Chapter 12 Activities - Nervous System
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Long fiber that carries nerve impulses to target
Axon
Bundle of axons
nerve (PNS)
Connection between adjacent neurons
synapse
Chemical secreted into gap at a synapse
neruotransmitter
Rapid automatic response to a stimulus
Reflex
Fatty covering that speeds up nerve impulses
myelin sheath
Structure at end of axon that produces neurotransmitters
axon terminal
High speed signals that pass along the axons of nerves
nerve impulses
Branching filaments conduction nerve impulses toward cell
dendrites
Sense organ or cells receiving stimuli from within and outside the body
Sense receptors
Reaction to a stimulus by muscle or gland
response
Part of nerve cell containing the nucleus
Cell body (soma)
Nerve cell that carries impulses from sense receptor to brain or spinal cord
sensory neuron
Nerve cell that connects sensory and motor neurons
relay neuron (interneuron)
Nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to muscle or gland
motor neuron
4 major functions of the nerous system
Sensation
Response
Integration
Higher level functions
neurons that carry messages from sensory receptors and send them to the central nervous system
Sensory Neuron
Neurons that carry messages away from the central nervous system and out to the rest of the body
Motor Neuron
When a neuron is stimulated enough, it fires a(n) _______ impulse down it’s axon to its neighboring neurons
Electrical
What transmits messages between the central and peripheral nervous systems.
Interneuron
A resting neuron has more negative charge on the _____ of it than in the extracellular space around it.
Inside
Neurons have a resting membrane potentially became outside there are a bunch of positively charged _____ ions.
Sodium
Inside there are positively charge ______ ions, but also bigger, negatively charge proteins
Potassium
Since there are more positive charges inside the outside, the neuron is negatively charged, or ______
Polarized
When an axon is in the middle of an action potential, it can’t respond to any other stimulus, no matter how strong. This is called the ______. The strength of the action potential remains the same. What does change is the ______
Refractory period
Frequency
Electrical Synapses send an ion current directly from one neuron to another though ______. The signal is never converted into another form. Chemical Synapses are slower and more abundant. They use neurotransmitters that diffuse across synaptic gaps. They can ____ the signal, allowing ways to control it.
synaptic cleft
Convert
_______ meeting point between two neuron
Gap junctions
Your nerve cells have two main settings for communication _______ and _______
Electrical
Chemical
What order do this events go in?
Potential difference across membrane reaches +40mV and voltage-gated sodium ion channels close.
Energy of a stimulus triggers some voltage-gated sodium ion channels to open, and sodium ions diffuse into axon cytoplasm
More potassium ions diffuse out of axon until membrane is hyperpolarized. The potassium channels close.
Axon membrane has a resting potential of -65 to -70m; voltage-gated sodium ion channels are closed
Voltage-gated potassium ion channels open, and potassium ions diffuse out of the axon
More voltage-gated sodium ion channels open, and more sodium ions diffuse into the axon
4, 2, 6, 1, 5, 3
A stable voltage across a neuron’s membrane is called its
Resting membrane potential
The range of a neuron’s resting membrane is _____ to _____
-30mV
-90mV
Causing the resting membrane potential is the uneven distribution of ____ between the inside and outside of the cell, primary _____ and _____
Ions
Na+
K+
When a membrane’s potential becomes more positive, it is said to become ______
Depolarized
If the membrane potential becomes more negative, it becomes ______
Hyperpolarized
There is another ion that is part of the cell, and is negatively charged, which is _____
CI
The resting potential of the neuron membrane is mostly due to the movement of _______ though leak channels
NA+, K+
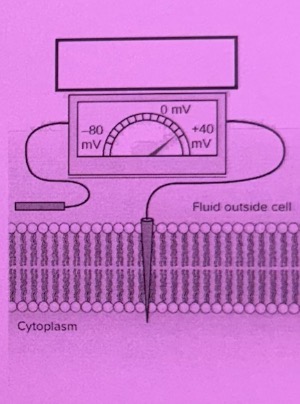
Depolarization
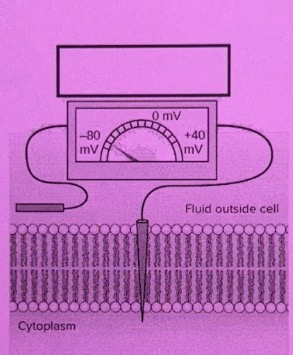
Resting
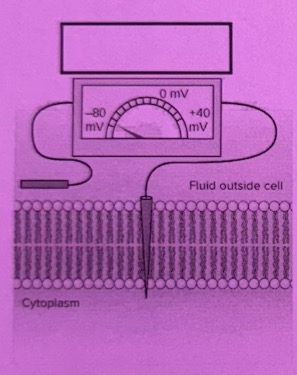
Hyperpolarization