2015 Exam short Q's
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is an antigen? Give an example of a harmless antigen.
is a substance that can trigger an immune response, typically recognized by antibodies. An example of a harmless antigen is pollen, which can provoke allergic reactions but is not inherently dangerous.
What is meant by humoral immunity? What product is involved in humoral immunity?
the production of antibodies by B cells. The primary product involved in humoral immunity is antibodies, which can neutralize pathogens and facilitate their removal.
What are the four characteristics of adaptive immunity?
specificity, diversity, immunologic memory, and nonself/self-recognition
what are commensal microbes
organisms that inhabit the body without causing harm, often providing benefits such as aiding digestion and preventing pathogenic infections.
What are pattern recognition receptors
Proteins on immune cells that detect pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and initiate immune responses.
What is an antibody
A protein produced by B cells in response to an antigen, which specifically binds to that antigen to neutralize or eliminate it.
What is an epitope
a specific region on an antigen that is recognized and bound by an antibody or a T cell receptor.
What is the basic structure of an antibody
An antibody is typically Y-shaped, consisting of two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains linked by disulfide bonds. It has a variable region that binds to specific antigens and a constant region that dictates its class and function.
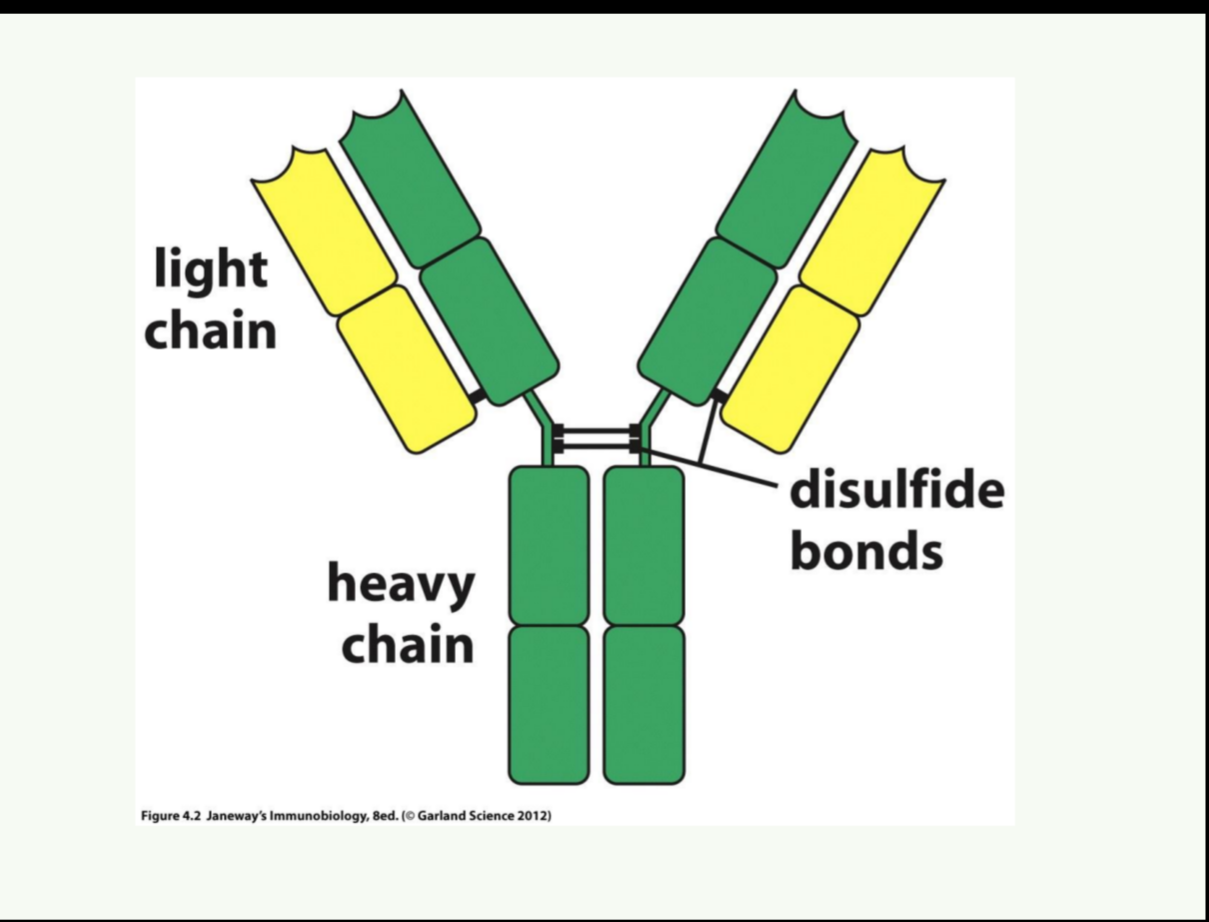
Name the different classes of antibody
IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, IgM
What is the complement system
is a complex network of proteins that enhances the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear pathogens from an organism, promoting inflammation and cell lysis.
Name two function of the complement system
It enhances phagocytosis and promotes inflammation.
What is the difference between natural passive immunity and artificial passive immunity
Natural passive immunity is acquired through the placenta or breast milk, while artificial passive immunity is obtained through the injection of antibodies.
What does the term Valency mean
it indicates the number of binding sites or the capacity of an antibody to link to antigens.
Name three types of vaccine technologies
live attenuated, inactivated, and subunit vaccines.