Management Exam 3
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
national culture
frameworks for classifying behavior patterns can help business people who work in different countries
- individualism vs collectivism
- power distance
- uncertainty avoidance
- tightness-looseness
individualism vs collectivism
assesses whether a culture values individual achievement and self-interest versus collective goals and harmony
power distance
the power inequality between superiors and subordinates
uncertainty avoidance
how members of a society respond to uncertainty or ambiguity
tightness vs looseness
degree to which a society enforces rules and punishes deviance
individualism
sense of self separate from others, value individual achievement, freedom, and competition
collectivism
self is interdependent with others, value group harmony, cohesiveness, consensus, and cooperation, avoid public confrontations
low power distance
expect managers to empower employees and draw on their expertise, social welfare programs reduce power gaps
high power distance
expect social inequality and that managers make decisions and tell employees what to do, large gap between rich and poor, respect for/fear of superiors
high uncertainty avoidance
need for structure and clear view, more formal rules, security is important
low uncertainty avoidance
comfortable with ambiguity, risks, and chaos, few rules, innovation and achievement are important
loose culture
characterized by flexibility, informal communication, and a relaxed approach to rules and procedures. It encourages creativity and adaptability among employees
tight culture
characterized by strict norms, formal communication, and a strong emphasis on rules and procedures. It prioritizes consistency and order in organizational behavior
ethical (or moral) relativism
there are no ethical standards that are absolutely true and that apply or should be applied to companies and people of all societies (when in Rome do as the Romans do)
lassez-faire economy
an economic system where transactions between private parties are free from government intervention, allowing for minimal regulation and control
John Maynard Keynes
free markets alone are not necessarily the most efficient means for coordinating the use of society’s resources
Adam Smith
the father of modern economics and a proponent of laissez-faire economics
socialism
wealth and power are shared and distributed evenly based on the amount of work expended in production
social democracy
allows private ownership of property and also features a large government
multinational corporations (MNCs)
public companies that operate on a global scale
ethical debates of multinational corporations
transfer jobs overseas where wage rates are lower
exploit natural resources
exploit labor markets of host countries
create unfair competition
United Nations global compact
a set of 10 principles that promote human rights, sustainability, and the eradication of corruption
global ethics issues
bribery
antitrust activity
healthcare
labor and right to work
compensation
bribery
more acceptable in some countries, the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) and the U.K. Bribery Act work to address bribery
antitrust activity
the anticompetitive practices create high barriers of entry for competitors, the Sherman Antitrust Act (1890) works to break this up
healthcare issues
factors such as access, patents, and global fraud are considered
labor and right to work issues
issues such as gender pay inequality and the right to join trade unions are considered
compensation issues
is the minimum wage a livable wage, what is executive compensation in comparison to workers?
leadership
the ability or authority to guide and direct others towards a goal
normative myopia
when managers overlook or stifle the importance of core values in their business decisions, results in ethical blindness
ethical blindness
propensity to rationalize an unethical action or turn a blind eye to it
ethical leadership influences
situational influences
individual characteristics
moderating influences
situational influences
role modeling
ethical context
individual characteristics
agreeableness
conscientiousness
neuroticism
machiavellianism
moral reasoning
locus of control
moderating influences
ethical context * moral intensity
ethical context * self monitoring
need for power * inhibition
moral reasoning * moral utilization
benefits of ethical leadership
positive impact on organizational culture
higher employee satisfaction and commitment
strong relationships with external stakeholders
strong impact on long-term market firm valuation
psychology of power
group participation and influence
confidence and action
social perception
perspectives not taken
power
the influence leaders and managers have over the behavior and decisions of subordinates
power bases
reward power
coercive power
legitimate power
expert power
referent power
power stratification and hierarchy
advantages:
- reduce conflict
- increase efficiency
- improve coordination
problems:
- emerge easily
- self-perpetuating
- justified by stereotypes
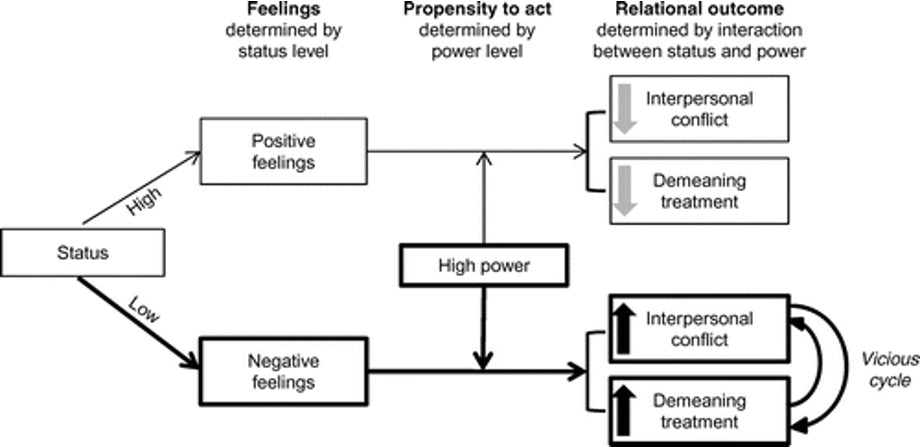
the peril of power without status
what makes a leader
emotional intelligence, twice as important as technical skills and cognitive abilities for jobs at all levels
emotional intelligence
the ability to manage oneself and one’s relationships with others, factors:
- self-awareness
- self-regulation
- motivation
- empathy
- social skills
self-awareness
having a deep understanding of one’s emotions, needs, strengths, weaknesses, values, and goals
self-regulation
ability to control or redirect disruptive impulses and moods
motivation
work for reasons beyond money or status, pursue goals with persistence
empathy
ability to understand the emotional make-up of people
social skills
proficiency in managing relationships and networks
leadership styles
coercive
authoritative/visionary
affiliative
democratic
pacesetting
coaching
contingency theory of leadership
a leader is effective when their leadership style fits the situation
coercive style
“do what I say”
leads by demanding immediate compliance
most effective in emergency situations
creates resonance by reducing ambiguity
authoritative (visionary) style
“come with me”
most effective when change requires a new vision
creates resonance by moving people towards a shared dream
affiliative style
“people come first”
most effective when healing broken organizations
creates resonance by connecting people to each other
democratic style
“what do you think”
leads through building consensus and participation
most effective when you need buy-in
creates resonance by valuing input and increasing participation
pacesetting style
“do as I do, now”
leads by setting high standards for performance
most effective when getting quick results from highly motivated and competent people
creates resonance meeting challenging and exciting goals
coaching style
“try this”
leads by developing people for the future
most effective when helping employees to improve performance and develop long-term strengths
creates resonance by developing others to fulfill individual and organization needs
leader-member exchange theory
leaders form unique relationships with followers through social interactions, leaders who have positive and respectful relationships with employees can increase job satisfaction and commitment to the firm
leader-follower congruence
When leaders and followers share the same vision, ethical expectations, and objectives for the company
ethical business conflicts
when there are two or more positions on a decision that conflicts with organizational goals
conflict management styles
competing
avoiding
collaborating
accommodating
compromising
competing style
high assertiveness, low cooperativeness
avoiding style
low assertiveness, low cooperativeness
collaborating style
high assertiveness, high cooperativeness
accommodating style
low assertiveness, high cooperativeness
compromising style
medium assertiveness, medium cooperativeness
the RADAR model
recognize, avoid, discover, answer, and recover
recognize (RADAR)
recognize ethical issues
avoid (RADAR)
avoid misconduct when possible
discover (RADAR)
discover ethical risk areas
answer (RADAR)
answer stakeholders concerns when an ethical issue comes to light
recover (RADAR)
recover from a misconduct disaster
kakkar and sivanathan
individuals prefer dominant leaders rather than prestige leaders both locally (within towns and cities) and at the national level when faced with the situational threat of economic uncertainty
gender and leadership stereotypes
for women to emerge as leaders, they must display the traits commonly associated with leadership, however when women display the traits associated with leadership they suffer another set of consequences
technology disruption
when innovation replaces existing systems and habits
artificial intelligence
allows machines to learn and perform tasks that typically require human intelligence
AI benefits and risks
benefits:
- eliminates repetitive tasks
risks:
- unintended bias
- implementation issues
- data issues
big data
large volumes of structured and unstructured data that need to be transmitted at very fast speeds
big data benefits and risks
benefit: can inform business strategies
risk: concerns for consumer privacy
drones
unmanned aerial devices that can be used to take aerial images, make deliveries, and collect environmental data
drones benefits and risks
benefit: reduce risks to employee health and safety
risk: consumer privacy concerns
robotics
can be programmed to perform humanlike actions and carry out custom tasks
robotics benefits and risks
benefit: can protect employee well-being
risk: safety of the robotics and job loss
privacy issue
data protection, issues such as cookie use and employee privacy, acts like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) work to address these issues
surveillance
tools include cameras, beacons, biometric technology (facial recognition), these tools have racial bias
intellectual property
intangible ideas and creative materials, protections include copyright, trademark, and patent protection
cybercrime
committing crimes via technology, include malware and fraud
the digital divide
the varying levels of access to technology across social, geographical, and geopolitical groups
manipulation of behavior
the use of information to manipulate behavior, online and offline, in a way that undermines autonomous rational choice
biotechnology price inequality
biotechnologies often cost too much to be beneficial to the masses (childhood genetic testing)
chief privacy officer (CPO)
an executive responsible for developing and implementing policies and procedures related to privacy protection, involves technology assessments