NSG 3107: Neurological Conditions
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Increased intracranial pressure
Raised level of pressure within the skull above the normal and healthy level
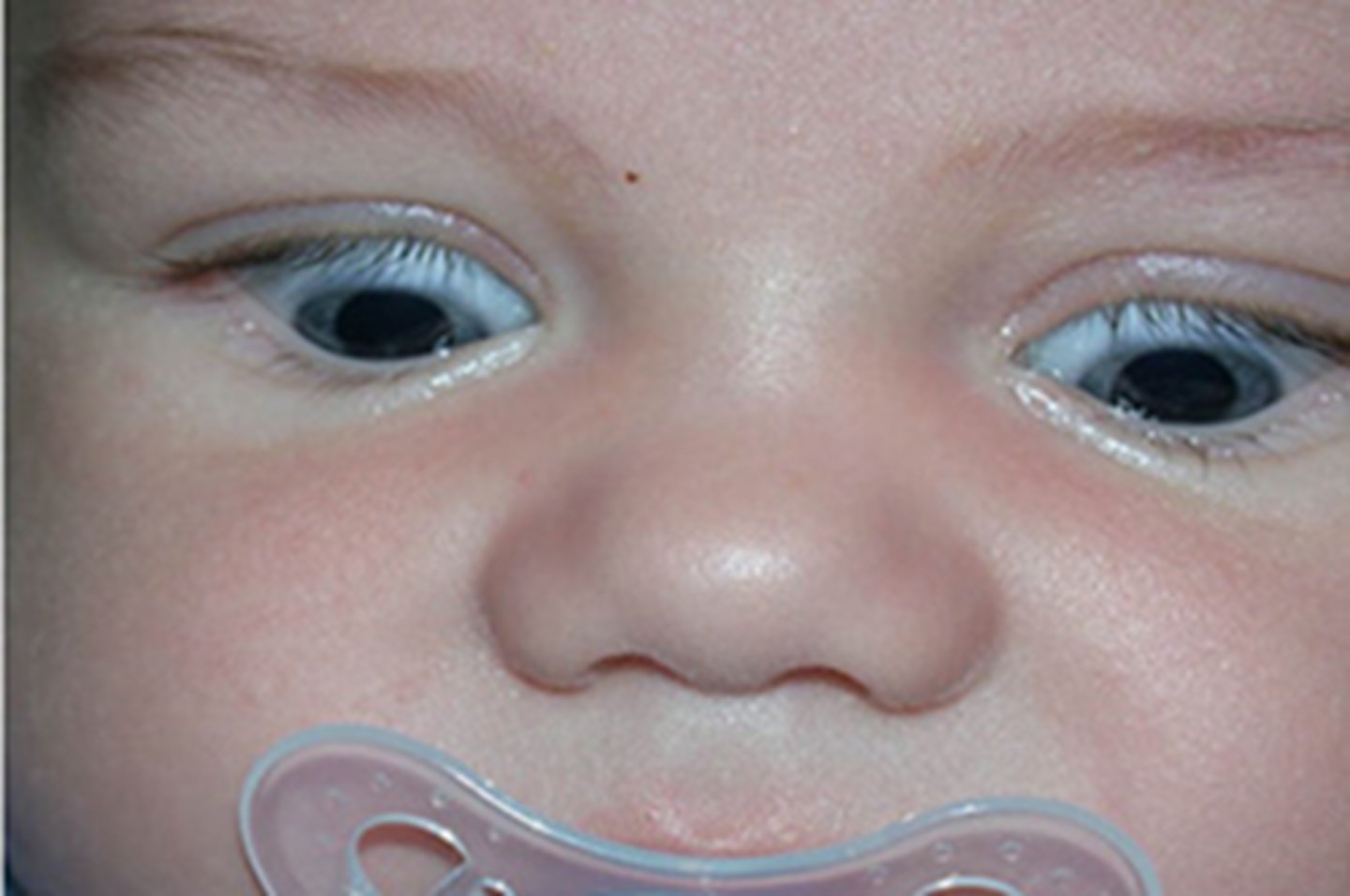
ICP signs in infants
Bulging fontanels, separated cranial sutures, irritability, drowsiness, high-pitched cry, setting sun sign
ICP signs in children
Headache, nausea, forceful vomiting, blurred vision, seizures, indifference/drowsiness, diminished physical activity
Late ICP signs
Bradycardia, decreased motor response to commands, decreased sensory response to painful stimuli, alterations in pupil size, flexion/extension, Cheyne-Stokes respirations, papilledema, decreased consciousness, coma
Consciousness
Term that implies awareness; 2 components: alertness and cognitive power
Awareness
Ability to respond to sensory stimuli and have subjective experiences
Alertness
Arousal-waking state, including the ability to respond to stimuli
Cognitive power
Ability to process stimuli and produce verbal and motor responses
Altered state of consciouness
Refers to varying states of unconsciousness that may be momentary or may extend for hours, days, or indefinitely
Unconsciousness
Depresses cerebral function; the inability to respond to sensory stimuli and have subjective experiences
Coma
State of unconsciousness from which the patient cannot be roused even with powerful stimuli
True
True or false? The earliest indicator of changes in neurological status is levels of consciousness
Full consciousness
Awake and alert; oriented to person, place, and time; behavior is appropriate for age
Confusion
Impaired decision making
Disorientation
State of mental confusion to time, place, or identity
Lethargy
Limited spontaneous movement, sluggish speech, drowsy, falling asleep quickly
Obtundation
Severe reduction in LOC; child arouses with very strong stimulus but is close to comatose state
Stupor
Remaining in a deep sleep, responsive only to vigorous and repeated stimulation or moaning responses to stimuli
Persistent vegetative state
Permanently lost function of the cerebral cortex, eyes following objects only by reflex or when attracted to direction of loud sounds; all limbs spastic but can withdraw from painful stimuli; hands showing reflexive grasping, face grimacing, some food swallowed, groaning or crying without uttering words
Pediatric GCS
3-part assessment of eyes, verbal response, and motor response
8
A score of __ or below on the pediatric GCS is generally defined as a coma
3
A score of __ indicates extremely decreased LOC and is the worst possible score on the pediatric GCS
Opiate or barbiturate poisoning
What condition are pinpoint pupils commonly observed in?
After seizures, eye trauma, or during atropine poisoning
When might widely dilated pupils be observed?
Lesion on same side
What does a unilateral fixed pupil usually suggest?
Cranial nerve VI damage
What can post-traumatic strabismus indicate?
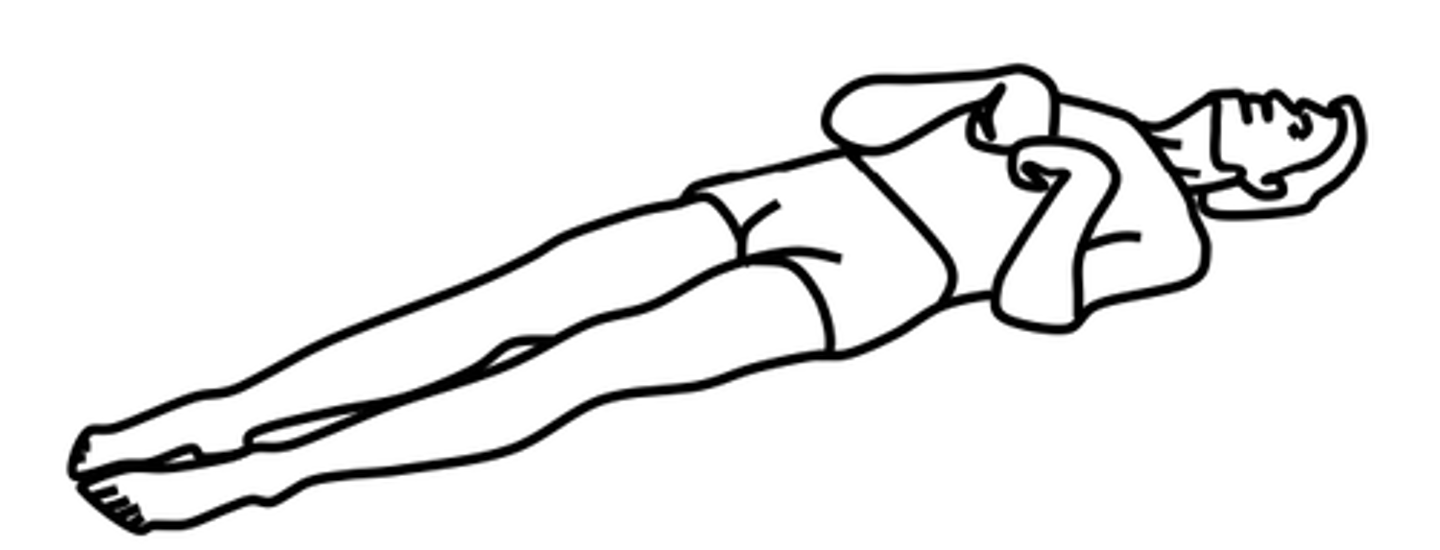
Decorticate
Flexion posturing; seen with severe dysfunction of the cerebral cortex or with lesions to corticospinal tracts above brainstem
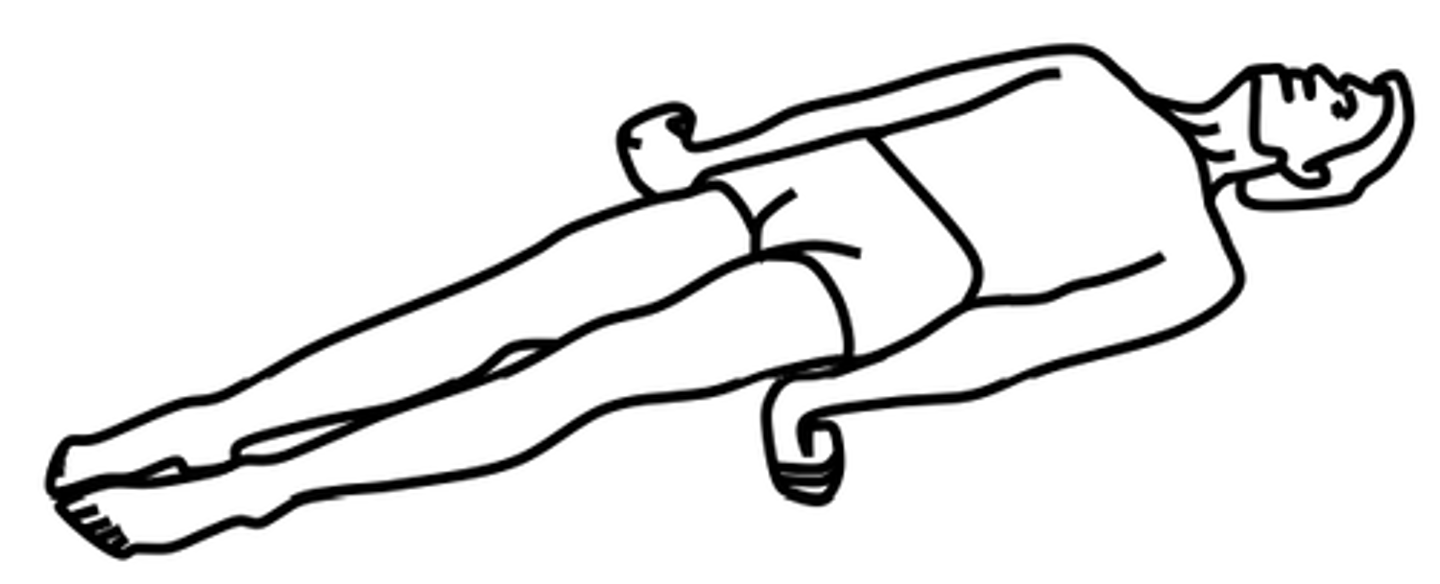
Decerebrate
Extension posturing; sign of dysfunction at level of midbrain or lesions to brainstem
Electroencephalogram
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface; measured via electrodes placed on the scalp
4 minutes
Cerebral hypoxia lasting more than ______ may cause irreversible damage
Indications for ICP monitoring
GCS of <8 OR GCS eval >8 but with respiratory assistance, deteriorating neurological condition, subjective judgement regarding clinical appearance and response
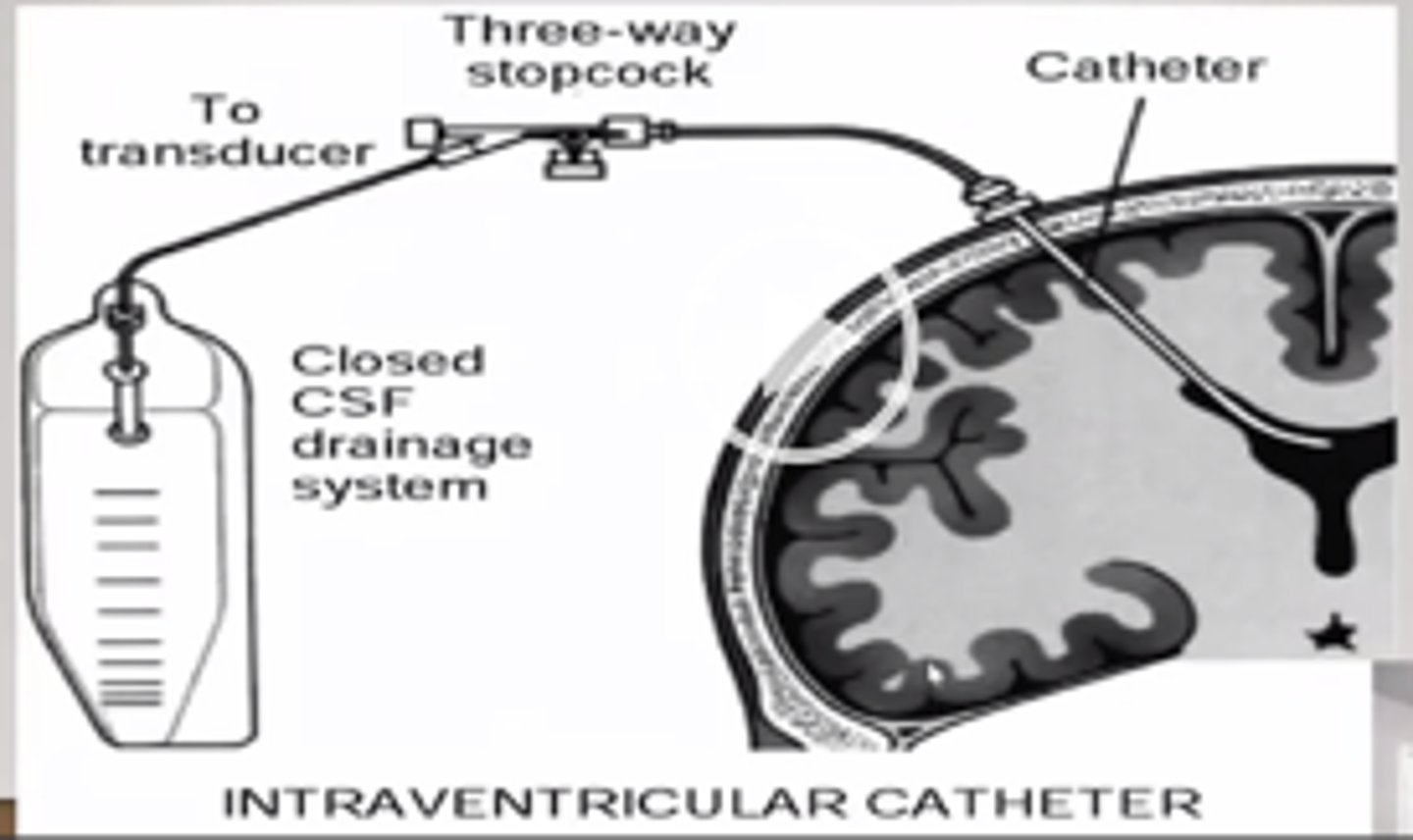
Intraventricular catheter
Gold standard of ICP monitoring; burr hole in skull allows entry into lateral ventricle on nondominant side; provides means for recalibration when measurement drift occurs
Subarachnoid bolt
Device placed in subarachnoid space and epidural sensor is placed between dura and skull
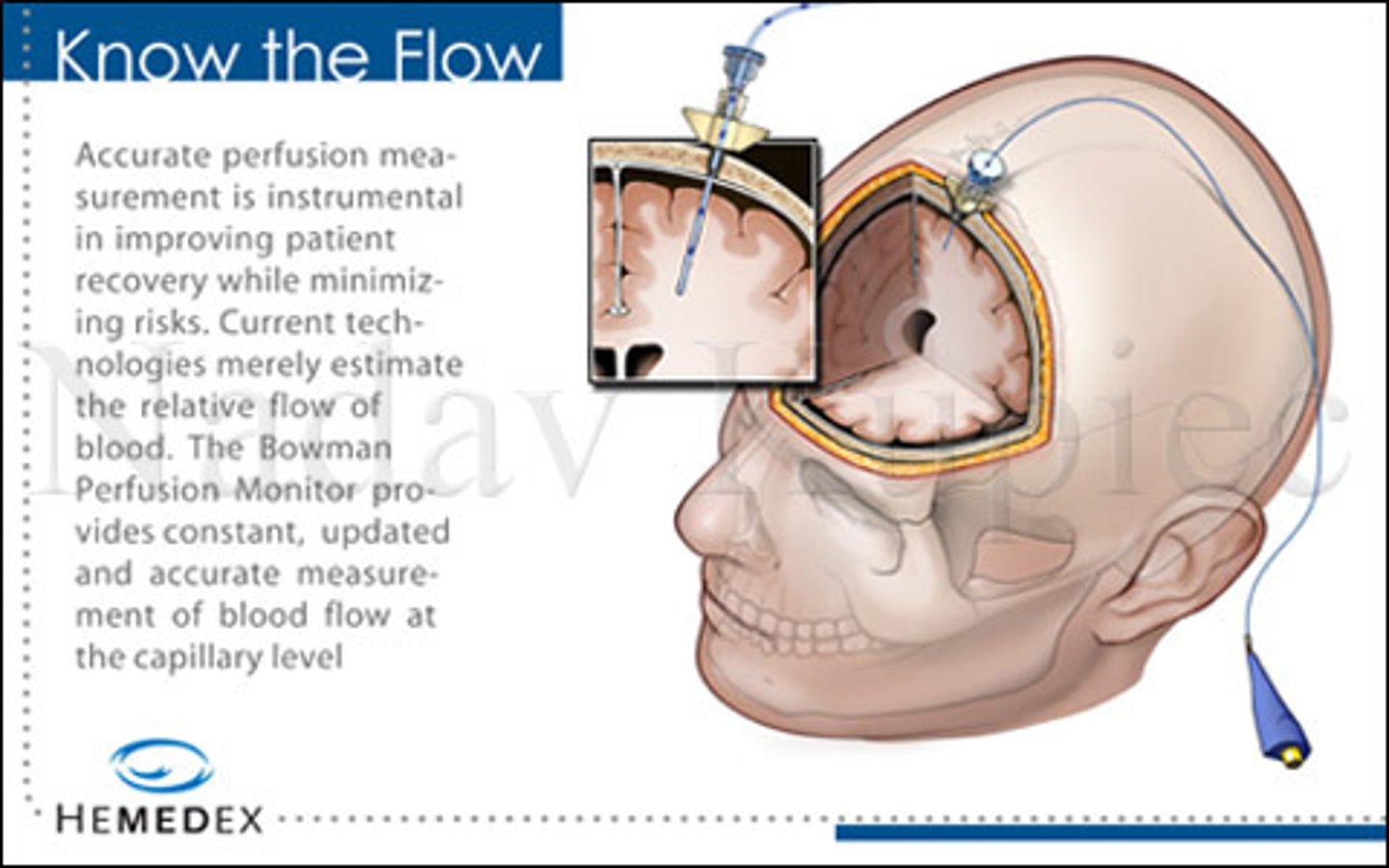
Epidural sensor
Provides readout of ICP with a stopcock assembly and transducer
Anterior fontanel pressure monitor
Detects impulses from pressure sensor and converts them to electrical energy which is then converted to visible waves or numeric readings on a oscilloscope; may be inaccurate if poorly placed
Head injury
Pathological process involving scalp, skull, meninges, or brain as a result of mechanical force
Primary head injury
Head injuries that occur at the time of trauma and include skull fracture, contusions, intracranial hematoma, and diffuse injury
Acceleration-deceleration injury
Head injury typical of a car crash in which the head comes to a sudden stop, but the brain continues to move back and forth inside the skull, resulting in bruising to the brain
Coup
Bruising at the point of impact
Contrecoup
Injury to the brain at a point directly opposite the point of contact
False (children present with increased blood volume)
True or false? Children with an acceleration-deceleration injury demonstrate diffuse generalized cerebral swelling produced by increased water content rather than by increased blood volume as seen in adults
Shearing stress
Effect of brain movement which may tear small arteries and cause subdural hemorrhages (letter D in the image)
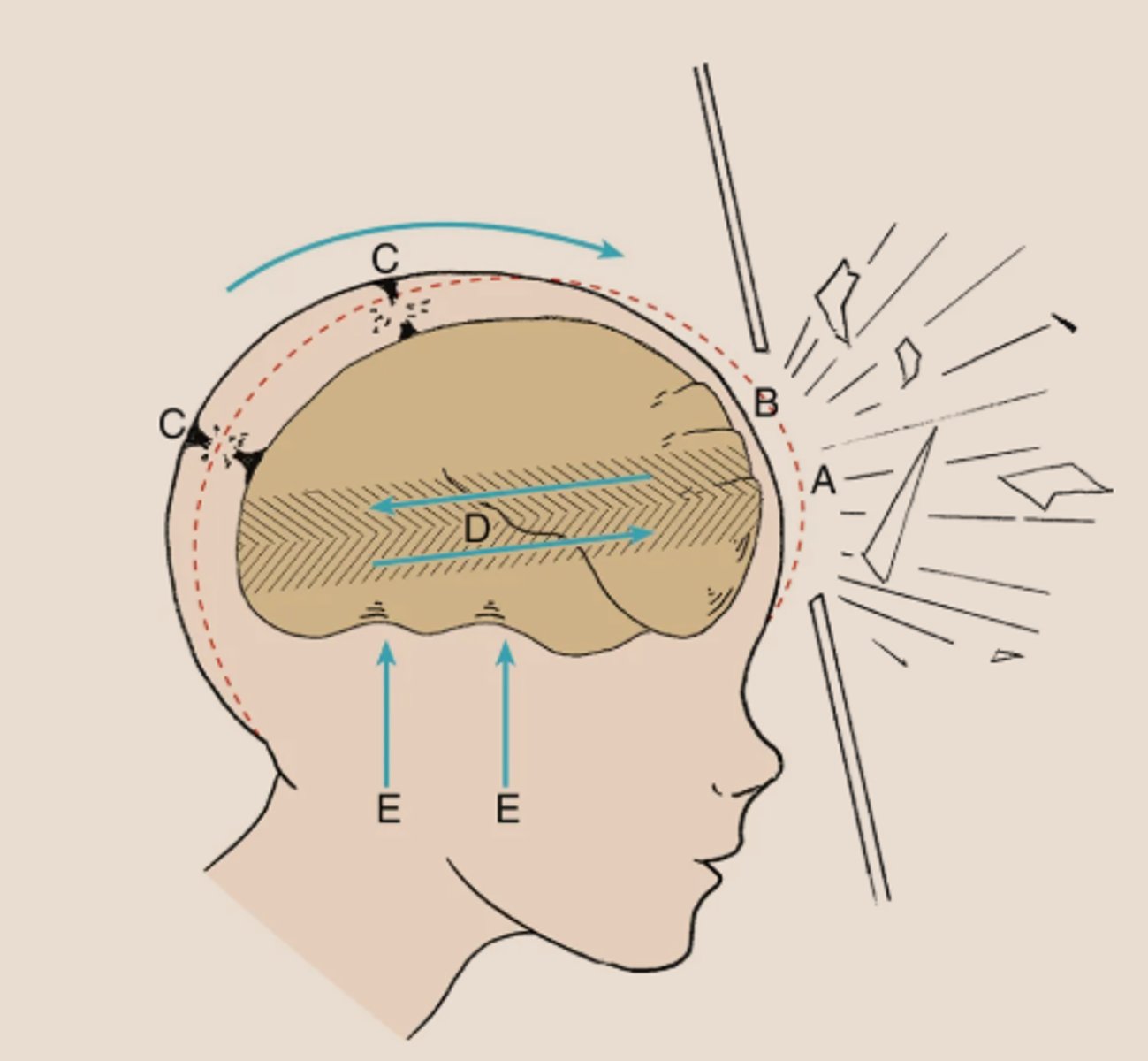
Concussion
Transient disturbance of brain function often traumatically induced that involves a complex pathophysiological process
Contusion and laceration
Terms used to describe visible bruising and tearing of cerebral tissue
Occipital, frontal, temporal lobes
What are the 3 areas of the brain susceptible to contusion or laceration?
Traumatic head injury due to child maltreatment
Previously known as shaken baby syndrome or abusive head trauma; violent shaking that may occur as a result of the inconsolable infant crying; results in lifelong complications; brain rotates within skull which tears neurons and BVs
Skull fractures
Result from direct blow or injury to skull and often associated with intracranial injury; immature skull can withstand greater increase in deformities before fracture, so the force must be extreme
Linear fractures
Single fracture line that starts at the point of maximal impact but does not cross suture lines; overlying hematoma or soft tissue swelling
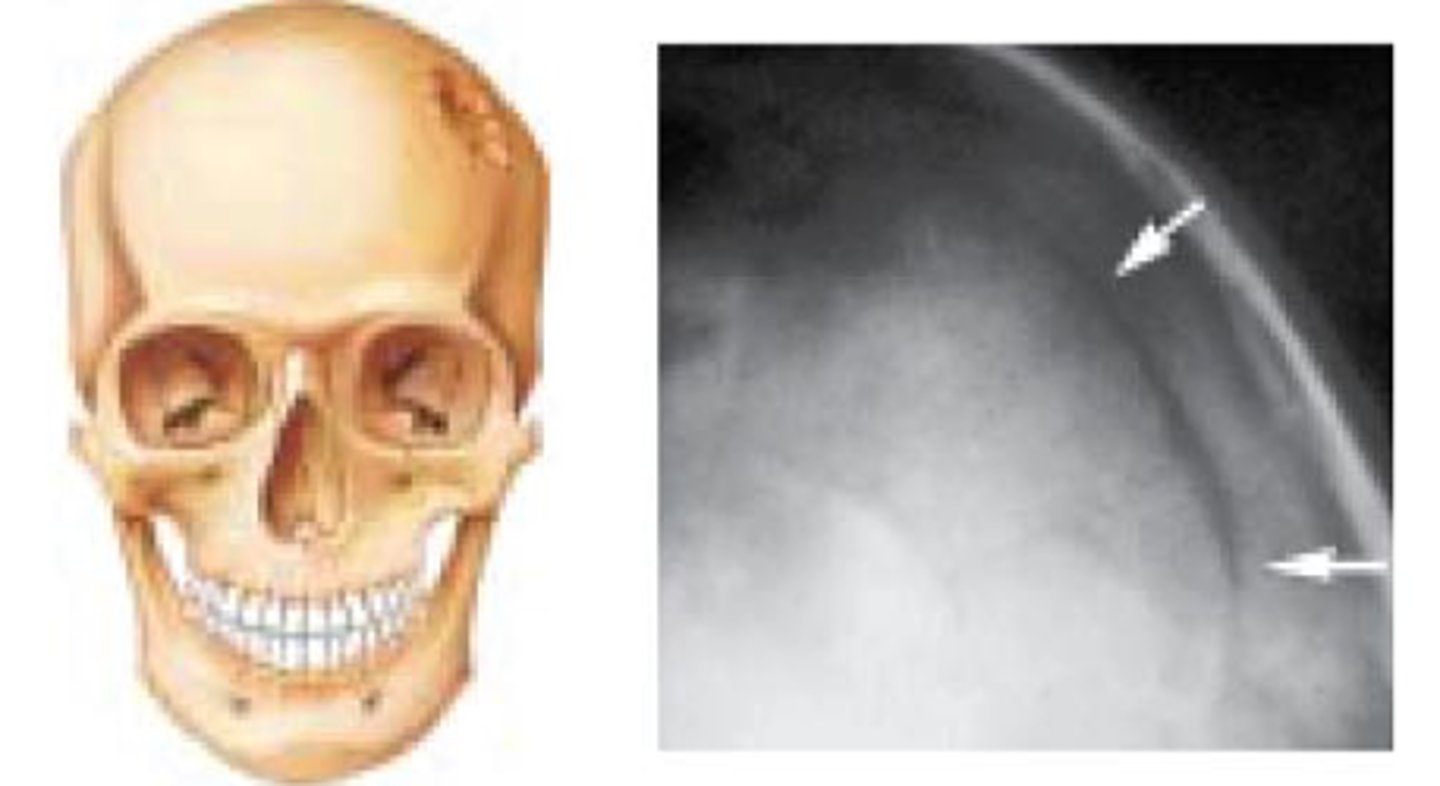
Depressed fractures
Bone is broken into several irregular fragments that are pushed inward; direct underlying parenchymal damage; suspected when heads appears misshapen
Comminuted fracture
Multiple associated linear fractures; usually result from intense impact such as repeated blows against an object; may suggest child maltreatment
Basilar fractures
Involve bones at the base of the skull in either the posterior or anterior region; usually result in a dural tear; fracture line is very close to brainstem, so this type of fracture is considered a serious head injury
Open fracture
Fracture that causes communication between skull and scalp or surfaces of upper respiratory tract; increase risk of cNS infection
Growing fracture
Skull fractures with underlying dural tear that fails to heal properly; enlargement caused by leptomeningeal cyst, dilated ventricles, or herniated brain
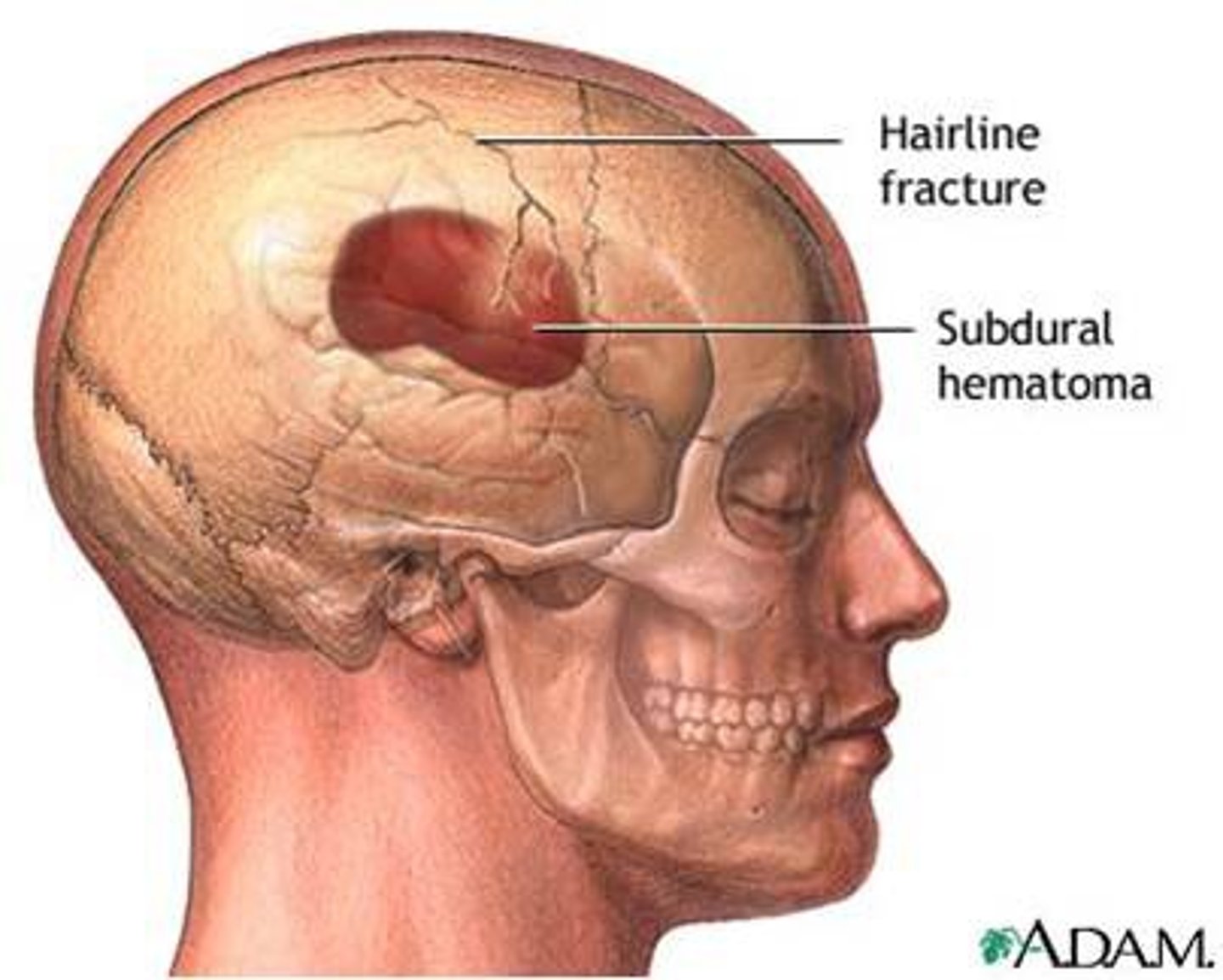
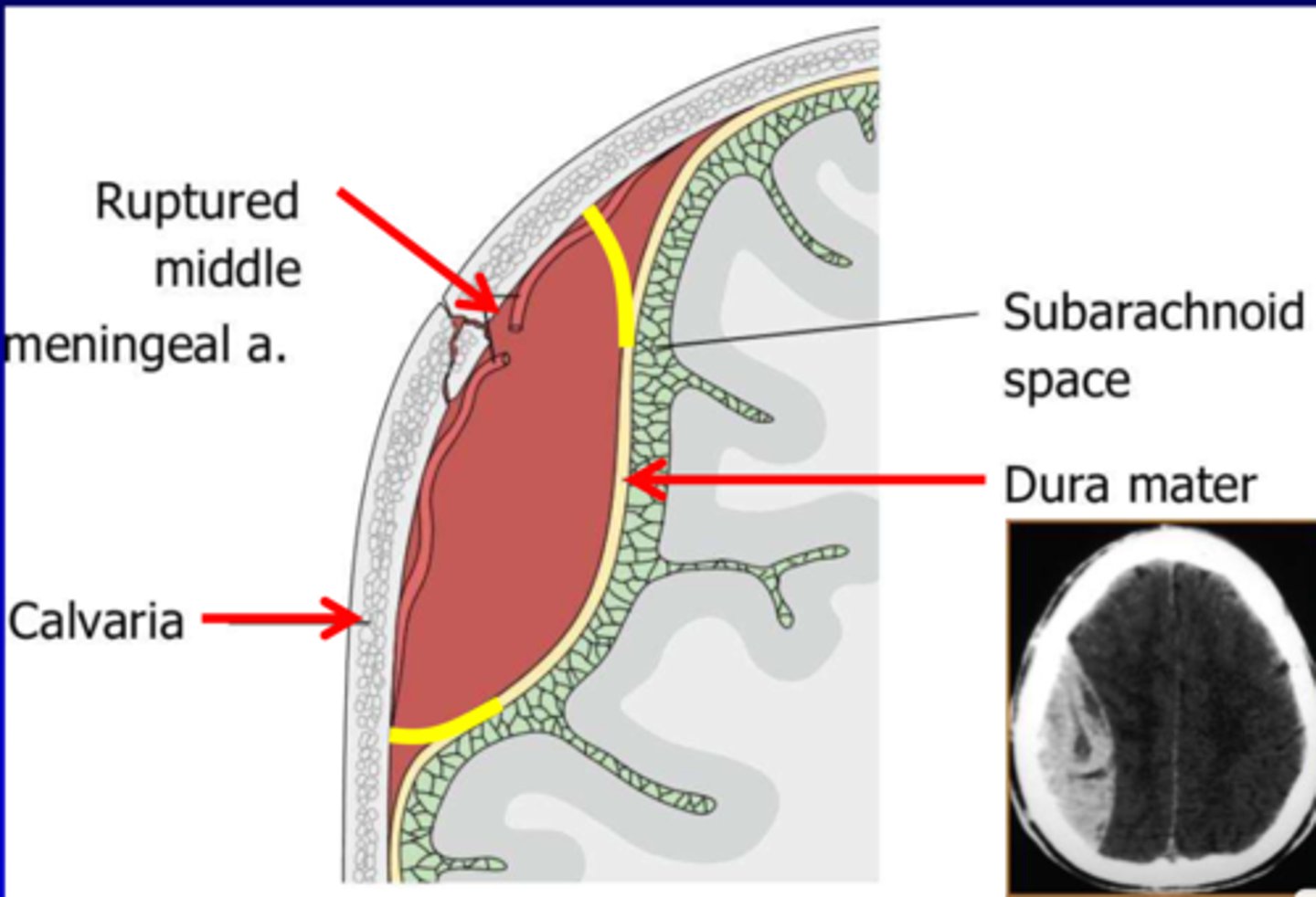
Epidural hemorrhage
Bleeding between dura and skull to form a hematoma; causes dura to be stripped from bone = underlying brain contents forced downward and inward as brain expands
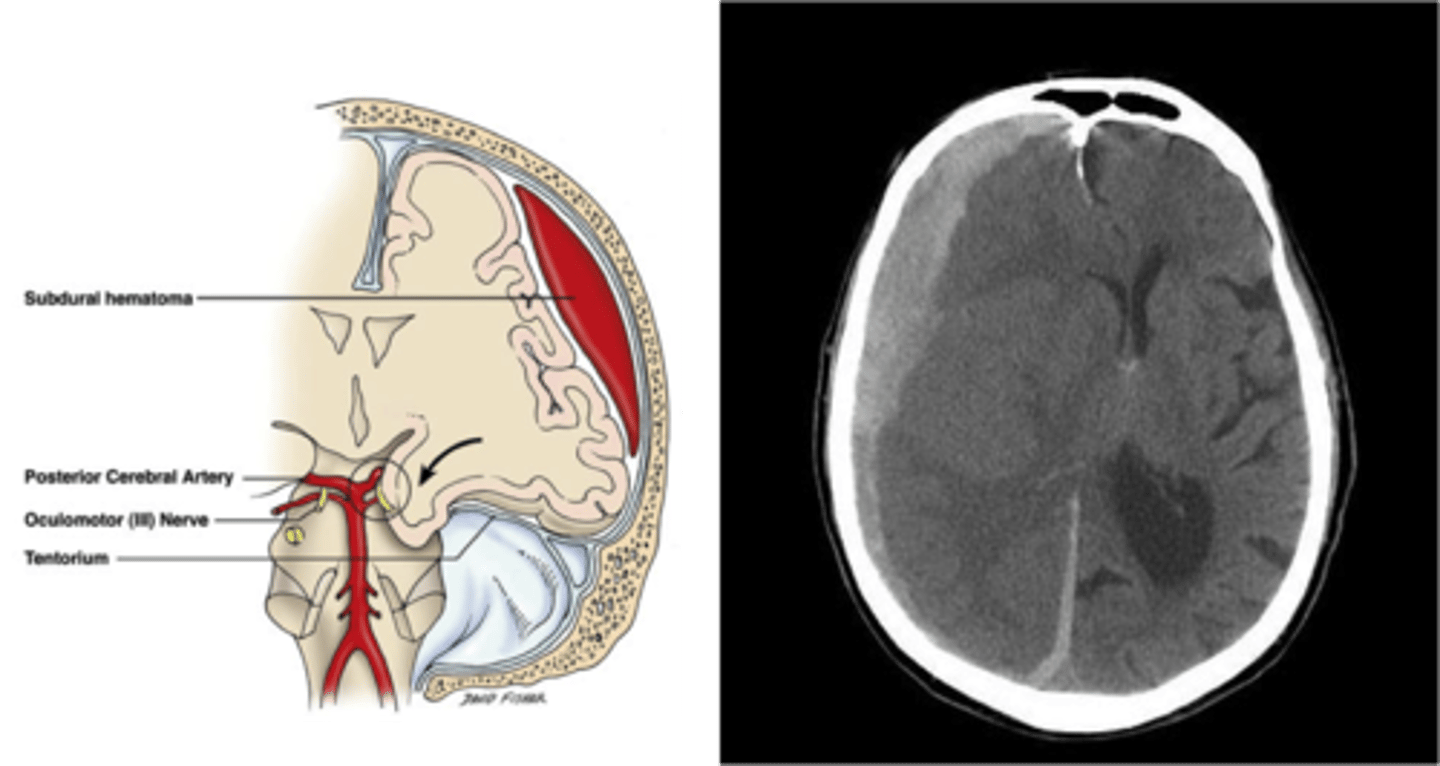
Subdural hemorrhage
Bleeding between dura and arachnoid membrane as a result of rupture of cortical veins that bridge the subdural space; spreads thinly and widely until it is limited by dural barriers
24-72 hours
When does cerebral edema peak after a traumatic head injury?
ABC assessment, evaluation for shock, spinal cord injury assessment
A child falls on her head at home an sustains a head injury. What are your priority assessments?
Rest until the patient is asymptomatic
What is the hallmark treatment for concussions?
True
True or false? A sleeping patient with a head injury should be awakened every 2 hours to reassess for changes in responsiveness
Submersion injury
Injury occurring up until the time of drowning-related death; includes any person who experiences distress from near-drowning submersion or immersion in liquid that results in death
Bacterial meningitis
Acute inflammation of meninges and CSF; medical emergency; vascular dissemination from a focus of infection elsewhere
Hemophilus influenzae type B
Which vaccine has dramatically decreased the amount of cases of meningitis in Canada?
Lumbar puncture
What is the definitive diagnostic test for bacterial meningitis?
S&S of bacterial meningitis
Fever, chills, headache, vomiting, photophobia, nuchal rigidity
Nursing care for bacterial meningitis
Quiet with minimal stimuli, HOB elevated, side-lying position, monitor pain, family support
Nonbacterial meningitis
Aka aseptic; causative agents are principally viruses
Enteroviruses
What are the most common cause of viral meningitis?
Encephalitis
Inflammatory process of the CNS that is caused by a variety of organisms; result of direct invasion of CNS by virus or postinfectious involvement of CNS after viral disease
Reye syndrome
Disorder defined as toxic encephalopathy associated with other characteristic organ involvement; fever, impaired consciousness, and disordered hepatic function
Acetylsalicylic acid
There is a potential association between ____ therapy for treatment of fever in children and development of RS
Excessive and disorderly neuronal discharges
What causes a seizure?
True
True or false? Seizures are a symptom of an underlying disease process
Epilepsy
Condition characterized by 2+ unprovoked seizures more than 24 hours apart; caused by variety of pathological processes in the brain
Acute symptomatic seizure
Seizure disorder associated with head trauma or meningitis
Remote symptomatic seizure
Seizure disorder caused by brain injury such as encephalitis, meningitis, or stroke
Cryptogenic seizure
A seizure disorder with no clear cause
Idiopathic seizure
Seizure disorder that is genetic in origin
Focal seizures
Local onset and start in an area of cells on one side of the brain; person maintains awareness although may not be able to talk during the seizure
Generalized seizures
Seizures which involve both hemispheres of the brain and are without local onset; loss of awareness; aka tonic-clonic seizures
Tonic phase
Lasts 10-20 seconds/2-3 minutes; immediate loss of consciousness followed by contraction of entire body musculature; apneic - may become cyanotic
Clonic phase
Lasts 30 seconds to 30 minutes; violent jerking movements as trunk/extremities undergo rhythmic contraction/relaxation
Status epilepticus
Seizures occur at intervals too brief to allow child to regain consciousness between seizures; requires emergency intervention, can lead to exhaustion, respiratory failure, death
Seizure management
Medication therapy, ketogenic diet, vagus nerve stimulation, surgical therapy, treatment for status epilepticus
Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy
Refers to the death of someone with epilepsy, usually during or immediately following a seizure; most common epilepsy-related cause of mortality
False
True or false? Restraining the child's arms in an important step in injury prevention when caring for a child who is seizing
Febrile seizures
Seizures that result from sudden high fevers, particularly in children
True
True or false? Tepic sponge baths are not recommended to treat febrile seizures
8 weeks
By when should the posterior fontanel close?
6 months
By when should the fibrous suture lines and interlocking of serrated edges occur?
18 months
By when should the anterior fontanel close?
Craniosynostosis
Premature closure of cranial sutures; inhibits perpendicular growth and skull is forced to grow in a direction parallel to fused suture = distorted head shape

Positional plagiocephaly
Flattening of one side of an infant's head from prolonged lying in one position; teach parents to position infant's head to side when lying them on their back
10-15 minutes TID
What is the recommended amount of tummy time for infants?
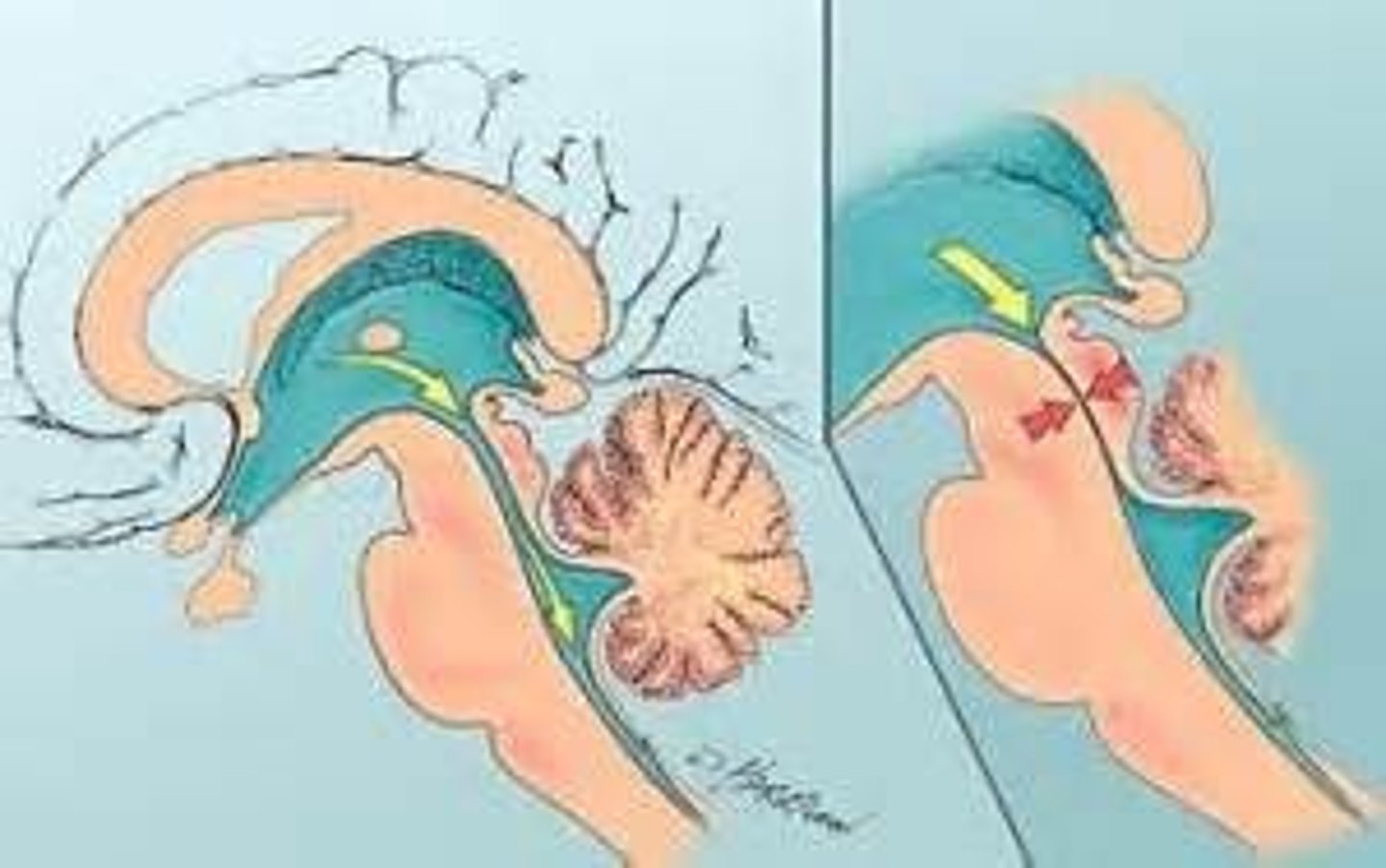
Hydrocephalus
Condition caused by imbalance in production and absorption of CSF in ventricular system; communicating and noncommunicating types
Communicating hydrocephalus
Impaired absorption of CSF fluid within the subarachnoid space, obliteration of the subarachnoid cisterns, or malfunction of the arachnoid villi

Noncommunicating hydrocephalus
Obstruction to the flow of CSF through the ventricular system
Ventriculoperitoneal shunt
Tube used to drain fluid from brain ventricles into the abdominal cavity; treatment for hydrocephalus; risk of infection greatest 1-2 months after placement