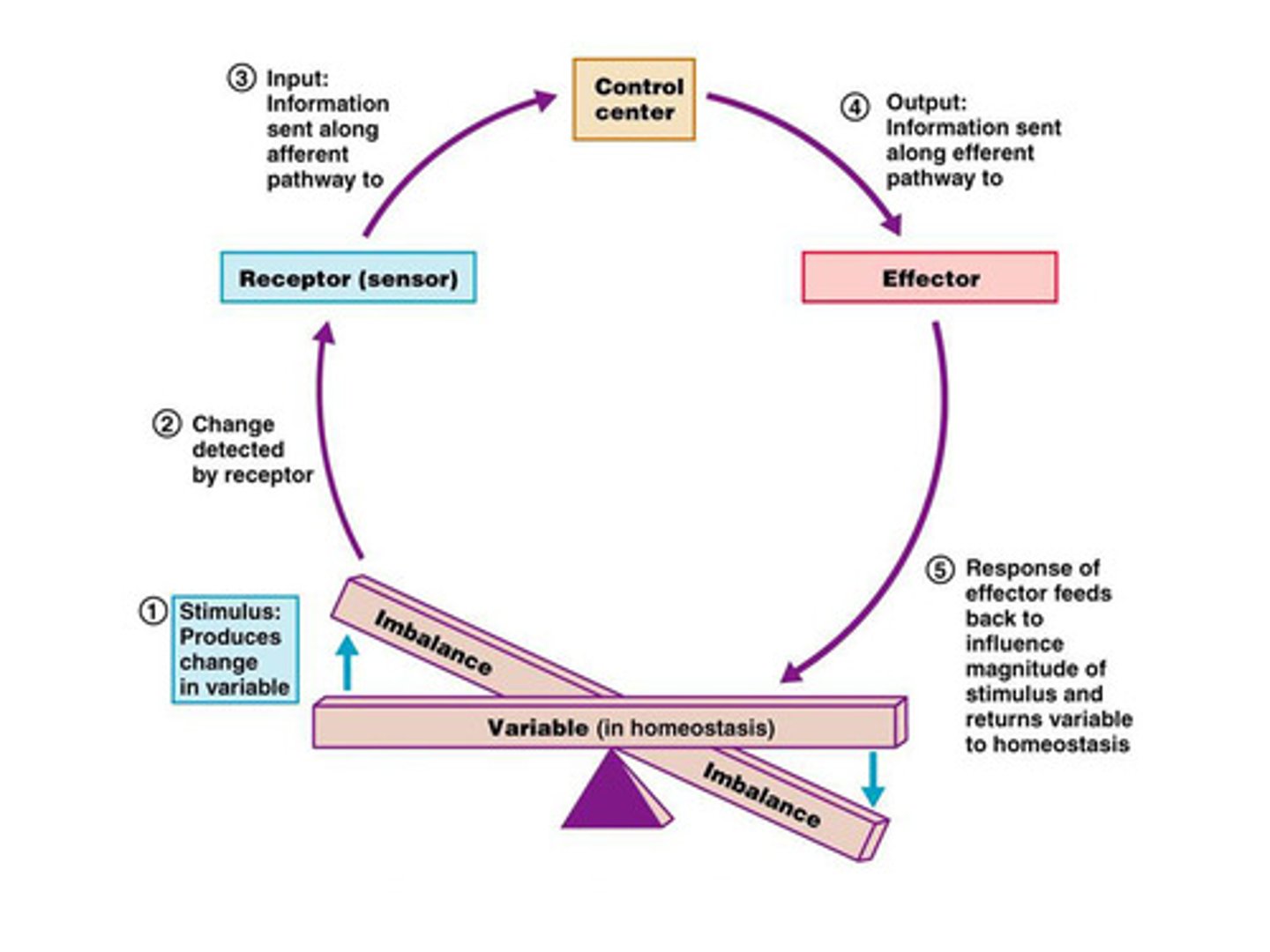
control center
determines the set point in feedback, recieves from receptor and sends info efferently to effector
effector
responds to the feed back from the control center, shuts off or enhances stimulus
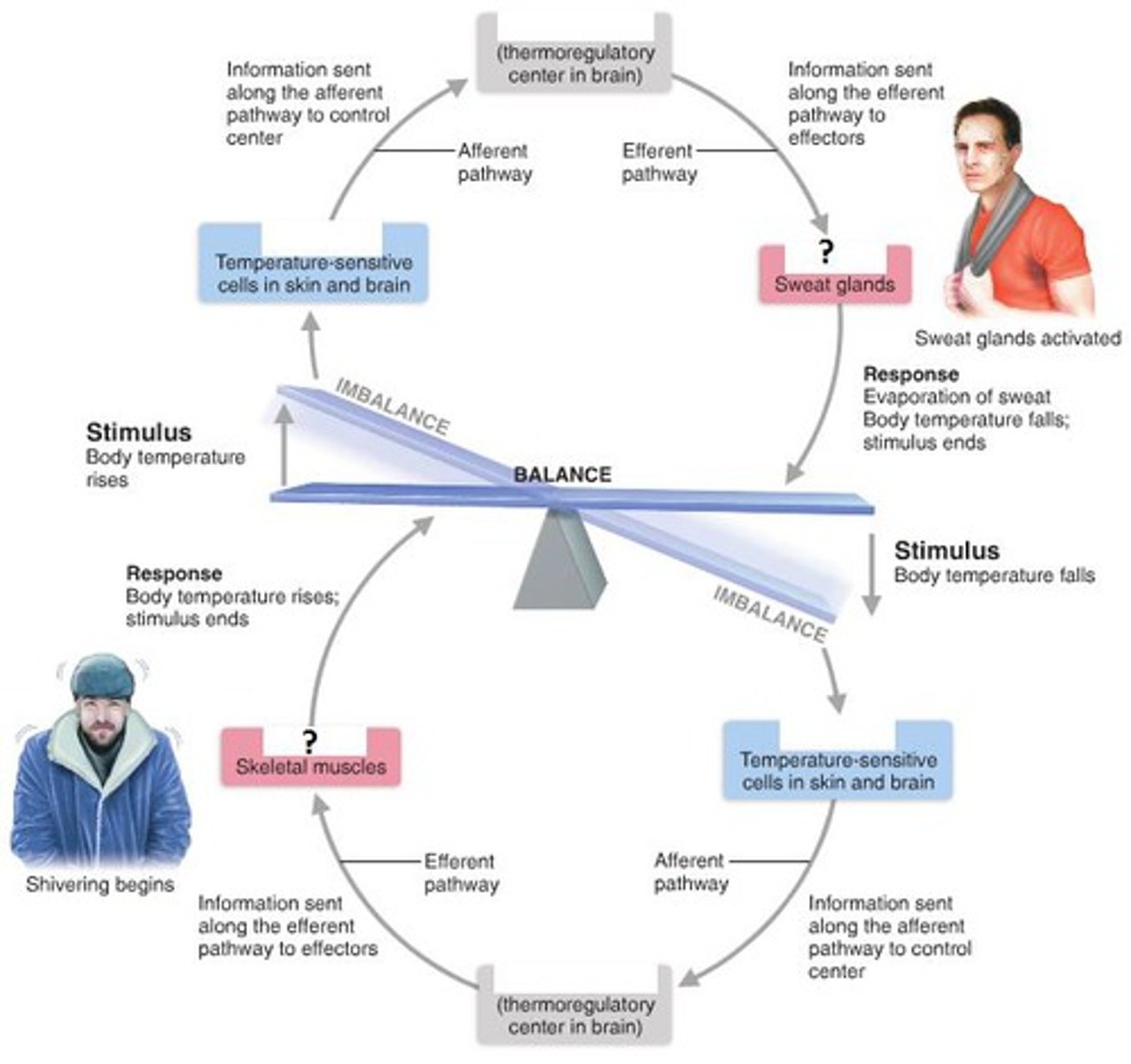
negative feed back
homeostatic control mechanism that shuts off original effect of stimuli or reduces intensity.
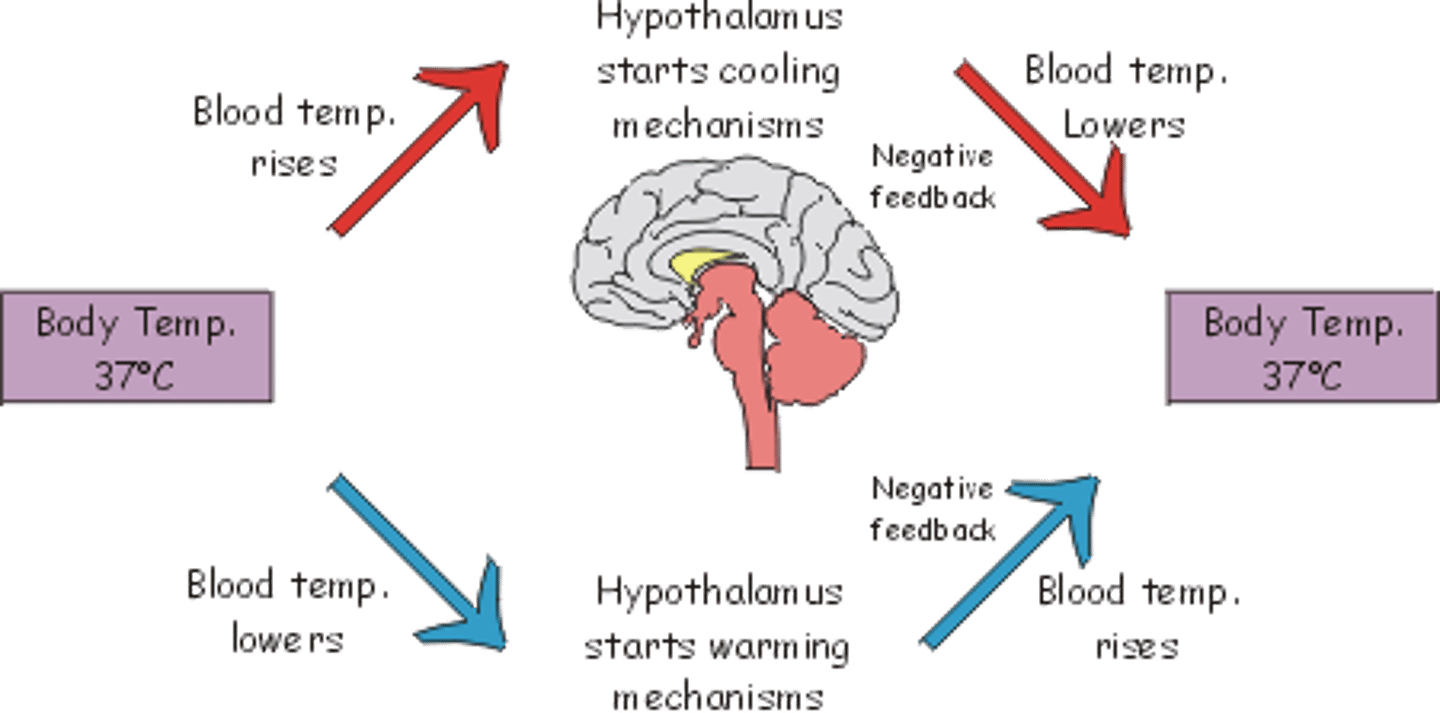
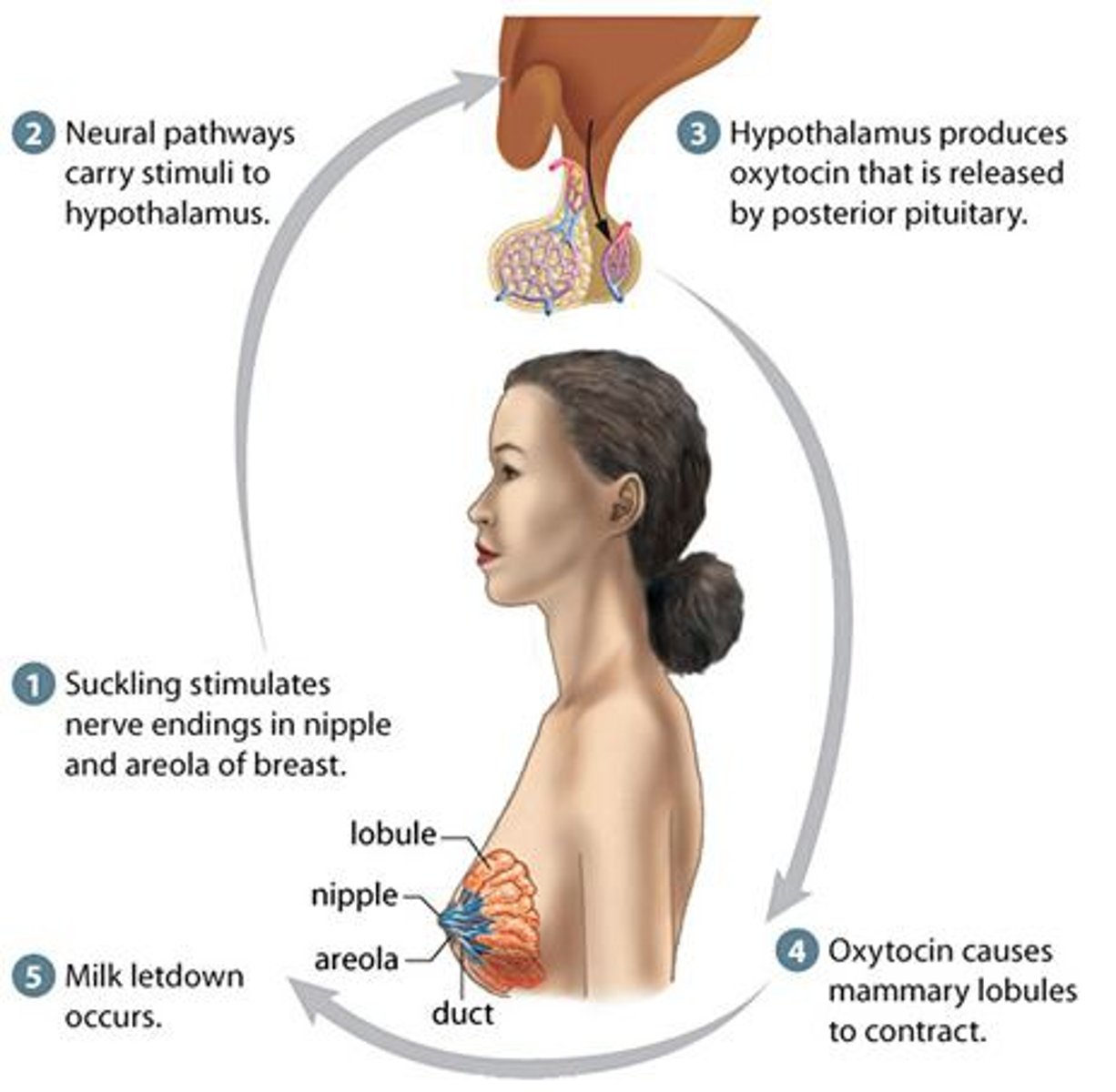
positive feedback mechanism
homeostatic control mechanism that enhances the original stimulus so that the response is accelerates
anatomical position
body standing errect with palms facing forward and thumbs pointing away from the body
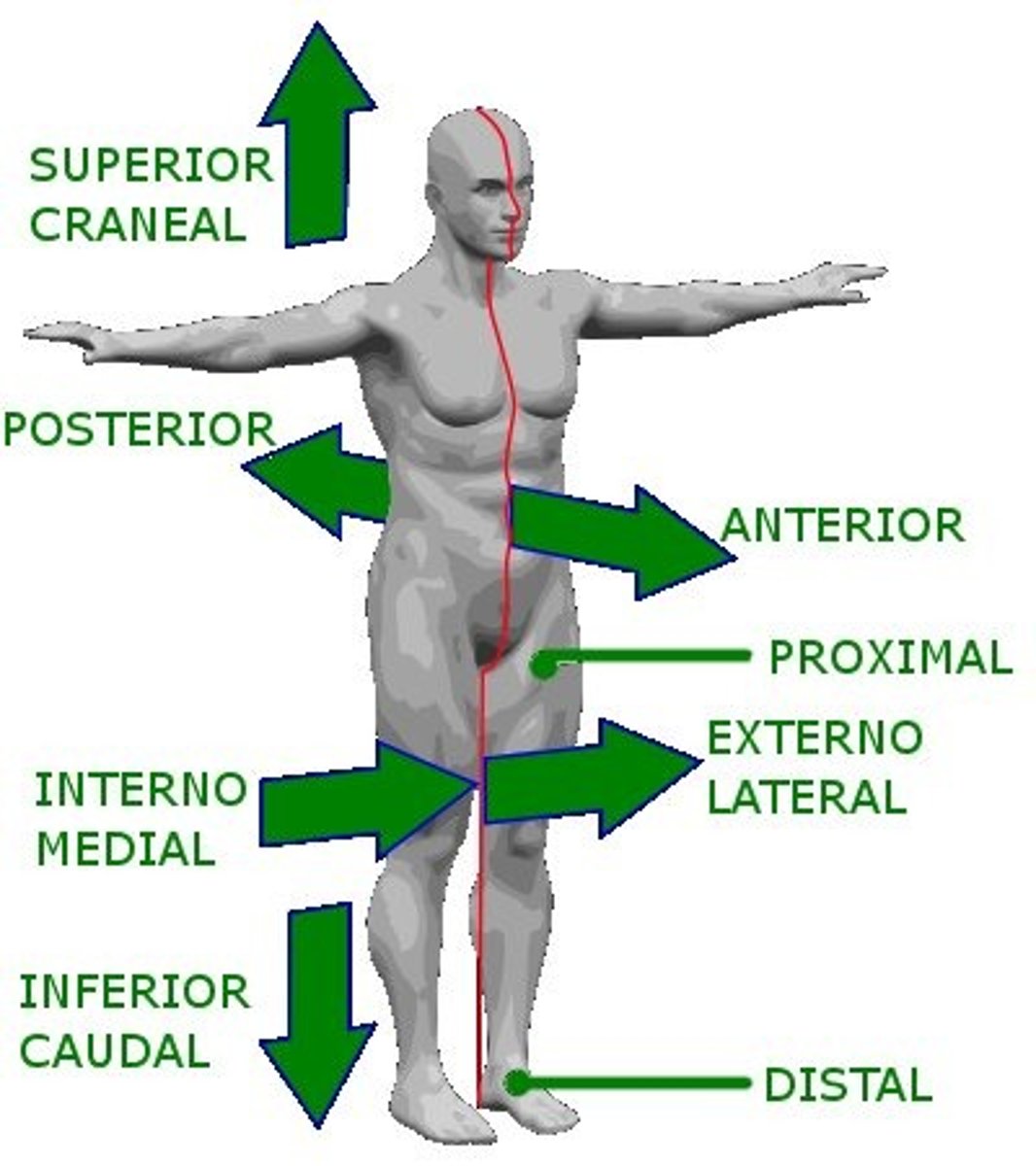
directional terms
explain where one body structure is in relation to another
axial parts
makes up main axis of body including head, neck and trunk
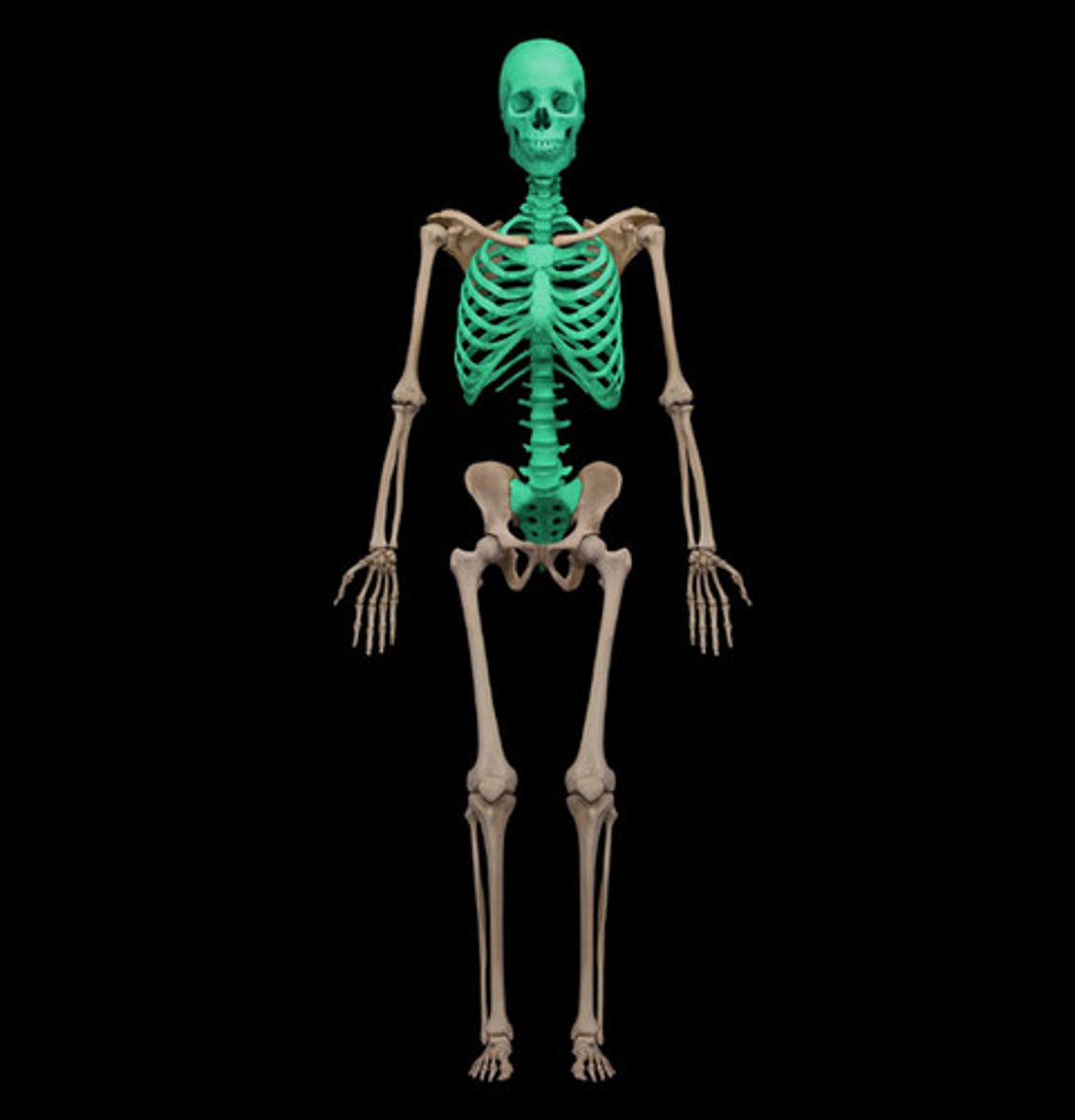
appendicular parts
consists of limbs
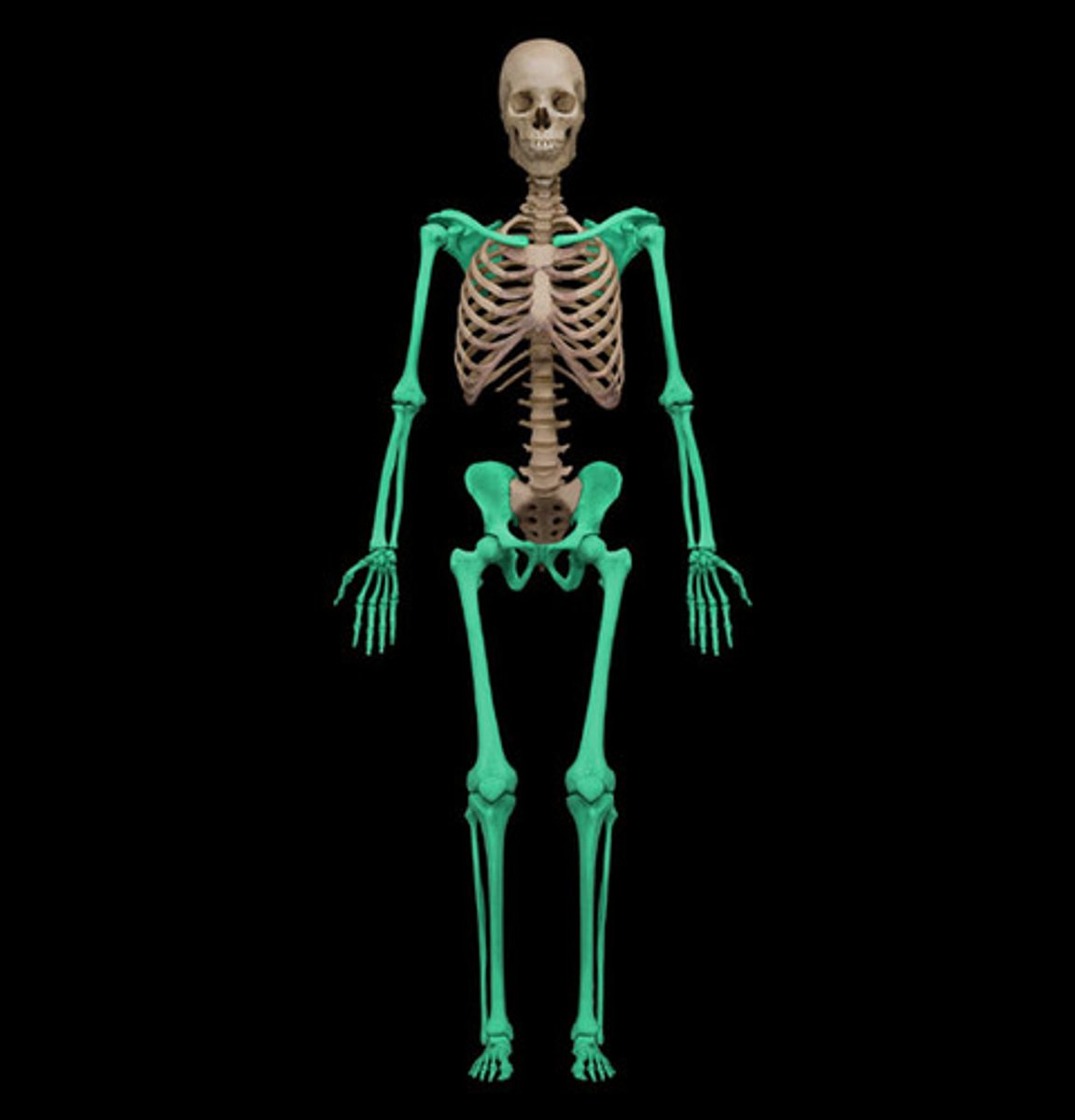
regional terms
terms used in anatomy that refer to certain areas of the body.
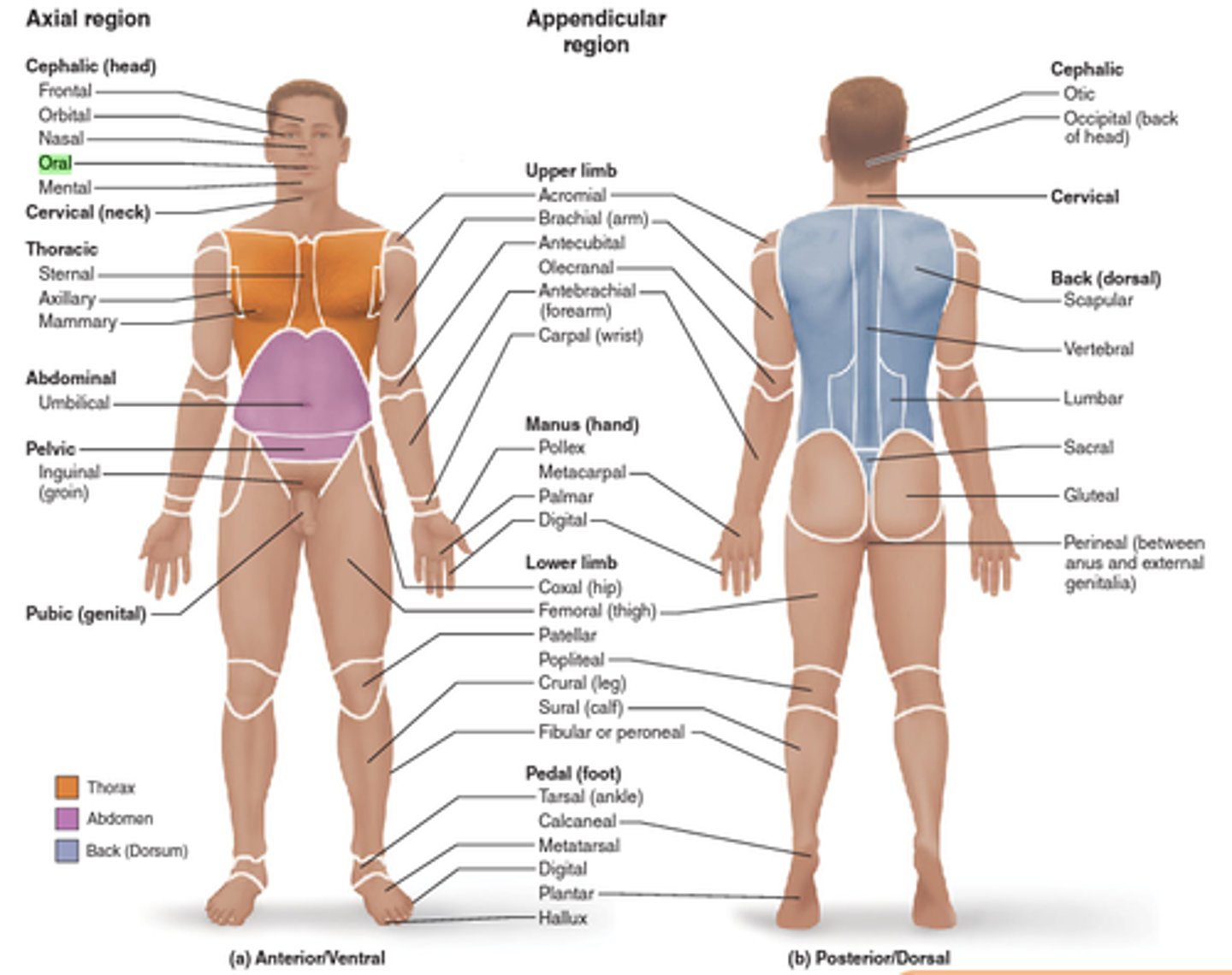
abdominal
trunk inferior to ribs
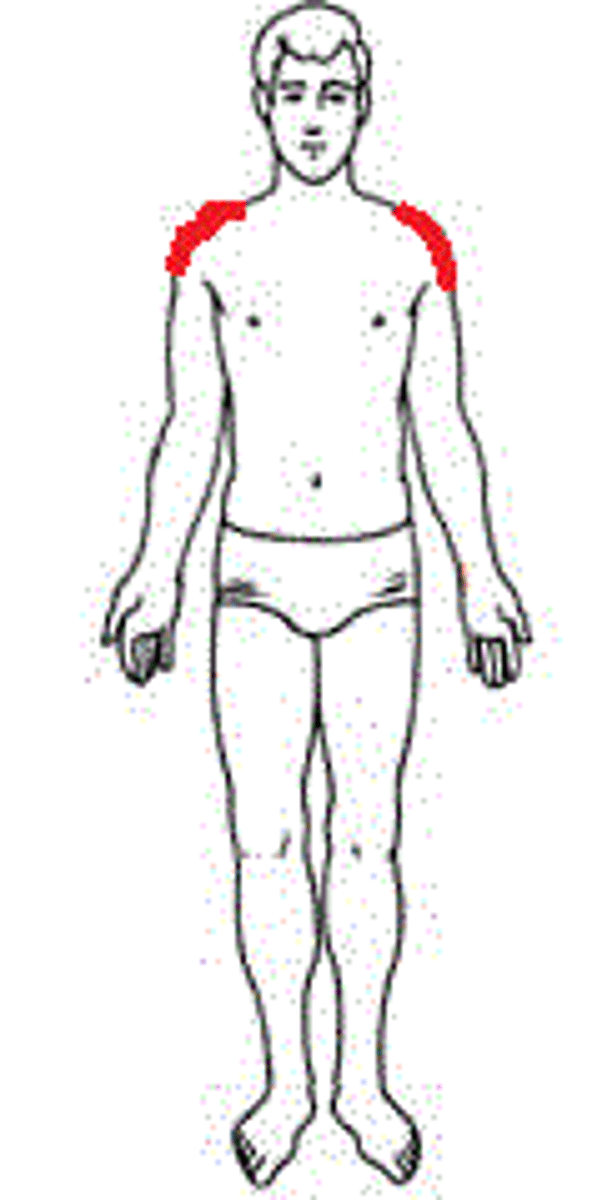
acromial
point of shoulder
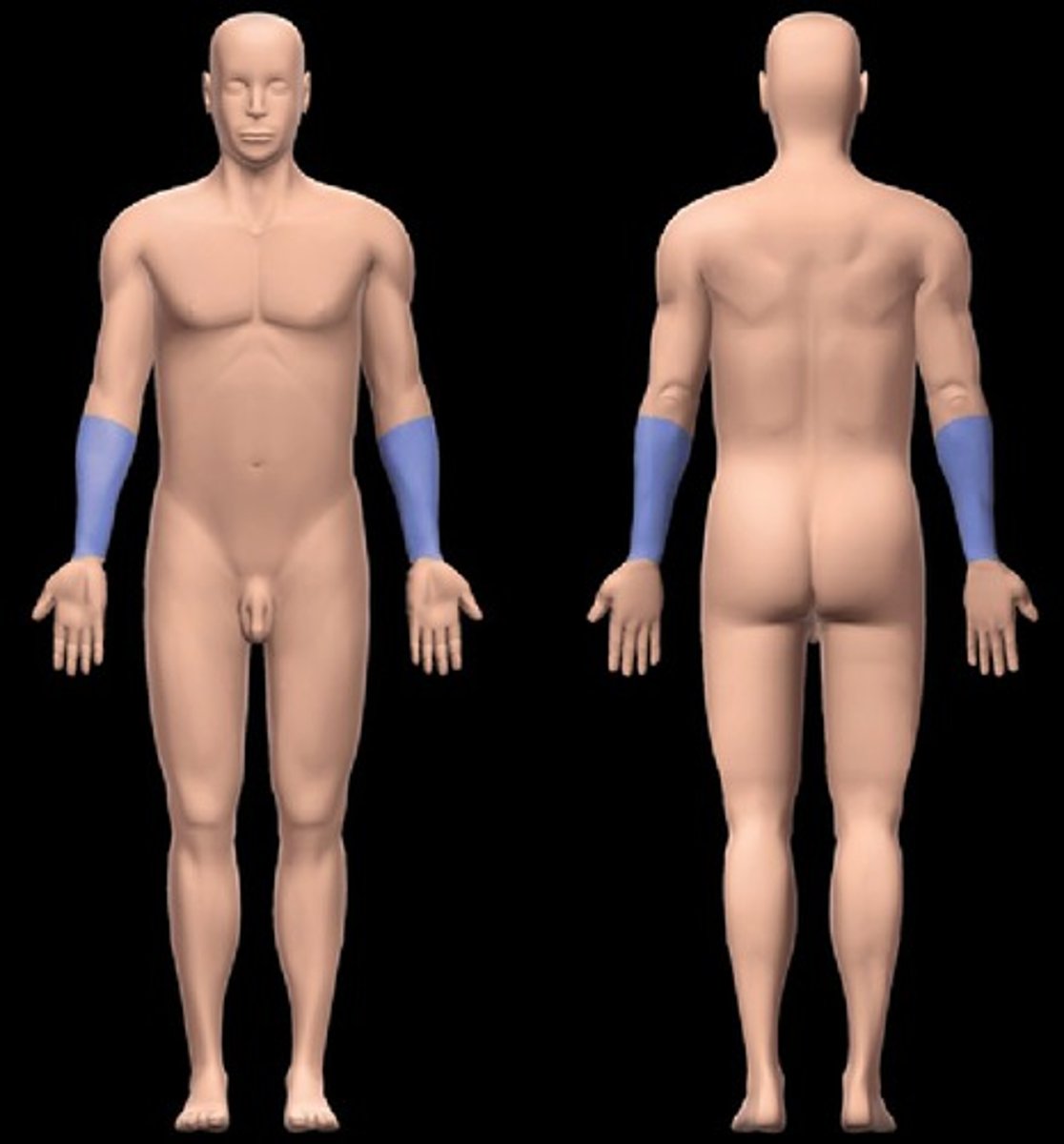
antebrachial
forearm
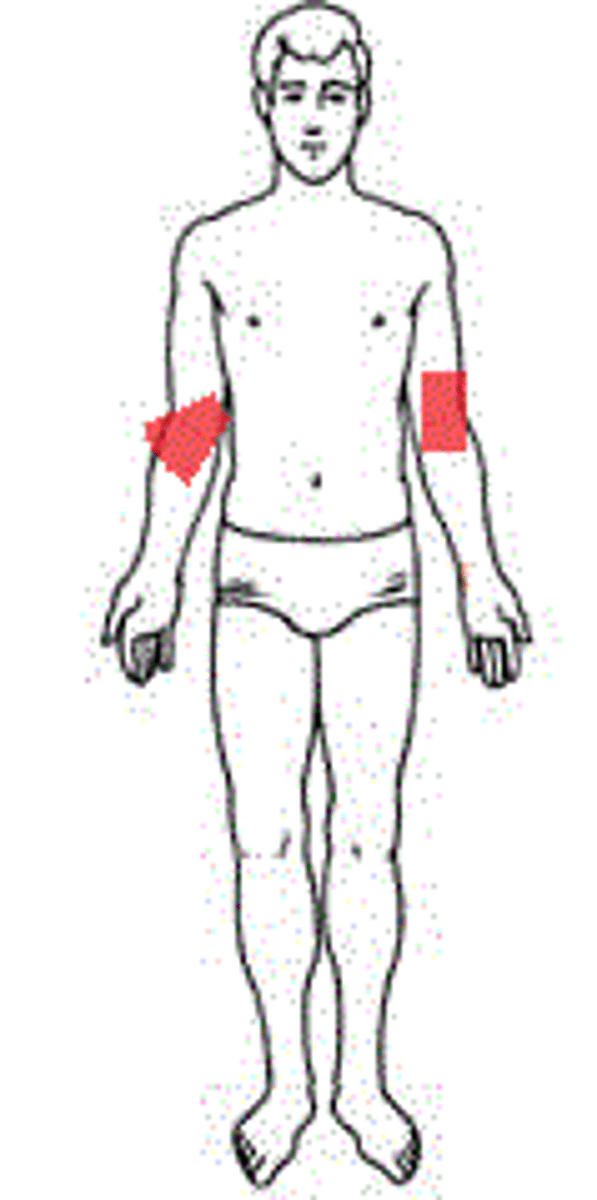
antecubital
anterior surface of elbow
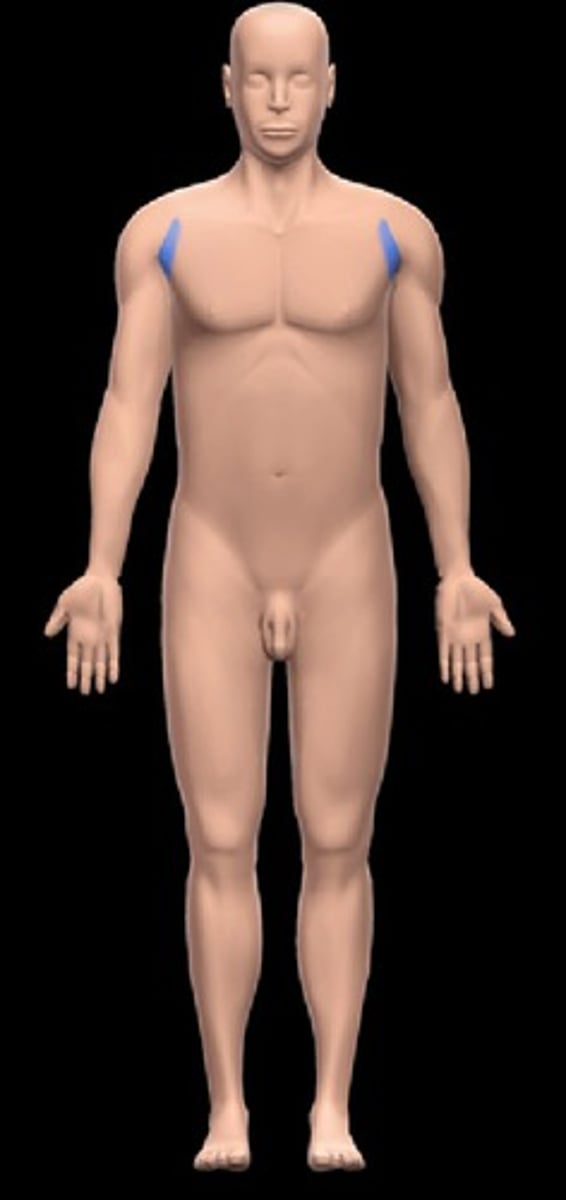
axillary
armpit
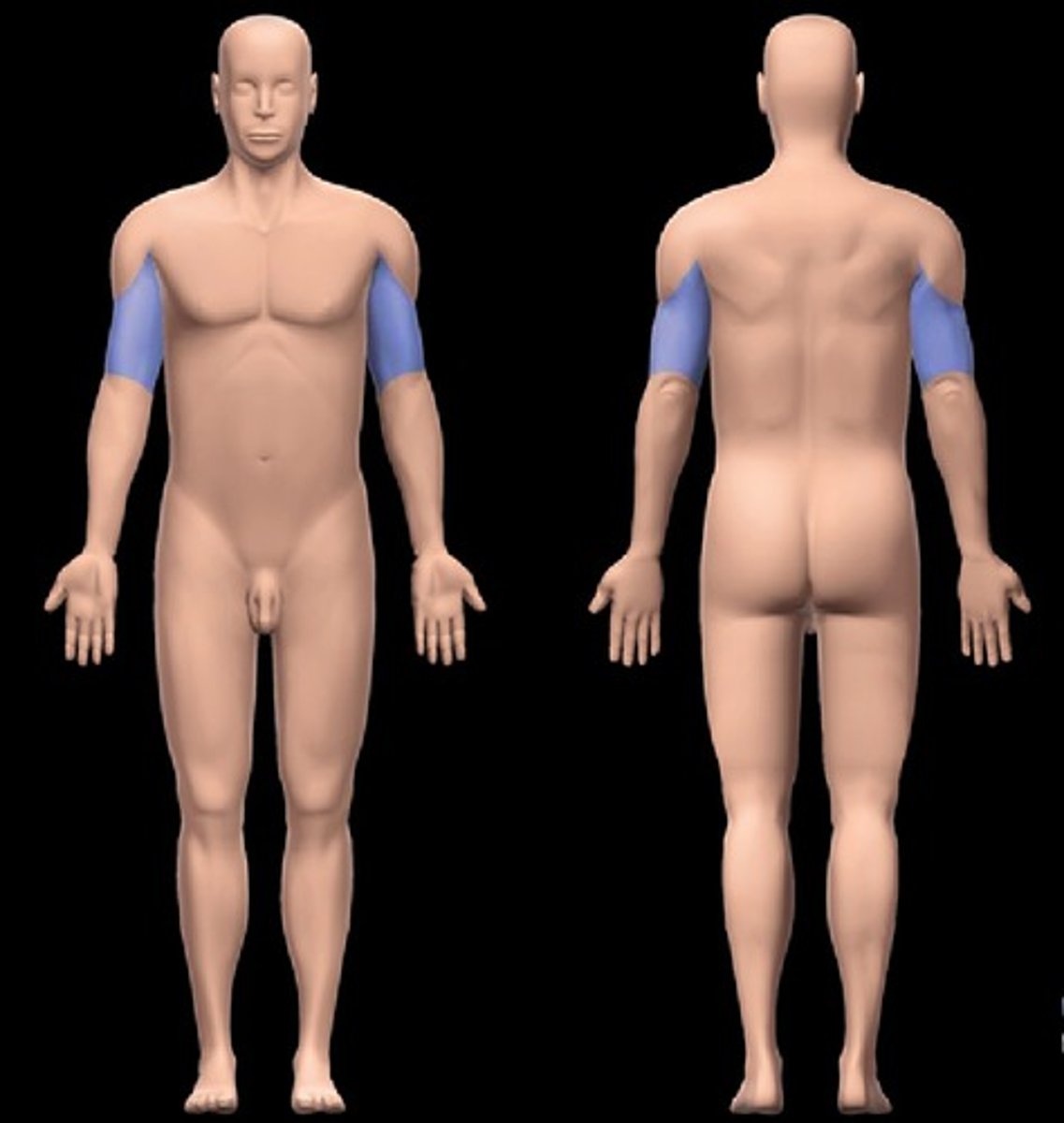
brachial
upper arm
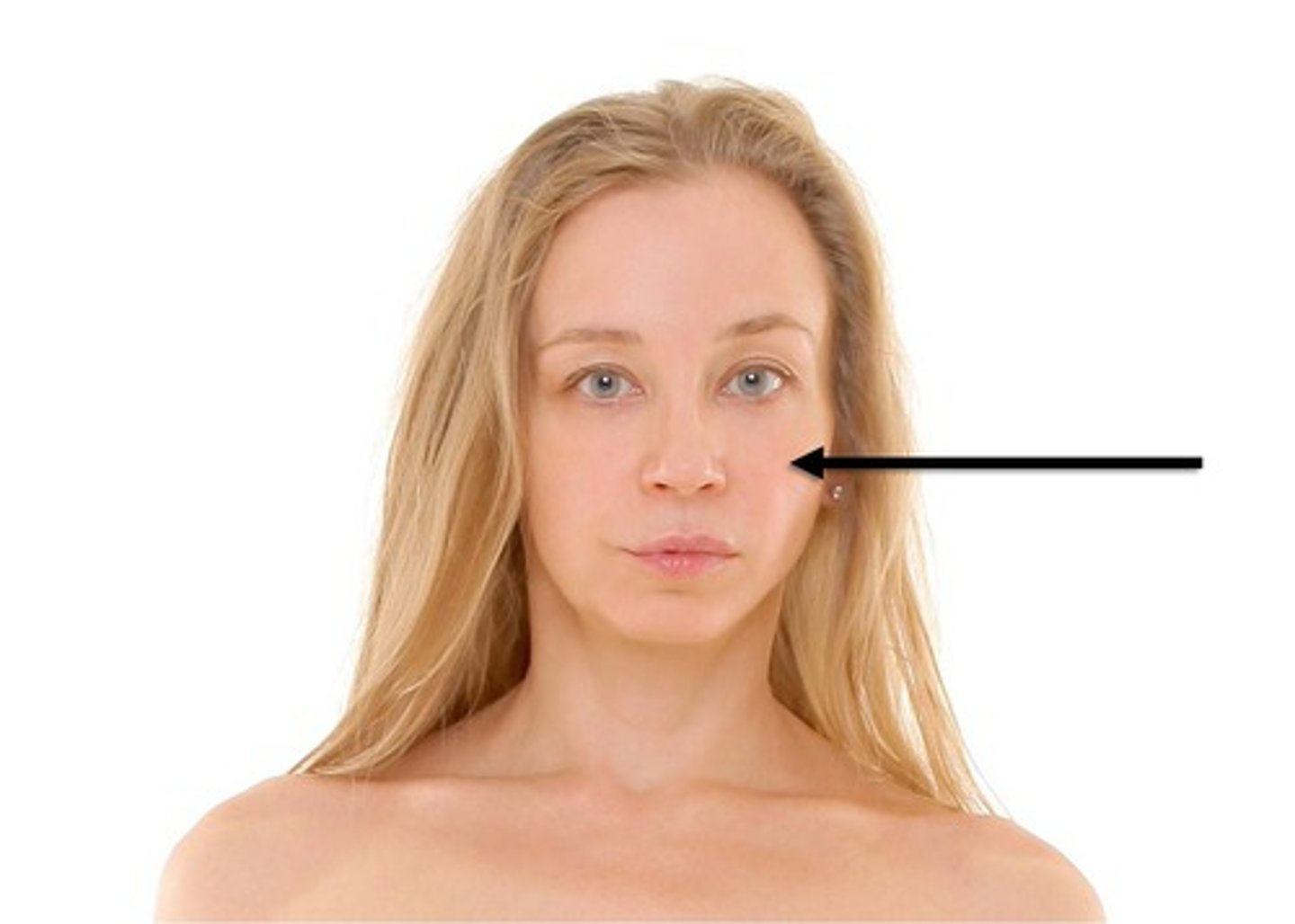
buccal
cheek
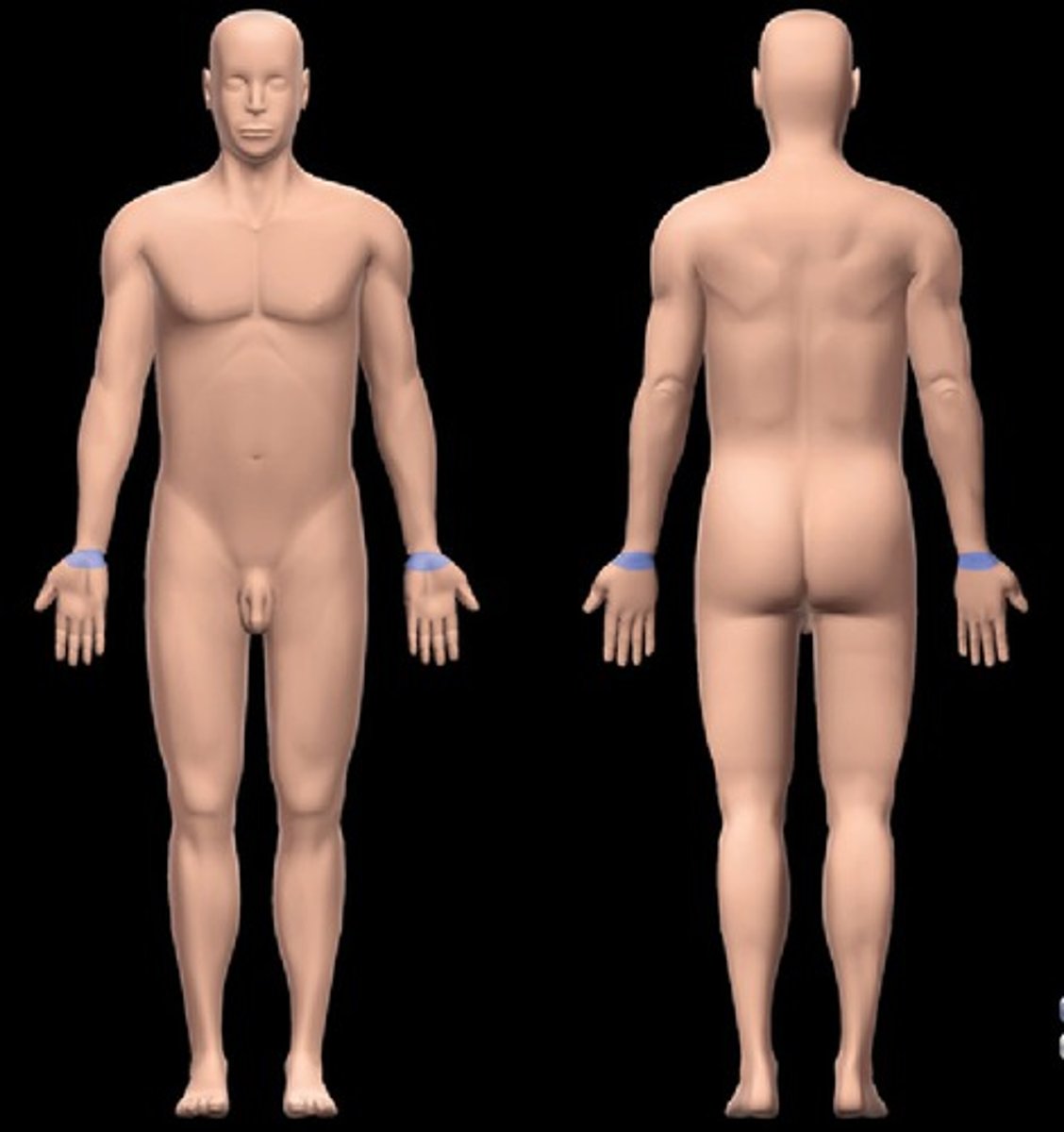
Carpal
wrist
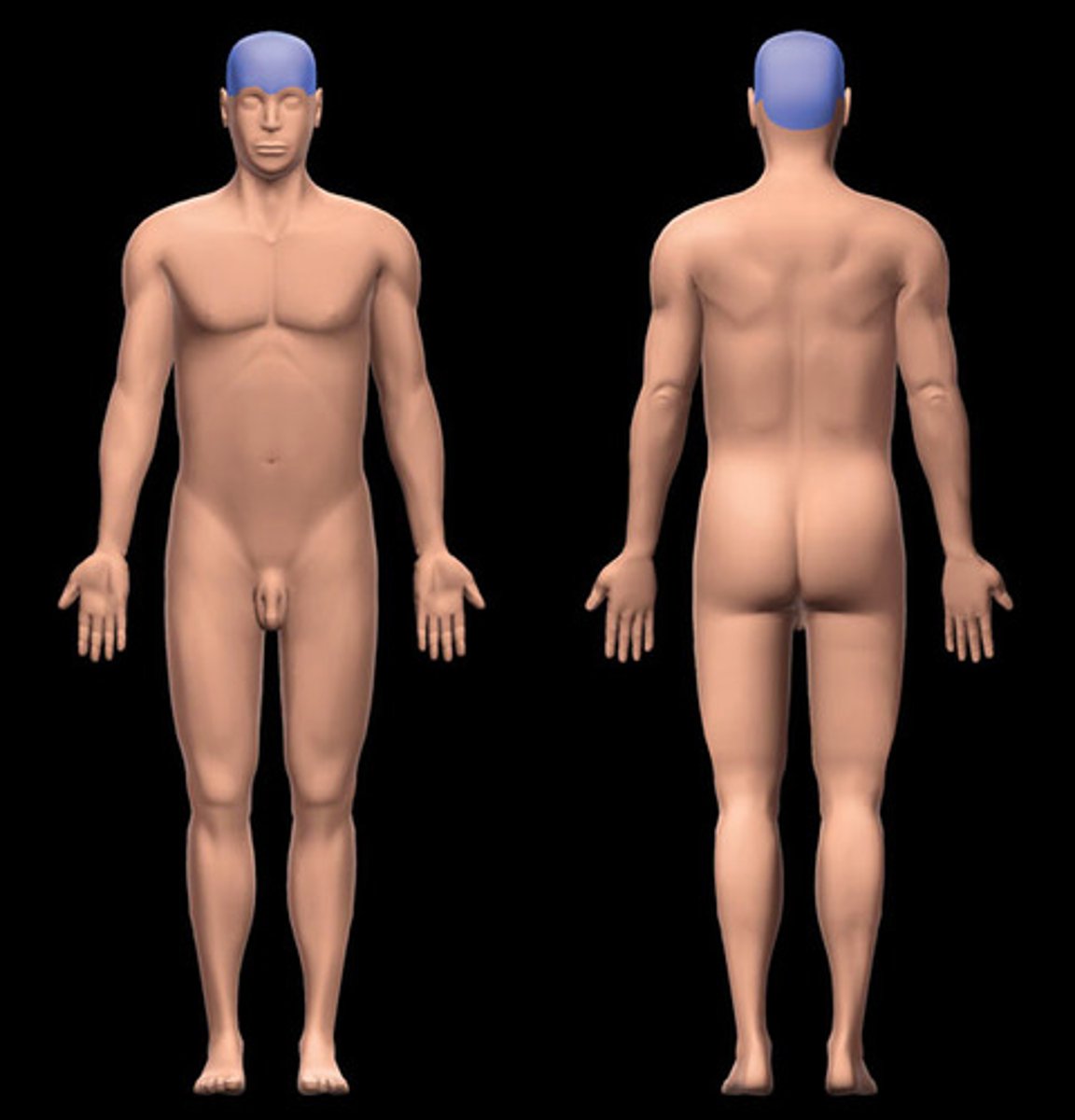
cephalic
head
coxal
hip
crural
leg
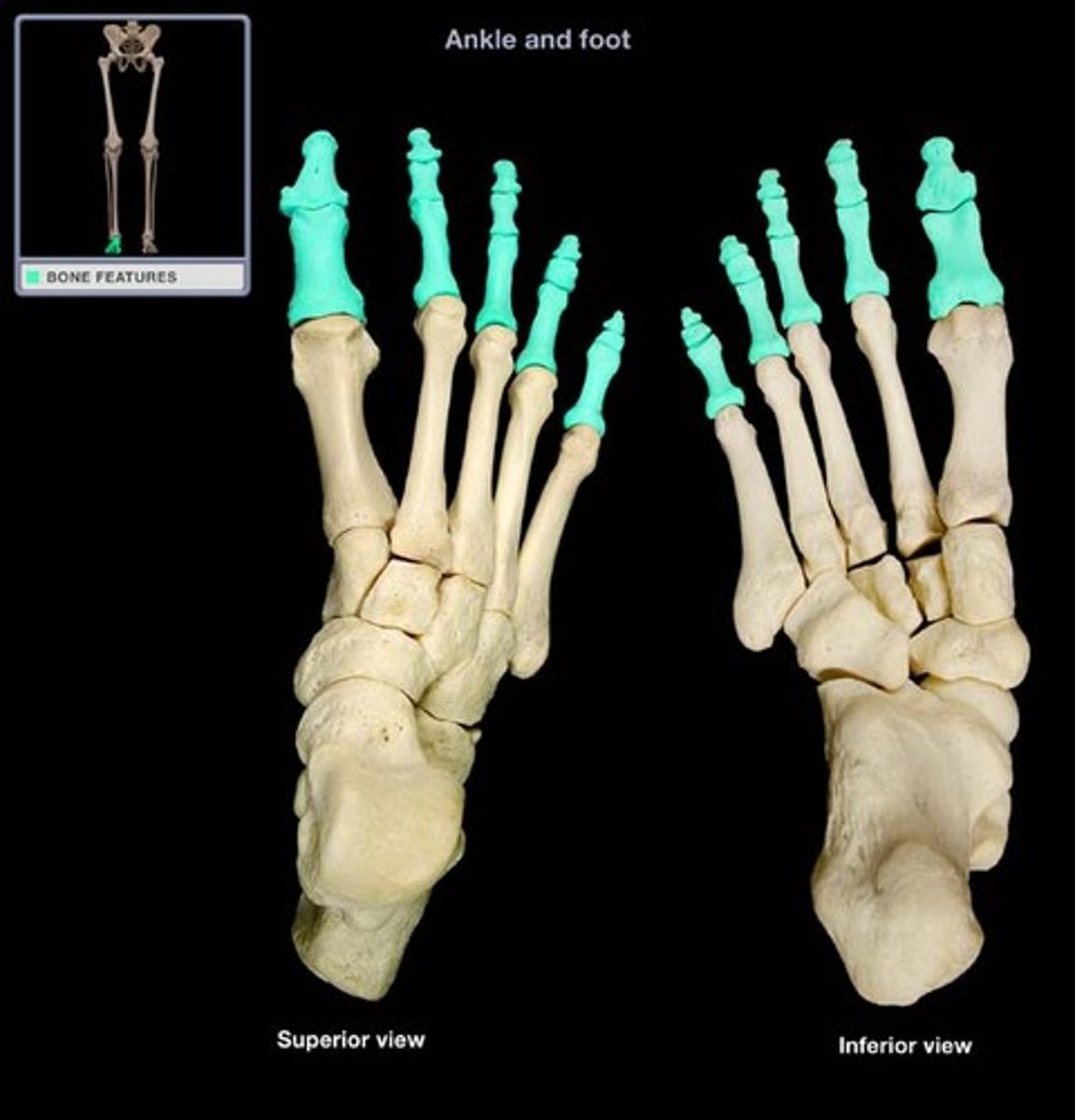
digital
fingers/toes
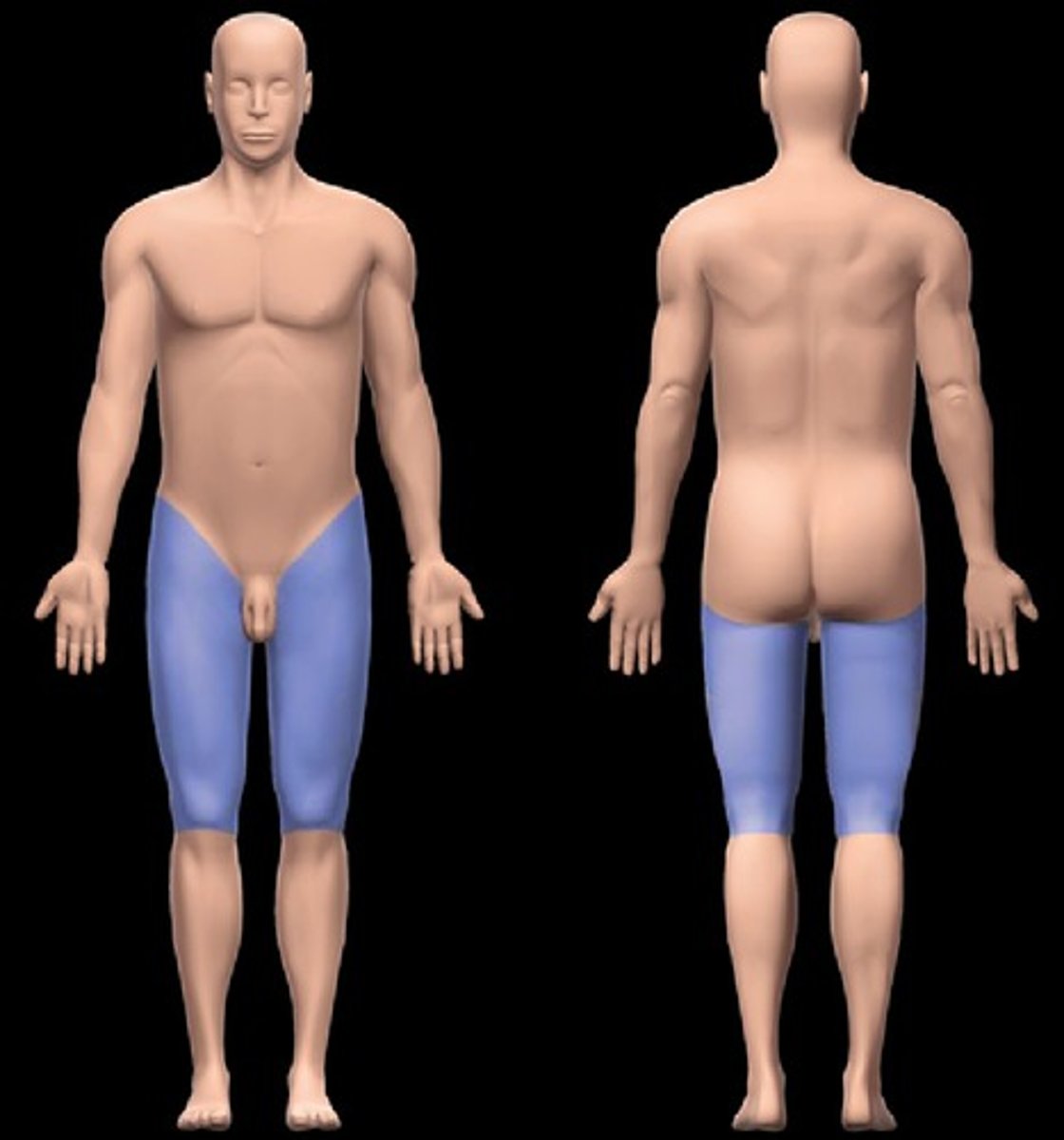
femoral
thigh
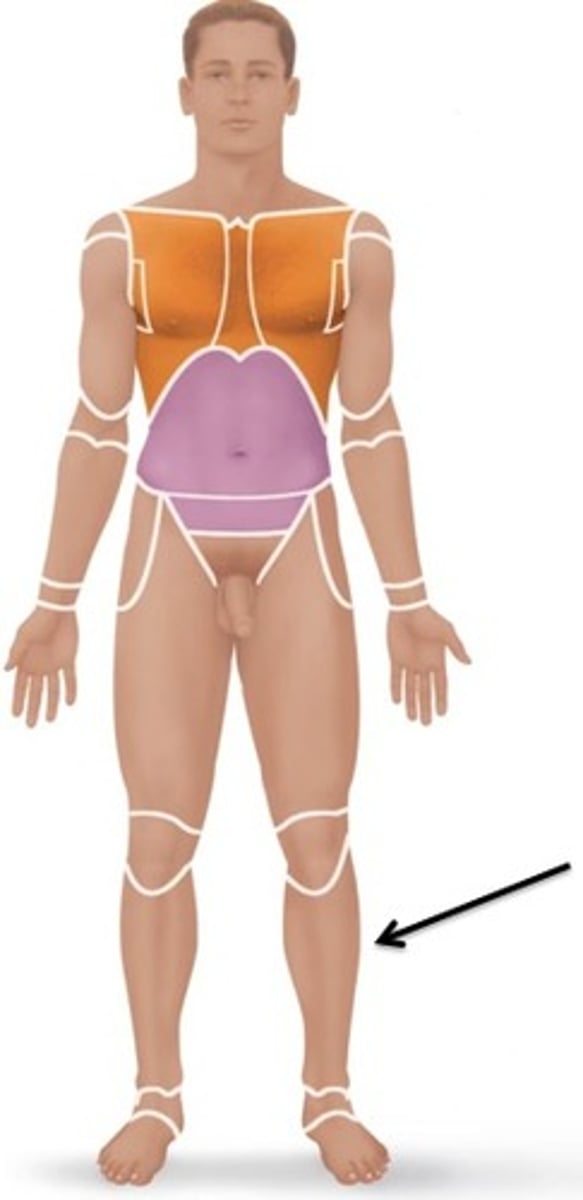
fibular
side of leg
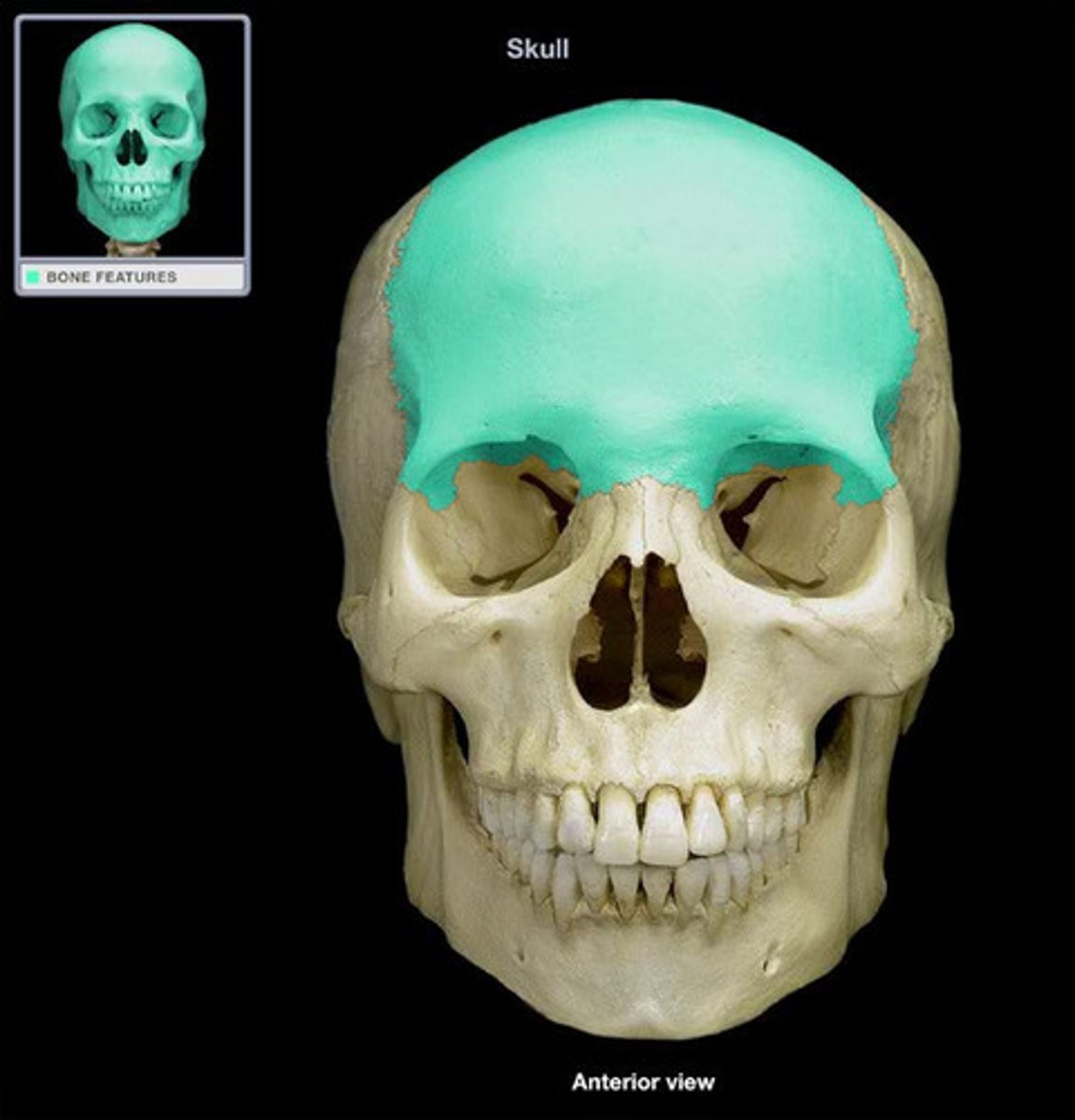
frontal
forehead
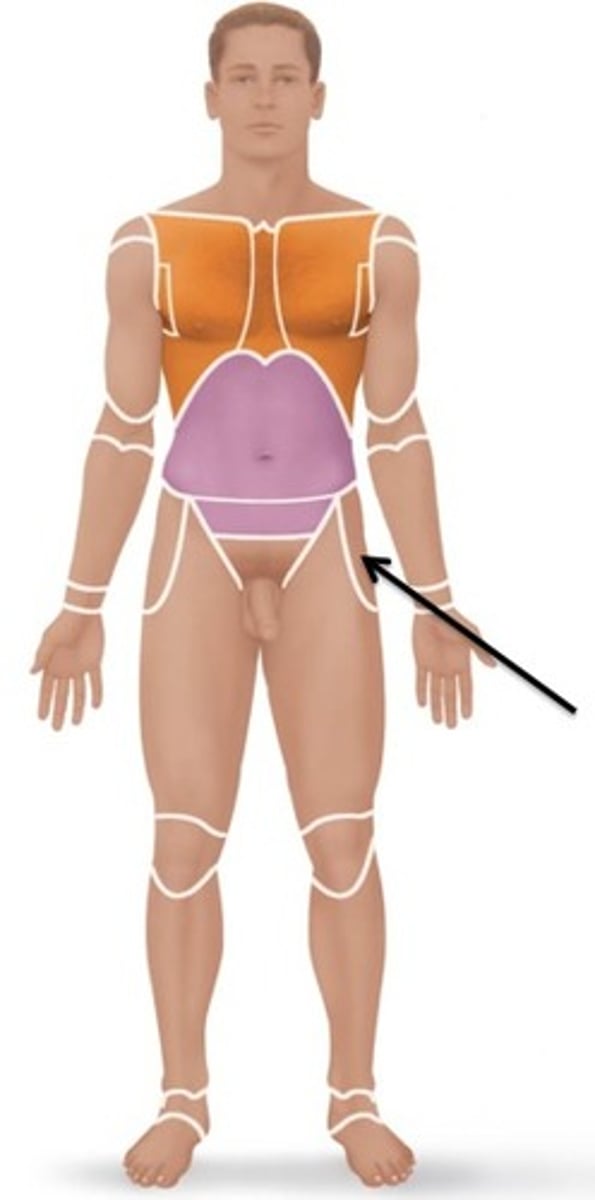
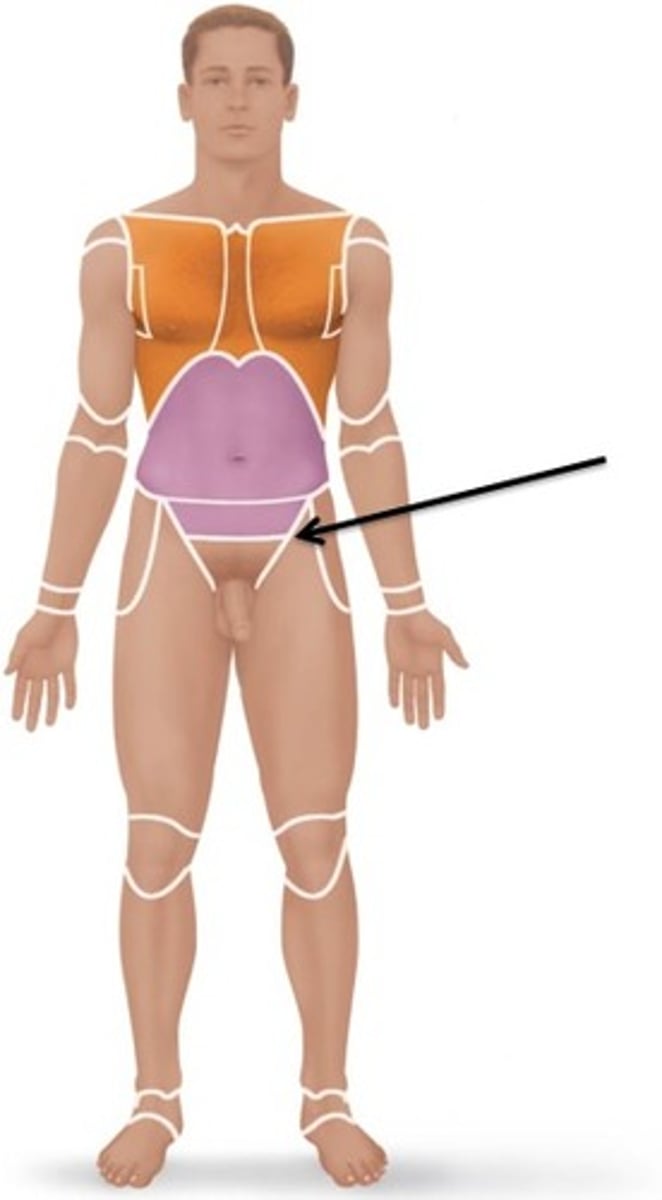
inguinal
groin area
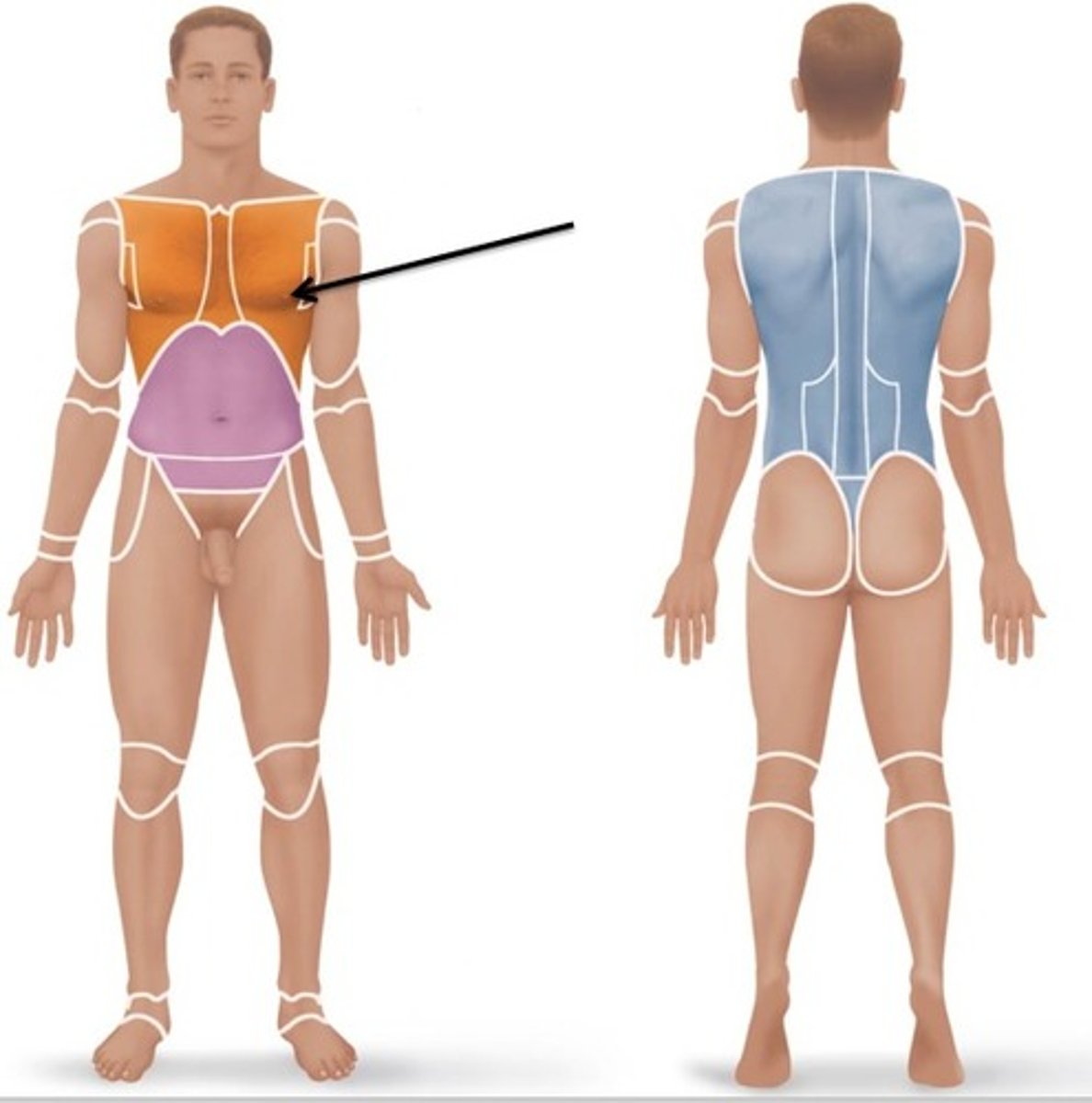
mammary
breast region
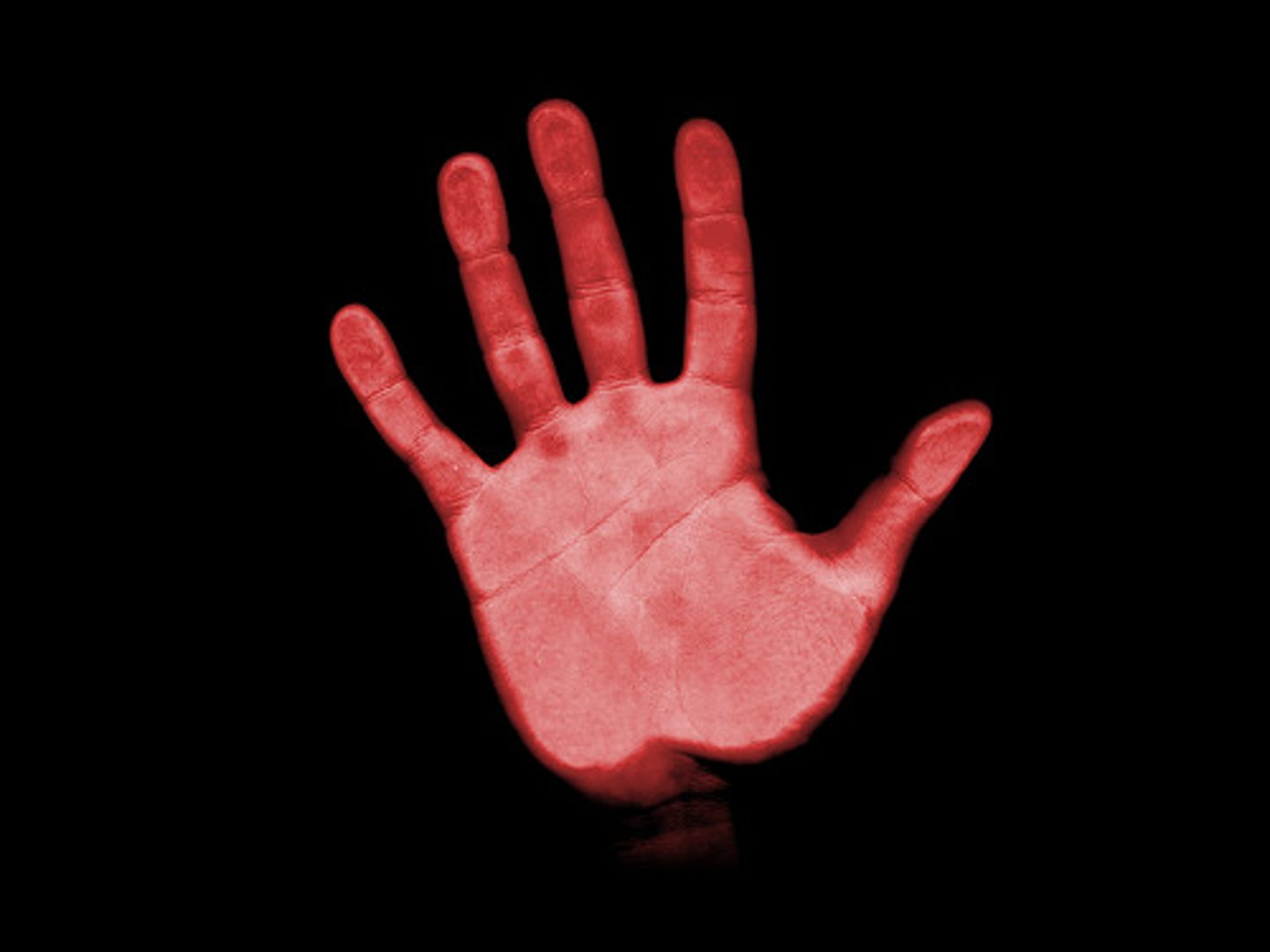
manus
hand

pelvic
pelvis region
nasal
nose
oral
mouth
orbital
eye
palmar
palm
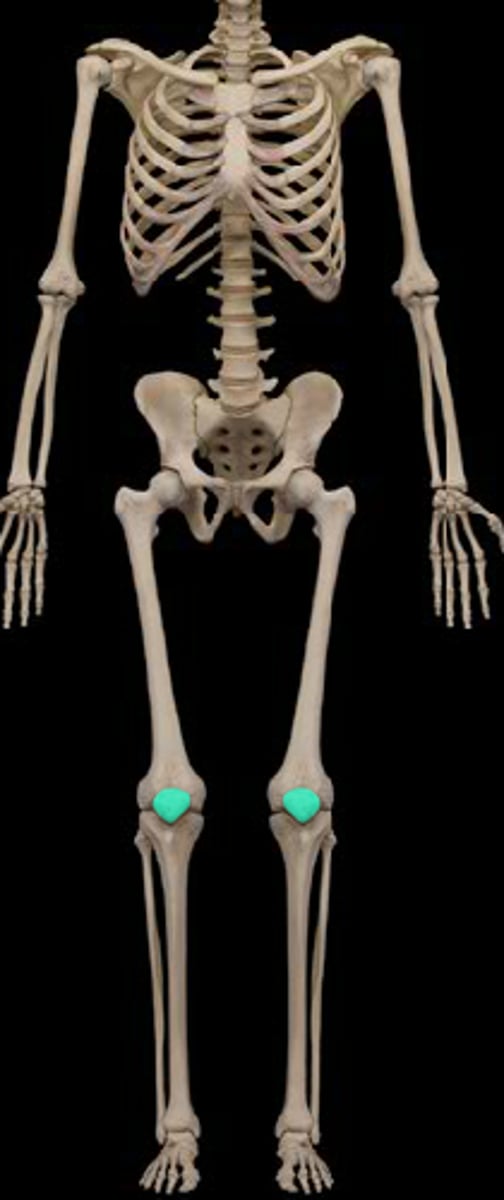
pateller
anterior knee
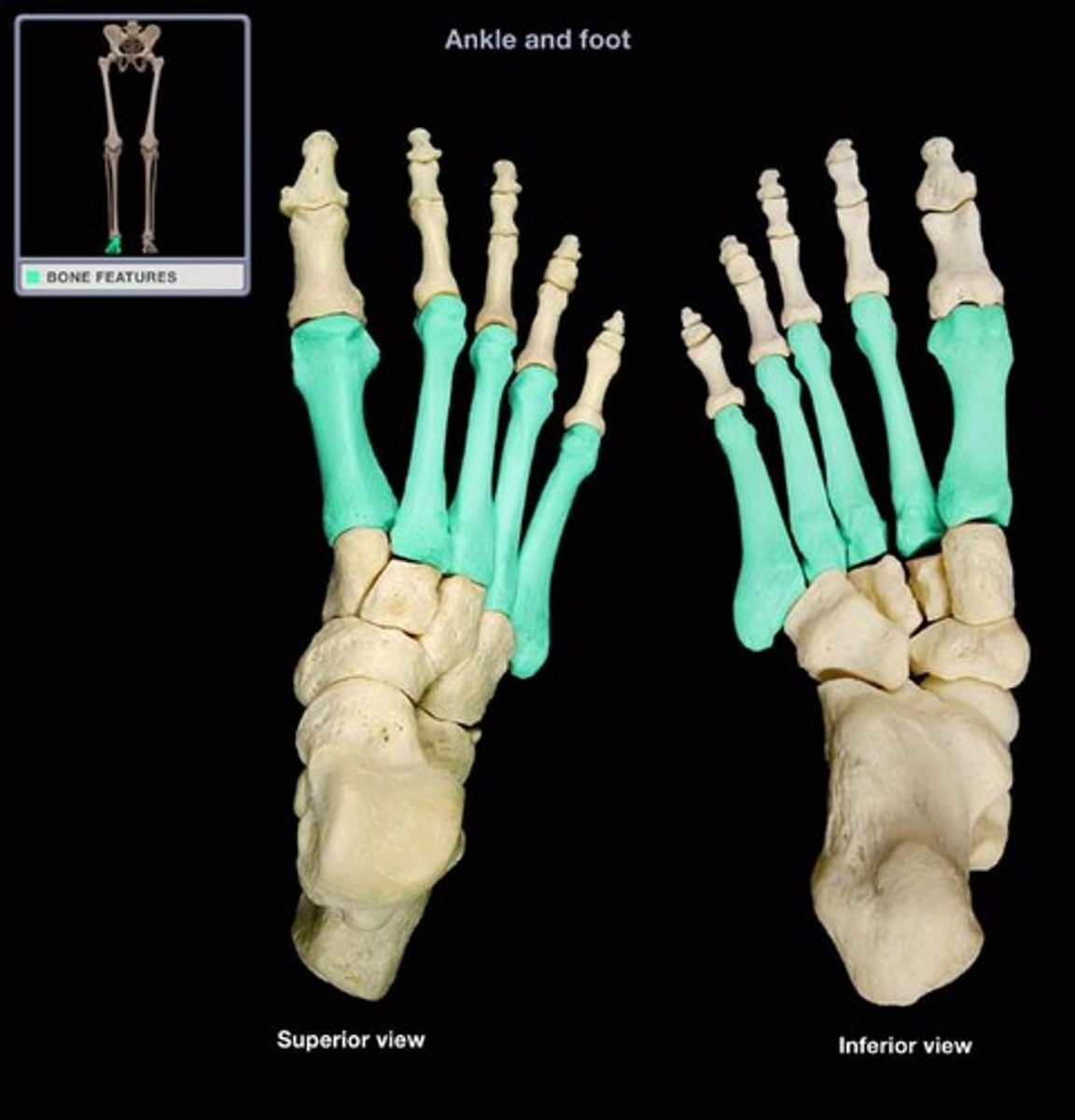
pedal
foot
tarsal
ankle
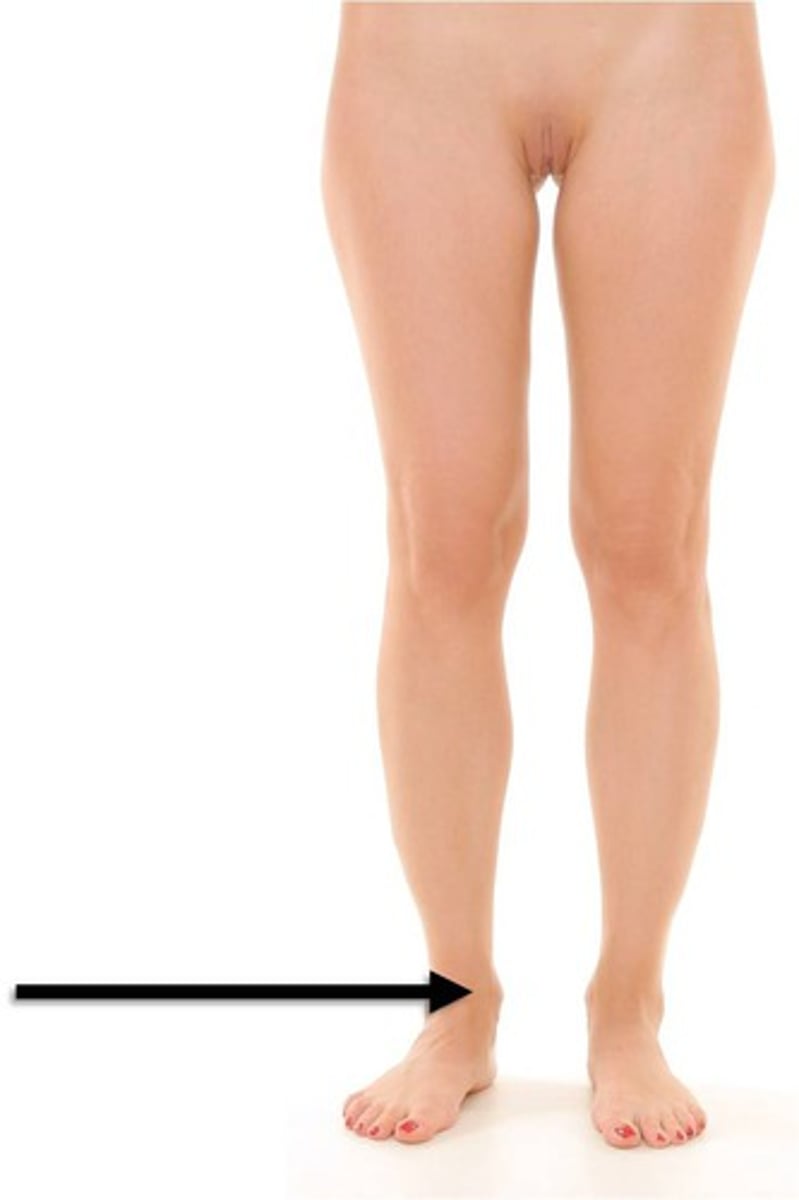

metatarsal
top of foot
calcaneal
heal
dorsal
back
gluteal
butt
lumbar
lower back
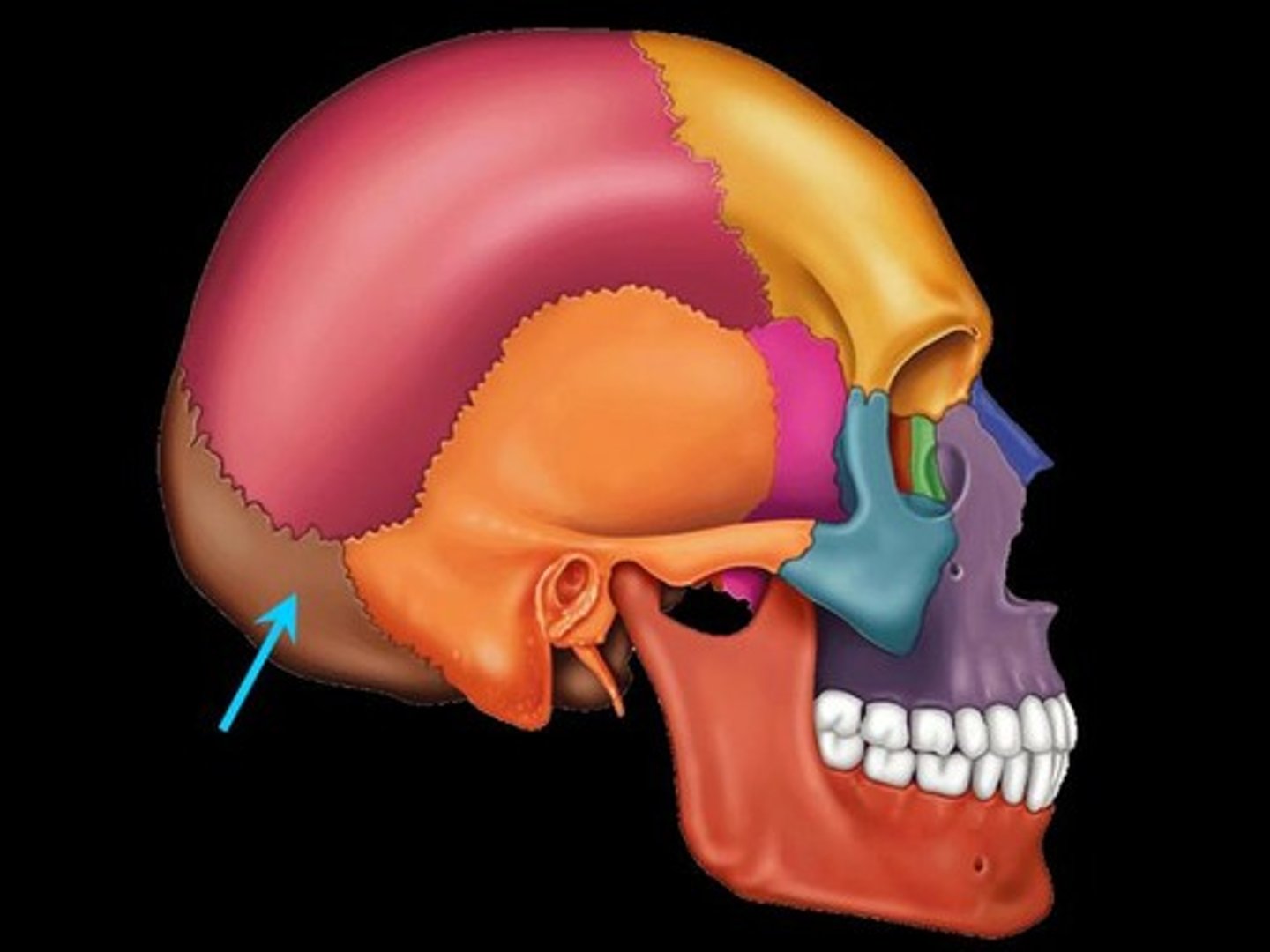
occipital
posterior head
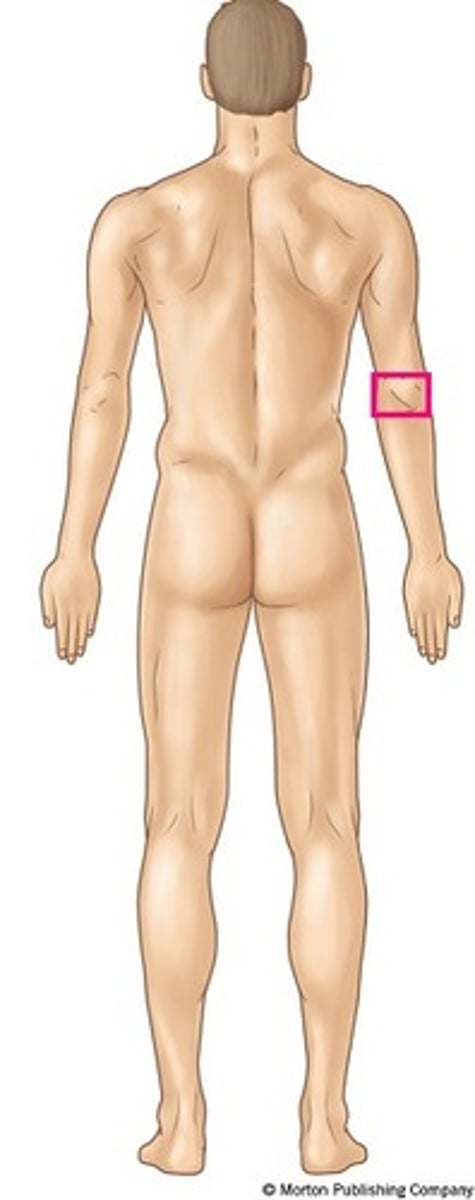
olecranal
posterior elbow
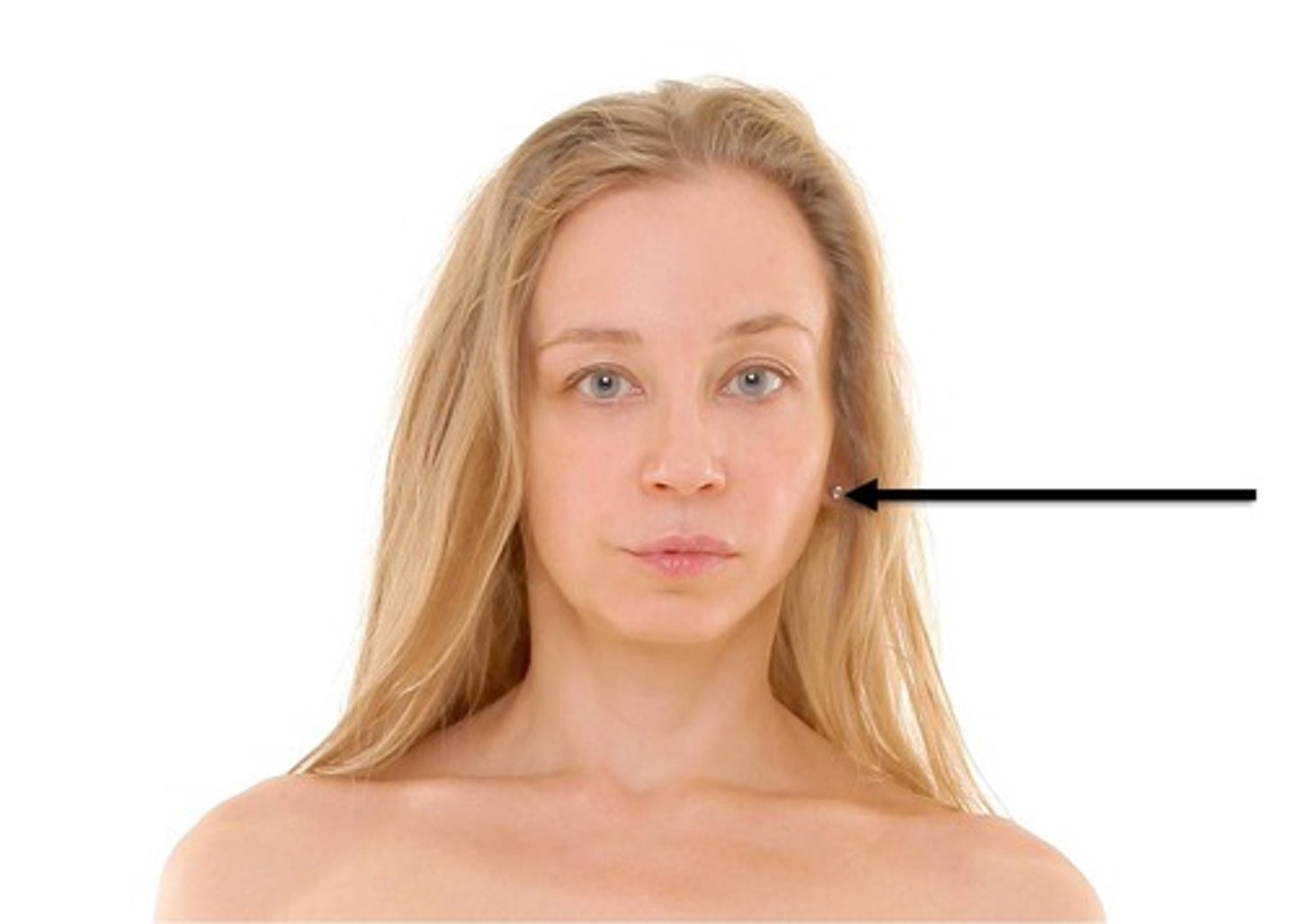
otic
ear
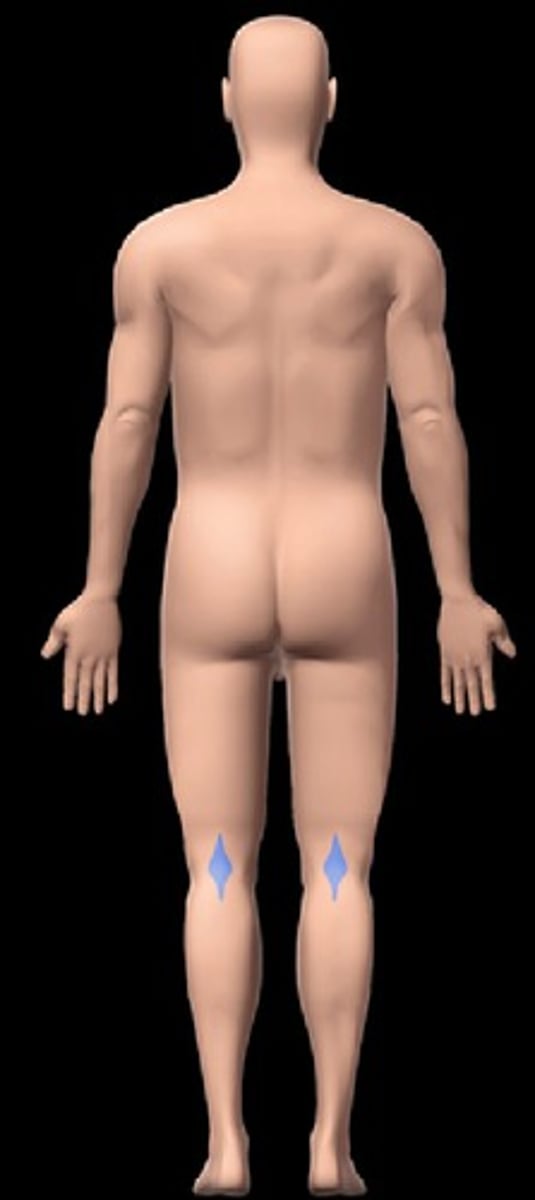
popliteal
posterior knee
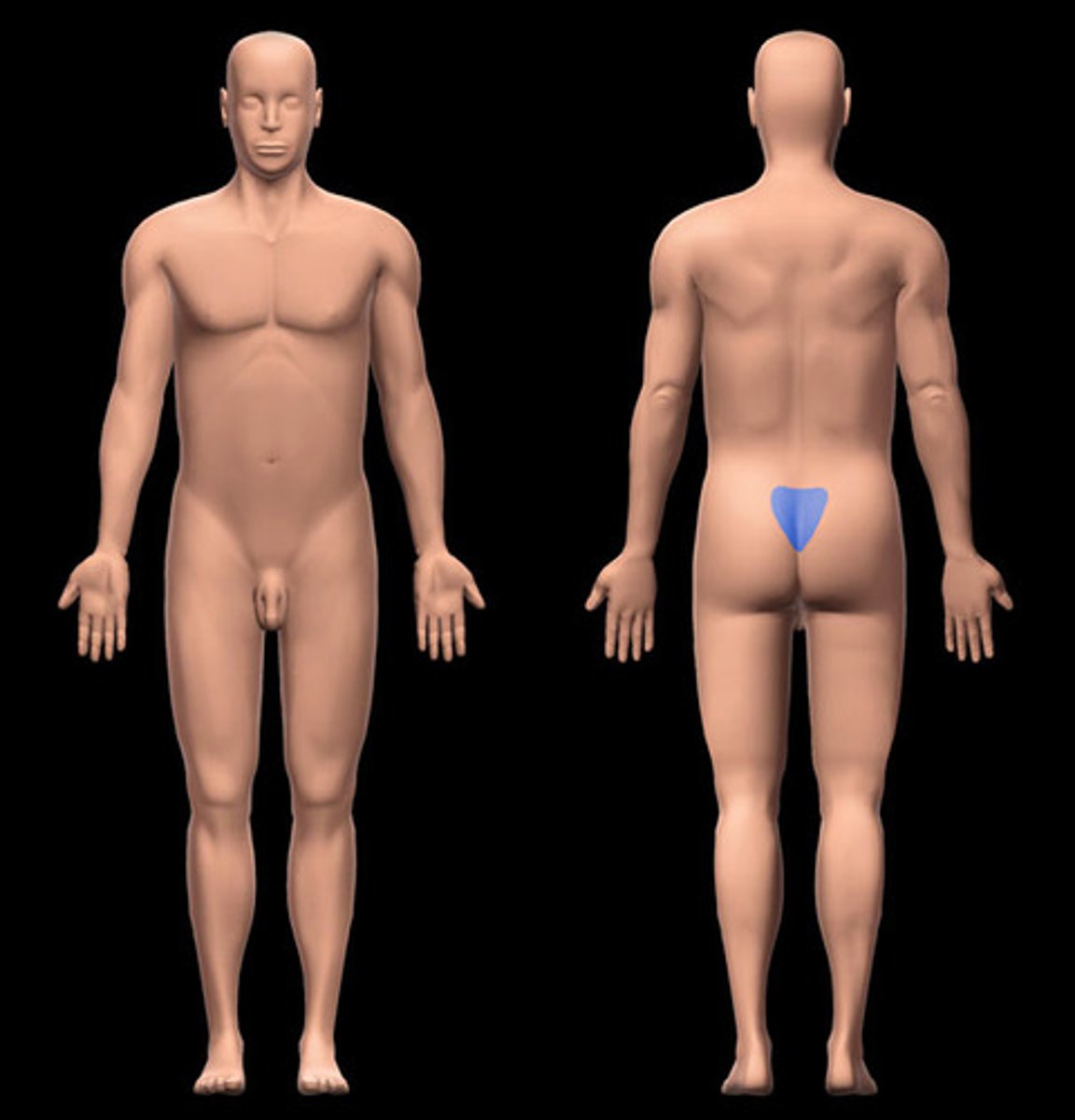
sacral
area between hips
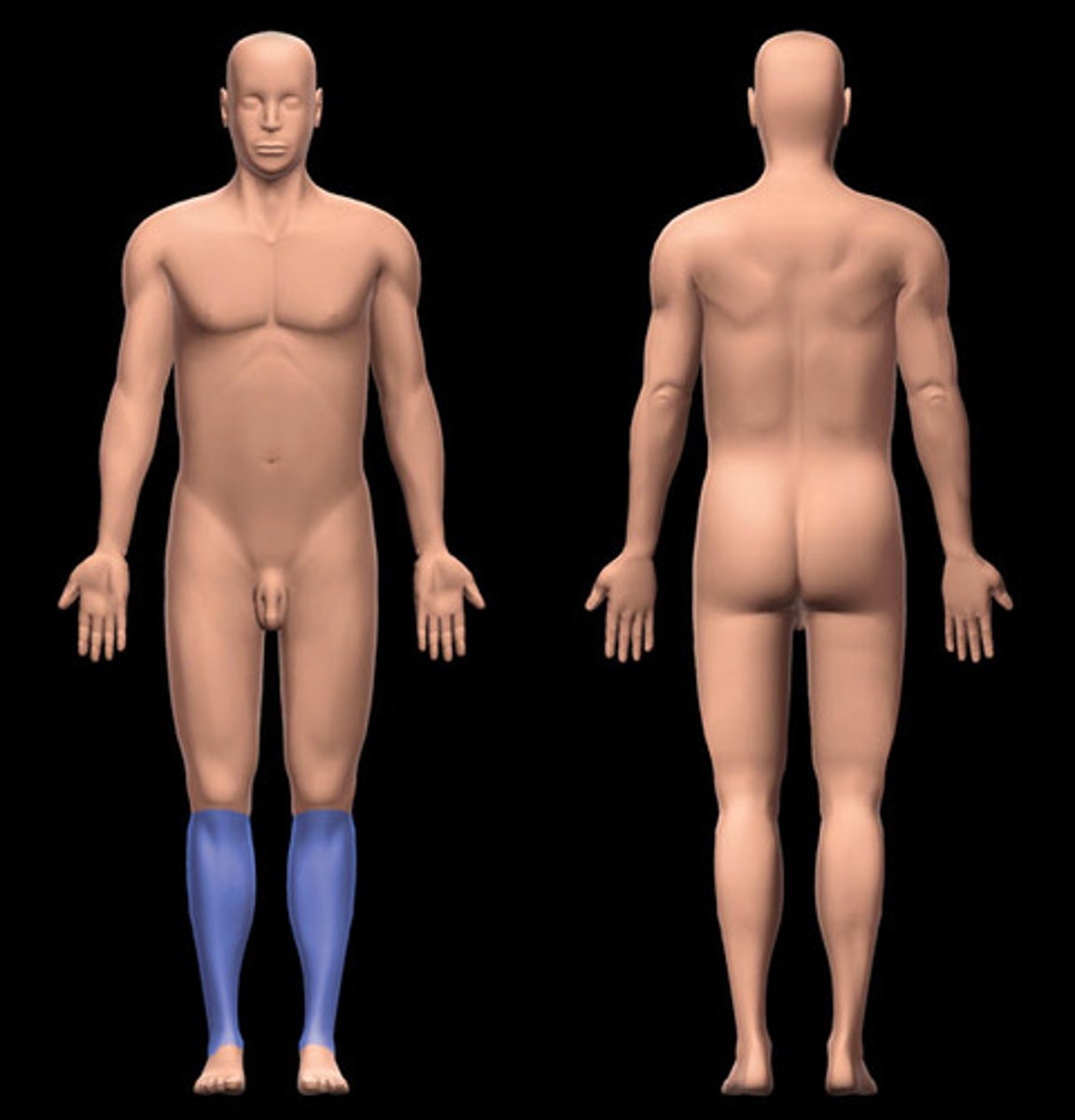
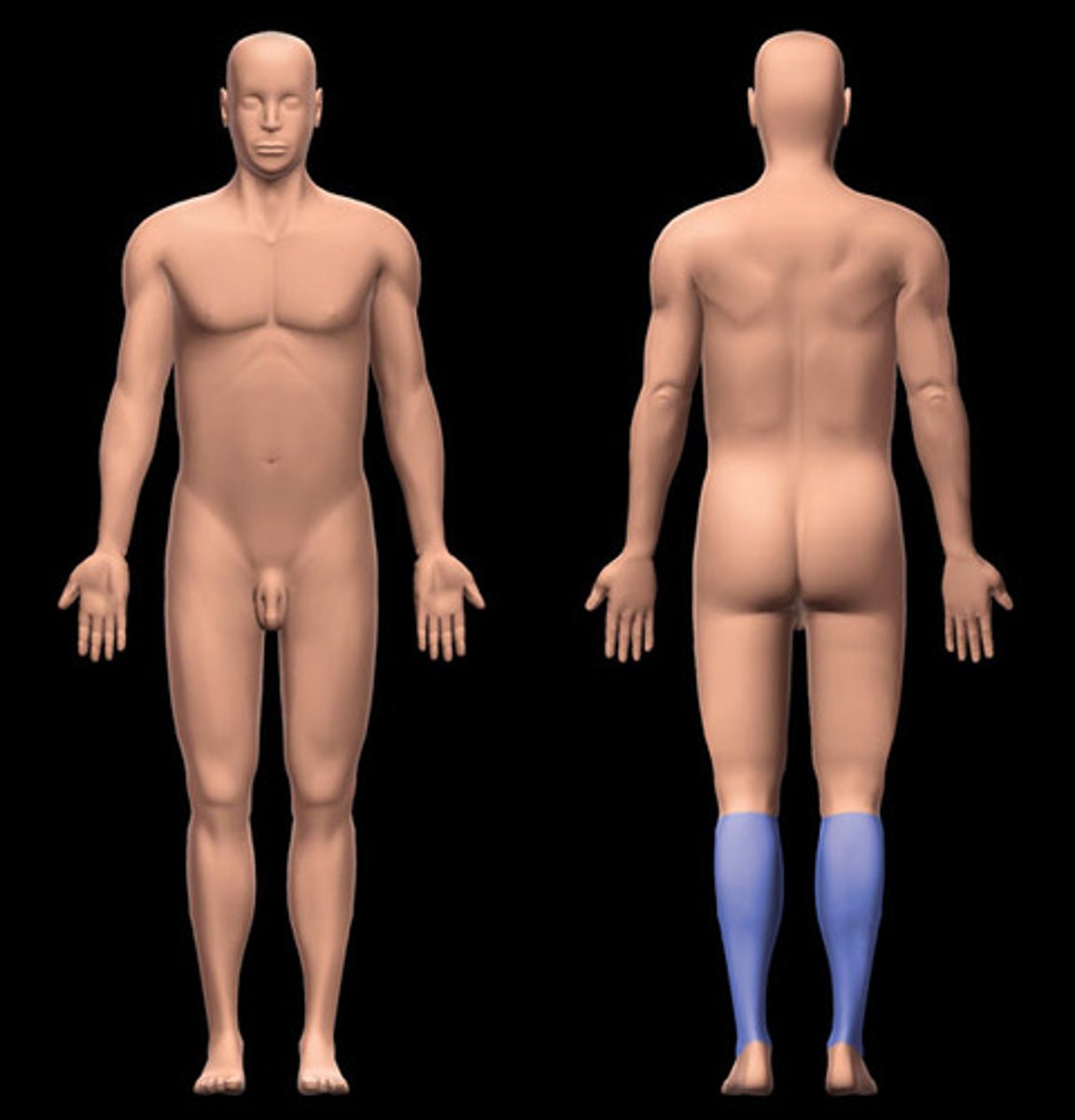
sural
calf
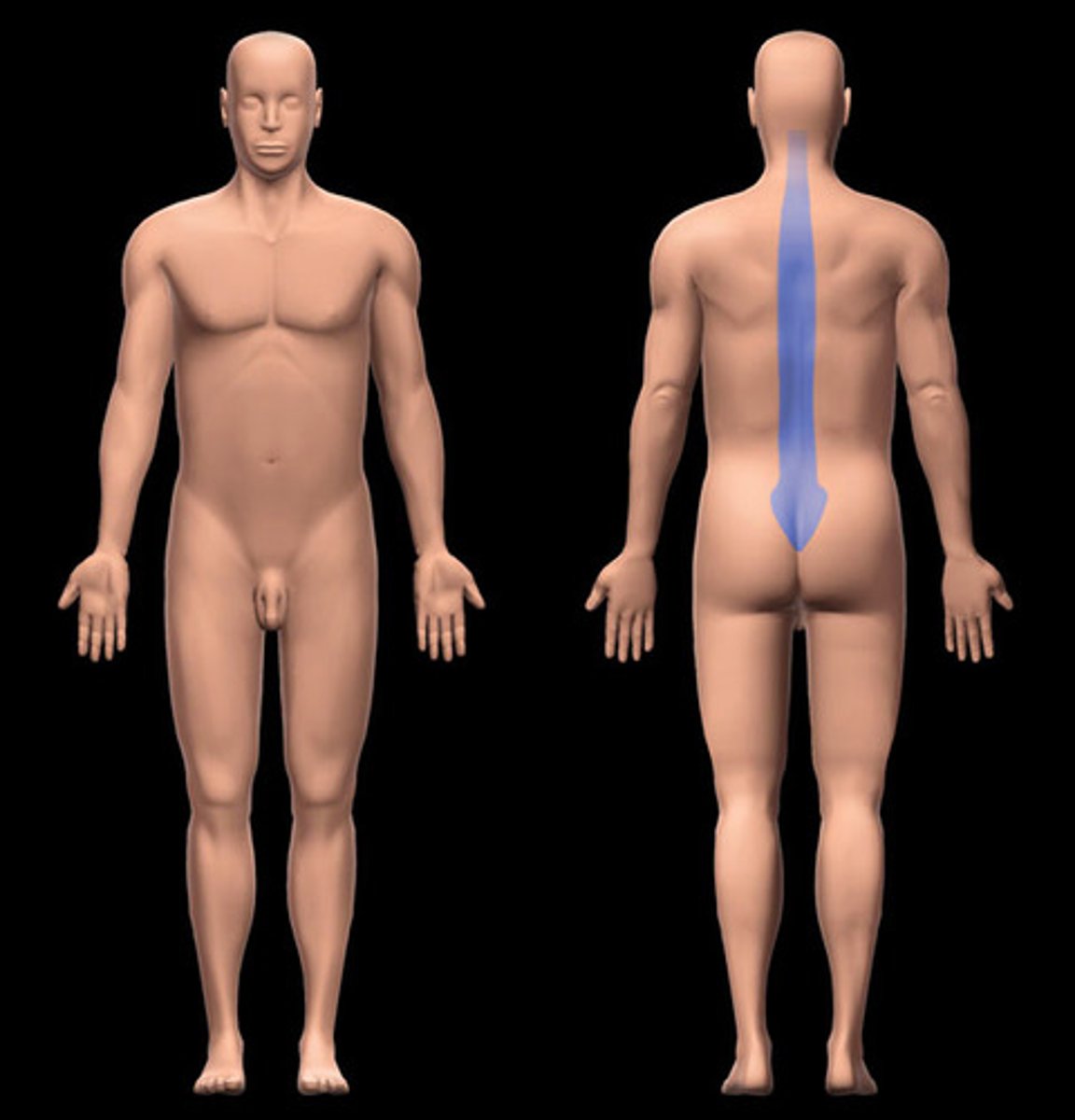
vertebral
spine
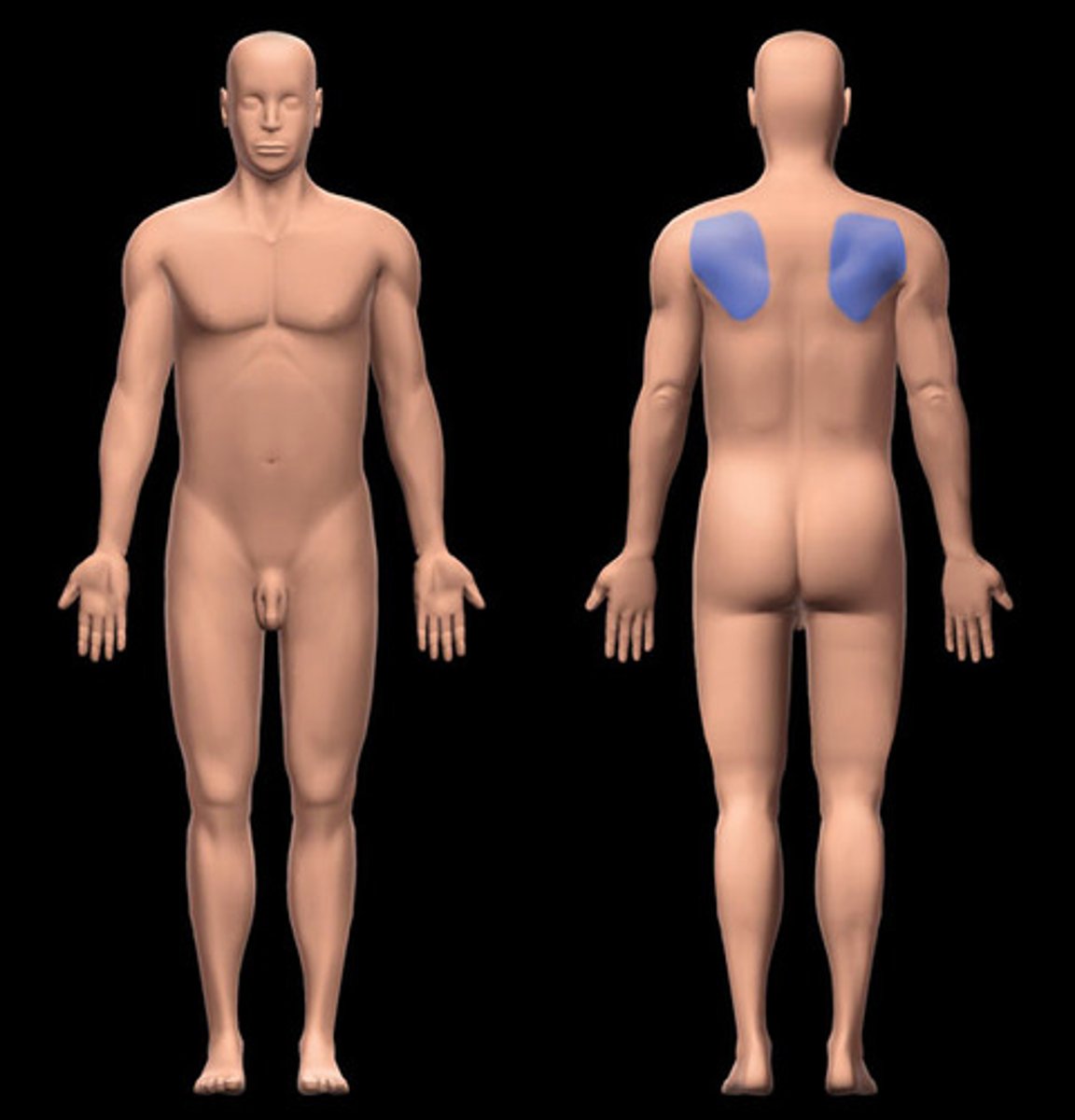
scapular
shoulder blade region
superior
toward the head
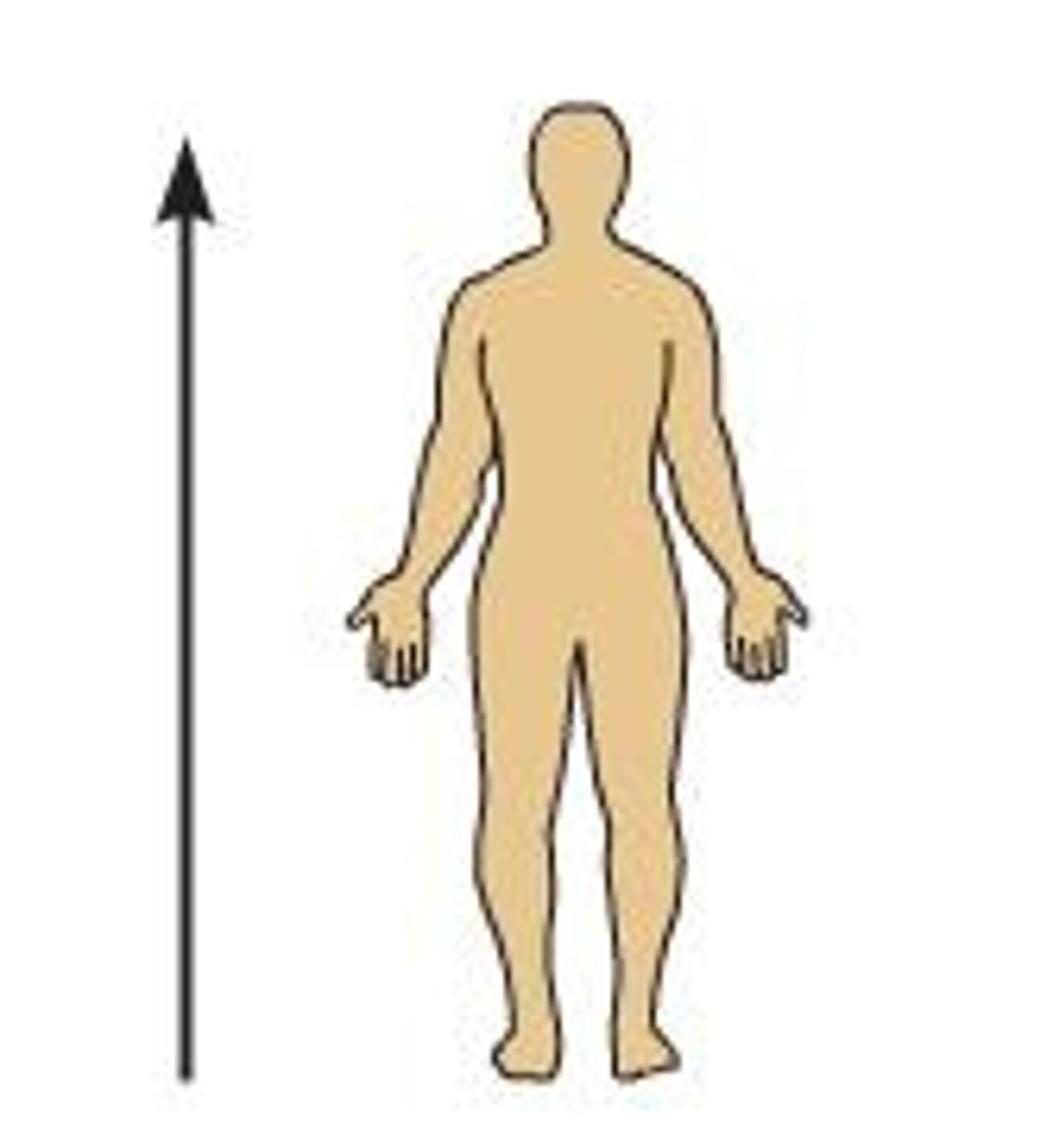
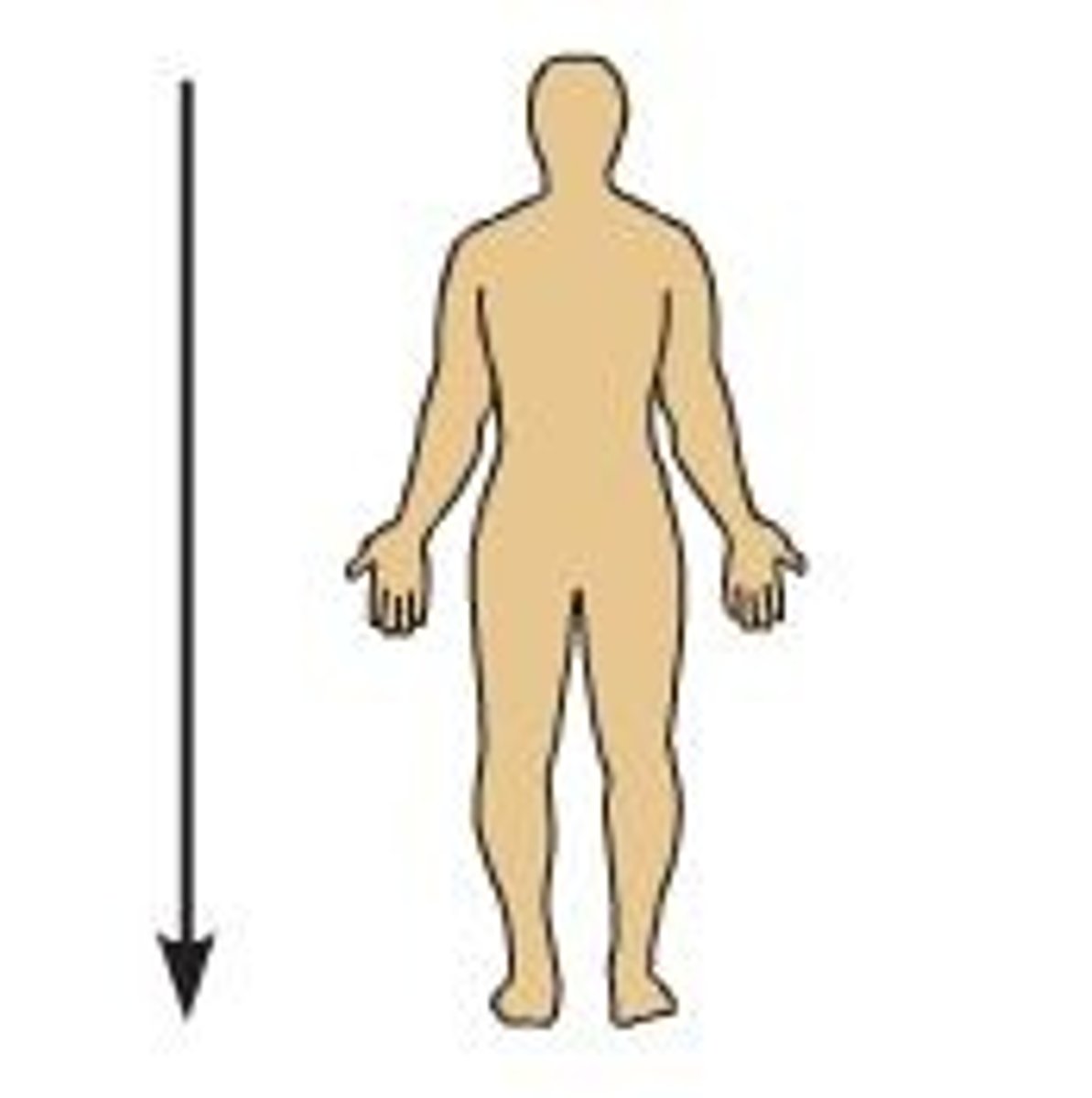
inferior
toward the feet
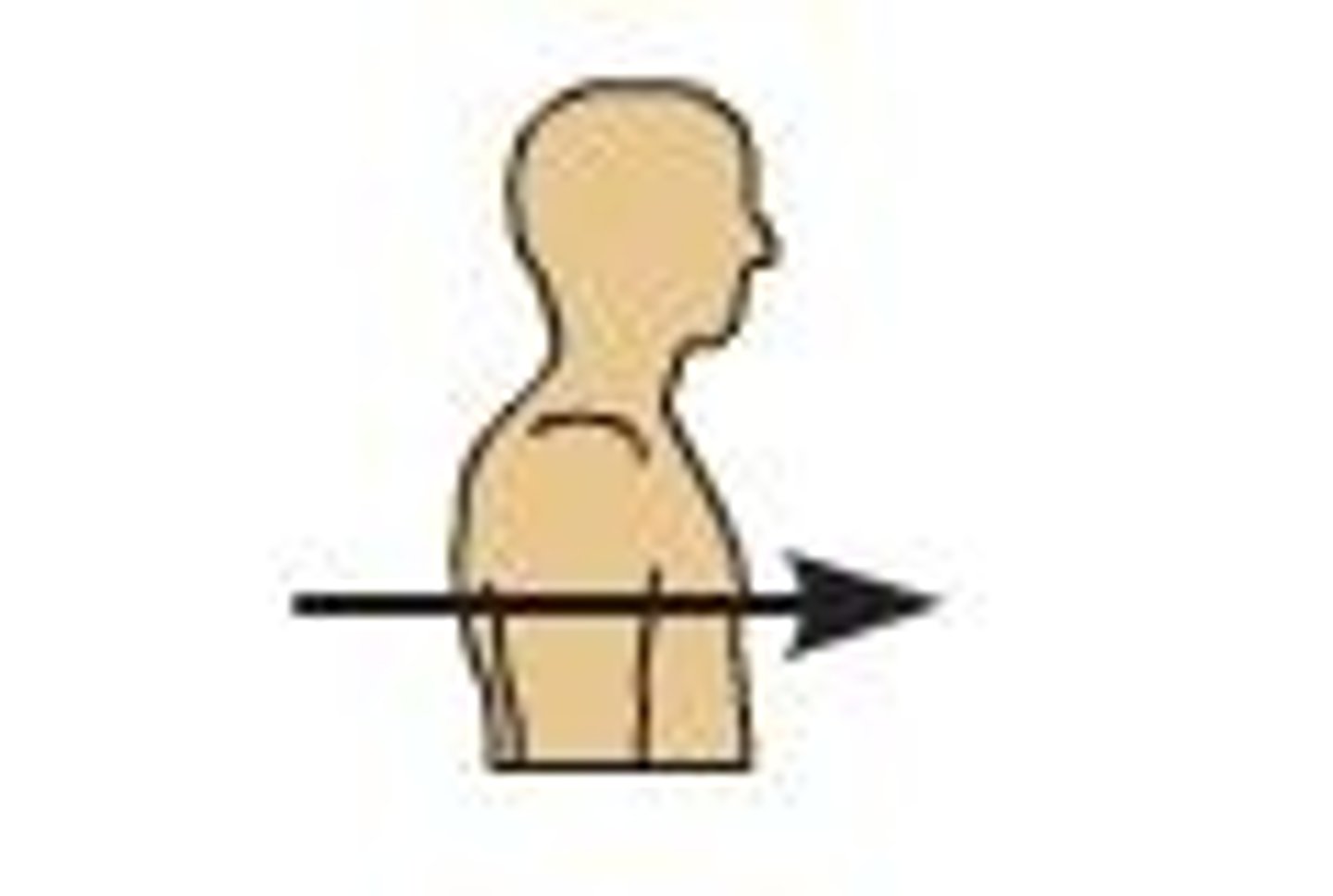
anterior
toawrd front
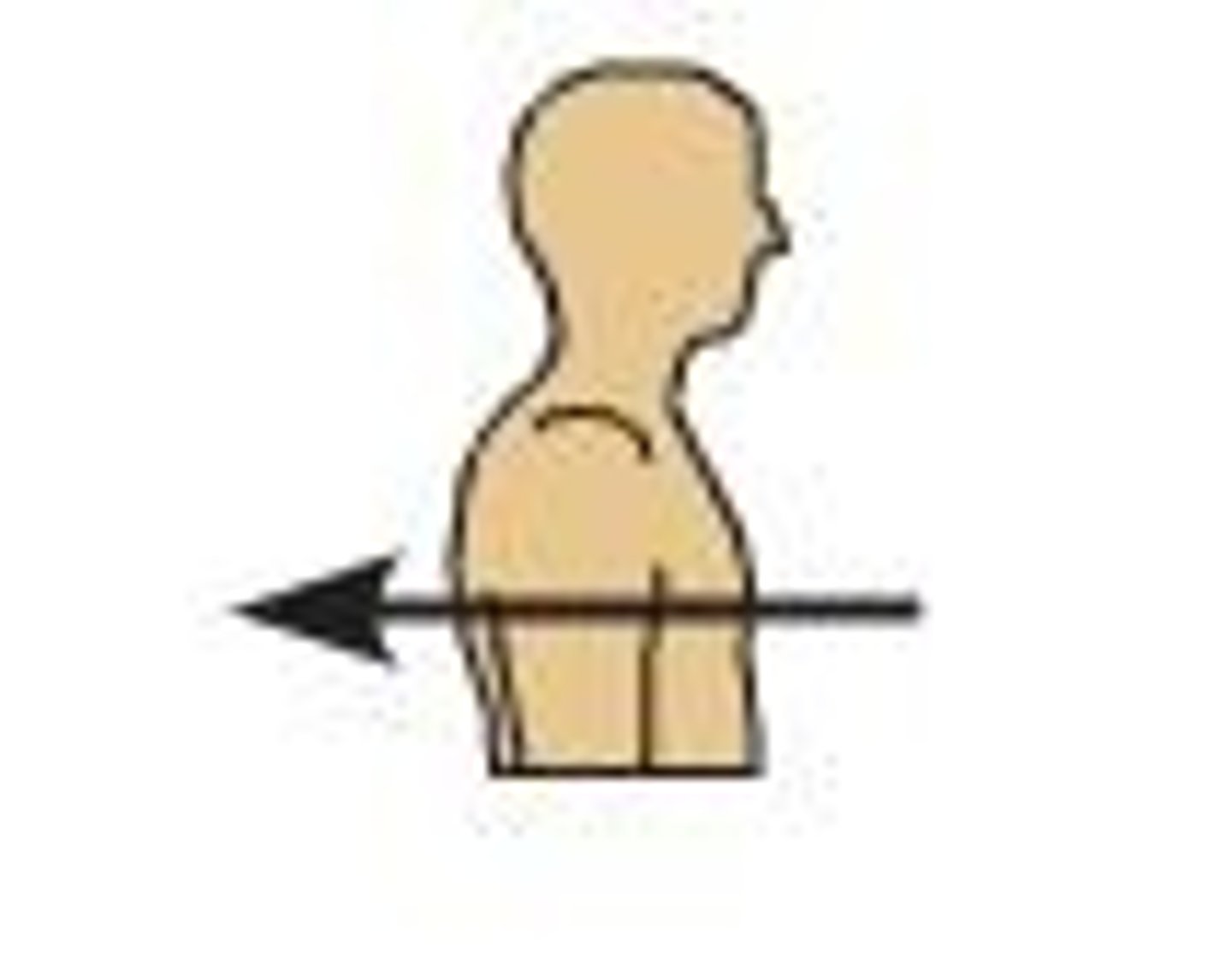
posterior
toward the back
medial
toward the middle line
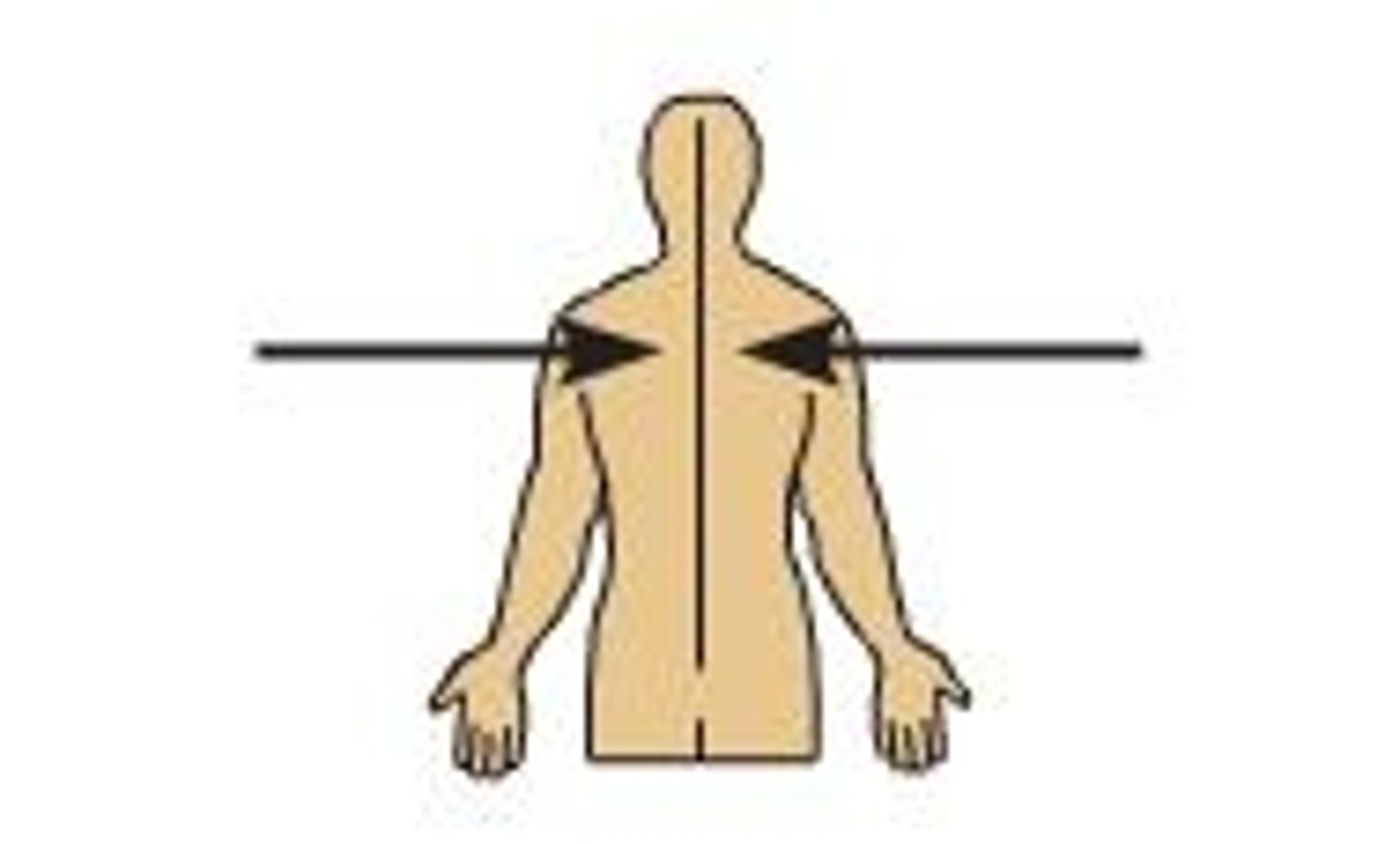
lateral
away from the mid line
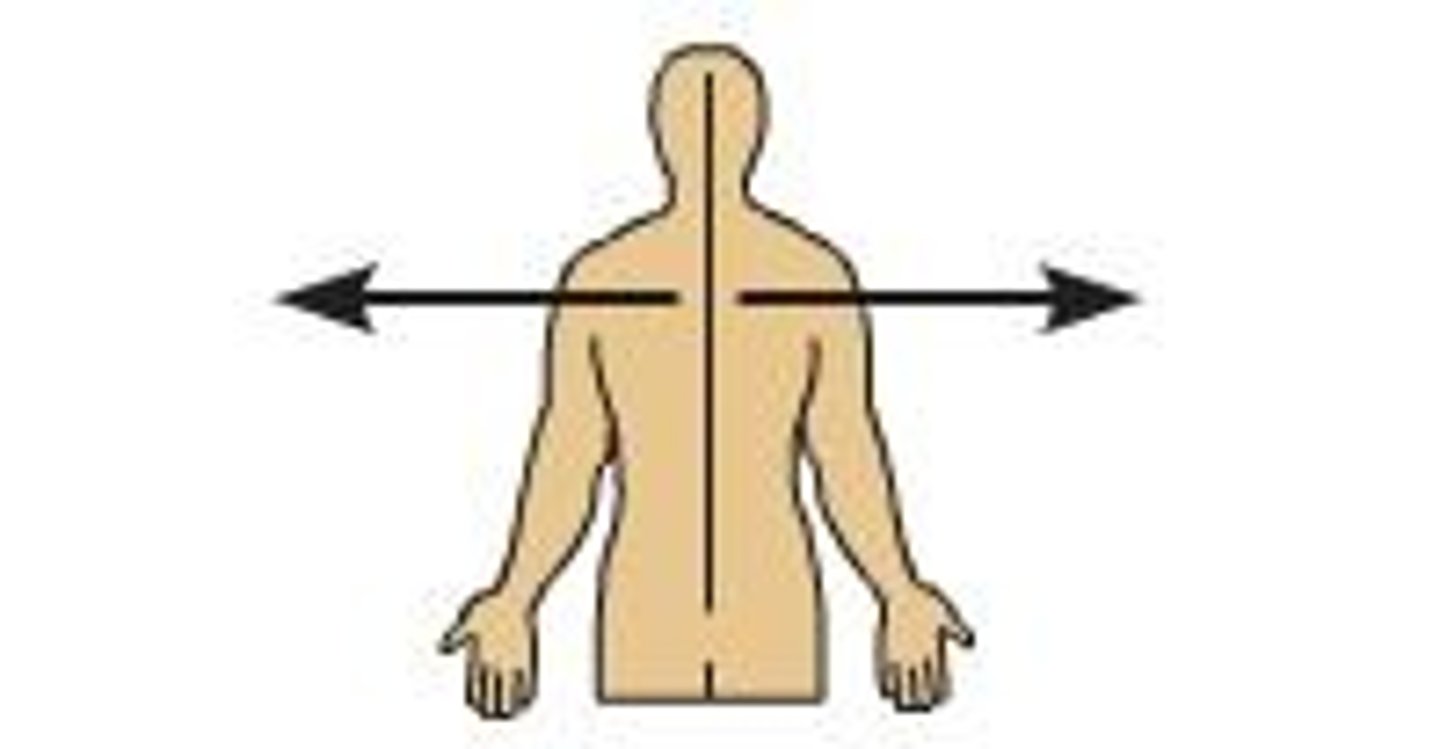
intermediate
between medial and lateral
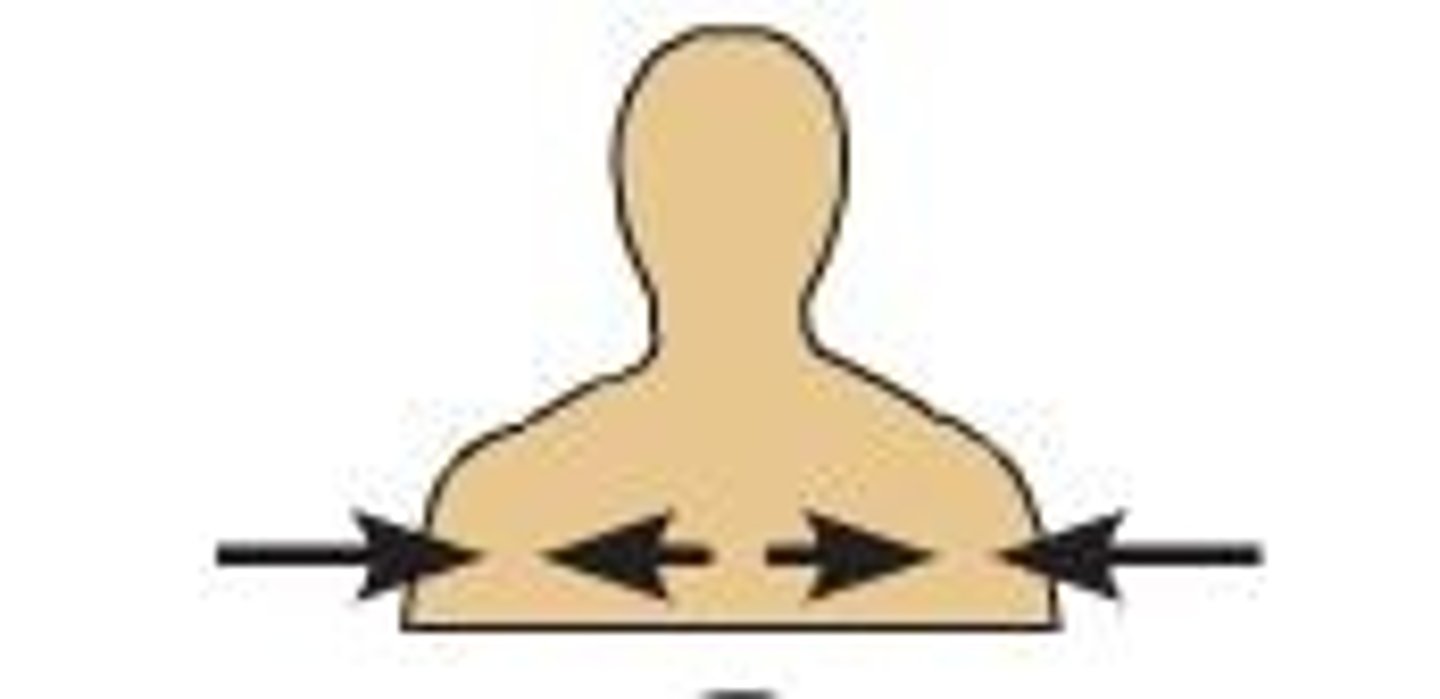
proximal
closer to the trunk
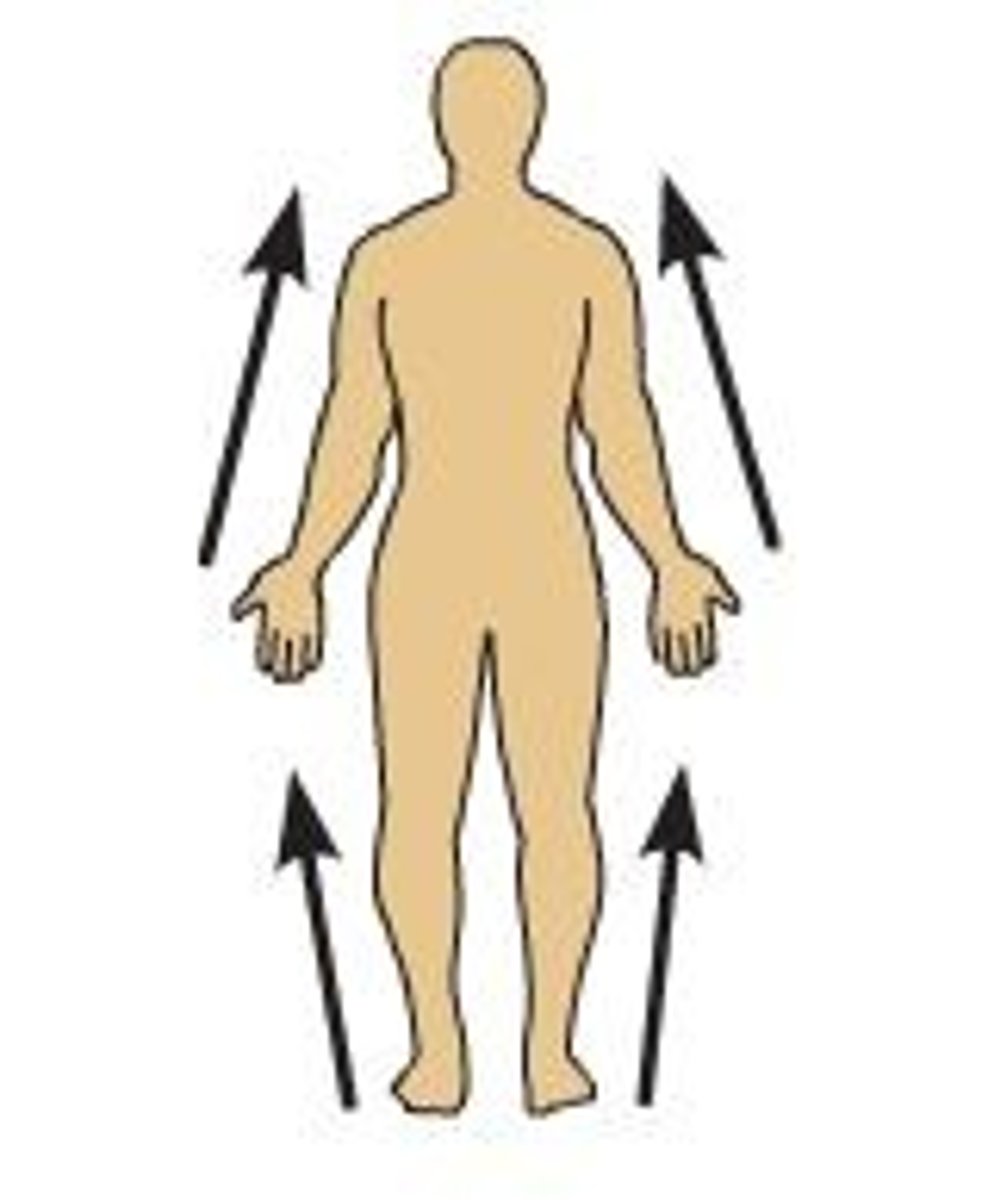
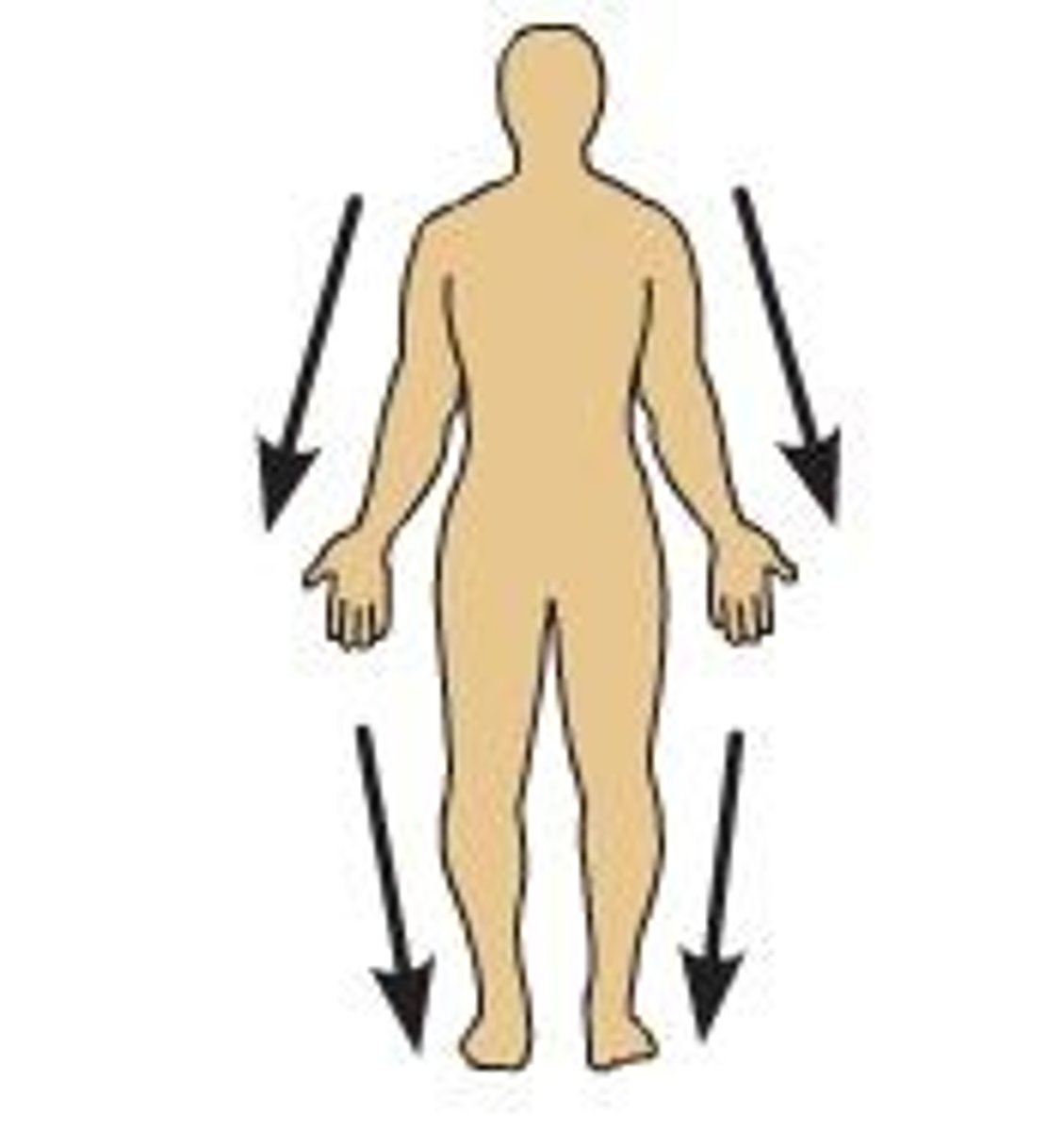
distal
further from the trunk
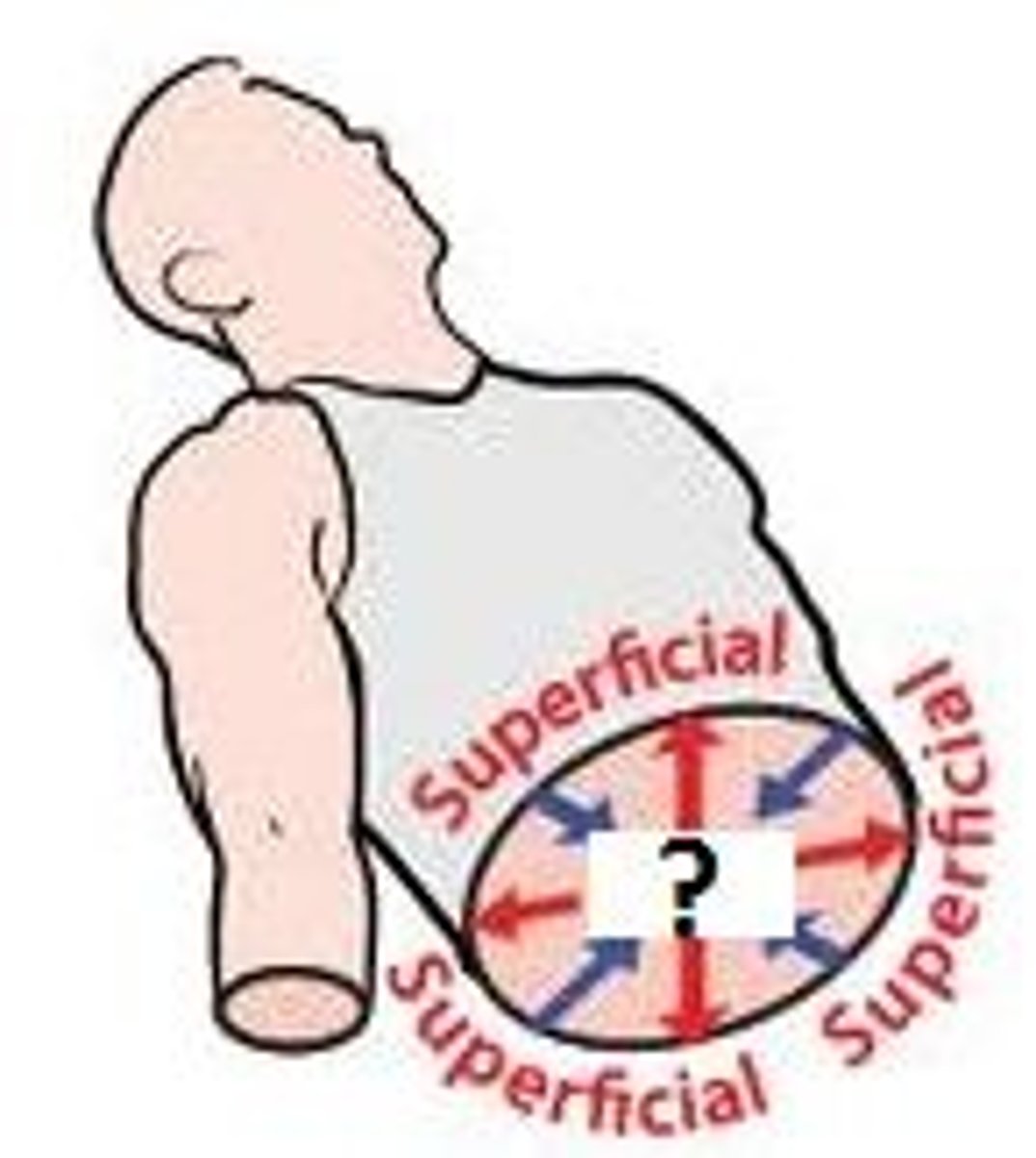
superficial
closer to the surface
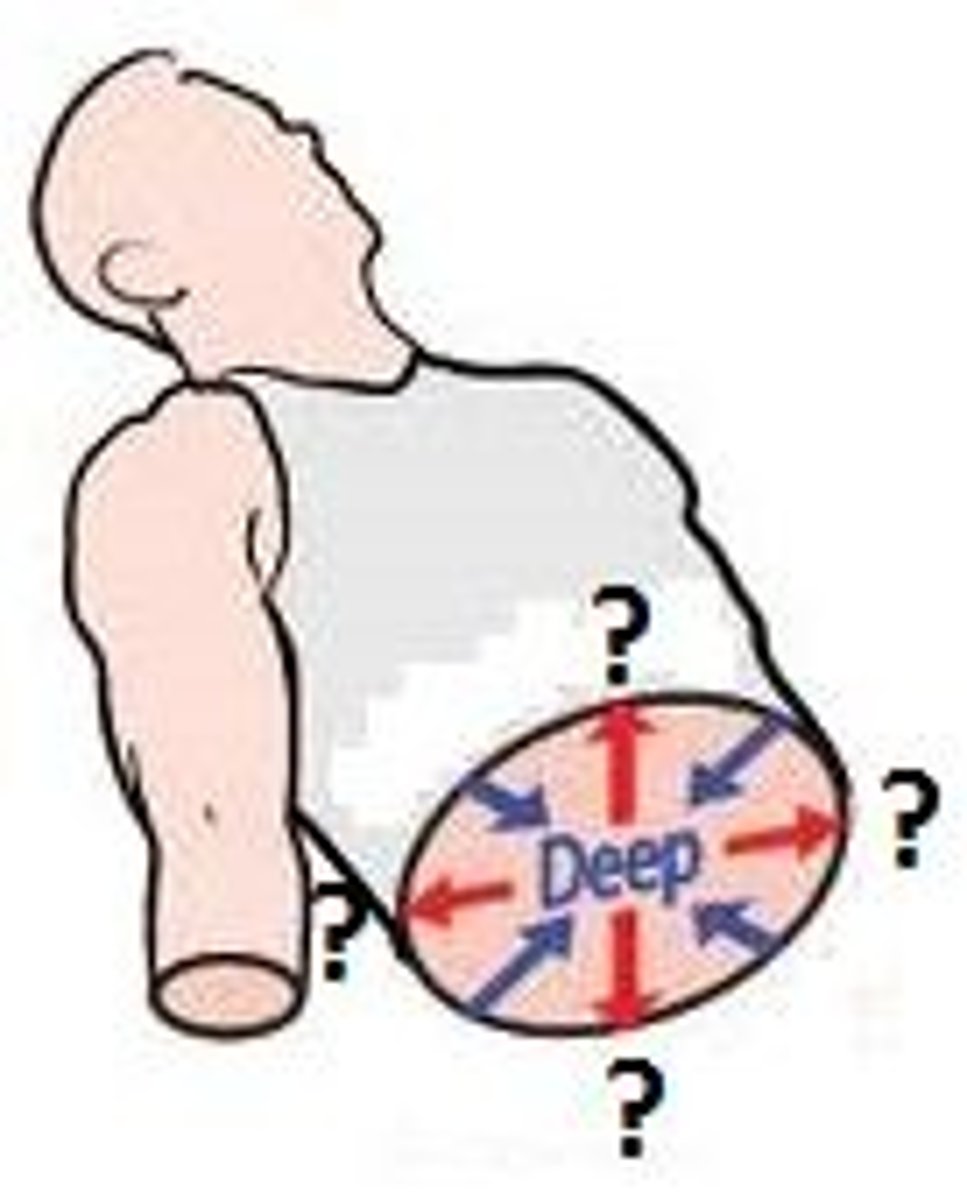
deep
away from the surface
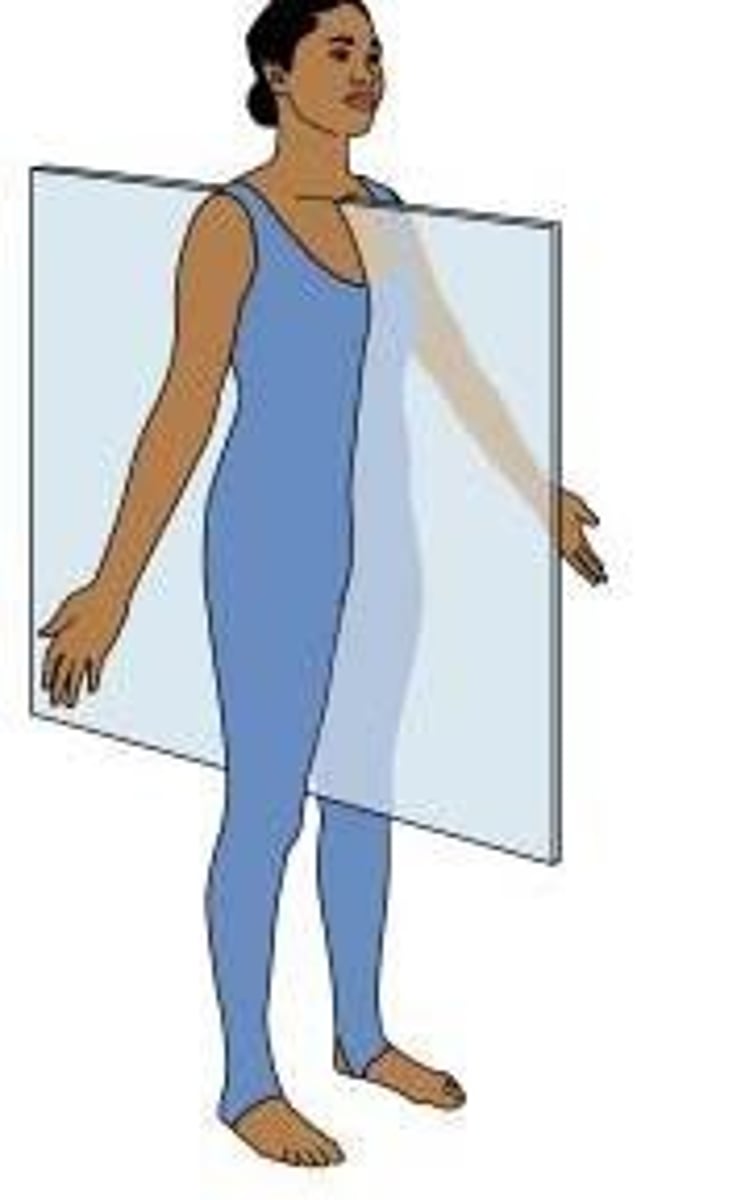
median or midsagittal plane
plane dividing body into left and right (median plane)
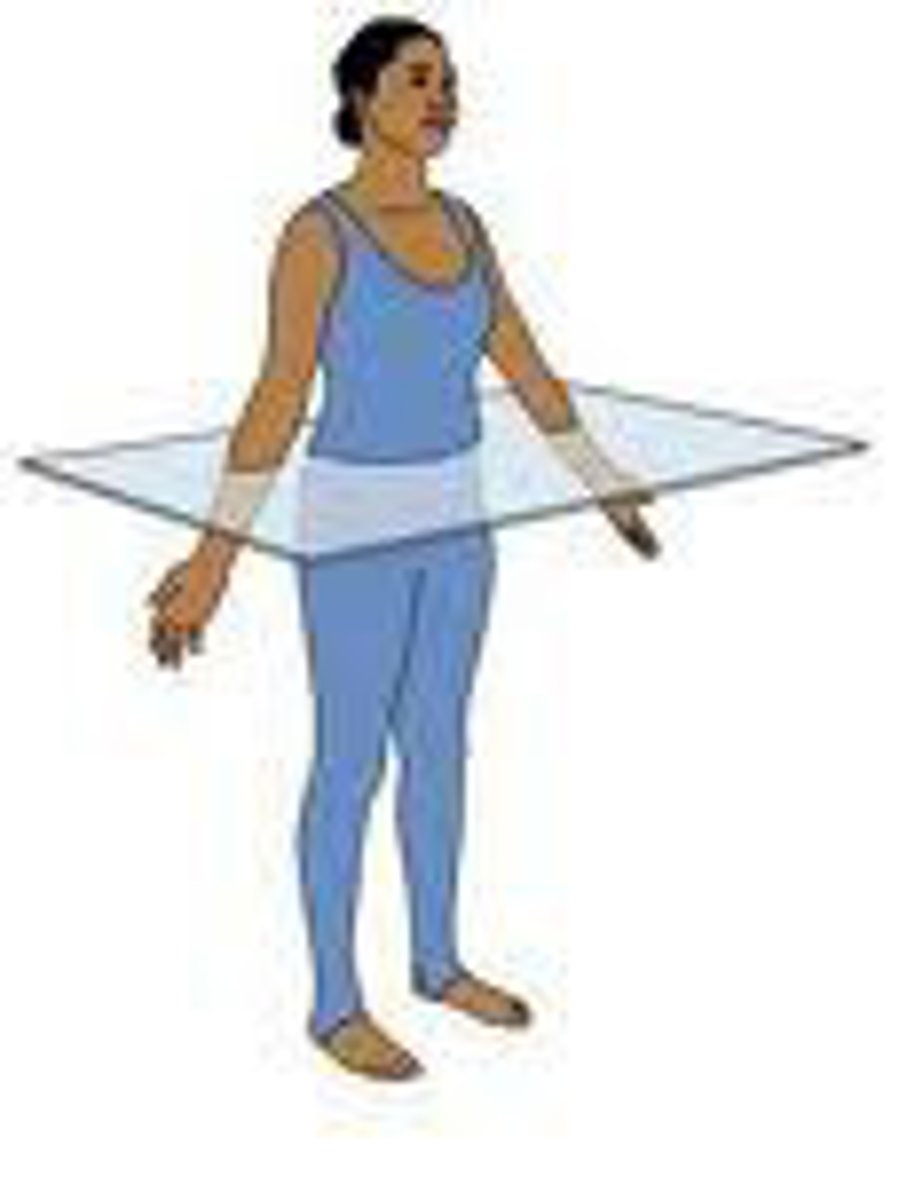
frontal plane
divides body into posterior and anterior (coronal plane)
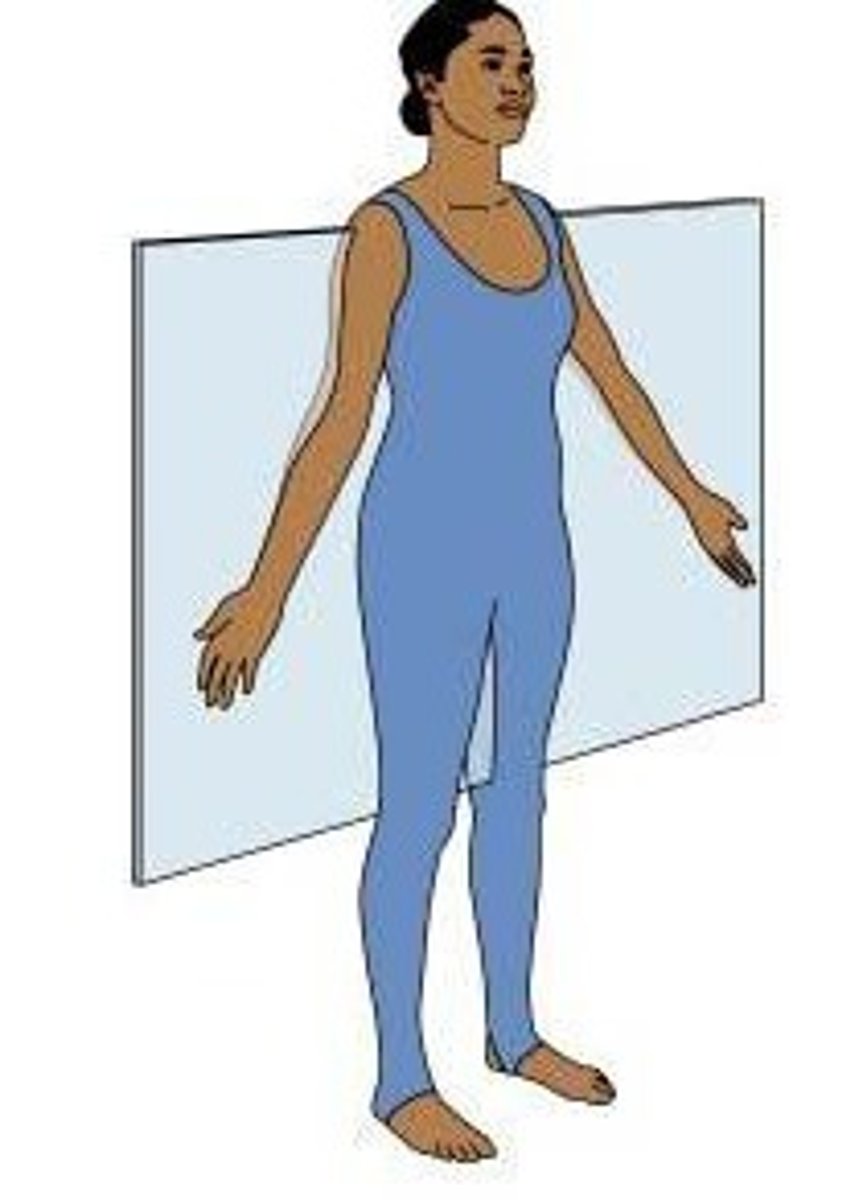
transverse (horizontal) plane
cross section, divdes body into inferior and superior
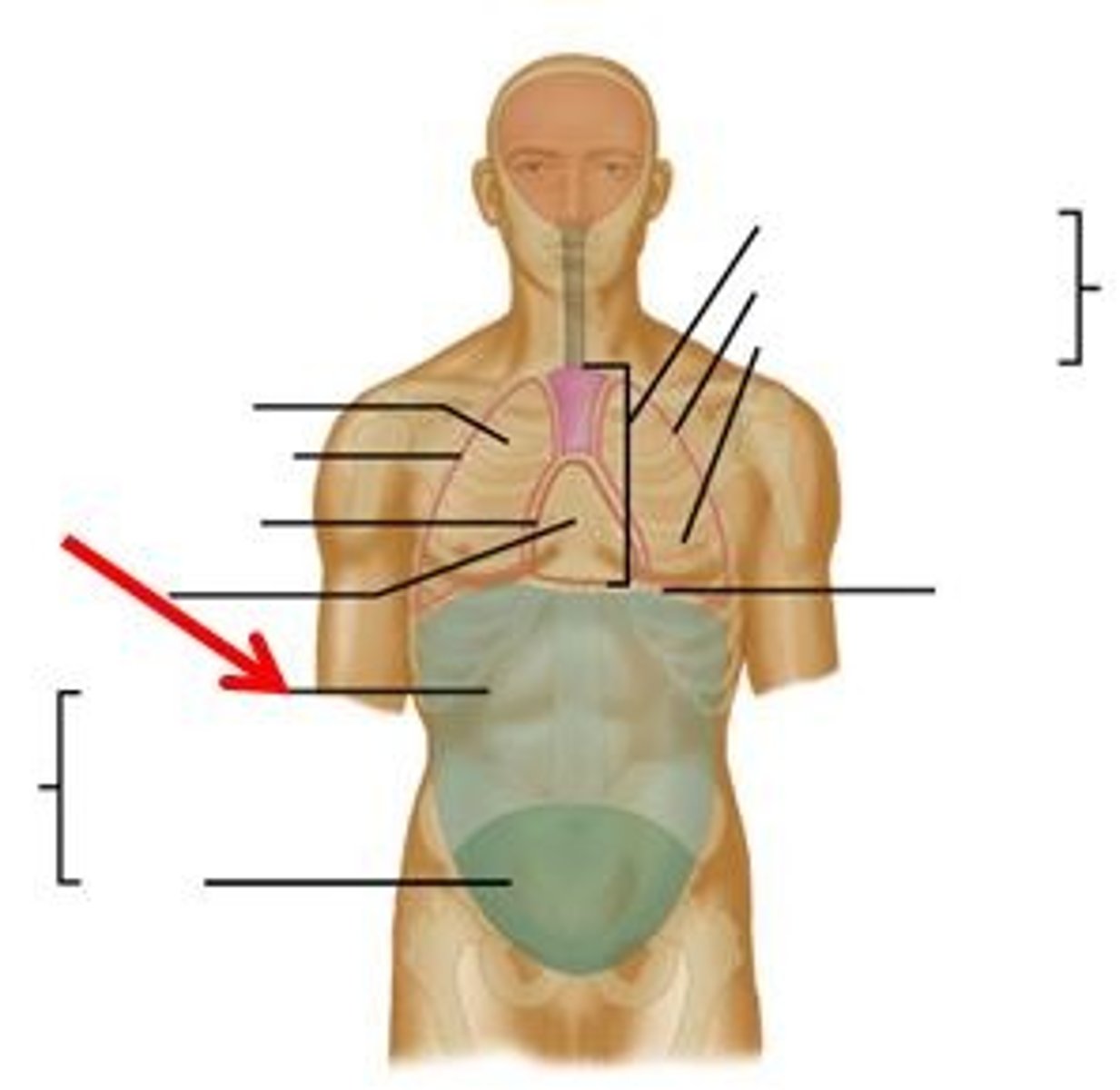
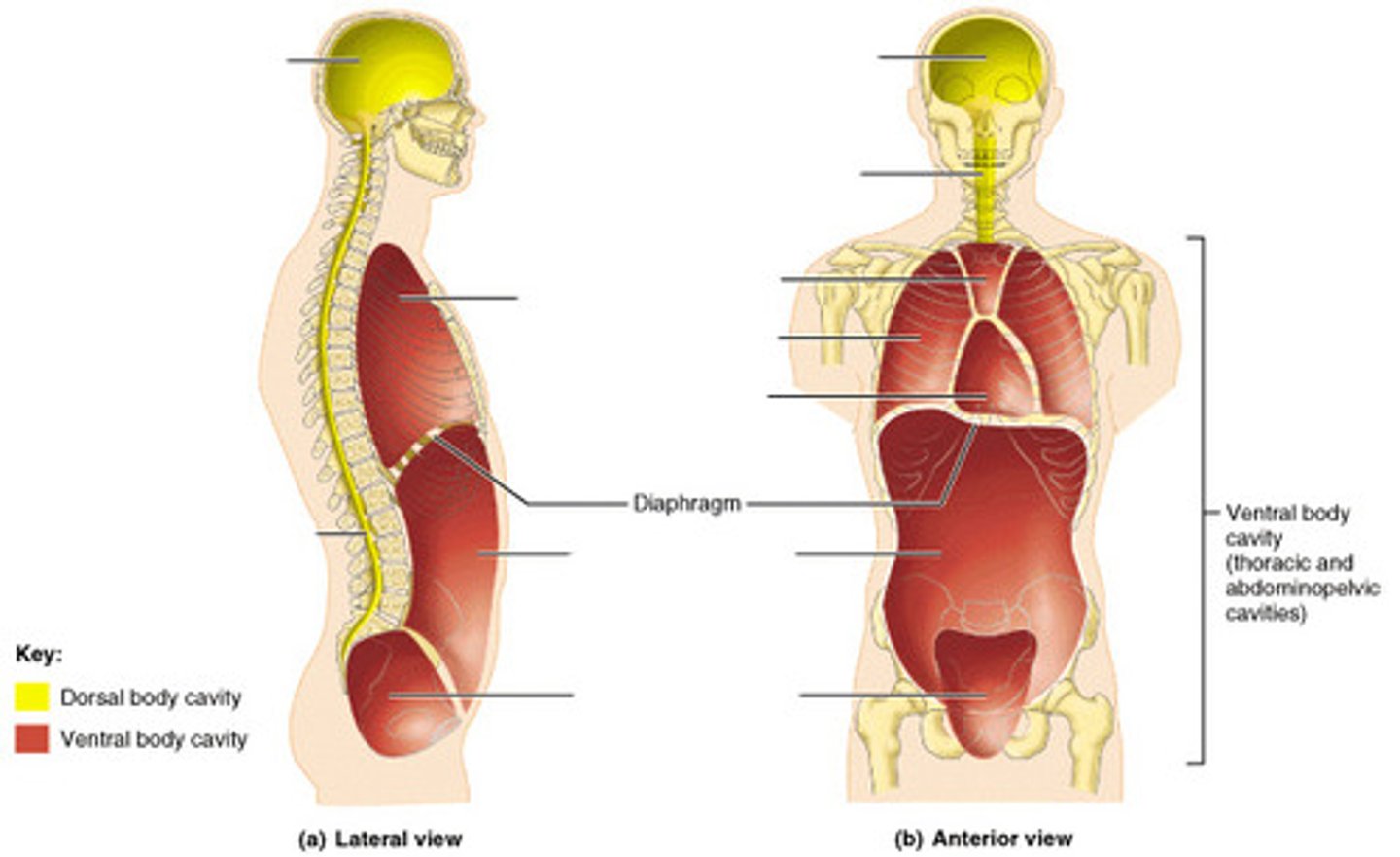
dorsal cavity
protects nervous system organs and contains cranial and vertebral cavity
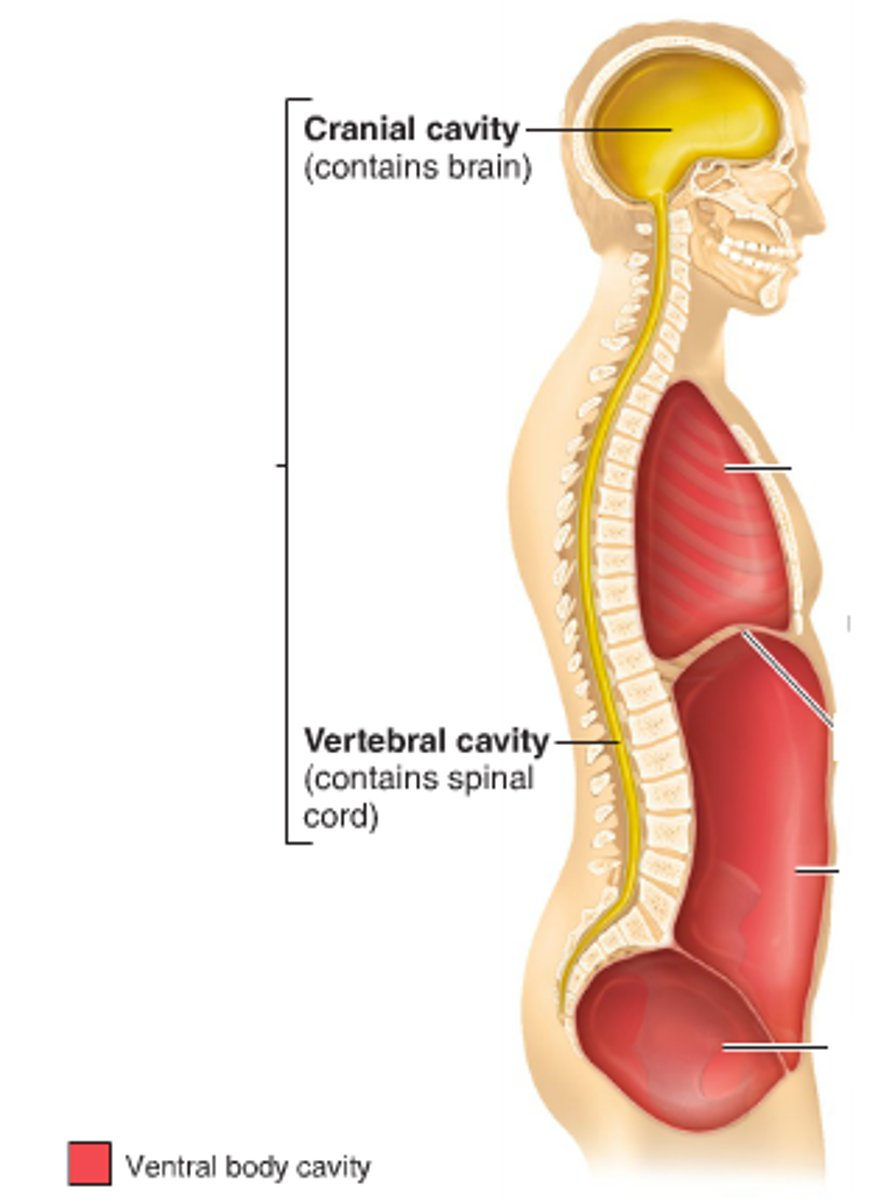
thoracic cavity
cavity containing the heart and lungs
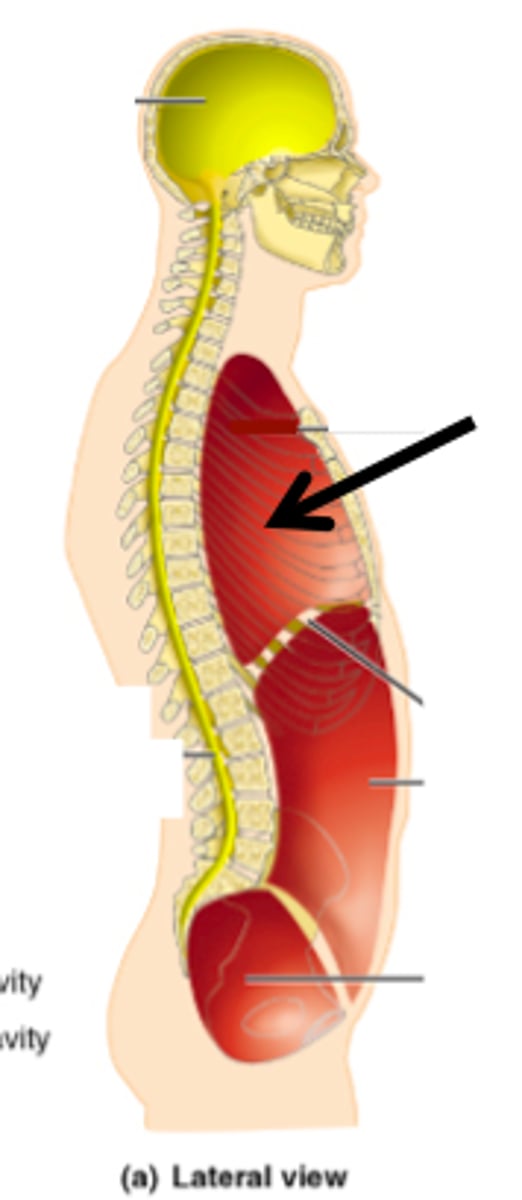
ventral body cavity
cavity containing the thoracic and abdomino-pelvic cavities
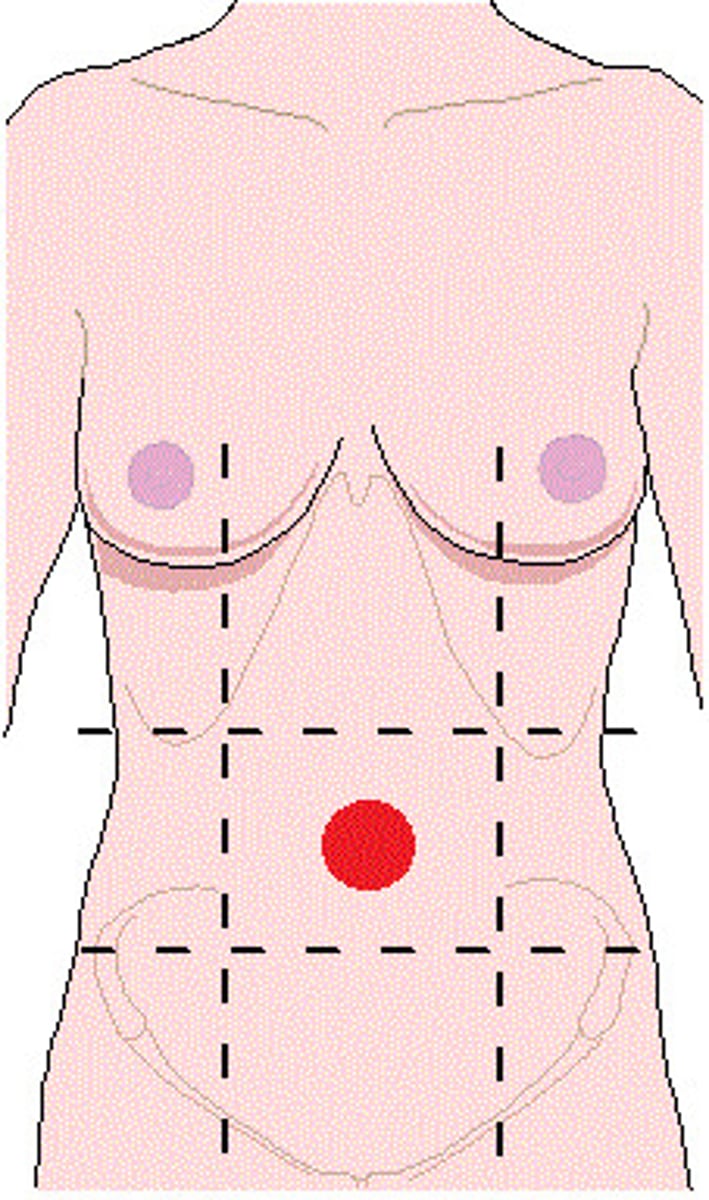
umbilical region
center most region of abdomen
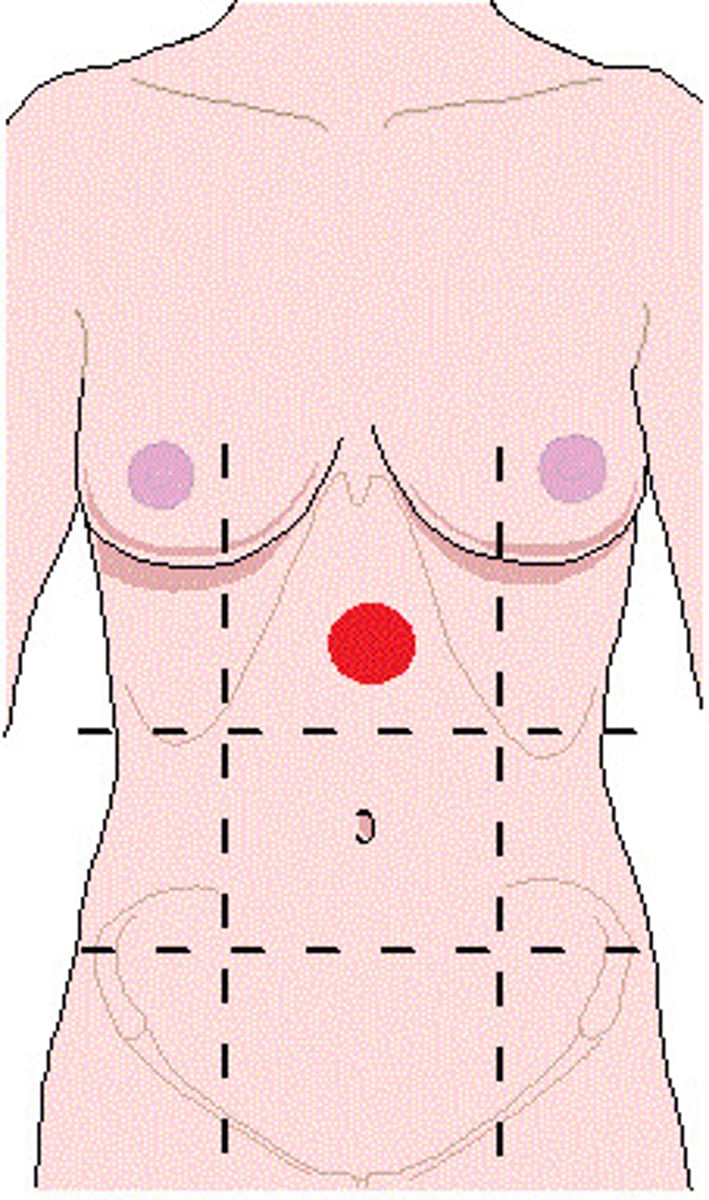
epigastic region
superior to umbilical region
hypogastric region
inferior to the ubilical region in the abdomen