Earth Systems Lecture 7
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Magma Generation
Evidence that things may not be fixed
-Fit of current land masses
-Geological evidence (identical rocks and similar mountain ranges)
-Fossil evidence
-Paleoclimatic evidence (continental drift)
-Ocean floor bathymetry
-Paleomagnetic evidence (sea floor spreading)
-Paeleomagnetic plus dating evidence
-Direct Measurements
Continental drift
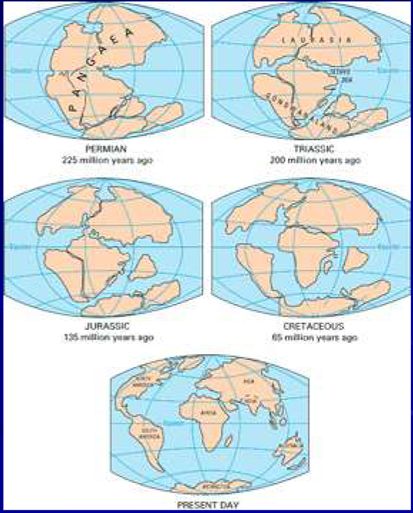
-Progressive breakup of Pangaea into modern-day continents
-Similar process to sea ice break-up
Rejection of Continental Drift Hypothesis
-No evidence of continents “breaking through” oceanic crust
-Driving mechanism unclear
Tectonic Plates of Earth
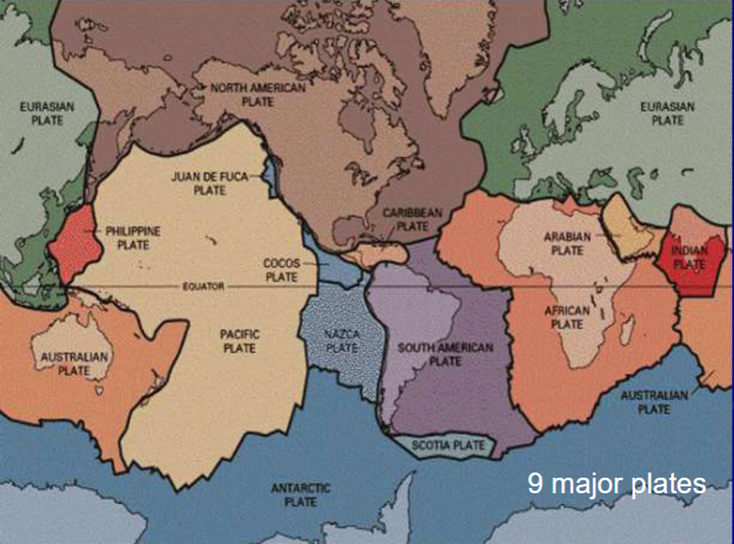
Plates are “rigid” - resist internal deformation
Differential movement concentrated at their margins
Three types of lithospheric plate:
– Oceanic
– Continental
– Both (with an internal passive margin)
Three types of active plate margin:
– Divergent (constructive or rifting)
– Convergent (subduction, collisional or destructive)
– Transform
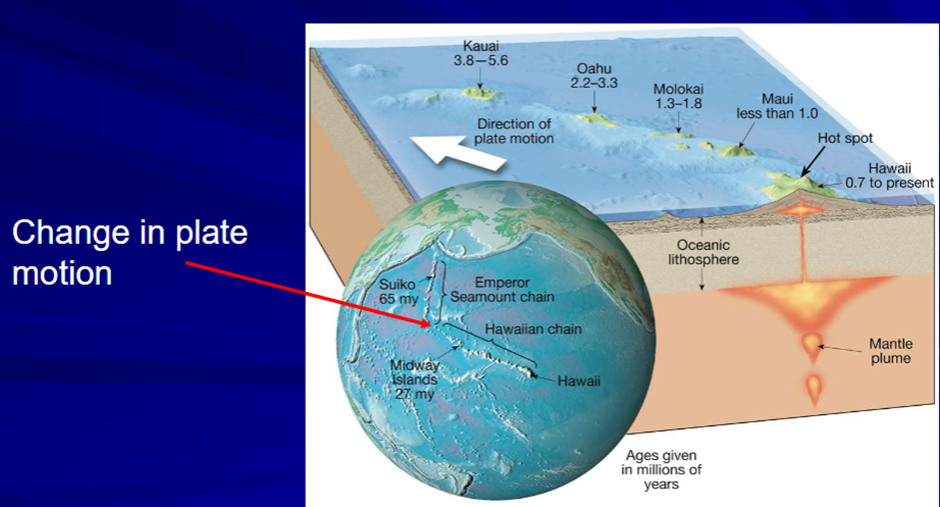
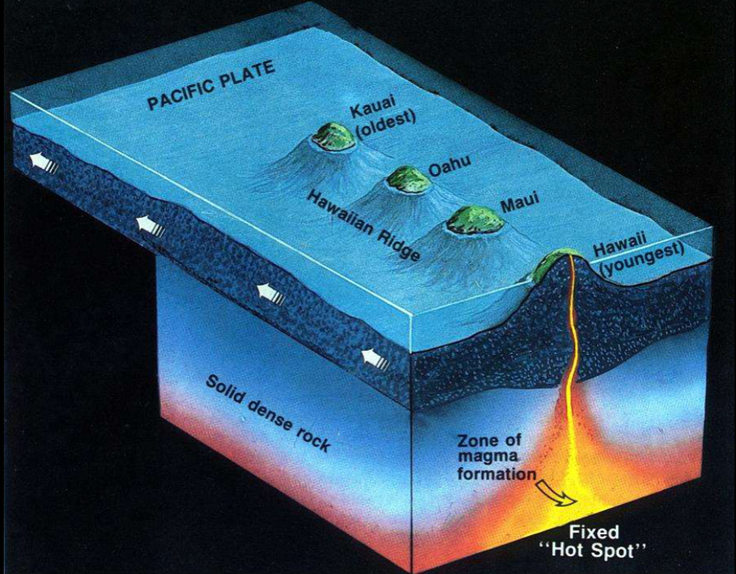
Hot Spots
-Caused by mantle plumes
-Plumes do not move, plates do
-Hawaiian Islands: Bend at 40Ma
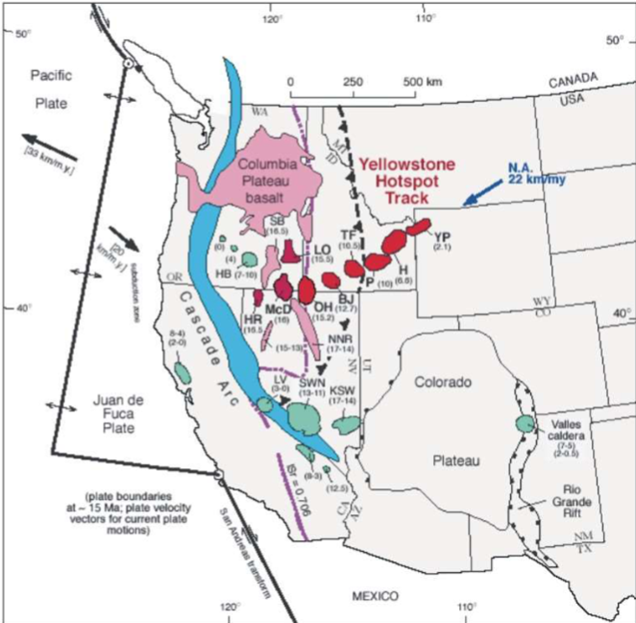
Supervolcano- Yellowstone
Yellowstone is an intra-plate volcano. Over the past 17 Ma, successive eruptions have
erupted lava over 5 states, forming a string of calderas as the North American plate moves across a stationary hotspot.
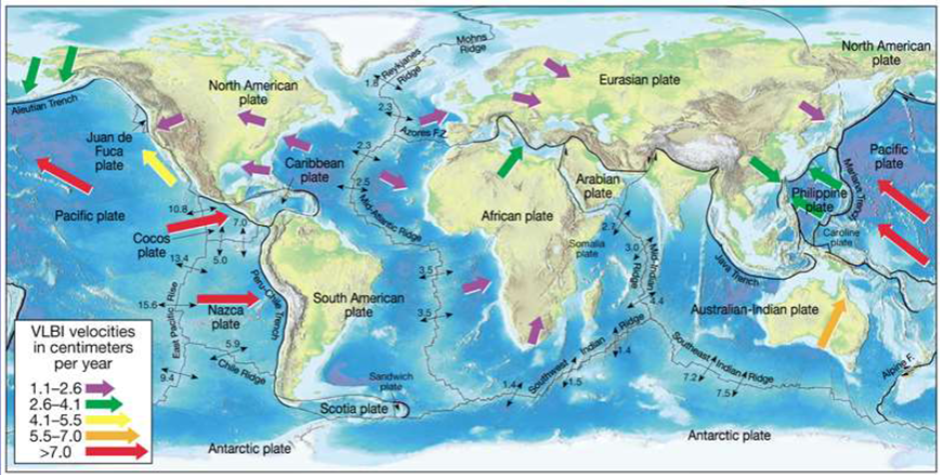
Relative Plate Motions
Measured relative to Hot Spots & other plates using palaeo-magnetism
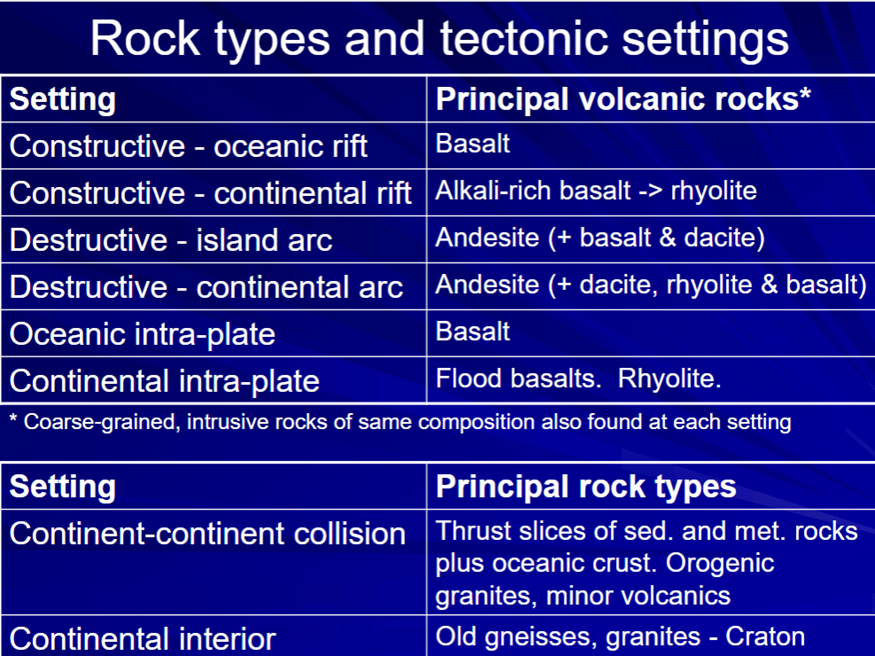
Rock Types and Tectonic Settings
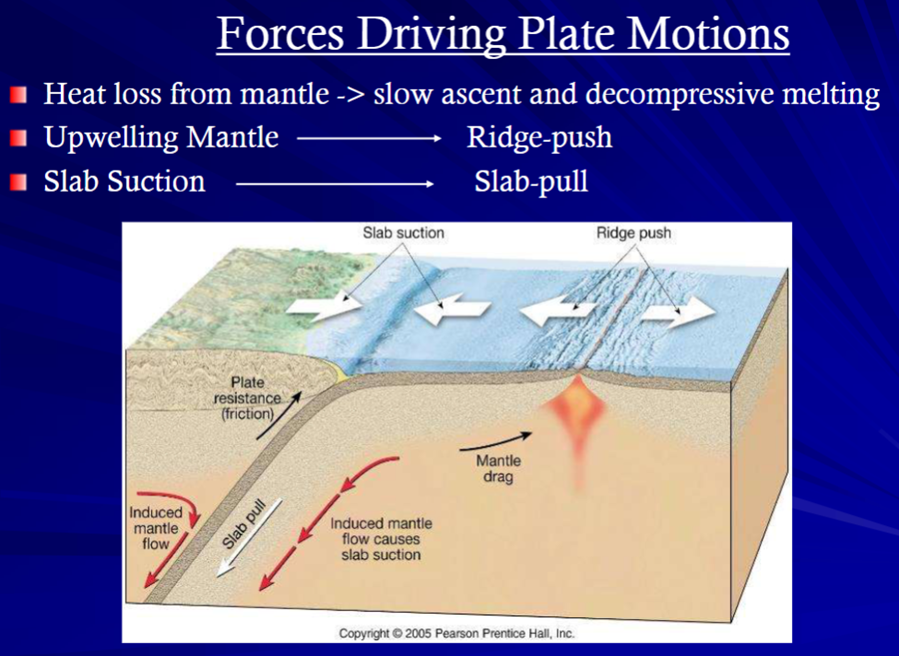
Forces Driving Plate Motions
Importance of Plate Tectonics
First holistic model that explains Earth’s dynamics and heat loss:
–Distribution of earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain ranges, trenches
–Spatial distribution of rocks – e.g. volcanic rocks at plate margins
–Distribution of mineral resources
–A key driver in the evolution, radiation and extinction of species – past and present.
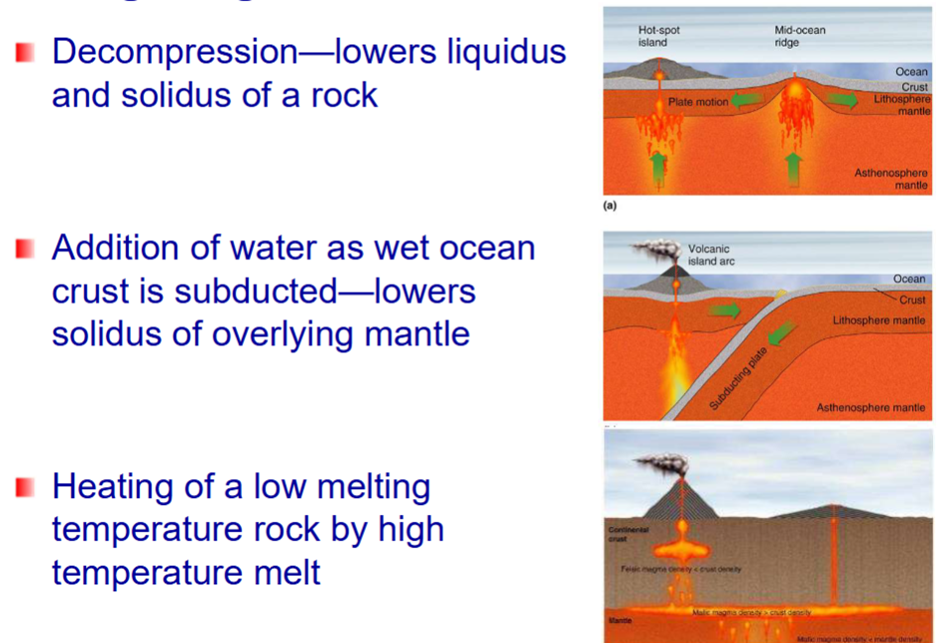
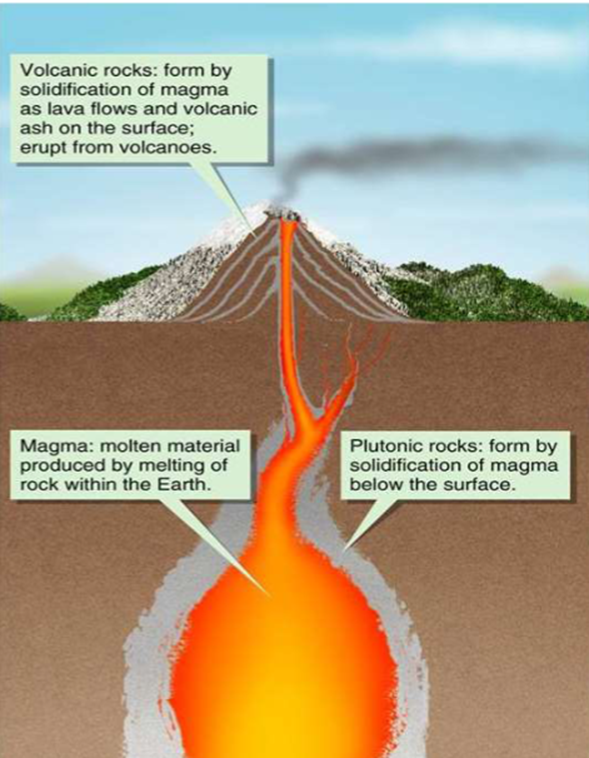
Igneous Processes
-melting of rock to form magma
-solidification into rock.
Environments in which Igneous Rock Forms
–Plutonic environment. Crystallisation below the surface in plutonic bodies. Slow cooling gives coarse-grained rocks.
–Volcanic environment. Crystallisation at the surface as volcanic eruptions produce lava and pyroclastics. Rapid cooling produces fine-grained or glassy rocks.
Form from molten magma
-Volcanic rocks above ground (extrusive or explosive)
-Plutonic below ground (intrusive)
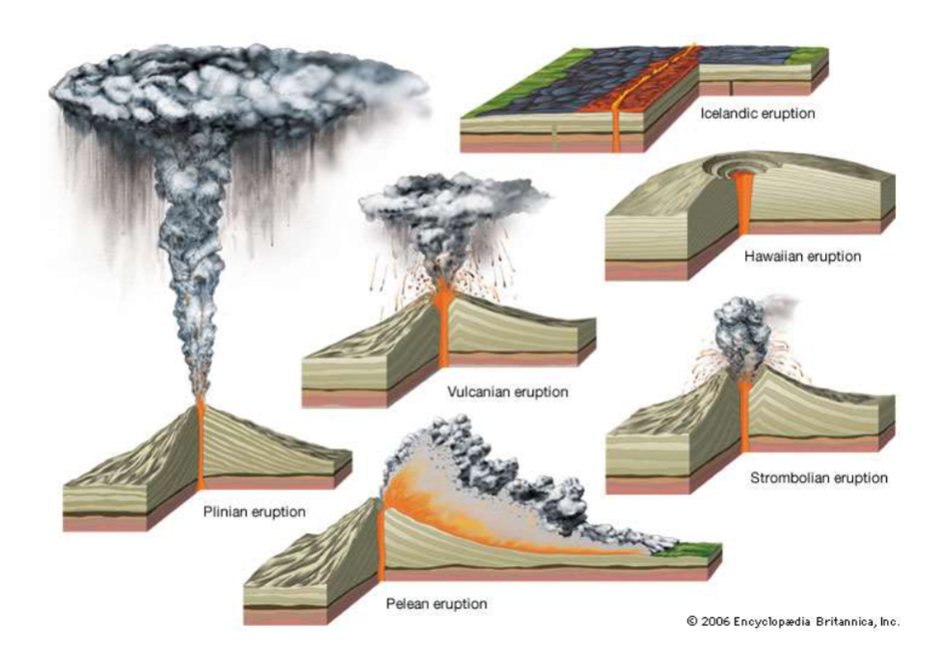
Types of Volcanoes


Gas content and Viscosity
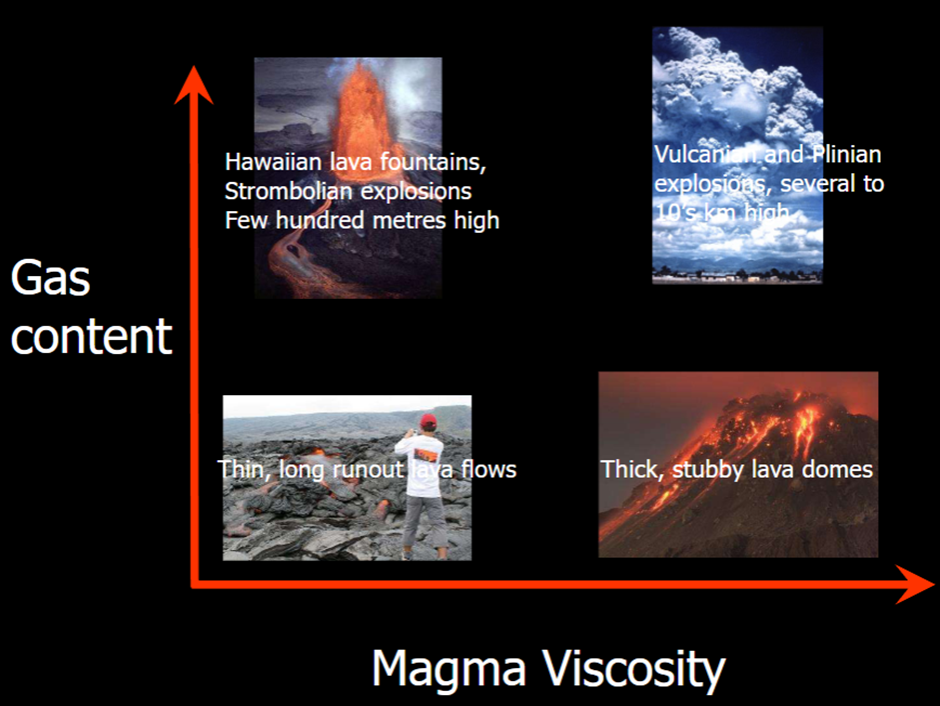
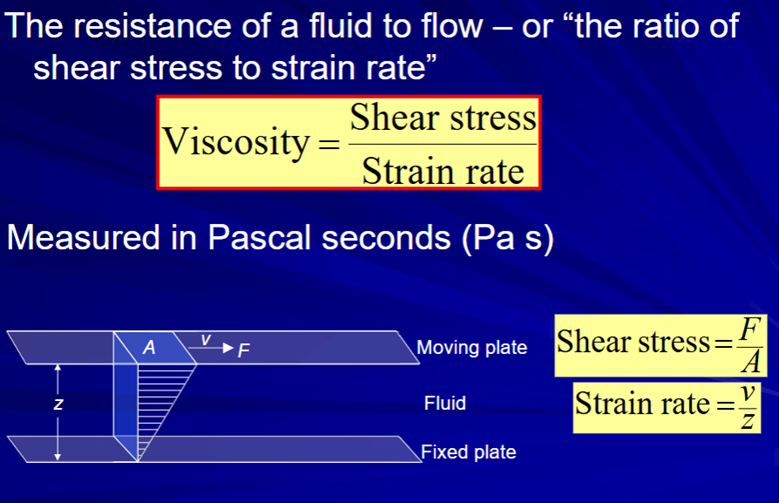
Viscosity of lavas and common fluids
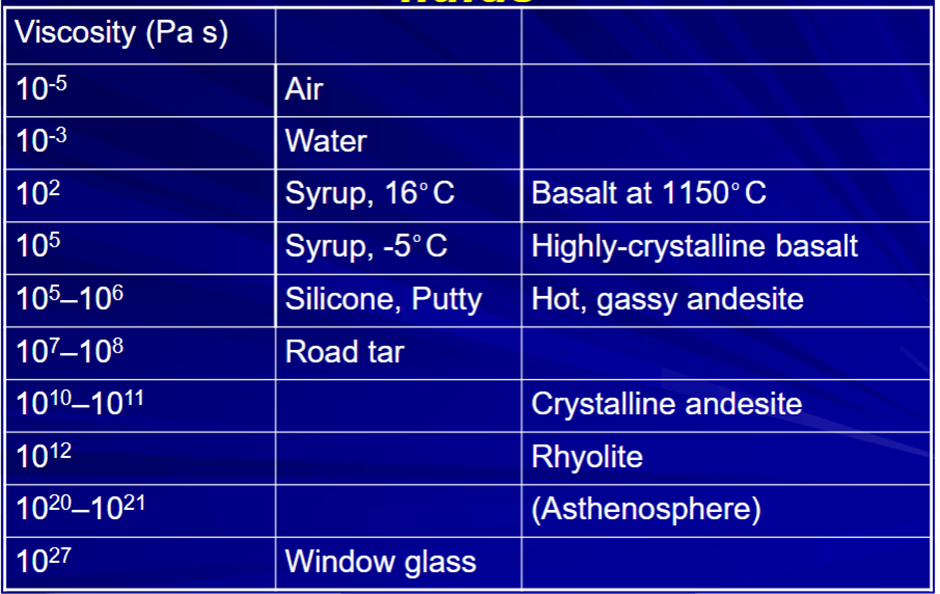
Viscosity is a controlling factor in many processes

Stokes law- gas escape


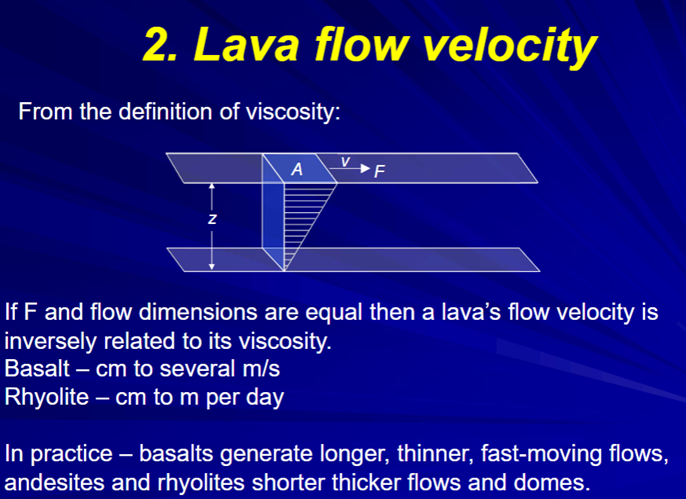
Lava flow velocity
What controls magma viscosity

Explosive eruptions
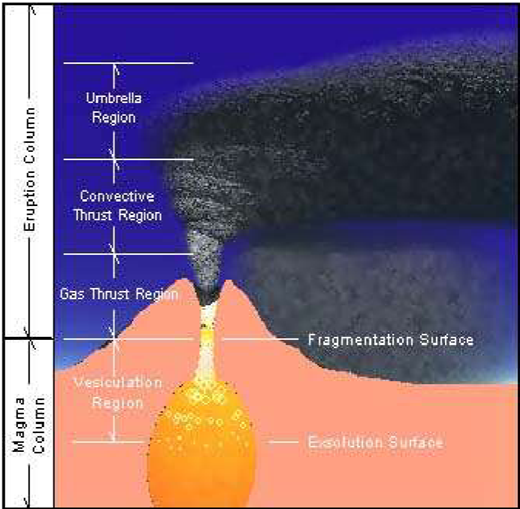
Fragmentation of magma yields a spray, or jet, of liquid (magma), gas and particles (crystals) from the vent.
Explosiveness tends to be low in low viscosity, such as basalts—and much higher in silicic magmas (Plinian eruptions generally involve silicic magma).
Strombolian eruptions
Short-lived, explosive outbursts of lava ejected a few tens or hundreds of meters into the air.
Lava fragments travel in parabolic ballistic paths before accumulating around the vent to construct the volcanic edifice.
Typically, these eruptions form scoria cones.
Vulcanian Eruptions
Canon-like explosions that are short-lived, with high- velocity ejections of bombs and blocks.
Plinian explosion
Gases dissolved in magma are the driving force behind volcanic explosions. When
magma at 900 C with 5 wt% of dissolved water, is suddenly brought from depth
to the surface……the magma would increase in volume by 670 times.
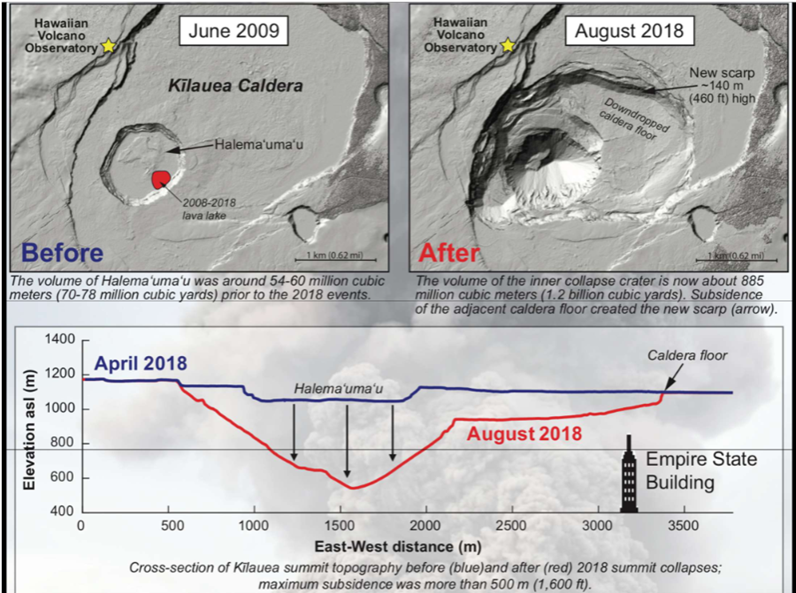
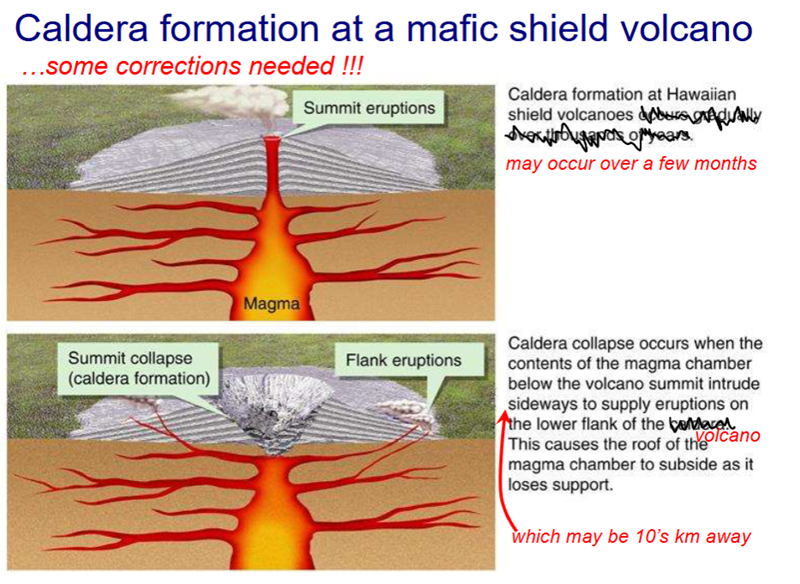
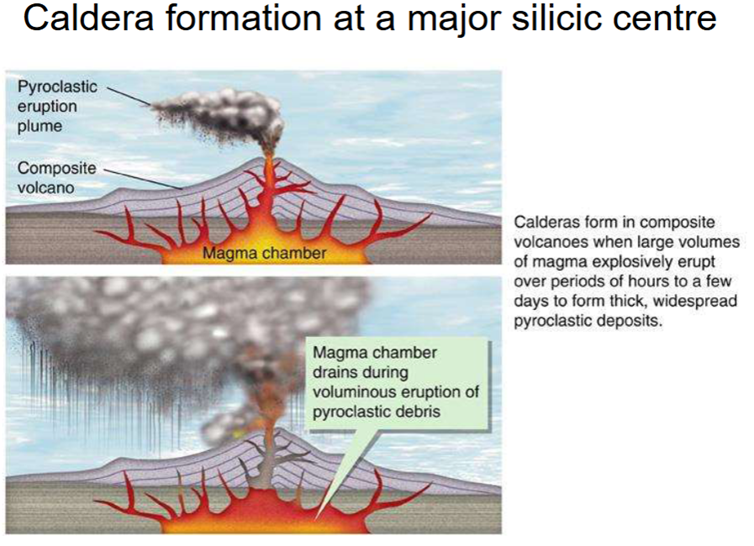
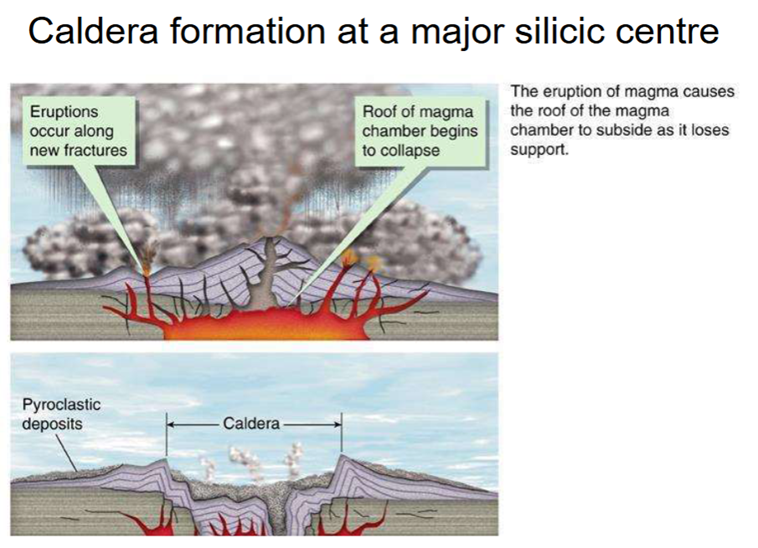
Caldra forming eruptions
Associated with the biggest volume eruptions and involve the structural collapse of the
volcano due to the volume of magma evacuated
Form a summit depression, nominally greater than 1 mile across.