Section 1: Gustation
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What are the 2 chemical senses?
taste (gustation) and smell (olfaction)
What is the difference between special senses and general senses?
Special senses include: taste (gustation), smell (olfaction), vision, hearing, equilibrium. General senses include touch, temperature, pain, proprioception.
Where are special senses and where are general senses found?
Special senses are localized in complex organs and general senses are scattered throughout the body.
What are the five primary taste qualities?
Sweet, salty, sour, bitter, umami.
Which ion mediates salty taste?
Na⁺ influx through ENaC.
Chemical senses detect environmental chemicals via _______________.
chemoreceptors
The nervous system perceive flavor by using what 2 senses?
gustation and olfaction
Chemicals that stimulate gustatory receptor cells are called:
tastants
What ion mediates sour taste?
H⁺ (proton) channels and blocking K⁺ channels.
What causes a sweet taste?
sugars (fructose, sucrose), artificial sweeteners
What ions mediate a bitter taste?
K+, Mg2+, quinine, caffeine.
Which taste is characterized as a “delicious, savory” taste?
Unami
What are the organs of taste?
Tongue, palate, pharynx, and epiglottis.
When observing the areas of sensitivity on the tongue, the ________ taste is localized at the back of the tongue, and the ________ taste is at the tip.
the bitter taste is localized at the back and the sweet taste is at the tip.
Which taste uses mGluR (Glutamate/MSG) or T1R1/T1R3 receptors?
Unami
________________ are small protuberances on the upper surface of the tongue that contain ____________________.
Papillae, that contain taste buds,
What type of lingual papillae is very large, circular papillae in an inverted V-shaped row at the back of the tongue?
Vallate papillae
What type of lingual papillae is mushroom-shaped and scattered over the entire tongue.
Fungiform papillae
What type of lingual papillae is located in small trenches on the lateral margins of the tongue?
Foliate papillae
What type of lingual papillae degenerate in early childhood?
Foliate papillae
What type of papillae has NO taste buds is used for texture sensing?
Filiform papillae
How many taste buds/papilla are there in vallate papillae?
100-300 taste buds/papilla
How many taste buds/papilla are there in fungiform papillae?
5 taste buds/papilla
How many taste buds are there per person?
2,000 - 5,000 taste buds/person
What are the 3 types of cells in the taste bud?
taste receptor cells, supporting epithelial cells, and basal epithelial cells.
How many taste receptor cells are there per taste bud?
50-150 per taste bud
_______________ cells are also known as stem cells in taste buds.
Basal epithelial cells
The apical end (near the surface of the tongue) is the chemically sensitive part and has ______________ that project into the _______ ______.
microvilli that project into the taste pore
True or False:
Taste receptor cells are neurons.
FALSE THEY ARE NOT!!
__________________ cells form synapses with ___________ afferent axons near the bottom of the taste bud.
Taste receptor cells form synapses with gustatory afferent axons near the bottom of the taste bud.
What is the lifespan of taste receptor cells?
10 - 14 days
____________ ______________ is induced upon activation of taste receptor cells.
Receptor potential
_________ of the taste receptor membrane causes voltage-gated ___________ channels to open, which triggers neurotransmitter release: ______________ for sour and salty, and ___________ for unami.
Depolarization; Ca2+ channels; Serotonin; and ATP
Some receptor cells respond primarily to ___________ of the five basic tastes, but some taste receptor cells and many gustatory axons show _________ response preference.
one; multiple

What type of taste does Cell 1, 2, and 3 mainly detect?
cell 1 = salty
cell 2 = sour
cell 3 = sweet
Taste receptor cells that are exclusively sensitive to ONE basic taste stimuli are called ________ cells.
specialist
Taste receptor cells that respond to multiple taste types are called _________ cells
generalist
Gustatory axons may receive synaptic input from just ONE type of taste cell are called _____________ axons.
specialist
Gustatory axons that receive synaptic input from multiple specialist taste cells, and/or generalist taste cells are called _________ axons.
generalist
______________ is the process by which an environmental stimulus causes an electrical response in a sensory receptor cell.
transduction
In salty taste transduction, tastants will:
pass directly through ion channels
In sour taste transduction, tastants may:
directly through ion channels or bind to and block ion channels
In bitter, sweet, and unami taste transduction, tastants will:
bind to G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that activate second messenger systems that open ion channels.
What kind of channels are involved in the salty taste transduction?
Na+-selective channels (“Amiloride-sensitive sodium channels)
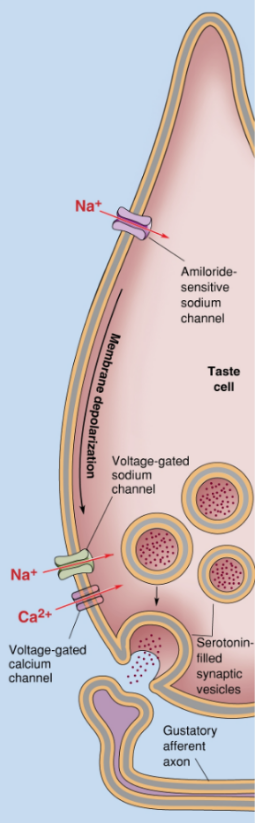
What taste transduction is shown in the figure?
salty
INSERT FIGURE FOR SOUR TASTANT
INSERT FIGURE FOR BITTER, SWEET, AND UNAMI TASTANTS?
What occurs during the transduction of sour tastant?
H+ binds and blocks K+-selective channels → depolarization → opens voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels near synaptic vesicles → release of neurotransmitters.
What occurs during the transduction of salt tastant?
Na+-selective channels stay open → Na+ influx causes membrane depolarization → stimulates voltage=gated sodium and calcium channels to open near synaptic vesicles → release of neurotransmitters.
COME BACK TO SLIDE 26 LATER TO GO THROUGH TRANSDUCTION OF BITTER, SWEET, AND UNAMI TASTANTS
Draw the gustatory pathway.
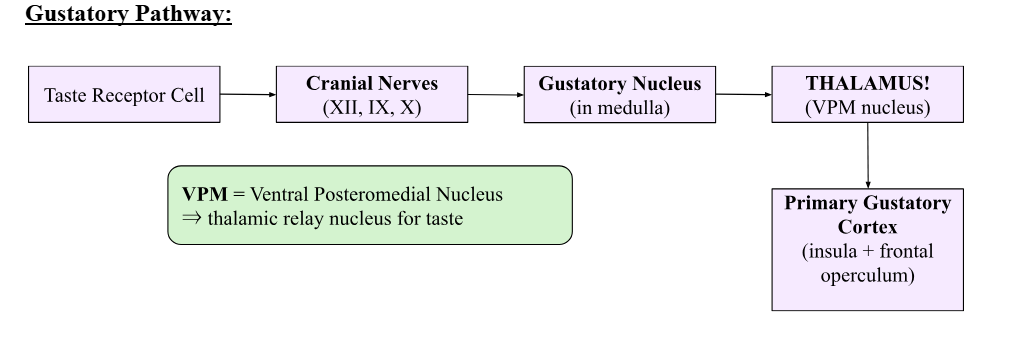
What three cranial nerves convey gustatory information?
Facial (VII), Glossopharyngeal (IX), Vagus (X)
Which CN carries taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue?
CN VII (facial).
What CN carries taste from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue?
CN IX (glossopharyngeal).
Which CN carries taste from epiglottis?
CN X (vagus).
What type of neural coding is this:
Each taste receptor type responds to ONLY one specific taste and is connected by separate sets of axons to neurons in the brain.
Labeled line hypothesis
What type of neural coding is this:
The response of a large number of broadly tuned neurons are used to specify the properties of a particular taste?
Population coding
Where is the primary gustatory cortex?
insula