Lake energy
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Primary production
The rate at which autotrophs (usually phytoplankton) convert solar energy to organic matter by the process of photosynthesis
Respiration
The rate at which OM is consumed (by both heterotrophs and autotrophs)
Lake metabolism
CO2 + H2O ←→ OM + O2
organic matter produced by primary production gets passed up the food chain and used in ______________
respiration
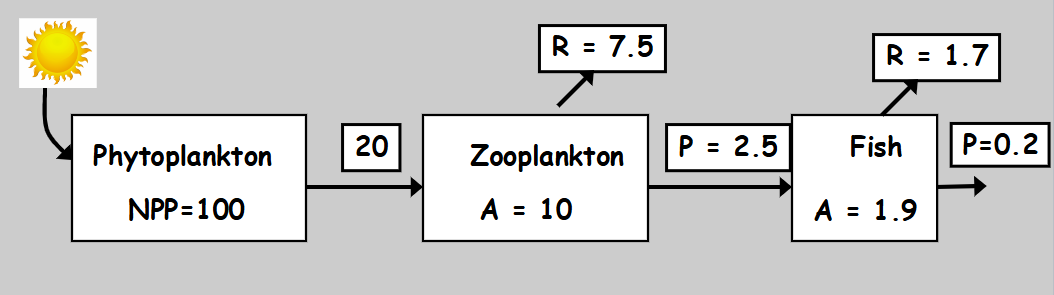
what are P and R
P = 100
R = 7.5 + 1.7 = 9.2
Where does the rest of NPP that isn’t respired go?
to detritus (dead organic matter) at the bottom of the lake
what dominates the transfer of carbon?
microbial loop
what is the central pool of energy in FW?
detritus
how is lake metabolism measured (new method)
High-frequency oxygen measurements with sensors
NEP =
GPP - R
total ____________ is the ultimate driver of the magnitude of R and GPP
phosphorus
NEP in low P (oligotrophic) lakes is typically…
less than or equal to zero (i.e., lake is heterotrophic and net C consumer)
NEP in eutrophic lakes is…
positive (i.e., lake is autotrophic and net C producer)
what is used to describe the difference in productivity between low-nutrient (oligotrophic) and high-nutrient (eutrophic) lakes?
trophic state
trophic state
a lake’s productivity in relation to its watershed
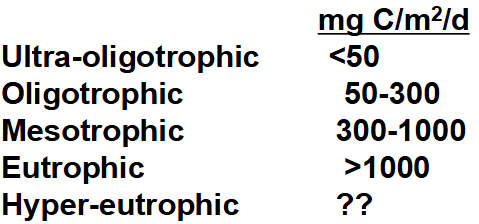
typical characteristics of an oligotrophic lake
low nutrients, deep, orthograde DO, low NPP, heterotrophic, C source, deep light penetration and Secchi, low algae/chl-a
typical characteristics of a eutrophic lake
high nutrients, shallow, clinograde DO, high NPP, autotrophic, C sink, shallow photic zone and Secchi, algae blooms
eutrophication
a change in lake trophic status over time (oligotrophic → eutrophic)
Over time, all lakes accumulate sediments, so they will naturally become ________ over thousands of years (e.g., kettle lakes filling in)
eutrophic
Nutrient pollution
one of the biggest threats to freshwaters (>90% of rivers)
Anthropogenic eutrophication (more rapid change in productivity) has affected…
the majority of waterbodies in the U.S.