Ch 2 The Muslim World Expands
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Ghazis
Warriors for Islam

Osman
tribal leader who captured the Byzantine city of Bursa; the Ottoman Empire's name is derived from his

Ottomans
Turkic people who advanced from strongholds in Asia Minor during 1350s; conquered large part of Balkans; unified under Mehmed I; captured Constantinople in 1453; established empire from Balkans that included most of Arab world.
Sultan
Muslim ruler
Timur the Lame
Conquerer from Samar-kand who burned Baghdad down and crushed Ottomans at Battle of Ankara

Mehmed II
Ottoman sultan called the "Conqueror"; responsible for conquest of Constantinople in 1453; destroyed what remained of Byzantine Empire.
had a period of arts in his time with pottery, rugs, silk, other textiles, jewelry, and arms and armour being made

Constantinople
The capital city of the Byzantine Empire. It was a great location for trade because it was located along major waterways (Bosporus Strait) and it was at the crossroads of Europe and Asia.
Had a palace called Topkapi (iron gate)
served as the private residence of the ruler and his family

Suleyman I
Ruler of the Ottomans also known as the Magnificent. The height of the Ottoman Empire was achieved under Suleyman. Reformed taxes, overhauled the government bureaucracy, also improved Court System (law giver).
believed in relious tolerence
had unique architectural designs

Devshirme
Ottoman policy of taking boys from Christian peoples to be trained as Muslim soldiers
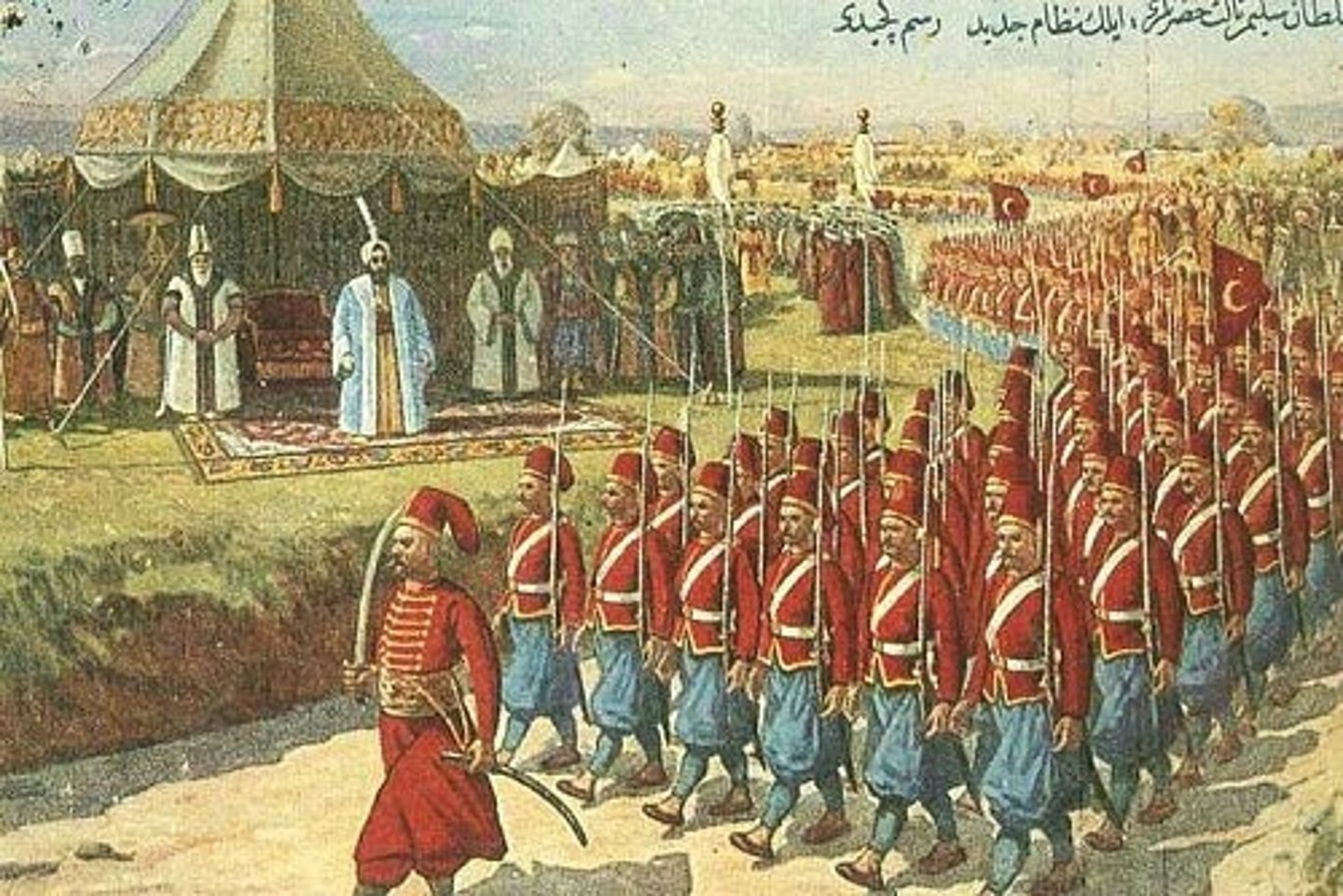

Janissaries
Infantry, originally of slave origin, armed with firearms and constituting the elite of the Ottoman army from the fifteenth century until the corps was abolished in 1826.

Millets
Communitites within the Ottoman Empire where Christians & Jews were allowed to follow their own culture, religion and land.
The Mosque of Suleyman
Combines tall, slender minarets with large domed buildings in the style of the Hagia Sophia.

Cultural Blending
this interaction of two or more cultures produces new languages and new ideas in art religion and society
paintings in the Mogols included Indian and Persian styles
The Safavid Empire
An empire that was a result of cultural blending. This empire drew from the traditions of Persians, Ottomans and Arabs
are Shias muslims
it blended Persian, Turkish, and Mongol cultures
Isma'il
A great Safavid ruler who, at the age of 14, conquered much of the territory that became the Safavid Empire. He was a religious tyrant who made Shi'ia the state religion.
first shah of the safavids

Shah
The title given to kings who ruled Iran
shahs declared Shia Islam to be a state religion
very strong minded and could talk with people with great familiarity
appointed people i government based on merit than birth.
played an active part in trade and manufacturing activity
Shah Abbas
A Safavid king of Persia who centralized government, created a powerful military, encouraged the growth of industry and reduced taxes of farmers/herders
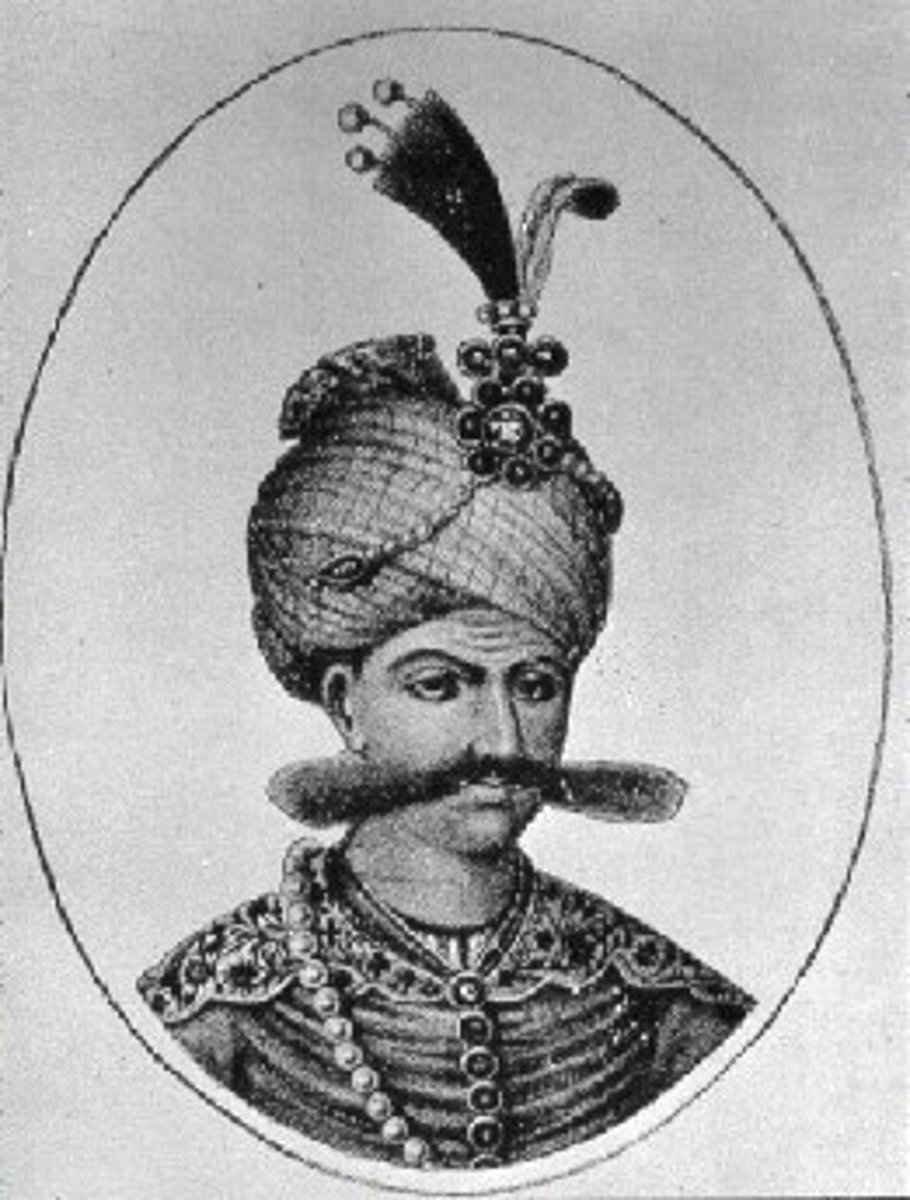

Golden Age of the Safavid Empire
The empire was able to establish a relationship with Christians and other members of the European community. They established trade, invited Chinese artists, and established a strong government.
Esfahan
Safavid capital built by Shah Abbas
the new capitial of Safavids.
Tabriz was the first one
Mughals
Islamic dynasty that ruled India from the sixteenth through the eighteenth centuries; the construction of the Taj Mahal is representative of their splendor; with the exception of the enlightened reign of Akbar, the increasing conflict between Hindus and Muslims was another of their legacies.
Babur
Founder of Mughal dynasty in India; descended from Turkic warriors; first led invasion of India in 1526; dies in 1530
captured Delhi
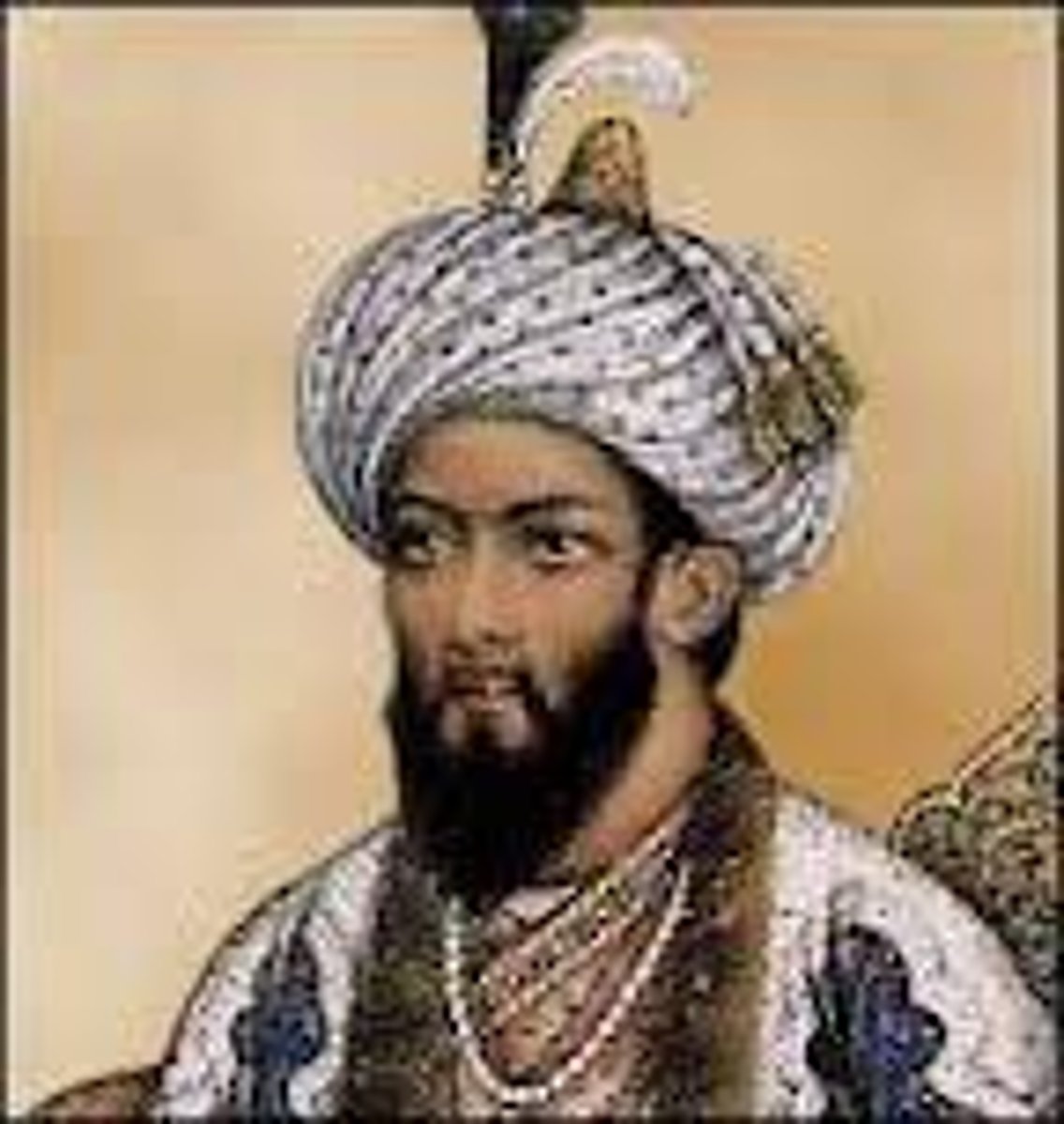

Akbar
Grandson of Babur only 14 when took the throne
Most illustrious sultan of the Mughal Empire in India (r. 1556-1605). He expanded the empire and pursued a policy of conciliation with Hindus.
adopted religious tolerence

Miniatures
Small individual Indian paintings intended to be held in the hand and viewed by one or two individuals at one time.
Sikhs
Nonviolent religious group that blended Buddhism, Hinduism and Sufism
Shah Jahan
Mogul emperor of India during whose reign the finest monuments of Mogul architecture were built (including the Taj Mahal at Agra) (1592-1666)
Mumtaz Mahal
The translation of her name means "the beloved ornament of the palace" and she was the inspiration behind the construction of the Taj Mahal.
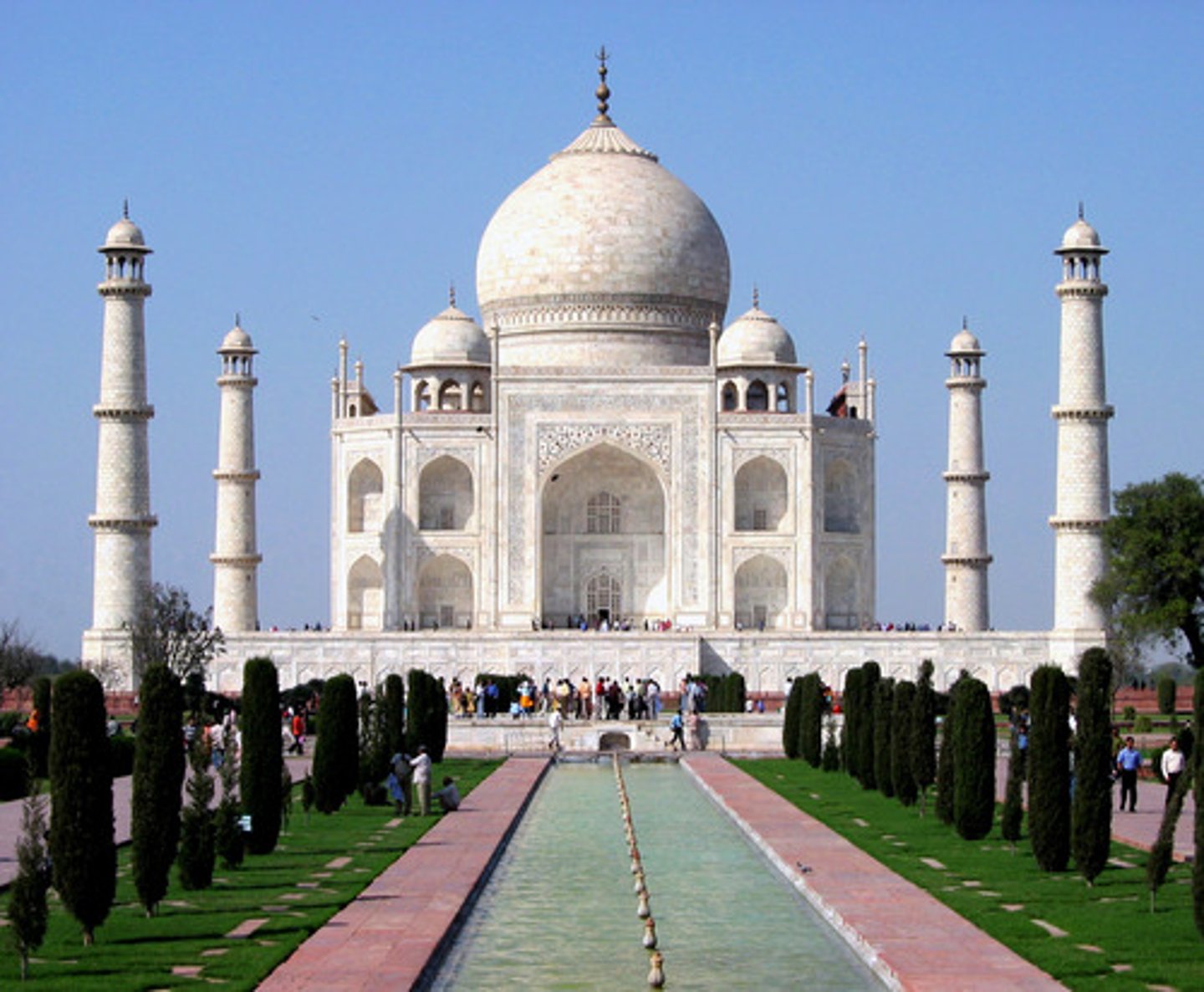
The Taj Mahal
A monument made by Shah Jahan for his wife who died during child birth
built in Agra in mid 17th century

Aurangzeb
Mughal emperor in India and great-grandson of Akbar 'the Great', under whom the empire reached its greatest extent, only to collapse after his death.
the most controversial ruler
forbade gambling and drinking
added taxes on non-muslims
prohibited new indian buildings in trying to get more Muslims
didn’t believe in religious tolerence
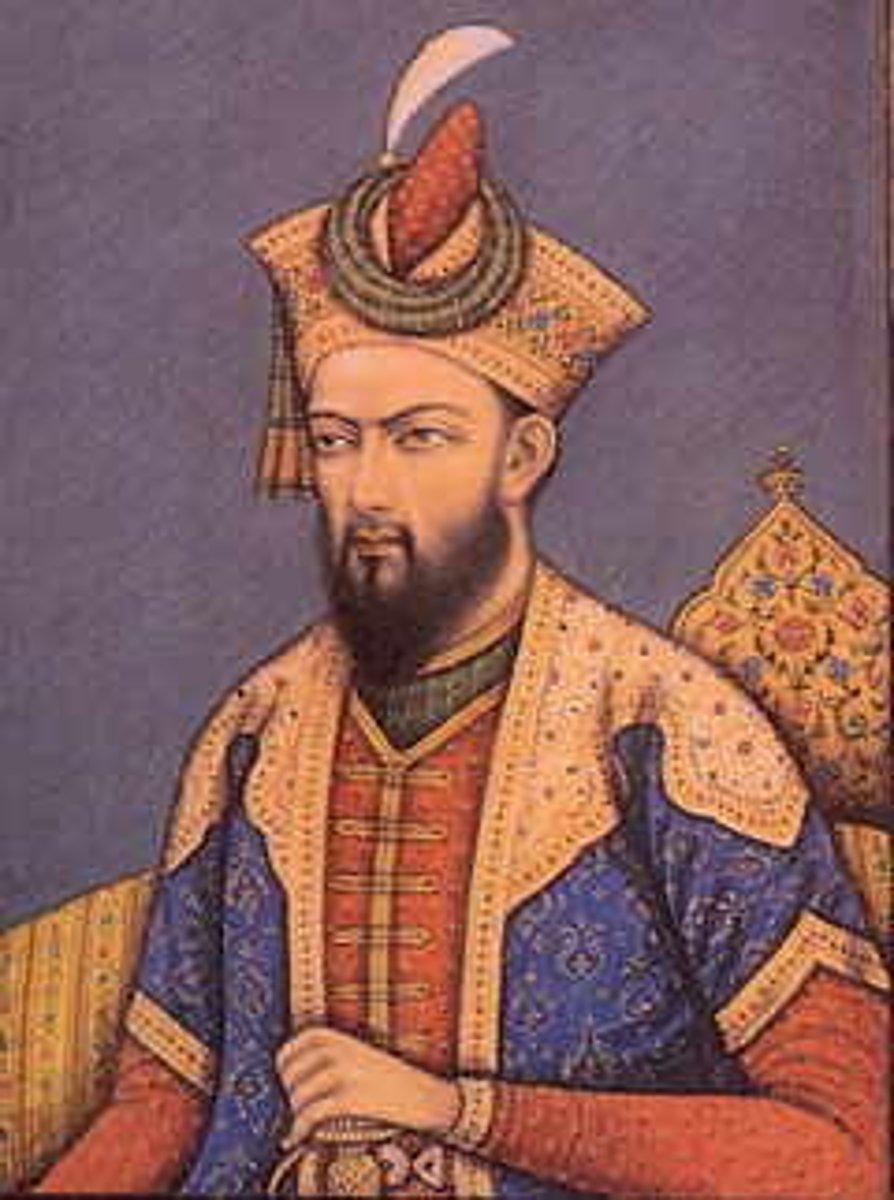

Selim the Grim
Ottoman sultan who conquers the Safavids in 1514; he also conquers Mecca, Medina, and Cairo
Battle of Kosovo 1389
The ottomans defeated the Serbs in this
Sultan Selim I
took control of Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Arabia(the original heartland of Islam)
also took control of Jerusalem, Makkah (Mecca, Madinah (Medina)
Pashas
collected taxes, maintained law and order, responsible to the Sultan’s court in Constantinople (for the Ottoman empire)
Harem
private domain of the Sultan. The wifes of the Sultan remained here. He usually has 4 wifes.
When the son of the mother become sultan the mother is now queen mother and is a major advisor to the throne
Grand vizier
chief minister who carried burdens of the state, led meetings of the concil.
Ottoman empire
divided into provinces and districts each governed by officals, assisted by beauaucrats who had been trained at the palace school for officals in Istanbul.
Senior officials
responsilbe for collecting taxes and supplying armies for the empire
Ulema
group of religious advisors
administered the legal system and schools for educating muslims.
Sinan
a person who built 81 mosques.
One of his famous mosques was Suleymaniye Mosque in Istanbul.
Justinian
byzantine emperor during Mehmed II rule
Bospouros
a strait of Constapotle that divides the peninsula and links the black sea with the Mediterranean.
Tabriz
a major battle between the Safavids and Ottomans which the ottomans won but then later lost control of it and the Safavids gained it back
religious othodoxy
pressure to conform to traditional beliefs
was common in the Safavid empire
Riza-i-Abbasi
most famous artist of Shah Abbas’s peroid. created exquisite works of safvid paintings
Khyber Pass
a pass into India
Zamindars
local officials who get temporary farmland
kept a portion of the taxes payed by peasants in lieu of salary
mostly hindus
Jahangir
father of Shah jahan
wife is Nur jahan
liked governing until liking his wife where the wife was given power and she used it for the family
Deccan Plateau
Shah Jahan expanded boundrais of the empire though successful campaigns in the _______ and the city of Samarqand, north of Hindu Kush.
sutte
hindu custom where people cremate a widow on her husband’s funeral pyre
Aurangzeb believed this as an Indian social evil and tried to eliminate it entirely
Kolkata
British trading forts were established in this place along with Chennai.
Robert Clive
military genius of the British who fought agisnt the French who tried to take control of the forts in Chennai
significance of capturing Constantinople in 1453
It united Ottoman territories, controlled key trade routes, and marked the end of the Byzantine Empire
Why did these empires eventually decline
Weak leadership succession, loss of trade routes to Europeans, internal rebellions, and failure to modernize military technology