OPERATIVE EXAM 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
intertubular dentin
Dentin located between the dental tubules
peritubular dentin
Dentin that surrounds and lines the dental tubules
peritubular
dentin with HIGHER mineral DENSITY
hardness and texture
what is the most reliable clinical factor to distinguish caries affected/infected dentin?
slow, focused, asymptomatic
caries progression in ENAMEL
lateral spread, faster, asymptomatic
caries progression at DEJ
lateral and axial spread, follows dentinal tubules, pulpal communication, becomes symptomatic
caries progression in DENTIN
rapid, symptomatic
caries progression in PULP
symptomatic, swelling, infection (systemic)
caries progression in PERIAPICAL TISSUE
caries affected dentin
DEMINERALIZED by bacterial acids, reduced permeability zone to protect pulp, REMINERALIZABLE
caries infected dentin
BACTERIA PRESENT, significantly SOFTER than normal dentin, destruction by enzymatic and acidic activity for AMORPHOUS MASS
enamel surface and crystal network disrupted
why is complete remineralization not possible once lesion is CAVITATED?
lactic acid
MOST POTENT cariogenic acid produced by STREP MUTANS
small molecules (ex: lactate and hydrogen peroxide)
what is enamel permeable to?
enamel tufts
bush-like HYPOMINERALIZED regions extending from DEJ into ENAMEL
enamel lamellae/ craze lines
HYPOMINERALIZED defects extending from ENAMEL —> DEJ
more permeable closer to pulp
how does the PERMEABILITY of DENTIN change?
higher density and larger diameter tubules
why is deeper dentin more permeable?
critical enamel pH
highest pH at which there is a LOSS of mineral from tooth surface
carious lesion
what forms at pH 4.5-5.5
erosion
what forms at pH <4.5
acid-attack creates porosites that scatter light
why is initial demineralization white?
cavitation
loss of surface enamel layer due to continued demineralization
sound
no surface change
initial
earliest clinically detectable lesion, MILD DEMINERALIZATION, limited to ENAMEL or shallow dentin
moderate
early cavitation with localized enamel break down (code 3) or underlying shadow (code 4)
advanced
distinct cavity with visible dentin
initial (and up to D1 non-cavitated)
what lesions are reversible?
false negative diagnosis
missing lesion due to inadequate detection methods (ex: not cleaning or air drying) or errors in assessment
false positive diagnosis
incorrectly identifying a lesion that isn't present due to misinterpretation or over-diagnosis
don’t use x-ray radiation
common feature of QLF, FOTI, OCT, and diagnodent caries diagnostic aids
clinical observation that can be subjective
what are common caries classification method initial caries activity assessment mainly based on
combination of visual assessment, x-rays, and OCT
method for better diagnostic outcome of caries detection
comparing older and newer xrays
what can help in assessment of lesion activity
initial
radiolucent lesion may extend to DEJ or outer 1/3 of enamel
moderate
radiolucent lesion extends into middle 1/3 of dentin
advanced
radiolucent lesion extends into inner 1/3 of dentin
after cleaning and drying
when should caries assessment be done?
#, surface, origin, stage, activity
how are caries documented?
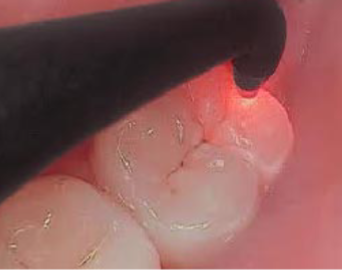
diagnodent
A laser fluorescence device used to detect carious lesions in teeth by measuring the fluorescence emitted by decayed tooth structure, HIGHER=more decay
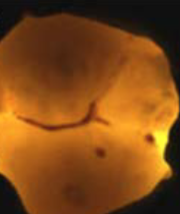
quantitative light-induced fluorescence (QLF)
A diagnostic method that uses light to detect dental caries and assess enamel changes by measuring the amount of light reflected from tooth surfaces, decay appears DARK

fiber-optic transillumination (FOTI)
uses visible light to illuminate tooth structure, allowing for the detection of caries and cracks based on the patterns of light passage
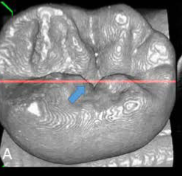
optical coherence tomography (OCT)
crreate 3D image nased on NIR light reflection to visualize internal tooth structure and identify carious lesions with high precision
fluorohydroxyapatite
more resistant to acid than hydroxyapatite
Ca, P, F
elements ESSENTIAL in REMINERALIZATION
true
T/F carious lesion excavation and filling DOES NOT eliminate caries progress
severity, activity, quantity, distribution, and history
what should be taken into account in caries risk assessment?
at least outer 1/3 dentin (D1) with high caries risk (or at any higher stage)
when is restoration indicated?
false
T/F dental caries undergoes ONLY demineralization during lesion. development
resin infiltration technique
a minimally invasive method for treating early carious lesions by infiltrating the lesion with a resin material to halt progression
sodium fluoride
which fluoride has the LOWEST antimicrobial property
esthetic restore of front teeth
when would silver diamine fluoride NOT be used?
true
T/F exposed to high conc. fluoride there may be acute or chronic fluoride toxicity
chlorhexidine di-gluconate
cavity cleansing agent effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria
5000 ppm sodium fluoride
prescription strength tooth paste for high-risk caries contains?
salivary flow, sealants, fluoride,good diet, antibacterials
CAMBRA system PROTECTIVE factors
bacteria, absence of saliva, poor diet
CAMBRA system RISK FACTORS
white spot, restorations, enamel lesions, cavities
CAMBA system DISEASE INDICATORS
caries experience
strongest predictor of caries risk
false
T/F caries risk has NO role in restorative treatment planning for existing lesions
adhesive dentistry
what is largest contributor to minimally invasive dentistry
caries experience, systemic health, diet, plaque amount, bacteria, saliva flow and buffering, dentist judgment
caries risk factors considered using EUROPEAN system
true
T/F more complex dental restoration cost more, require more time, and are more likely to fail
false
T/F cavity preparation design and principle are the same for all restorative materials whether they use adhesive or not
false
T/F ICON resin infiltration is indicated for the majority of moderate interproximal caries lesions with cavitation
hydrochloric acid
what type of acid is used to remove. the surface layer of lesions in resin infiltration technique
up to E2 not cavitated lesions
what can resin infiltration be used for
true
T/F retreatment ALWAYS leads to a LARGER resttoration
extent of disease and existing groove patteerns
primary determinants of OUTLINE FORM in minimally invasive dentistry
caries-free dentin everywhere
what is the in restorations
pulpal health (over complete caries removal)
what should be prioritized when working close to pulp florrs
true
T/F xylitol gums are usually more effective than regular sugar-free gums in remineralizing white spot lesions
saliva, fluoride conc, surface layer, activity
factors that affect initial lesion REMINERALIZATION
oreserve healthy tooth structure
primary goal of minimally invasive dentistry