pulmonary circulation
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Deep venous thromboembolism (DVT) patho
-stasis blood flow: impaired blood flow
-endothelial damage: trauma
-hypercoagulability
DVT RF
-pregnancy
-surgery
-immobility
-hypercoagulable disorder
-smoking
-obesity
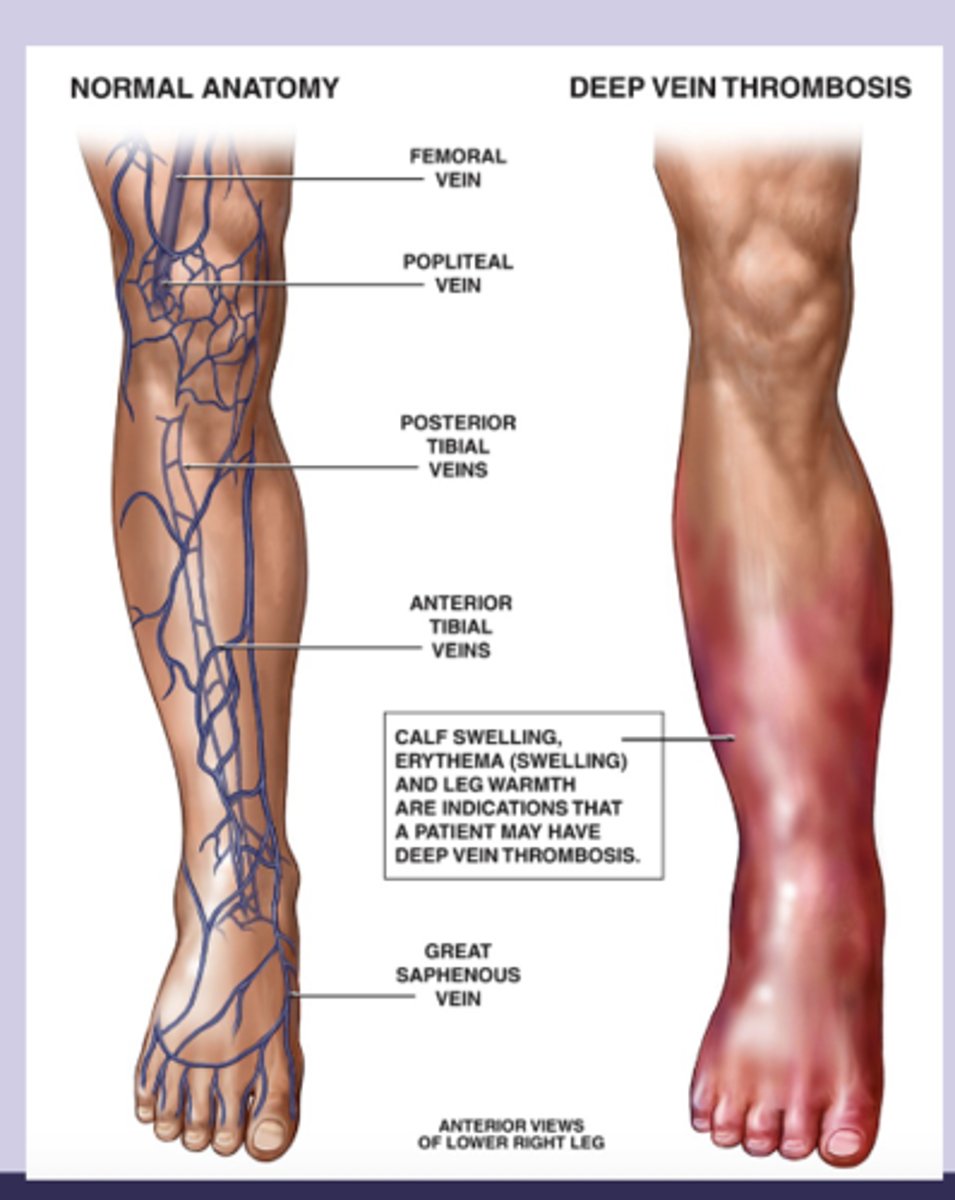
DVT sx
-lower extremity sx: swelling, pain, warmth, erythema
-usually unilateral
-difference in calf or thigh circumference
-tenderness
-dilated superficial veins
-malignancy
-homans sign: calf pain on dorsiflexion
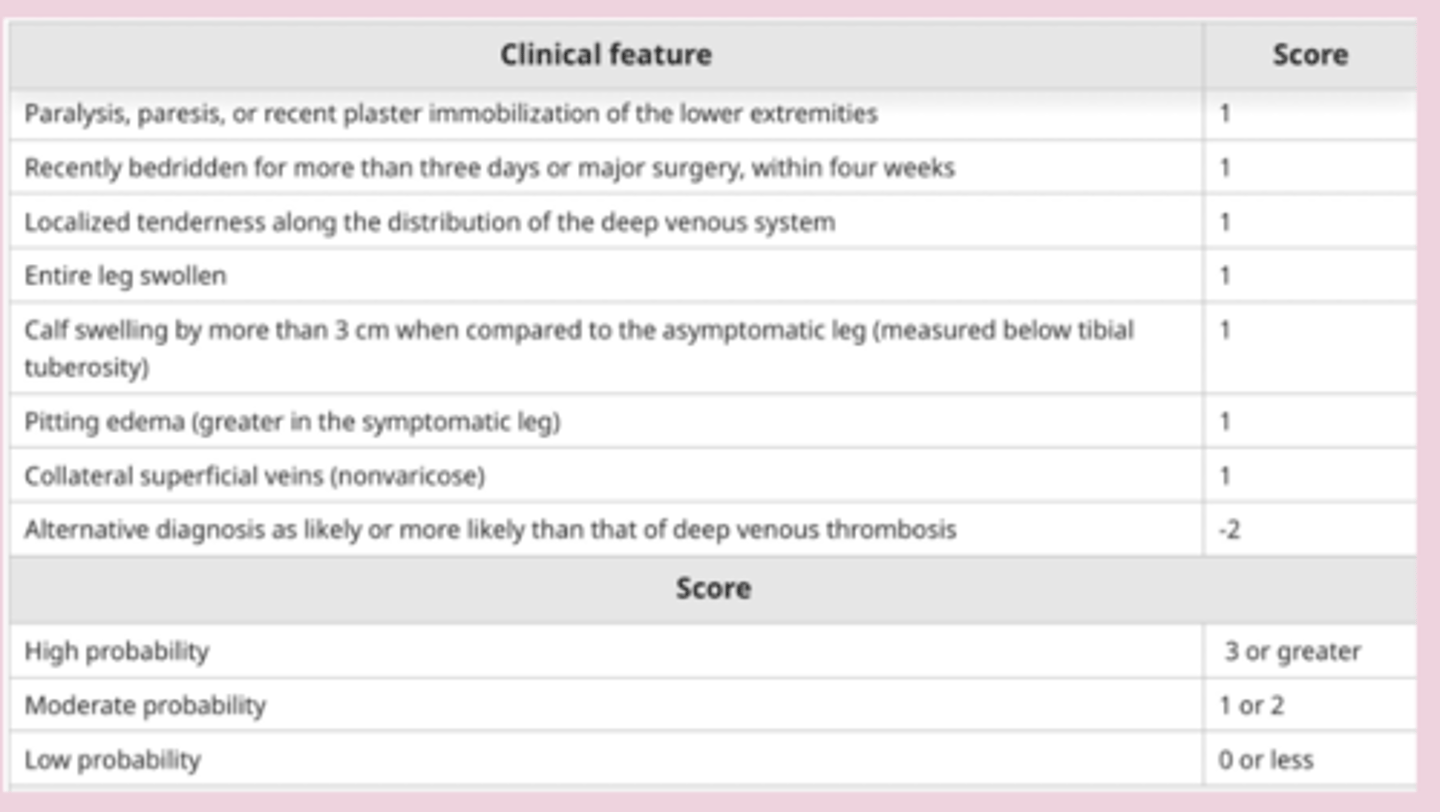
DVT dx
-pre test probability: using Wells score
-d-dimer: low level using to r/o VTE with low PTP
-diagnostic: compression venous ultrasonography= "wink"
-veins collapse under light pressure
-artery pulsate
acute LE DVT tx
blood cultures w/o absolute contraindication= anticoagulation
-proximal DVT with absolute contraindication= IVC filter placement
-40% of distal DVT= resolve
absolute contraindications
-active major bleeding
-acute intercranial or spinal hemorrhage
-major trauma
-high bleeding risk surgery
-severe bleeding diathesis
-severe thrombocytopenia
DVT tx
-stable pt: rivaroxaban, apixaban
-high risk bleed: unfractionated heparin
-cancer: LMW heparin
-kidney failure: unfractionated heparin
-pregnant: LMW heparin
anticoagulation tx
-warfarin: coumadin, dosed by INR
-heparin: unfractionated (IV), LMW (enoxaparin)
-DOACs: thrombin activity, Xa
-factor Xa inhibitor: rivaroxaban, apixaban
bridging heparin
-warfarin: start warfarin and continue heparin until INR is >2 for at least 2 measurement taken 24 hrs apart
-LMW: stop IV hep within 1 hour start LMWH or SUBQ hep
-DOAC: start when heparin is stopped
pulmonary embolism (PE)
most commonly caused by embolization of a thrombus from leg that enters the pulmonary artery circulation and obstructs a vessel
PE patho
-endothelial injury, promote platelet adhesion, blood stasis and hypercoagulation > more coagulants to accumulate than usual > obstruction
PE RF
-hx of VTE
-virchow'sP triad
-rogers risk score: postoperative VTE allows for appropriate prophylactic measures
PE sx
-sudden onset SOB
-pleuritic chest pain increased with inspiration
-unilateral leg swelling (DVT)
-dyspnea , tachycardia
-maybe cough, hemoptysis
-tachypnea, crackles, diaphoresis, fever, neck vein distension
-massive: shock, syncope, cyanosis
-persistent hypotension > MASSIVE PE = emergency CT pulmonary angiography
PE dx
-wells score
-ECG: dx other condition like MI
-CXR: helpful to find other cause
-venous ultrasound:
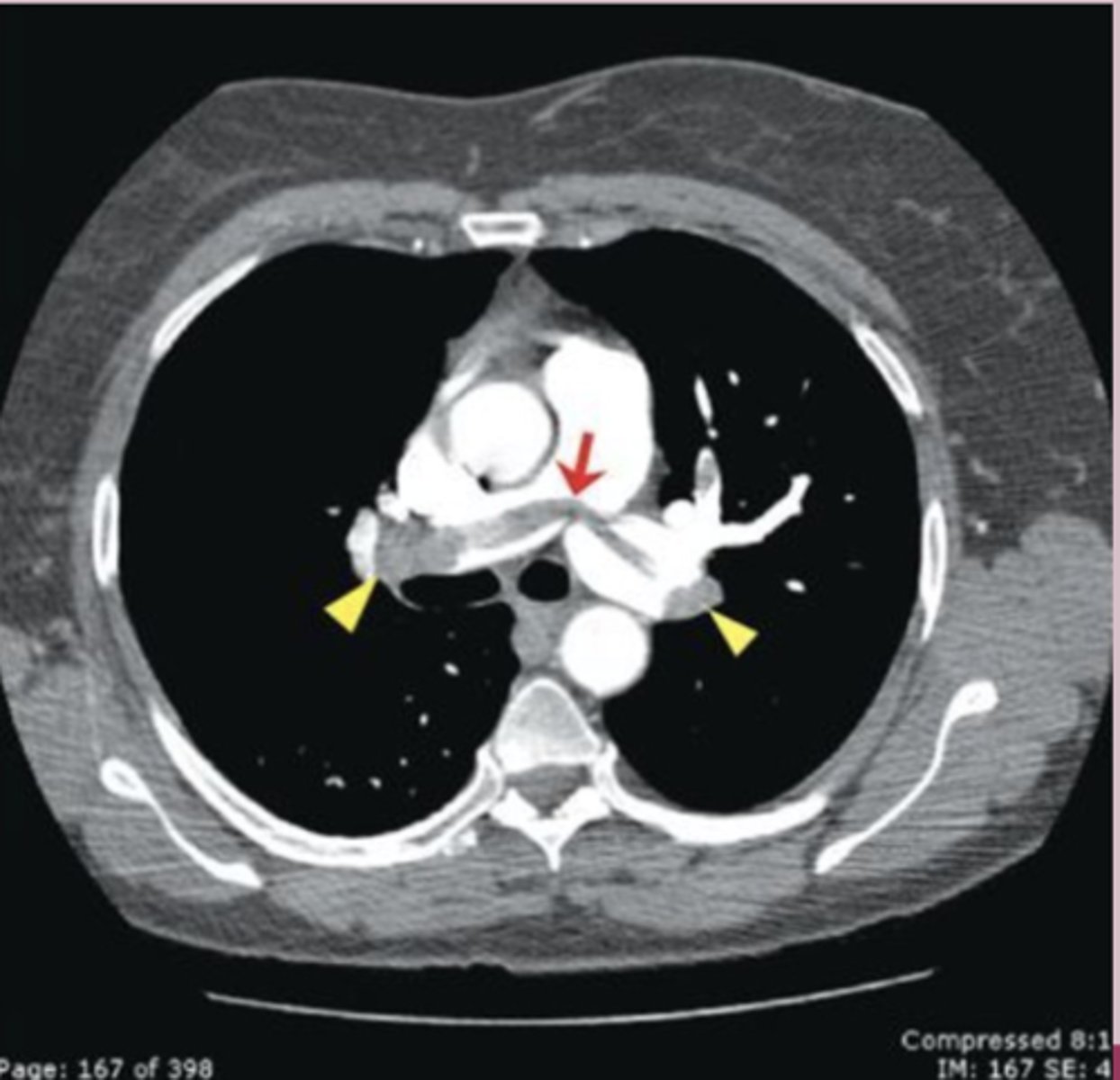
-CTA: first line
-V/Q scan: have contraindication to CTA
-pulmonary angiography: gold standard, rarely used
workup based on wells score
-low: PERC or D Dimer
-moderate: D DImer
-high: CTPA
CTA-first line
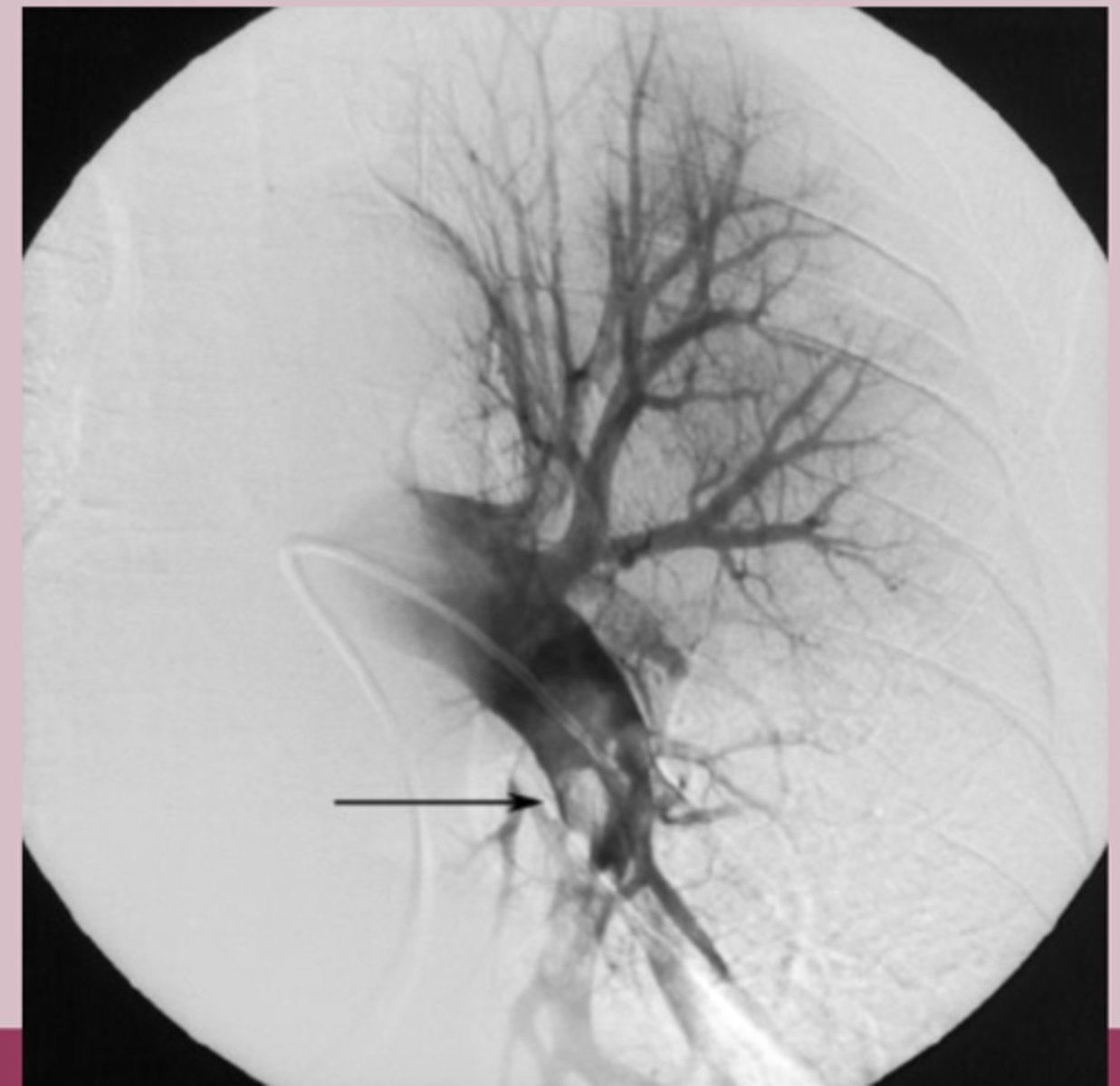
pulmonary angiography: gold standard
V/Q scan: pt who need CTA but have contraindication to contrast dye
PE lab workup
-CBC: hemoglobin, platelets
-CMP: renal function, LFT
-coagulation studies: PT/INR, PTT
-NT-pro BNP: ventricular cardiomyocytes seen in volume and pressure overload
-D-Dimer
-ABG: hypoxia, respiratory alkalosis
PE classification
-unstable: massive or high risk PE results in hypotension
-systolic BP <90
-or drop in systolic BP >40 from baseline
-stable: small, mild or asymptomatic
-mild hypotension that stabilizes with fluid therapy
low and intermediate risk PE tx
-without cancer: rivaroxaban, apixaban
-long term: NOACs for 3 months
-with cancer: LMWH for 3-6 months
high risk PE, shock, or hypotension tx
-IV unfractionated heparin
-thrombolytic therapy if shock is present
PE surgery
-inferior vena cava filters: if anticoagulation is contraindicated
-catheter based thrombus removal: acute PE with sx of shock, hypotension, high bleeding risk, failed thrombolysis