bio 109- chapter 7- cellular respiration
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
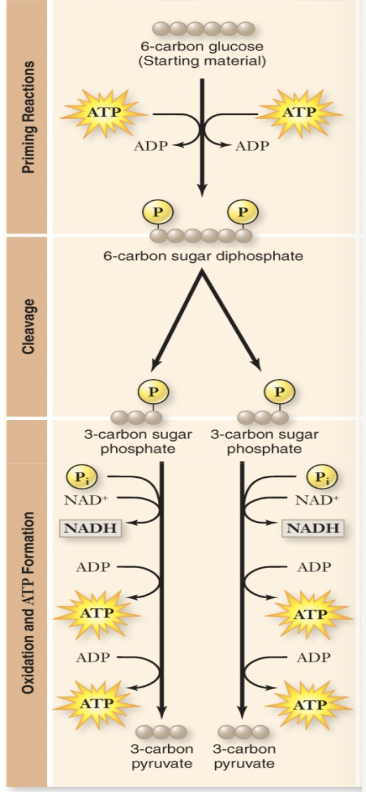
glycolysis
splitting glucose (6C into 2 pyruvates)
needs 2 NAD+ before ATP can be generated
occurs in the cytoplasm of every cell on the planet
destabilize costing 2 ATP, reduce 2 NAD+, form 4 ATP
net production: 2 NADH 2 ATP
electron carrier
nucleic acid that reversibly binds to high energy electrons
oxidative phophorylation
pyruvate oxidation + krebs cycle + ETS + chemiosmosis
glycogenolysis
splitting glycogen into glucose molecules
animals convert stored glycogen to glucose
plants convert starch to glucose
gluconeogenesis
making glucose from non carbohydrates
make new sugars from non-carbohydrates
autotrophs
produce their own organic molecules
photoautotrophs, chemoautotrophs
use cellular respiration to extract potential energy from glucose

heterotrophs
consume organic molecules in other organisms
herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, parasites, detritivores, saprophytes
cellular respiration
how to get energy out of glucose
potential energy is in the electrons of covalent bonds
C-C bonds are broken in multiple steps
what are the two types of electron carriers
unenergized (oxidized)
energized (reduced)
all can be reversibly oxidized and reduced
they oxidize one molecule in order to reduce another one later on
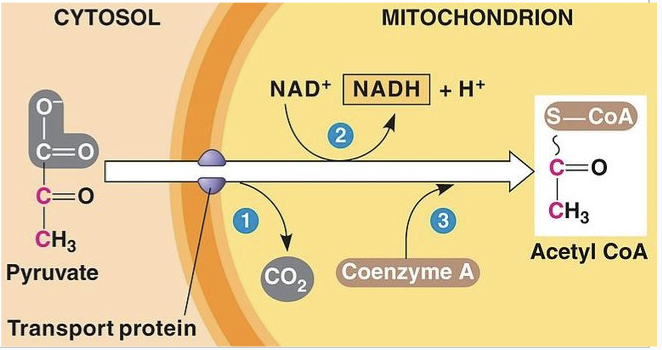
pyruvate oxidation
get even more energy/electrons out
needs 2 NAD+
occurs in the mitochondria (eukaryotes) or cell membrane/cytoplasm (prokaryotes)
oxidize 1 pyruvate into: 1 CO2 1 NADH 1 acetyl-CoA
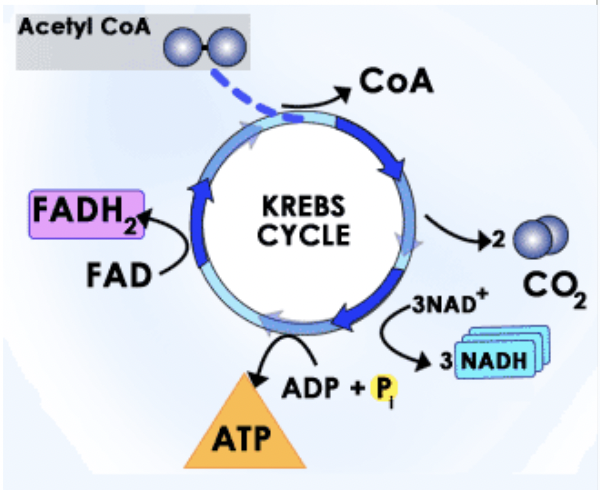
krebs cycle (citric acid cycle)
occurs in the mitochondria (eukaryotes) or cell membrane (prokaryotes)
needs 6 NAD+ before ATP can be generated
oxidize 1 acetyl group (from acetyl-CoA) into:
2 CO2
1 ATP
3 NADH
1 FADH2
basically hydrolysis uses 3 H2O
two types of anaerobic respiration
methanogens (archaea)
reduce carbon dioxide
Sulfur bacteria
reduce sulfate
what are two types of fermentation
ethanol fermentation
lactic acid fermentation
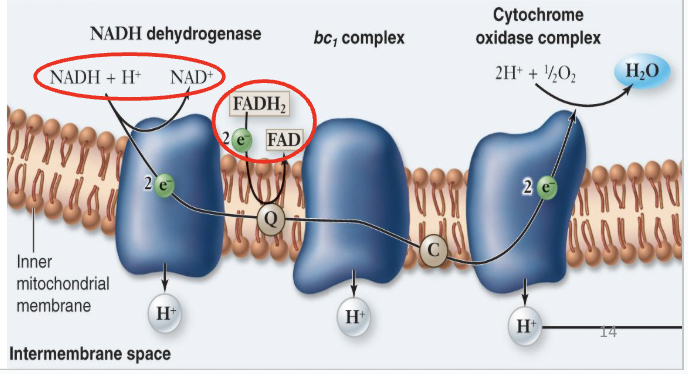
electron transport system
occurs in mitochondria (eukaryotes) or cell membrane (prokaryotes)
electrons from NADH and FADH2
energy used to pump H+ ion (active transport)
aerobic
O2 is final electron acceptor
anaerobic
different final electron acceptor
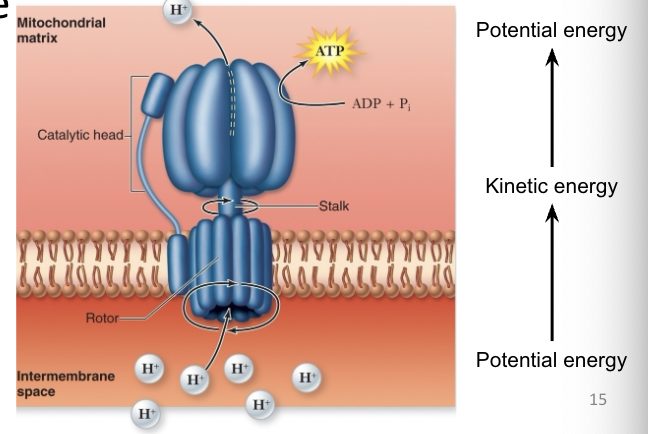
chemiosmosis
occurs in mitochondria (eukaryotes) or cell membrane (prokaryotes)
membranes are re,atively impermeable to H+
H+ ions flow through ATP synthase (facilitated diffusion)
32 ATP per glucose