Cardiology
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
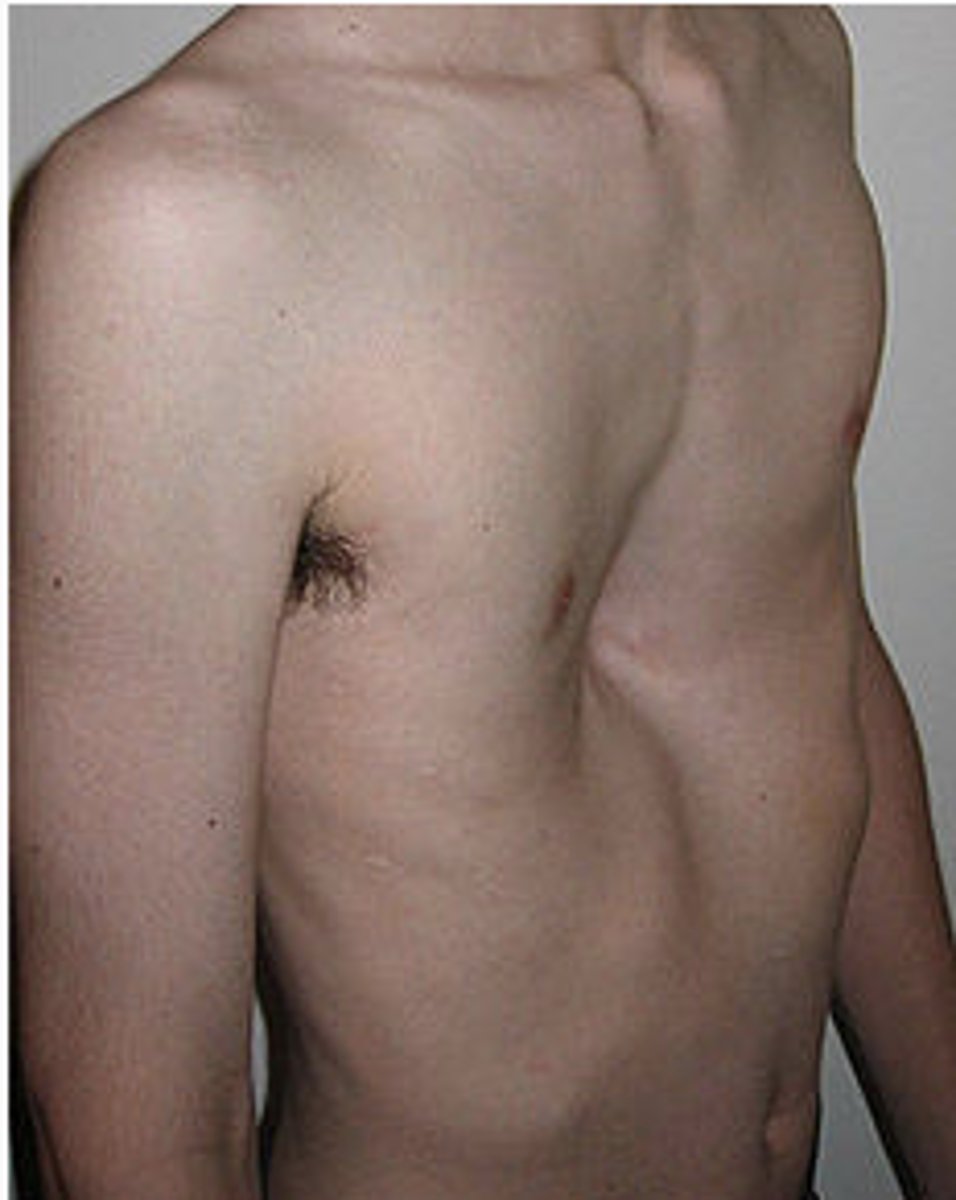
pectus excavatum
-depression of the chest wall
-symmetrical or asymmetrical
-associated with: congenital heart disease, PCD, neuromuscular disorder
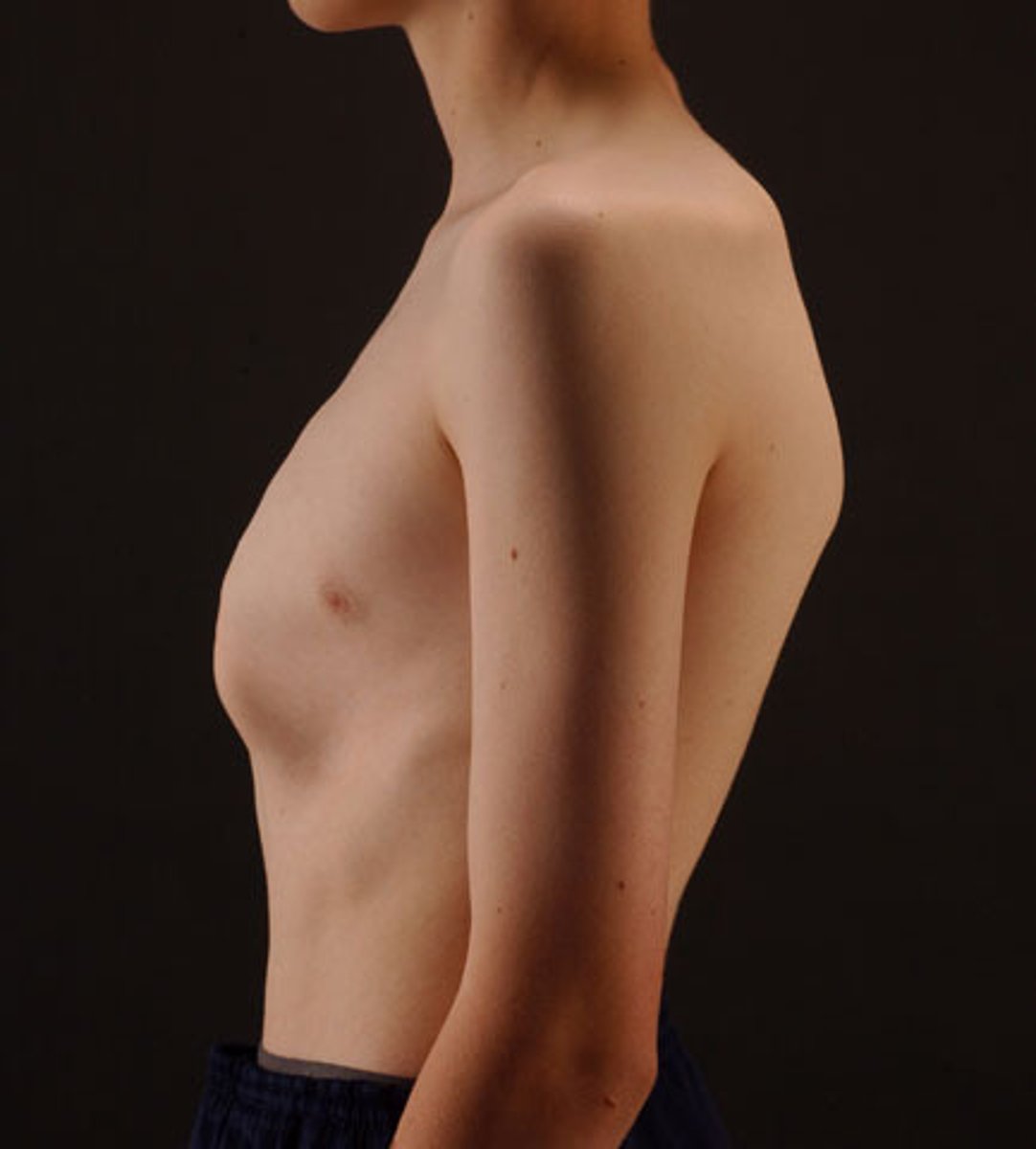
pectus carinatum
-protrusion of upper or lower portion of the sternum
-males
pectus tx
-surgical repair
murmurs
-heart sound caused by turbulent blood through the heart
-most common cardio finding
-intensity, quality, location, radiation, variation
-dx: echocardiogram
innocent murmurs
-common and benign
-produced by turbulent blood through NORMAL heart
-DO NOT represent structural or congenital heart disease
-tx: resolves without intervention
newborn murmur
-first few days of life
-heard in left sternal border
-soft I-II/VI, low pitch, short
-tx: disappears by age 2-3 weeks
Still's murmur
-most common innocent murmur of early childhood
-2-7 years of age
-heard between apex and the lower left sternal border
-mucical or vibratory, short, early systolic murmur
-best heard when supine
-louder while febrile
innominate murmur or carotid bruit
-most common in older child or adolescent
-supraclavicular area
-harsh long systolic ejection murmur
-accenuated by light pressure on carotid artery
venous hum
-musical hum
-heard loudest on right infraclavicular area
-appears after 2 years of age
-best heard when sitting
pulmonary ejection murmur
-appears age 3, continues through adolescence
-localized to upper left sternal border
-best heard supine and diminishes with valsalva
congenital heart disease can be caused by
-environmental factors: maternal diabetes, alcohol, infection
-genetics
-acyanotic and cyanotic (blue) types
cyanotic diseases
-teralogy of fallot
-pulmonary atresia
-hypoplastic left heart syndrome
-transposition of the great vessel
acyanotic
-artial septal defect
-ventricular septal defect
-patent ductus
-corarctation of the aorta
atrial septal defect
-common
-RF: advanged maternal age, downs, turners
patho: opening in the artial septum permitting the shunting of blood between atria
-left to right shunt
atrial septal defect types
-ostium secundum defect= most common
-ostium primum defect
-sinus venous defect
-coronary sinus defect
atrial septal defect sx
-asymptomatic
-older exersice intolerance, easy fatigue, heart failure
-systolic murmur, wide fixed split S2 that DOSE NOT VARY with respiration
atrial septal defect dx
-echocardiogram
-EKG: right artial enlarge
-CXR: cardiomegaly
atrial septal defect tx
-small: <5mm observe
-large: surgical
patent foramen ovale (PFO)
-opening between left and right atria
-no septal tissue missing
-sx: asymptomatic
-CLOT: always consider in CVA pt under 55
-dx: echocardiogram
-tx: antiplatelet therapy
-surgical PFO closure
ventricular septal defect (VSD)
-hole between ventricles
-left to right shunting of blood
-sx: small: asymptomatic
-large: failure to thrive, difficulty feeding, respiratory infection, congenital heart failure
-if L to R shunt for too long it will switch to R-L shunting leading to cyanosis
-murmur: high pitch, harsh, holosystolic
ventricular septal defect (VSD) dx/tx
-dx: echocardiogram
-tx: small: asymptomatic, will spontaneously resolve with first 2 years
-large: surgery
-complication: eisenmenger syndrome
eisenmenger syndrome
-occurs from unrepaired congenital heart defect that goes on for so long
-reversal of shunt causing right to left shunting = cyanotic
atrioventricular septal defect
-common in children with downs 40%
-patho: defect between both atria and both ventricules
-mixing oxygen and deoxygenated blood
atrioventricular septal defect sx
-partial presents like ASD
-failure to thrive, tachy, diaphoresis w feeds
-systolic murmur with diastolic murmur
-dx: echocardiogram
-tx: surgery required in first year
patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
-normal in fetal circulation, should not be there when bay comes out
-females, preterm babies
-patho: shunting of blood between aorta and pulmonary artery
patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) sx
-failure to thrive
-tachypnea
-diaphoresis with feeds
-wide pulse pressure
-murmur: continuous machinery murmur heard throughout chest but best at LUSB
patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) dx/tx
-dx: echocardiogram
-tx: IV indomethacin (prostaglandin)
coarctation of aorta
-patho: narrowing of proximal thoracic aorta
-male
-associated with turners syndrome
coarctation of aorta sx
-differences between arterial pulses nd blood pressure in upper and lower extremities pathognomonic
coarctation of aorta dx/tx
-dx: echocardiogram
-tx: surgical repair
cyanotic congenital heart disease
-severe defects we leave the PDA open
-IV prostaglandins E1 to stabilize prostaglandin
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) types
-most common cyanotic CHD
-ventricular septal defect
-right ventricle hypertrophy
-right ventricular outflow tract obstruction
-overriding aorta
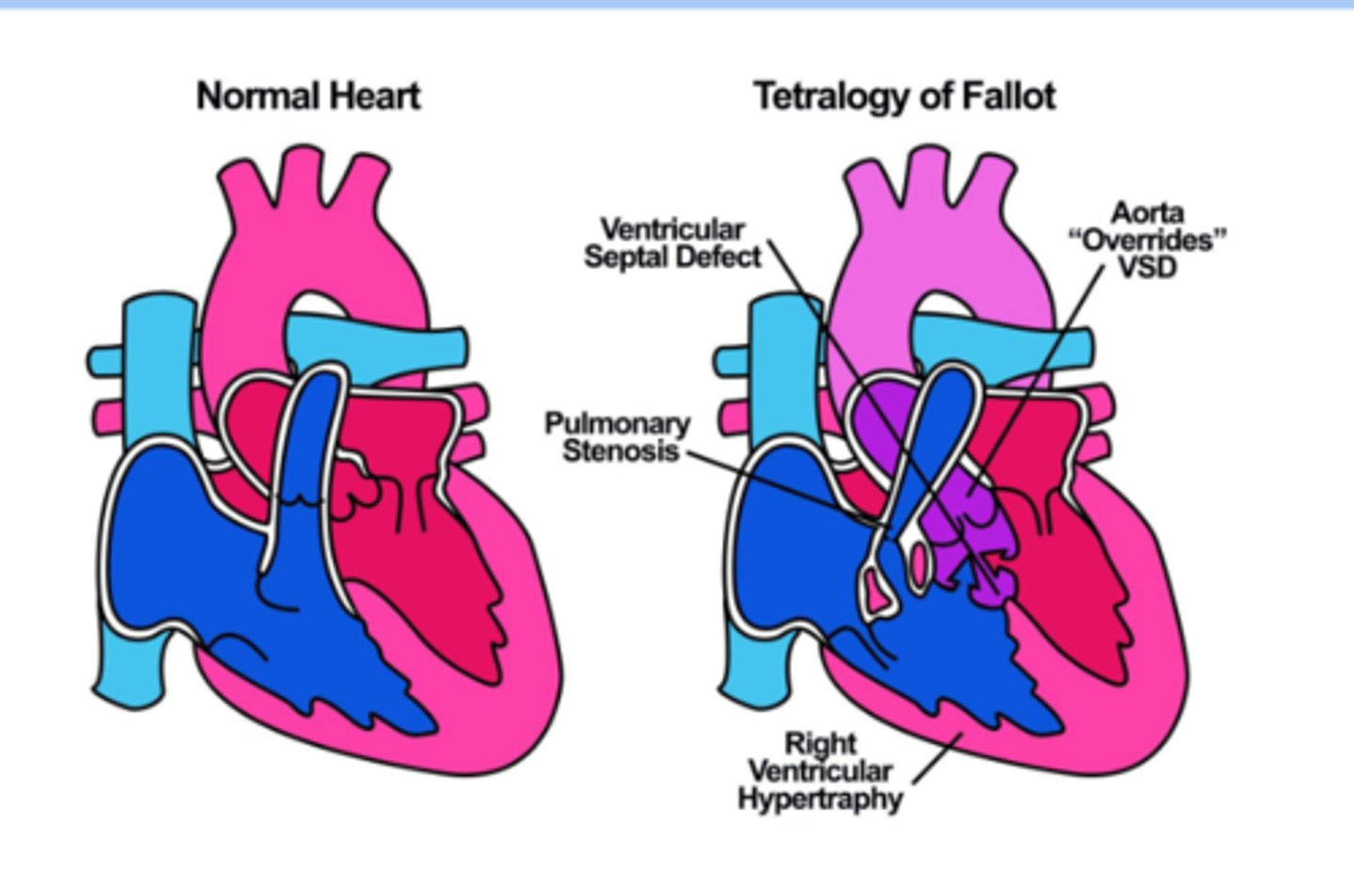
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
-patho: obstruction of RV outflow with large VSD causes a right to left shunt at ventricular level > arterial desaturation > cyanosis
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) sx
-vary on RV outflow obstruction
-mild obstruction > minimaal cyanosis or acyanosis
-severe: cyanotic from birth
-murmur: harsh systolic, left to mid upper sternal border
-all acyanosis by 4 months
-easy fatigue and dyspnea
-digital clubbing
Tet spell or Tet squats
-hypoxemic cyanotic episodes = hallmark
-sudden onset of cyanosis and child squats downs and sx improve

Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) dx
-echocardiogram
-CXR: boot shaped heart
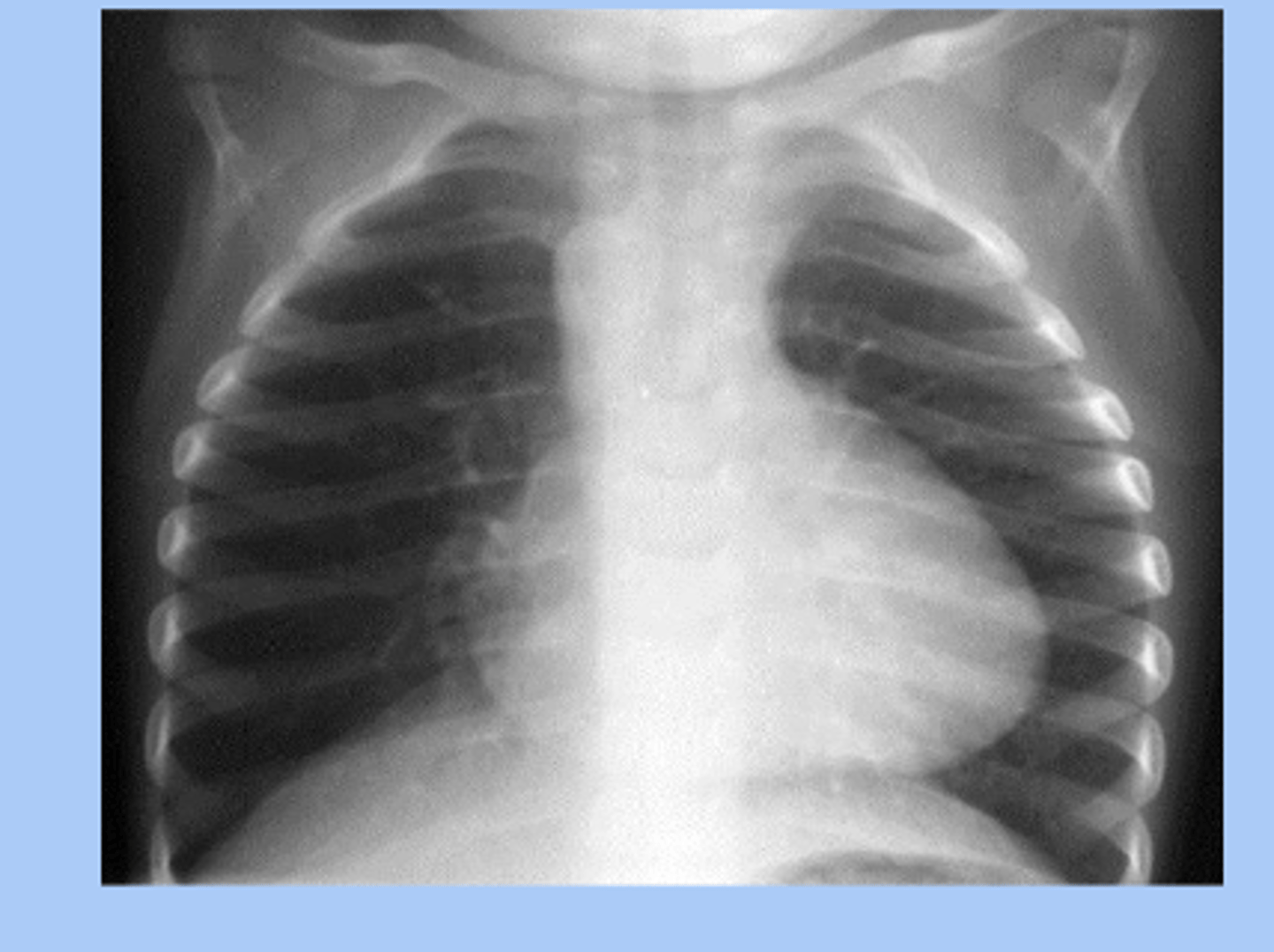
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) tx
-surgical repair needed
-severe newborn: PDA may be open
-tet spell: squat or knee to chest
pulmonary atresia
-cyanotic
-malformation of pulmonic valve > obstruction of RV outflow > absent connection between the right ventricle and pulmonary ateries
pulmonary atresia sx
-pt may be stable
-cyanosis
-holosystolic murmur
pulmonary atresia dx/tx
-dx: echocardiogram
-tx: IV prostaglandin
-surgical repair
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
-cyanotic
-diminutive left ventricle and small left sided structures
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome sx
-neonates: stable at birth bc ductus is patent
-deteriorate rapidly as ductus closes > shock and acidosis secondary
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome dx/tx
-dx: fetal echocardiogram
-tx: IV prostaglandin at delivery to maintaine patent docus arteriosus
-surgical repair
Transposition of the Great Vessels
-cyanotic
-patho: aorta arises from the RV and pulmonary artery from the LV (switched)
Transposition of the Great Vessels sx
-neonates are large
-profound cyanosis at birth
-respiratory distress
-significant murmur present in some systolic
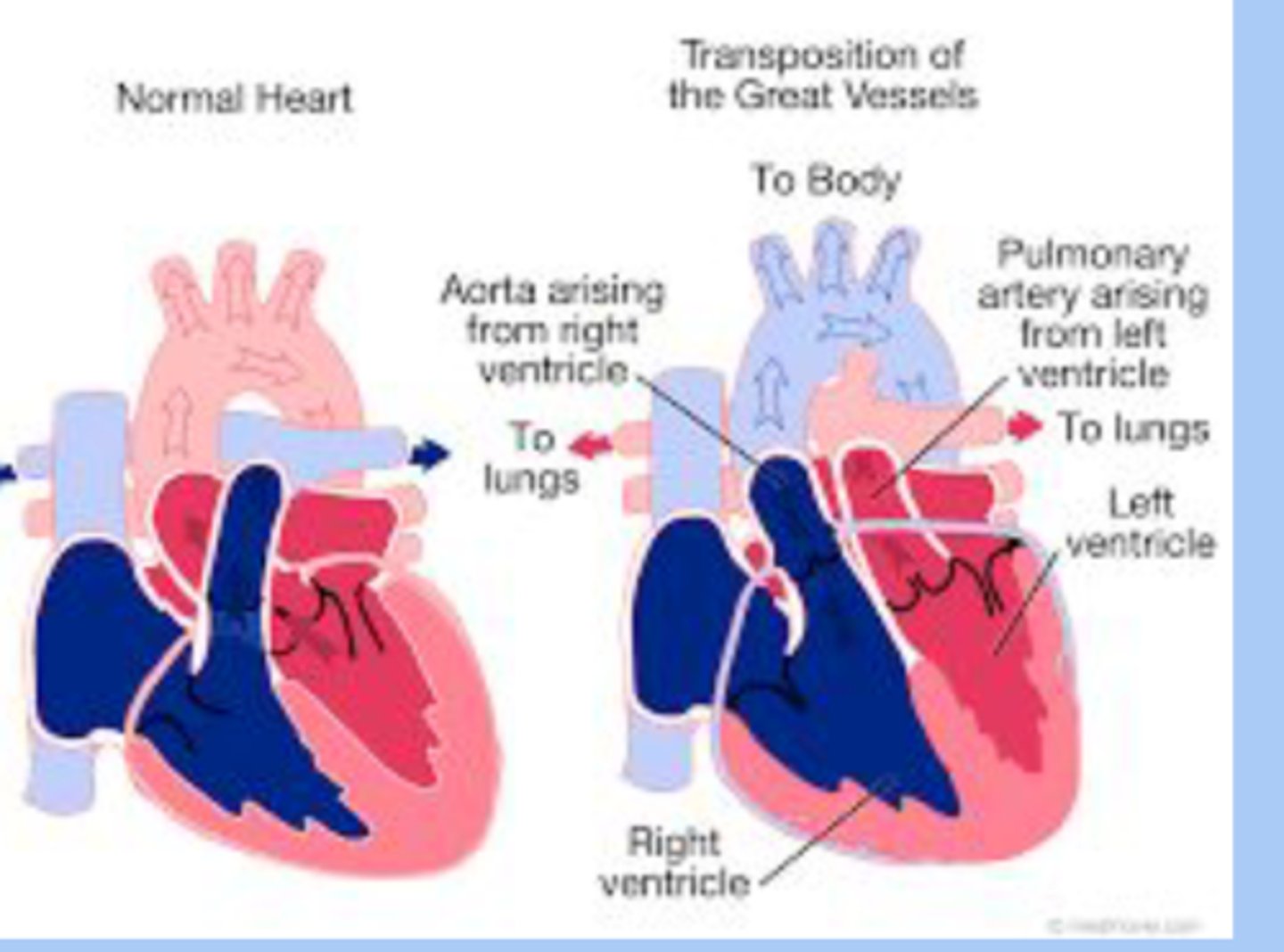
Transposition of the Great Vessels dx/tx
-dx: echocrdiogram
-tx: early corrective surgery
kawasaki disease
-mucocutaneous vasculitis
-viral cause suggested
-< 5yo
-japanese and korean descent
kawasaki disease sx
-fever >5 days and at least four of the sx
-conuunctivits
-lip cracking and fissuring, strawberry tonue, inflammation of oral mucosa
-polymorphous exanthem
-redness and swelling of hands and feet
-cardio manifestation
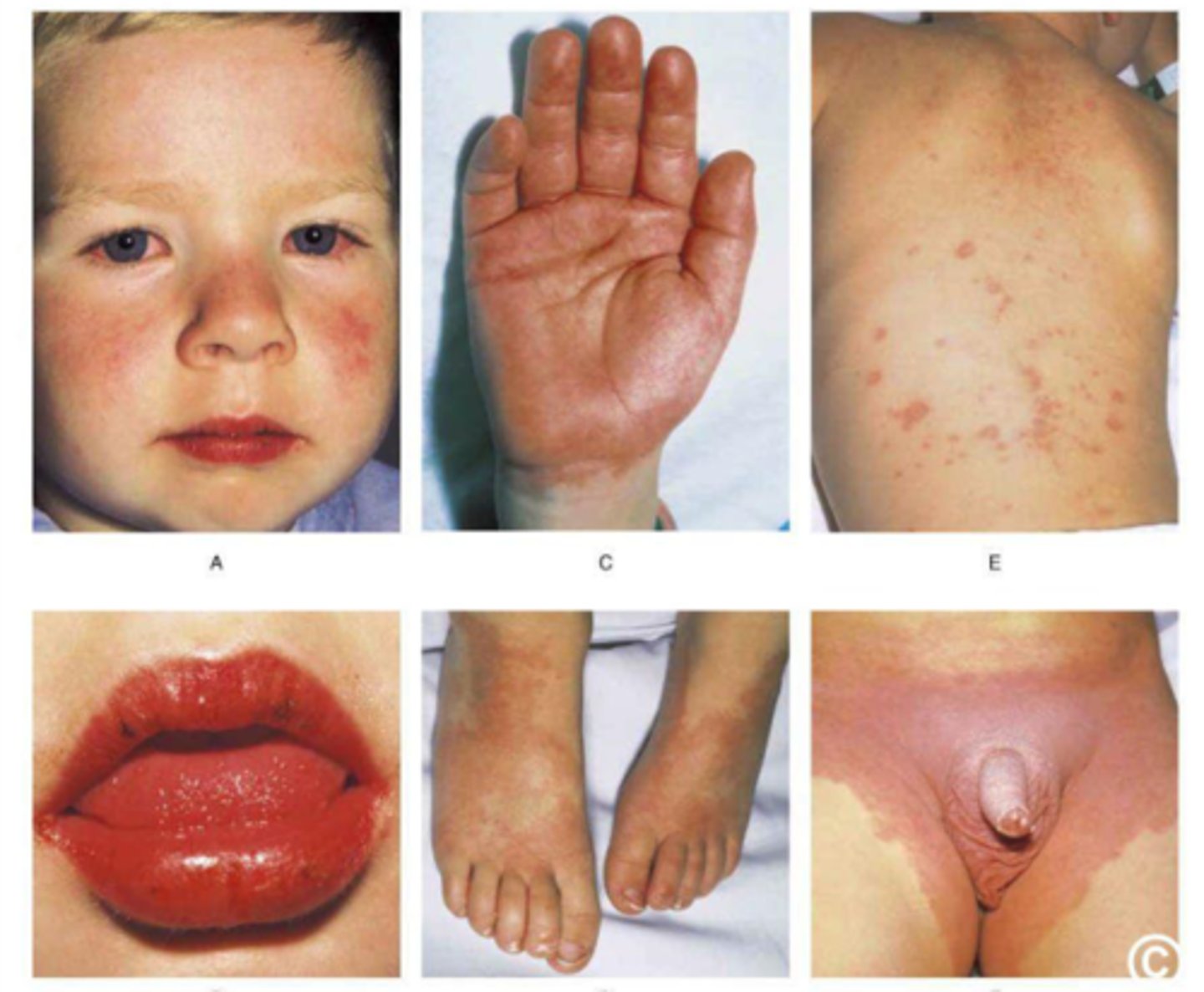
kawasaki disease dx/tx
-dx: elevated WBC, ESR, CRP
-echocardiogram
-tx: IVIG and high dose aspirin