Unit one: Energy and matter, lesson 1-13
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/135
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
1
New cards
WHIMS
Workplace hazardous materials information system
2
New cards
Matter
anything that has mass and takes up space
3
New cards
Polyatomic ion
cluster of atoms that act like single unit in a chemical compound
4
New cards
Element
an atom that can't be broken down into simpler substances
5
New cards
Compound
2 or more united elements, that can be separated chemically into simpler elements
6
New cards
what's Heterogenous mixture
-composition varies
- different parts of mixture are visible
- different parts of mixture are visible
7
New cards
what's a homogenous mixture
- different parts aren't visible
- composition is constant
- composition is constant
8
New cards
Nucleus
positively charged core of an atom is made up of protons and neutrons
9
New cards
what is an electron
- located outside nucleus
- negative charge
- (???) can be lost, shared or gained
- negative charge
- (???) can be lost, shared or gained
10
New cards
what is a neutron
- located in the nucleus
- no electrical charge
- helps stabilize structure of an atom
- no electrical charge
- helps stabilize structure of an atom
11
New cards
what is a proton
- located in nucleus of an atom
- positive charge
- number of (???) same as atomic number, determines its properties
- positive charge
- number of (???) same as atomic number, determines its properties
12
New cards
mass number
average mass of all isotopes of an atom ( and # of protons, neutrons)
13
New cards
valence electrons
the electrons in the last energy level (orbital or ring) of an atom
14
New cards
electron dot diagram (lewis dot diagram)
diagram displaying symbol and number of valence electrons
15
New cards
what is an ion
- charged atom where electrons aren't the same as protons
- either positive or negative
-
- either positive or negative
-
16
New cards
what is a cation
an ion with positive charge ( lost electrons )
17
New cards
what is a anion
an ion with negative charge (gained electrons )
18
New cards
ionic compound
compounds made of ions
19
New cards
molecular compound
made up of two nonmetals that form molecules by sharing electrons (covalent bonds)
20
New cards
valence energy level
the last energy level of an atom
21
New cards
what's crystal lattice
regular repeating patterns of ions in an ionic compound
22
New cards
ionic bond
a bond between ions, valence electrons transferred, attraction of opposite charges( bonds are strong)
23
New cards
covalent bond
a bond between molecules, no transfer, valence electrons are shared ( bonds are weak)
24
New cards
physical properties
anything causes a physical change
(ex: colour, density, melting point, boiling point, state of matter)
(ex: colour, density, melting point, boiling point, state of matter)
25
New cards
chemical properties
- how one substance reacts with another
- only identifiable once substance goes through chemical reaction
- only identifiable once substance goes through chemical reaction
26
New cards
Chemistry
study of matter and changes it undergoes
27
New cards
who invented the periodic table and related info
- Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869
- created periodic table from pattern he saw in 56 elements
- left gaps that were filled in as new elements were discovered
- created periodic table from pattern he saw in 56 elements
- left gaps that were filled in as new elements were discovered
28
New cards
How is the periodic table organized
in groups (families) and periods
29
New cards
what is a group
- aka families
- vertical columns
- (1-18) 18 (???) of them
- elements in each (???) have similar chemical properties
- vertical columns
- (1-18) 18 (???) of them
- elements in each (???) have similar chemical properties
30
New cards
what is a period
- horizontal rows
- 7 periods
- 7 periods
31
New cards
properties of metals
- good conductors of electricity &
heat
- solids at room temp, except
mercury
- positive ions
- give away electrons
heat
- solids at room temp, except
mercury
- positive ions
- give away electrons
32
New cards
properties of non-metals
- poor conductors of heat and electricity
- can be any state at room temp
- negative ions
- accept electrons
- can be any state at room temp
- negative ions
- accept electrons
33
New cards
properties of metalloids
- have properties that fall between metals and nonmetals
- may / may not form ions
-staircase elements
- may / may not form ions
-staircase elements
34
New cards
list the families
[group 1]- alkali metals
[group 2] - alkaline earth metals
[group 3-12] - transition metals
[period 6] - lanthanides
[period 7] -actinidines
[group 17] - halogens
[group 18] - nobles gases
35
New cards
what family is in group 1
the alkai metals
36
New cards
list the properties of the Alkali metals
- group 1
- sliver coloured
- very reactive
-reactivity increases going down
-react violently with water
- sliver coloured
- very reactive
-reactivity increases going down
-react violently with water
37
New cards
list the properties of alkali earth metals
- group 2
- react with oxygen forming oxides
- quite reactive
- react with oxygen forming oxides
- quite reactive
38
New cards
family is in group 2
the alkali earth metals
39
New cards
list the properties of transition metals
- groups 3-12
-contain "coinage" metals
-common metals
-contain "coinage" metals
-common metals
40
New cards
what family is in groups 3-12
the transition metals
41
New cards
what family is in period 6
the lanthanides
42
New cards
list properties of lanthanides
- period 6
- starts with lanthanum
- starts with lanthanum
43
New cards
what family is in period 7
the actinides
44
New cards
list the properties of the actinides
- period 7
- starts with actinium
- starts with actinium
45
New cards
what family is in group 17
the halogens
46
New cards
list the properties of the halogens
- group 17
- solids, liquids, gases
- extremely reactive
- reactivity decreases down the group
- react with metals to form salts
- react with hydrogen to form acids
- solids, liquids, gases
- extremely reactive
- reactivity decreases down the group
- react with metals to form salts
- react with hydrogen to form acids
47
New cards
what family is in group 18
the noble gases
48
New cards
list the properties of the noble gases
- group 18
- colourless gases
- very low reactivity
- colourless gases
- very low reactivity
49
New cards
all elements above 93 are_________?
synthetic, only formed in lab for a very short time
50
New cards
list the noble gases
Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon, Radon
51
New cards
list the halogens
Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine, Astatine
52
New cards
list the alkai earth metals
Beryllium, Magnesium, Calcium, Strontium, Barium, Radium
53
New cards
list the alkai metals
Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidium, Cesium, Franicum
54
New cards
what is an atom
- building blocks of all substances
- broken into 3 parts
1. protons
2. neutrons
3. electrons
- broken into 3 parts
1. protons
2. neutrons
3. electrons
55
New cards
what is the charge of an ATOM
neutral
56
New cards
what does the atomic number tell you
number of protons and electrons in an atom
57
New cards
how do you calculate the mass
# protons + # neutrons = mass number
58
New cards
why do we disregard the mass of electrons when calculating atomic mass?
electrons are so small, so we assume that a proton and neutron are worth 1 atomic unit (AMU)
59
New cards
where is the atomic number found
above the element symbol
60
New cards
where is the atomic mass found
below the element symbol
61
New cards
what is an isotope
an atom of the same element that has same number of protons but different number of neutrons
62
New cards
what is nuclear notation?
aka isotope notation, used to represent the different isotopes of an atom
* top number is the mass number
* bottom number is number of protons
* top number is the mass number
* bottom number is number of protons
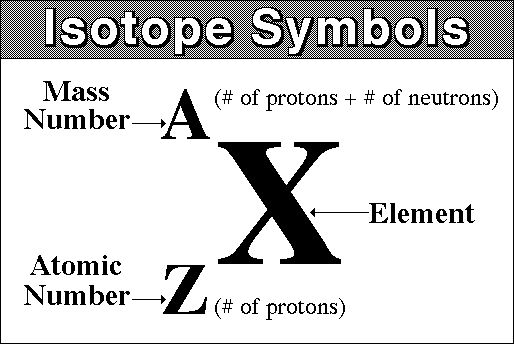
63
New cards
cations are always?
metals
64
New cards
anions are always?
non-metals
65
New cards
what's a stable octet (aka full octet)
when the last energy level has 8 electrons, meaning its full and stable
66
New cards
what's a mixture
combo of matter that can be separated by physical means
67
New cards
mixtures don't have a __________ composition?
definite
68
New cards
what's a pure substance
substance with a definite composition
69
New cards
what's a binary ionic compound
- made up of 2 elements
- formed between nonmetal and metal
- strong bonds cuz of oppositely charged ions
- formed between nonmetal and metal
- strong bonds cuz of oppositely charged ions
70
New cards
how does electron transfer of ionic compounds work?
2 elements react, valence electrons from metal transferred to nonmetal forming ionic bond
71
New cards
what are the elements never found by themselves in nature?
hydrogen - H2
fluorine -F2
iodine - I2
oxygen - 02
chlorine - Cl2
astatine - At2
nitrogen - N2
bromine - Br2
phosphorus - P4
sulphur - S8
fluorine -F2
iodine - I2
oxygen - 02
chlorine - Cl2
astatine - At2
nitrogen - N2
bromine - Br2
phosphorus - P4
sulphur - S8
72
New cards
what does the period number tell you
the number of orbitals ( energy rings)
73
New cards
what does the group number tell you
the number of valence electrons ( electrons filling the last ring)
74
New cards
what is an acid
compound that dissolves into water
forms a solution with a PH lower than 7
often contain hydrogen
forms a solution with a PH lower than 7
often contain hydrogen
75
New cards
what's a base
compound that dissolves into water,
forms a solution with a PH greater than 7
often contain hydroxide
forms a solution with a PH greater than 7
often contain hydroxide
76
New cards
properties of acids?
- taste sour
- aren't slippery
- PH less than 7
- Conductive
- aren't slippery
- PH less than 7
- Conductive
77
New cards
properties of bases?
-taste bitter
- slippery
- PH greater than 7
- conductive
- slippery
- PH greater than 7
- conductive
78
New cards
how do bases react to indicators
* turns red litmus paper blue
* turns bromythal blue, blue
* is a bluish purple on universal indicator
* turns phenolphthalein pink
* turns bromythal blue, blue
* is a bluish purple on universal indicator
* turns phenolphthalein pink
79
New cards
how do acids react to indicators
* turns blue litmus paper red
* is reddish pink on universal indicator
* turns bromoythal blue, yellow
* phenolphthalein stay colorless
* is reddish pink on universal indicator
* turns bromoythal blue, yellow
* phenolphthalein stay colorless
80
New cards
whats the PH scale
measure of how basic or acidic a solution is, with 0 being extremely acidic, 14 emtremely basic and 7 neutral
81
New cards
what's solubility?
ability of substance to dissolve in a certain solvent
82
New cards
define insolubility
meaning substance can't dissolve into a solvent
83
New cards
what's a precipitate?
solids (insoluble substances)
84
New cards
what's dissociation?
the splitting of ions of an ionic compound in water
85
New cards
what happens to the crystal lattice structure in dissociation?
the lattice breaks apart and ions are free to move around in solvent
86
New cards
what can happen when two ionic compounds are placed in water?
a precipitate can form between the free ions of the compounds
87
New cards
what's an exothermic reaction
where there's a release of energy and energy is a product
88
New cards
what's an endothermic reaction?
where there's an absorption of energy and energy is a reactant
89
New cards
the breaking of bonds is _____________?
endothermic
90
New cards
the forming of new chemical bonds is_______________?
exothermic
91
New cards
what's the law of conservation of energy
energy can be converted into different forms, BUT the total energy of the universe stays the same
92
New cards
what's the law of conservation of mass
total mass of reacting ( reactants) substances is always equal to the mass of resulting (products) substances
93
New cards
what are the exceptions to the acid naming rules?
- organic compounds ( made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen mainly) - when writing formula don't have to start with hydrogen
- sulfur ( add "ur" before the "ic" or "ous" when classically naming)
- phosphorus ( add "or" before the "ic" or "ous" when classically naming)
- sulfur ( add "ur" before the "ic" or "ous" when classically naming)
- phosphorus ( add "or" before the "ic" or "ous" when classically naming)
94
New cards
chemical reaction
a reaction that happens due to one or more substances changing to form different substances
- involves a change of energy (ex; temp change, emission of light, emission of sound, electrical energy)
- involves a change of energy (ex; temp change, emission of light, emission of sound, electrical energy)
95
New cards
chemical change
one or more substances changing to form different substances
96
New cards
how to know if a chemical change has occurred?
two of more of the evidences are apparent:
odour change, colour change, formation of a gas, formation of a precipitate, etc
odour change, colour change, formation of a gas, formation of a precipitate, etc
97
New cards
what's the best indicator of chemical reaction
a new substance is formed and cannot be reversed
98
New cards
in chemical reactions what needs to happen to energy?
be either absorbed or released
99
New cards
in a chemical equation the arrow signifies what?
the direction a reaction is going from the reactants and the products
100
New cards
chemical equations consist of ?
3 parts... reactants, products and the arrow that separates them