Biome and Aquatic Ecosystems
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/133
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
1
New cards
Why are plants used to define and area?
The are immobile and easily visible
2
New cards
What supports more vegetation?
Warmer climates and increased rainfall
3
New cards
Where are tundras found?
Areas ow low temp and precip, high latitudes
4
New cards
Arctic Tundra vs Alpine tundra
Arctic: High latitude
Alpine: High elevation
Alpine: High elevation
5
New cards
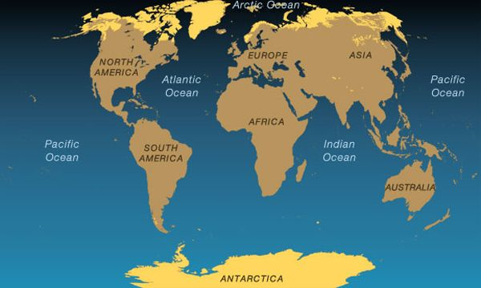
What biome exists in the highlighted area?
Tundra
6
New cards
What is temperature range of the tundra?
\-35-12 degree C
7
New cards
Term for permanently frozen spoil
permafrost
8
New cards
What is peat soil?
Partially decomposed vegetation cause by low decomp rate, occurs in tundra
9
New cards
What are some vertebrates of the tundra?
Arctic fox, caribou, snowshoe hare, snowy owl, ect.
10
New cards
Vertebrates characteristic of an ALPINE tundra
Mountain goat, pika
11
New cards
Characters of Taiga
Forested, high elevation, discontinuous permafrost
12
New cards
Where are taigas located ?
Areas of Russia and Canada
13
New cards
How do trees survive in taiga
Narrow shape of leaves for water retention, unique shape of tree
14
New cards
Characteristic evergreens of taiga
fir, spruce, pine
15
New cards
Why is fire important in the taiga?
Seed release from cones
16
New cards
Why is nitrogen limiting in taiga
much of it is tied up in undecomposed matter
17
New cards
Vertebrates of taiga
elk, lynx, moose, marten
18
New cards
Characters of temperate forests
lower latitudes, can be deciduous coniferous or mixed, fire important
19
New cards
What is a boreal-mixed forest ecotone
Gradation of boreal into northern temperate coniferous forests
20
New cards
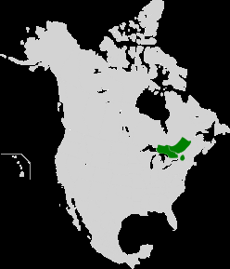
What is the forest in the map?
Jack Pine Forest
21
New cards
Where are montane coniferous forests located?
Rockies, Sierra Nevada, Cascade
22
New cards
Trees characteristic of montane coniferous forest
lodgepole, mt. hemlock, red fir, giant sequoia, ponderosa pine, costal redwoods
23
New cards
What is niche partitioning?
microclimate specializations
24
New cards
Where are the only primary growth in the US?
High in Appalachian mt.
25
New cards
Plant adaptions for rainforest vegetation
Large leaf tips, drip tips
26
New cards
What allows for rapid recycling of nutrients in rainforests?
Higher microdiversity
27
New cards
What are plants the root on the surface of other plants? Example?
Epiphytes, Bromeliads
28
New cards
Parasitic plant that leeches nutrients from host plants
Strangler vines
29
New cards
What are buttress roots?
Large wide roots on shallowly rooted trees
30
New cards
Characteristic of Heliconia
cup shaped, collects rainwater that hummingbirds collect, provides roost for tent bat
31
New cards
Tropical Rainforest vs Cloud Rainforest
Tropical: \~
32
New cards
What is unique about leaf cutter ants
They take leaves to colony to decompose and provide nutrients to fungi that the plants eat (mutualism)
33
New cards
Latitude of deserts
\~20-30 N and S
34
New cards
Max temps in desert
>50C
35
New cards
Hot vs Cool Desert
Hot- created by rising air from rainforest that dries and heats as it falls
Cool- created by a rain shadow
Cool- created by a rain shadow
36
New cards
Whats unique about kangaroo rat?
Creates metabolic water
37
New cards
Indicator species of Great Basin
Sagebrush
38
New cards
Indicator species of Chihuahuan
Creosote bush
39
New cards
Indicator species of Tallgrass prairie
Big bluestem
40
New cards
Indicator species of Sonoran
Saguaro cactus
41
New cards
Indicator species of deciduous temperate forest
hickory, oak
42
New cards
Indicator species of Mojave
Joshua tree
43
New cards
Indicator species of mixed grass prairie
Little bluestem
44
New cards
Indicator species of shortgrass prairie
Blue gramma
45
New cards
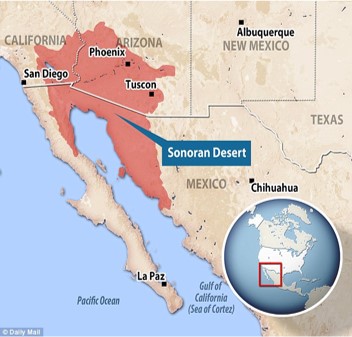
Desert?
Sonoran Desert
46
New cards
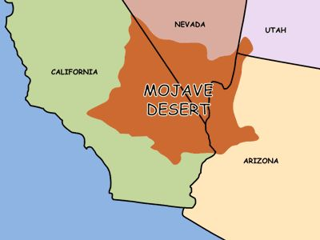
Desert?
Mojave
47
New cards
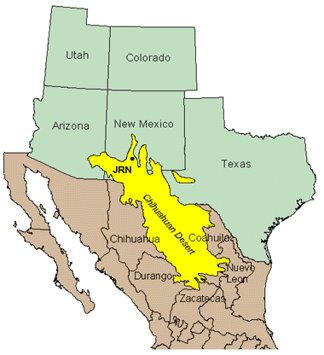
Desert?
Chihuahuan
48
New cards
What county makes up stopover point for migratory bird
Woods Co. (salt flats) and Alfalfa Co. (great salt plains)
49
New cards
What is the largest biome in N.A.? Historical percentage vs percentage now?
Temperate Grassland, 42% → 12%
50
New cards
How is the hydrological cycle powered?
solar radiation
51
New cards
Process where plants lose water through stomata
transpiration
52
New cards
Ways water is released into atmosphere
transpiration, respiration, evaporation
53
New cards
Percentage of water that is freshwater
2\.6
54
New cards
Percentage of freshwater held as ice
80%
55
New cards
Where is there maximum light penetration, and primary productivity in the water column
Photic/Euphotic Zone
56
New cards
Water zone where only blue and green light penetrates
Twilight/Dysphotic Zone
57
New cards
Water where no no light or photosynthesis occurs
Aphotic zone
58
New cards
What is the maximum depth of light penetration?
100m
59
New cards
Area in water where there is a significant drop in temp, what depth does it occur
Thermocline, 120-240m
60
New cards
What nutrients are limiting depth decreases
Nitrate and phosphate
61
New cards
Ocean Zone of highest primary productivity, shallow water, high light penetration
Neritic zone
62
New cards
Zone prone to evaporation and higher temps
Littoral zone
63
New cards
Range of continental slope
700-4000 m
64
New cards
Range of abyssal zone
4000-6000 m
65
New cards
Zone that is >6000m
Hadal zone
66
New cards
How deep can trenches get
36,000 ft
67
New cards
What is the term for cycling nutrient rich mud caused by wind
Upwelling
68
New cards
What causes “Red Tides”
Dinoflagellates containing xanthophyll
69
New cards
What causes ciguatera poisoning
Consuming something that has eaten another organism that has consumed dinoflagellates (biological concentration)
70
New cards
Charcters of Pfisteria
cyst form turns to trophozoite, malignant or benign, can cause large fish die off, 24 morphological types
71
New cards
What is equivalent to tropical forests in the ocean
Coral reefs
72
New cards
How much of calcium is taken up by coral reefs, what form?
1/2 that enters the ocean, CaCO3
73
New cards
How much carbon do coral reefs remove/year
700 billion Kg
74
New cards
What is coral
Cnideria (polyp)
75
New cards
What do coral use to bring in food
stinging nematocyst
76
New cards
What do dinoflagellates provide to coral?
nutrients, CO2
77
New cards
What type of algae helps in solidifying CaCO2 and strengthens exoskeleton
Coralline
78
New cards
What temperature range for coral?
20-35C
79
New cards
What are most coral in regards to salt content, what does this make them vulnerable to
Stenohaline (tolerable to narrow range), runoff
80
New cards
Why are coral usually in clear clen water?
Sediment effects light penetration, zooxanthellae shedding, and pollutes mucus string
81
New cards
What is the most common reef?
Fringing
82
New cards
Characteristic of fringing reef
Very close to shore, very shallow water, most vulnerable
83
New cards
Characters of a barrier reef
Usually located near a lagoon, can be near a fringing reef. protected by lagoon separating it from mainland
84
New cards
Characters of atoll
Occurs around volcano, volcano sinks into ocean, rarest of reefs
85
New cards
86
New cards
Deep sea zone above 200 m
Photic/ epipelagic zone
87
New cards
Deep sea zone from 200m to \~1000m
Mesopelagic zone
88
New cards
Deep sea zone 1000m-4000m
Bathypelagic zone
89
New cards
Deep sea zone 4000m-6000m
Abyssopelagic zone
90
New cards
Deep sea zone >6000m
Hadopelagic zone
91
New cards
How deep is Mariana trench?
36,070ft
92
New cards
Where does food come from in deep sea
Dense water carrying food from above
93
New cards
Where does oxygen come from in deep sea?
Overturning along the great ocean conveyor
94
New cards
What is the enzyme that produces light in photophores
Luciferase
95
New cards
How do deep water organisms control light production
controlling blood circulation
96
New cards
Purpose of photophores
attracting food and mates
97
New cards
Where are many photophores located?
Along ventral surface
98
New cards
What is counterillumination
photophores on ventral that break up silhouette
99
New cards
Adaptions of mesopelagic zone fish
small size, slower metabolic rate, less food intake, large eyes, large mouth
100
New cards
What is the phenomenon of very large fish in deep sea
Abyssal gigantism