Quiz 8- Articulations Lecture
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Connective tissue sacs lined with synovial membrane that act as cushions in places where friction develops are called ________.
bursae
ligaments
tendons
menisci
bursae
Which of the following are cartilaginous joints?
sutures
gomphoses
synchondroses
syndesmoses
synchodorses
Bending your head back until it hurts is an example of ________.
circumduction
extension
hyperextension
flexion
hyperextension
A fibrous joint that is a peg-in-socket is called a ________ joint.
suture
syndesmosis
gomphosis
synchondrosis
gomophosis
The cruciate ligaments of the knee ________.
attach to each other in their midportions
tend to run parallel to one another
prevent hyperextension of the knee
are also called collateral ligaments
prevent hypertension of the knee
Articular cartilage found at the ends of the long bones serves to ________.
produce red blood cells (hemopoiesis)
form the synovial membrane
attach tendons
provide a smooth surface at the ends of synovial joints
provide a smooth surface at the ends of synovial joints
The type of joint between the carpal (trapezium) and the first metacarpal is a ________ joint.
plane
condylar
hinge
saddle
saddle
Moving your jaw forward, causing an underbite, is called ________.
protraction
pronation
retraction
adduction
protraction
Presence of a synovial cavity, articular cartilage, synovial membrane, and ligaments are characteristics of what type of joint?
symphysis
synchondrosis
hinge joint
suture
hinge joint
Which ligament of the knee initiates the knee-jerk reflex when tapped?
the lateral patellar retinacula
the patellar ligament
the extracapsular ligament
the medial patellar retinacula
the patellar ligament
Saddle joints have concave and convex surfaces. Identify a saddle joint
of the skeleton.
metacarpophalangeal joint of the finger
interphalangeal joint of the finger
carpometacarpal joint of the thumb
carpometacarpal joint of the phalanges
carpometacarpal joint of the ring finger
carpometacarpal joint of the thumb
Only examples are the teeth in alveolar sockets where fibrous connection is found in the periodontal ligament that holds tooth to its socket.
Gomphosis
Synchondroses
Symphyses
Suture
Syndesmosis
gomphosis
All of the following are factors that influence synovial joint stability EXCEPT?
arrangement and tension of the muscles
arrangement and tension of the ligaments
structure and shape of the articulating bone
number of bones in the joint
strength and tension of joint ligaments
number of bones in the joint
A joint united by fibrocartilage tissue that usually permits a slight degree of movement is a ________.
syndesmosis
bursae
symphysis
gomphosis
suture
symphysis
Antibiotic treatment would be recommended for ________.
dislocation
rheumatoid arthritis
Lyme disease
osteoarthritis
gout
lyme disease
Movement in two planes is defined as:
Multiaxial
Nonaxial
Uniaxial
Gliding
Biaxial
biaxial
Fibrocartilage separates articular surfaces to improve “fit” of bone ends, stabilize joint, and reduce wear and tear:
Menisci
Articular cartilage
Fatty pads
Joint cavity
Articular cartilage
menisci
A fluid-filled sac or saclike cavity, especially one countering friction at a joint. It is described as a tiny water balloon with only a few drops of fluid in it, wedged between two surfaces.
synovial cavity
bursae
Joint cavity
Tendon sheath
Articular capsule
bursae
Which of the following is a true statement?
The head of the humerus articulates with the acromion process.
The lateral and medial patellar ligaments are also known as the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments
The annular ligament surrounds the head of the radius.
The rotator cuff is responsible for the flexible extensions at the elbow joint.
The greater tubercle of the humerus articulates at the coracoid process
the annular ligament surrounds the head of the radius
Flexion of the ankle so that the superior aspect of the foot approaches the shin is called ______.
plantarflexion
extension
flexion
hyperextension
dorsiflexion
dorsifelxion
Tendon sheaths can be best described by the following statement:
are extensions of periosteum
help anchor the tendon to the muscle
are lined with dense irregular connective tissue
act as friction-reducing structures
is necessary for the vascular packet to travel through
act as friction-reducing structures
Which of the following is NOT found surrounding the glenohumoral joint?
Glenoid labrum
glenohumeral ligaments
humoral cruciate ligament
humoral cruciate ligament
Which joints are correctly matched?
saddle; shoulder
wrist; saddle
interphalangeal; plane
elbow; pivot
ankle; hinge
ankle; hinge
What type of synovial joint is “E”
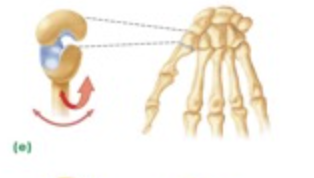
Ball and socket joint
saddle joint
Plane joint
Pivot joint
Hinge joint
saddle
The following structure is not found in the knee:
patellar ligament
Fibular collateral ligament
acromiotibular ligament
Medial patellar retinacula
lateral patellar retinacula
acromiotibular ligament