Med anatomy chapter 2
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
nervous system
controls muscles and glands, receives sensory input, integrates information, establishes and maintains mental activity
what is skeletal muscles controlled by?
the somatic system of the PNS
what are smooth muscles and cardiac muscles and glands controlled by?
autonomic division of the PNS
what are the divisions of the nervous system
central and peripheral nervous system
what are the division of the CNS
brain and spinal chord
what are the divisions of the PNS
motor and sensory
what are the division of the motor PNS system
somatic and autonomic
what are the divisions of the motor autonomic PNS system
sympathetic and parasympathetic
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
systematic nervous system
fight or flight; nervous system that we DO control; controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles
external stimuli
5 senses, temperature
what is the external stimuli controlled by
the somatic part of the PNS that leads to conscious feeling
somatic nervous system
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system. Enables voluntary actions to be undertaken due to its control of skeletal muscles
autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
internal stimuli
muscle length and tension, blood pH, pressure, blood glucose level, hormone control
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction
myelinated axons
axons covered with myelin sheaths
dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
splitting of dendrites
arborisation
cell body of axons
contains the nucleus and nissi bodies runs the processes houses DNA organelles rough endoplasmic reticulum and produce protein and neurotransmitters
nissi body
membranous sacs within cytoplasm of nerve cells that have ribosomes attached to their surfaces
axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
myelin sheath
A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next.
Nodes of Ranvier
a gap in the myelin sheath of a nerve, between adjacent Schwann cells. which allow conduction of electricity
axon terminals
Branches at the end of the axon that contain tiny pouches, or sacs, called synaptic vesicles.
synaptic bouton
A swelling specialized for the release of neurotransmitter that occurs at the end (or along) an axon - pre-synaptic (before the synaptic cleft)
Also known as an axon terminal or terminal boutons
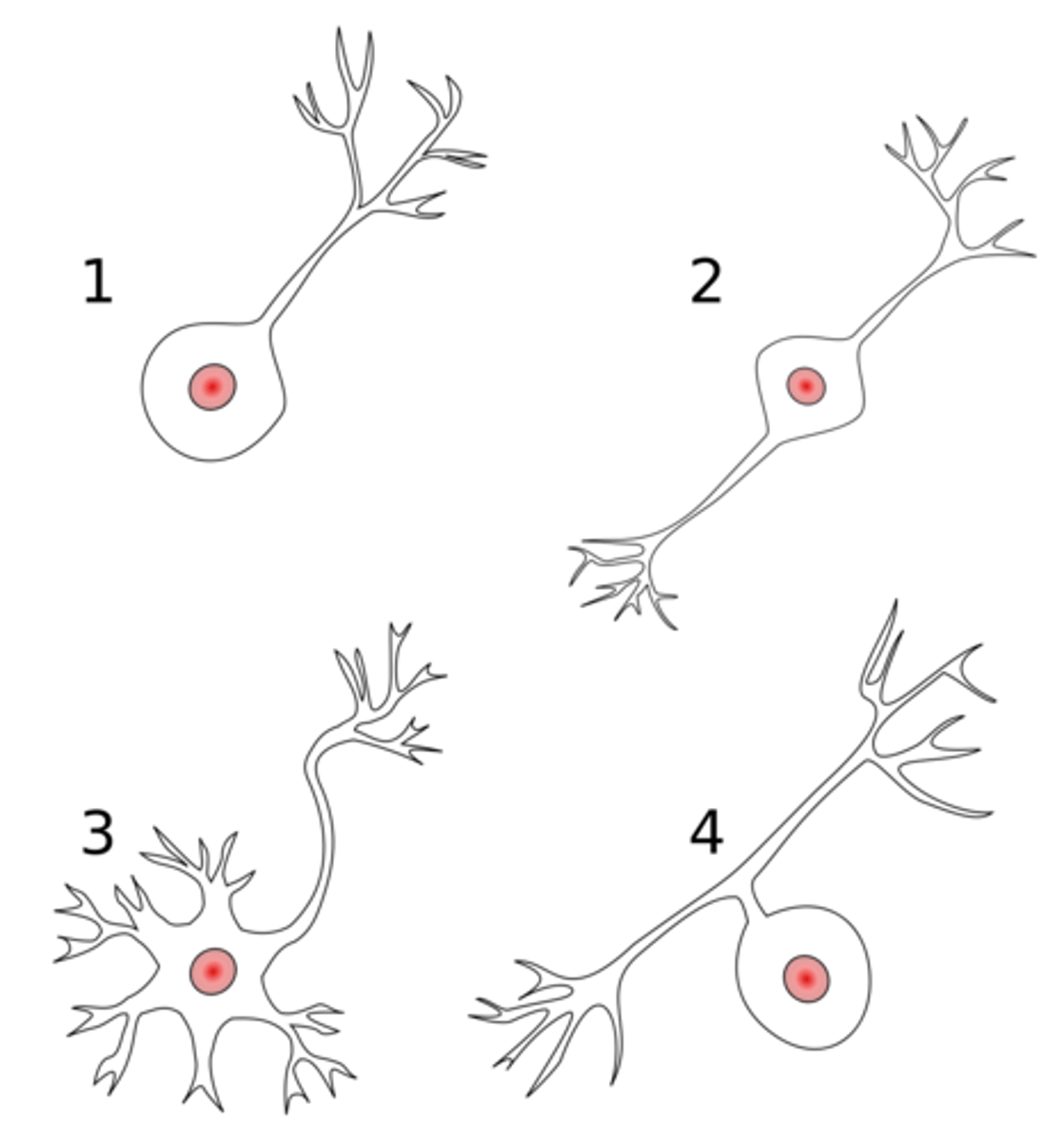
what is 1 in this image
unipolar
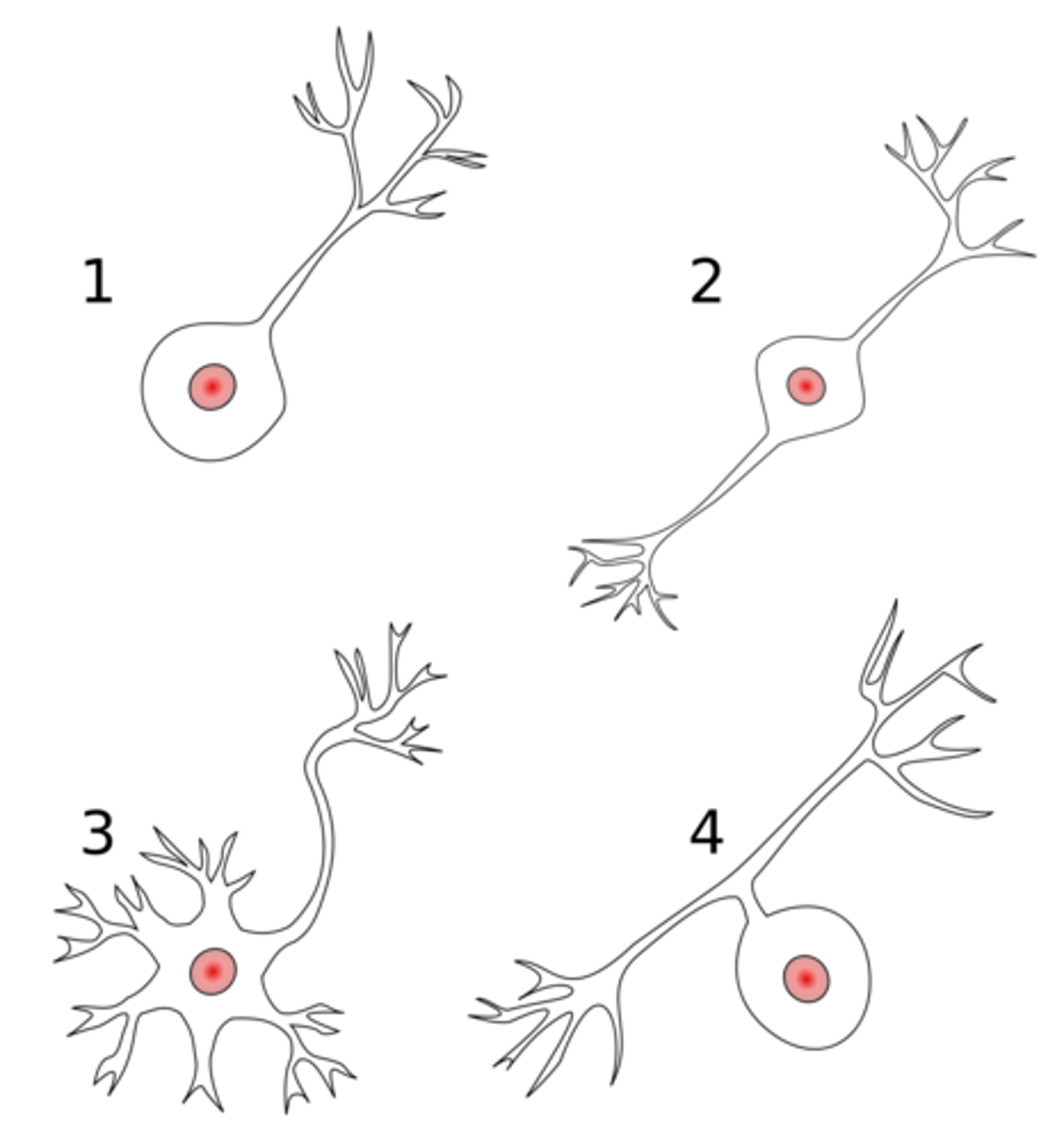
what is 2 in this image
bipolar
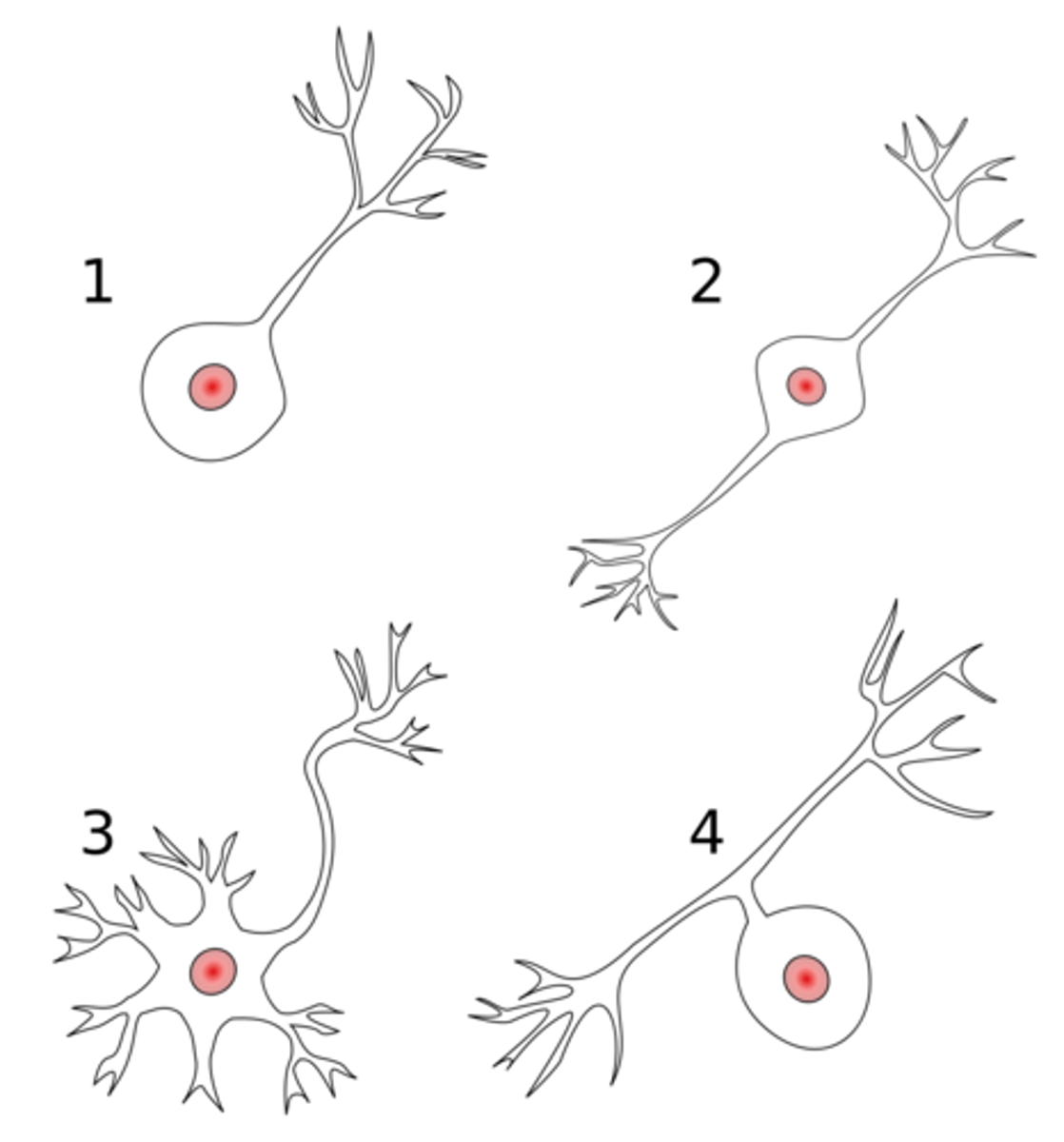
what is 3 in this image
multipolar
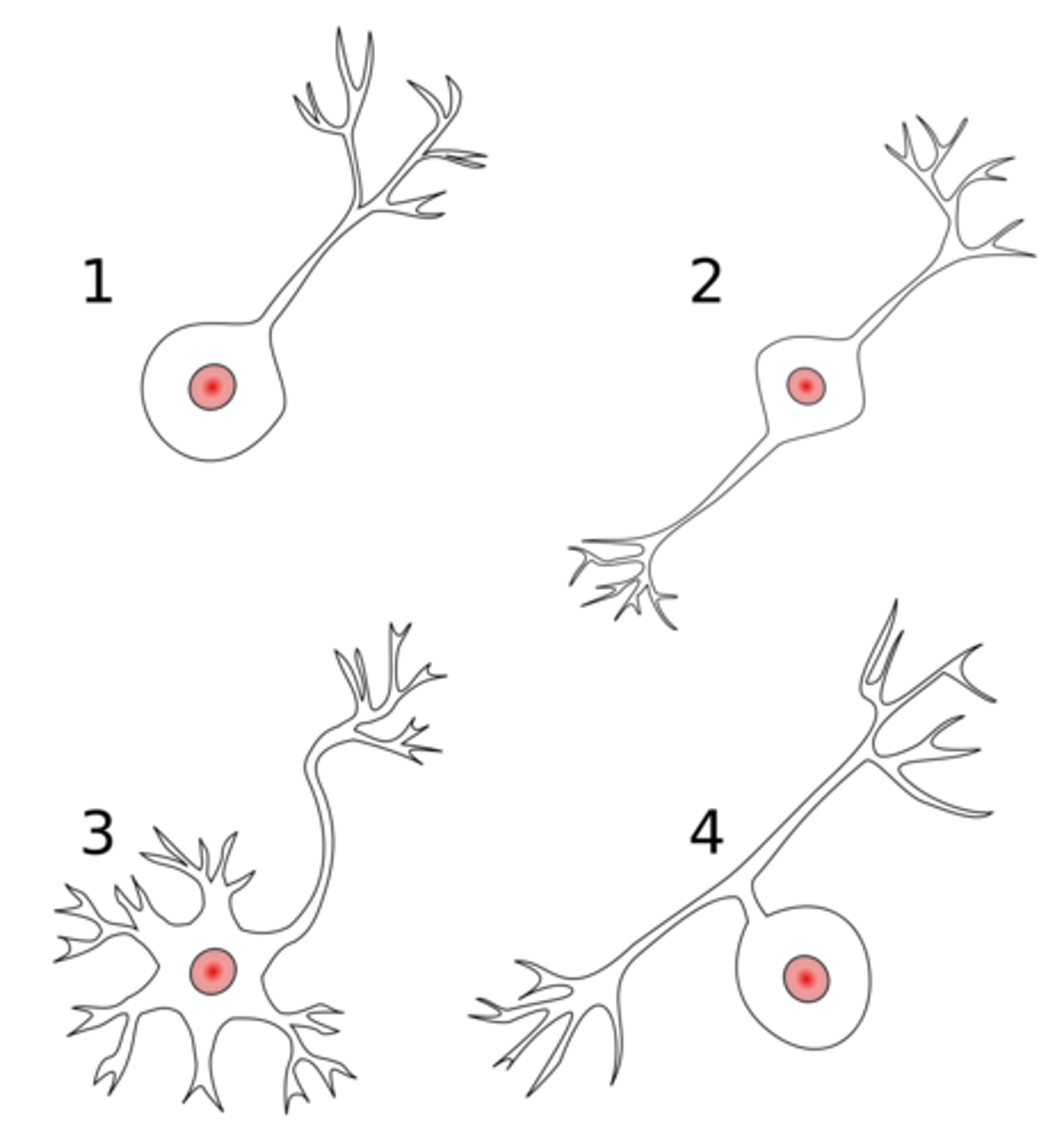
what is 4 in this image
pseudo uni polar
bipolar axons
neuron two poles one dendrite and one axon. Rare found for special senses
pseudo uni polar
peripheral axon and the central axon, they do not have dendrites. In sensory neurons. efferent
multipolar neuron
A neuron with a single axon and multiple dendrites; the most common type of neuron in the nervous system. stimulate muscles.
axon hillock
Cone shaped region of an axon where it joins the cell body.
schwann cell
Supporting cells of the peripheral nervous system responsible for the formation of myelin.
nissl body
Rough ER
chemicals released in synaptic boutons
neurotransmitters
action potentional
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
neuromusclar junction
point of contact between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle tissue
neuroglandular junction
synapse between neuron and gland
How does action potential work?
1. When an axon is not stimulated, its membrane has resting potential.
2. An action potential excites the neuron's membrane. If the excitation reaches the threshold of the axon, some gates/channels open at the start of the axon. Sodium ions, concentrated outside the membrane, rush into the cell, attracted by the negative charge. The influx of positively charged sodium ions is the action potential. As the positive charge enters the axon at one point, it stimulates the next point along the axon, which then starts opening sodium channels and repeats the process.
3. The sodium gates snap shut after being opened for a few milliseconds. The potassium gates remain open. Potassium does not flow as rapidly as sodium, but continues longer. The potassium ions carry a positive charge. Their exit drives the inside of the axon back to resting potential.
4. Eventually, the sodium-potassium pump removes the extra sodium ions and recaptures escaped potassium ions.
lipid found in myelin sheath
cholesterol
afferent
sensory towards the CNS
efferent
motor away from the CNS
Oligodendrocytes
Type of glial cell in the CNS that wrap axons in a myelin sheath.
white matter
Whitish nervous tissue of the CNS consisting of neurons and their myelin sheaths.
grey matter
The portions of the central nervous system that are abundant in cell bodies of neurons rather than axons. Unmyelinated.
histology of an axon
axon, surrounded by a myelin sheath, covered in schwann cells and the nodes of ranvier
histology of the axons (p.e.e)
axons, myelin sheath, endoneurium, fascicle, perineurium, epineurium
Cell body collection in CNS
nucleus
cell bodies in PNS
ganglion
axons in CNS
tract
axons in PNS
nerve
CNS
lies in the vertebral column in the dorsal cavity of the back
where is grey and white matter stores in the brain
grey peripherally, white centrally
where is grey and white matter located in the spinal chord
grey centrally white peripherally
dorsal
sensory information
ventral
motor information
what does the dorsal root ganglion contain
cell bodies for sensory axons
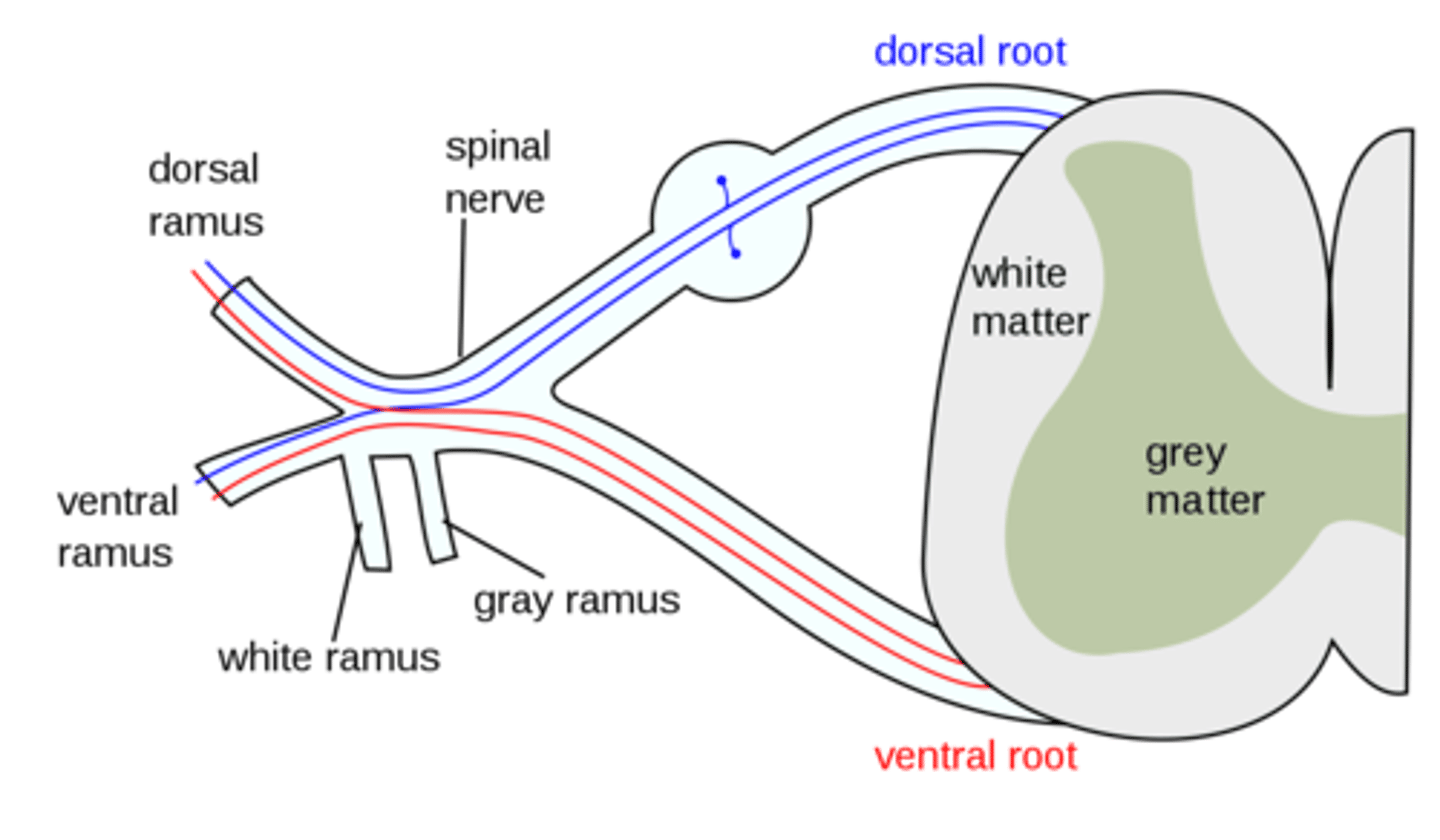
do the ventral and dorsal primary rami carry sensory motor or mixed info
mixed
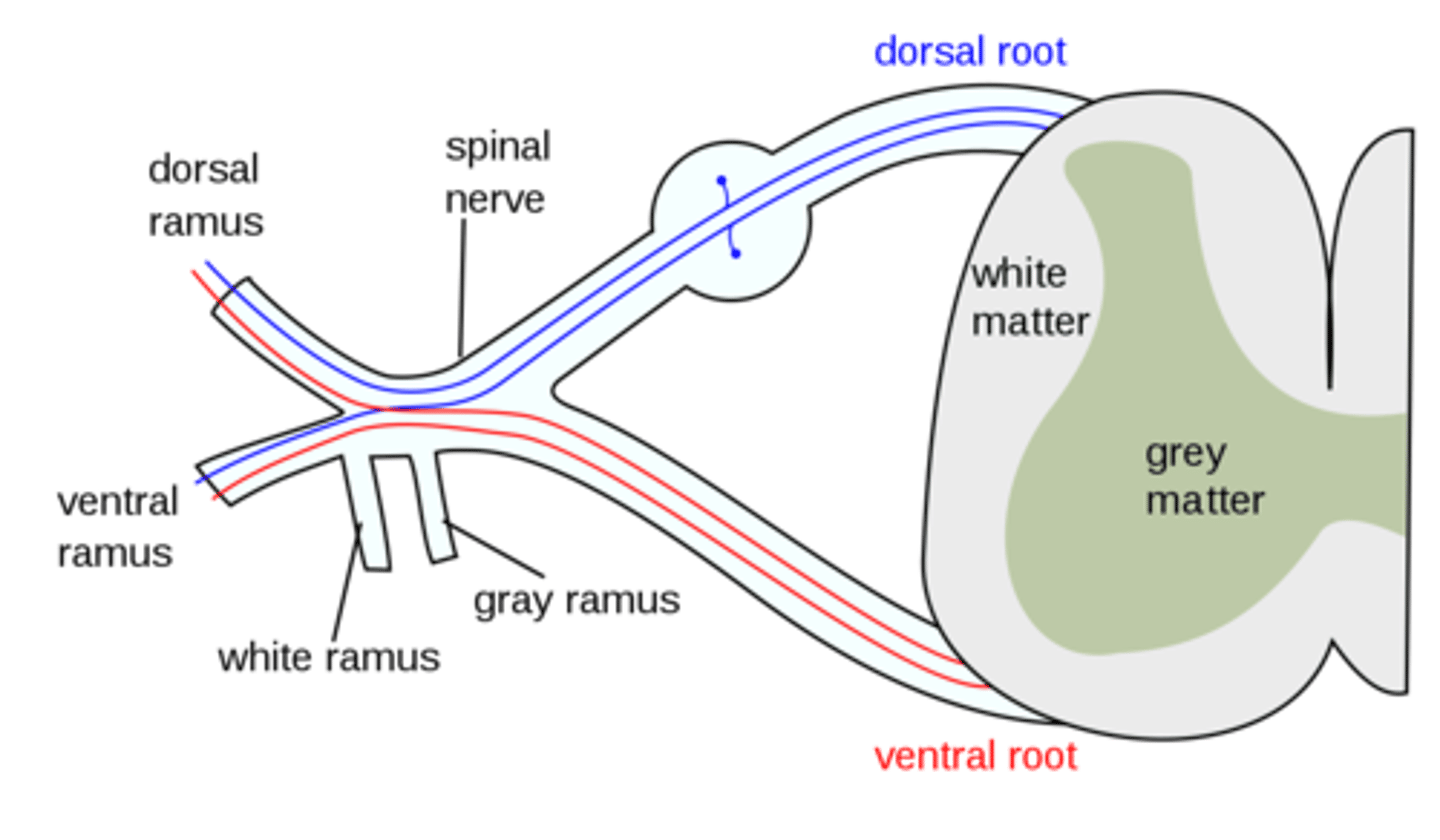
are the rootlets roots and rami part of the CNS or PNS
PNS
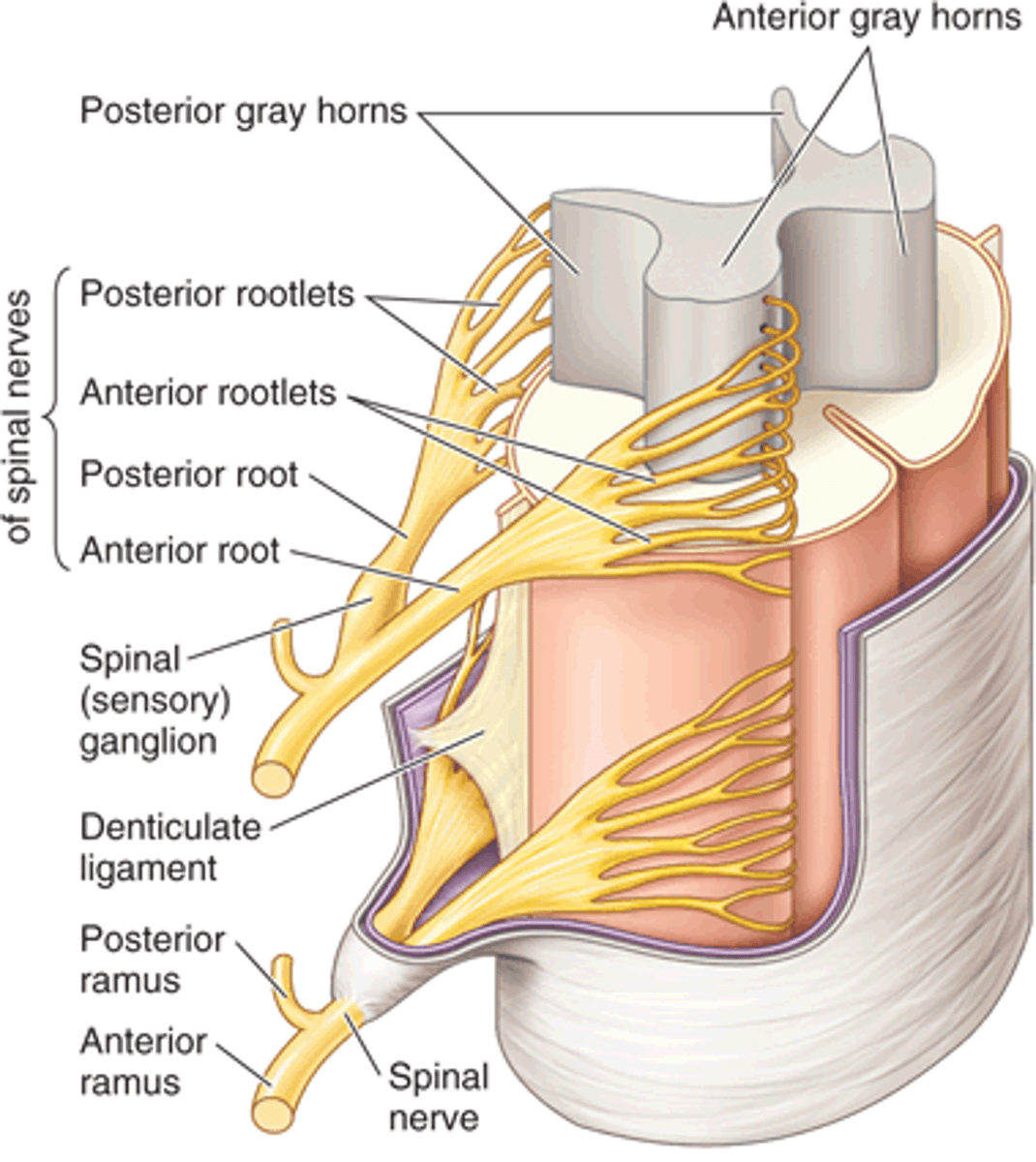
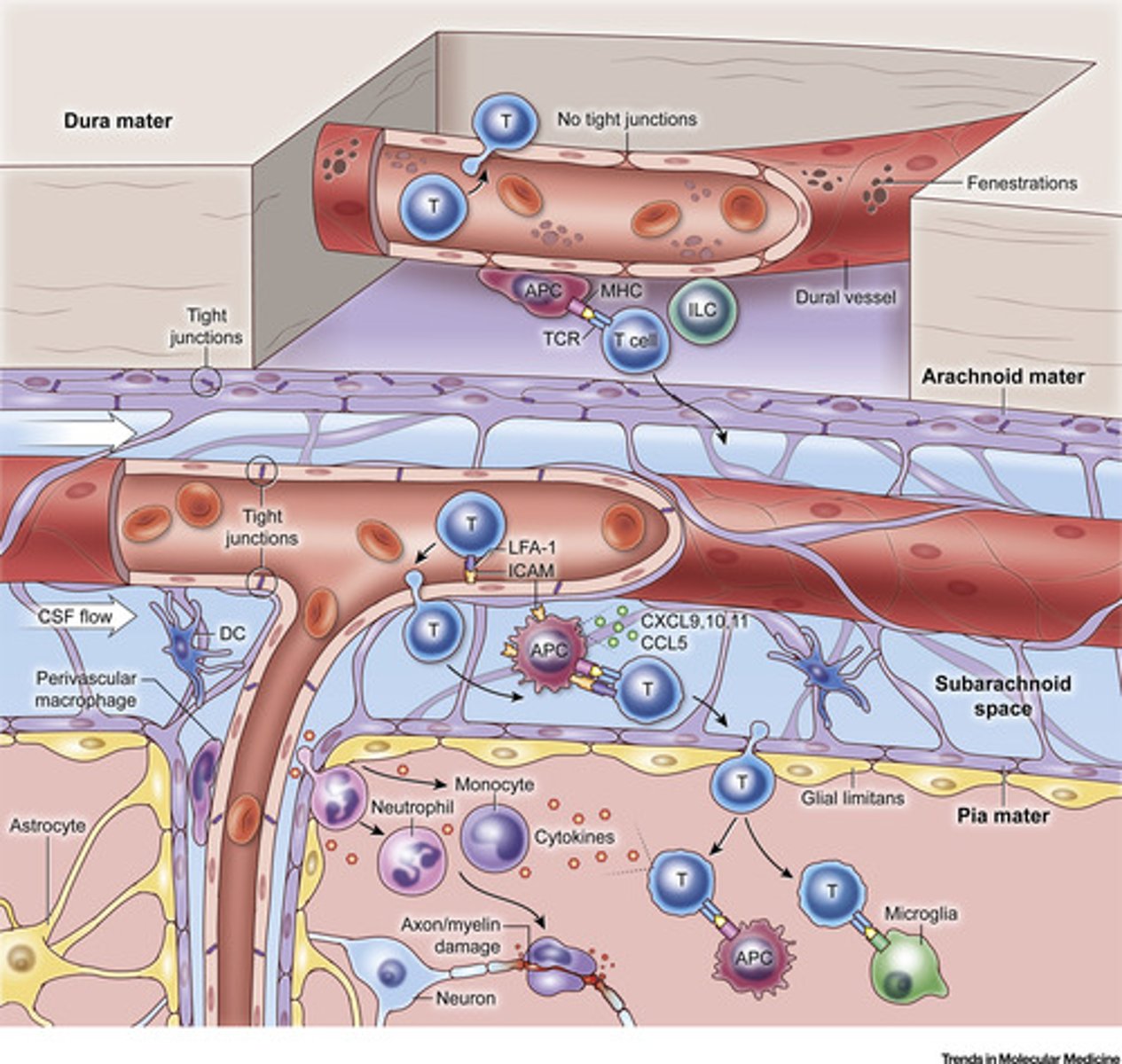
Meninges
three protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
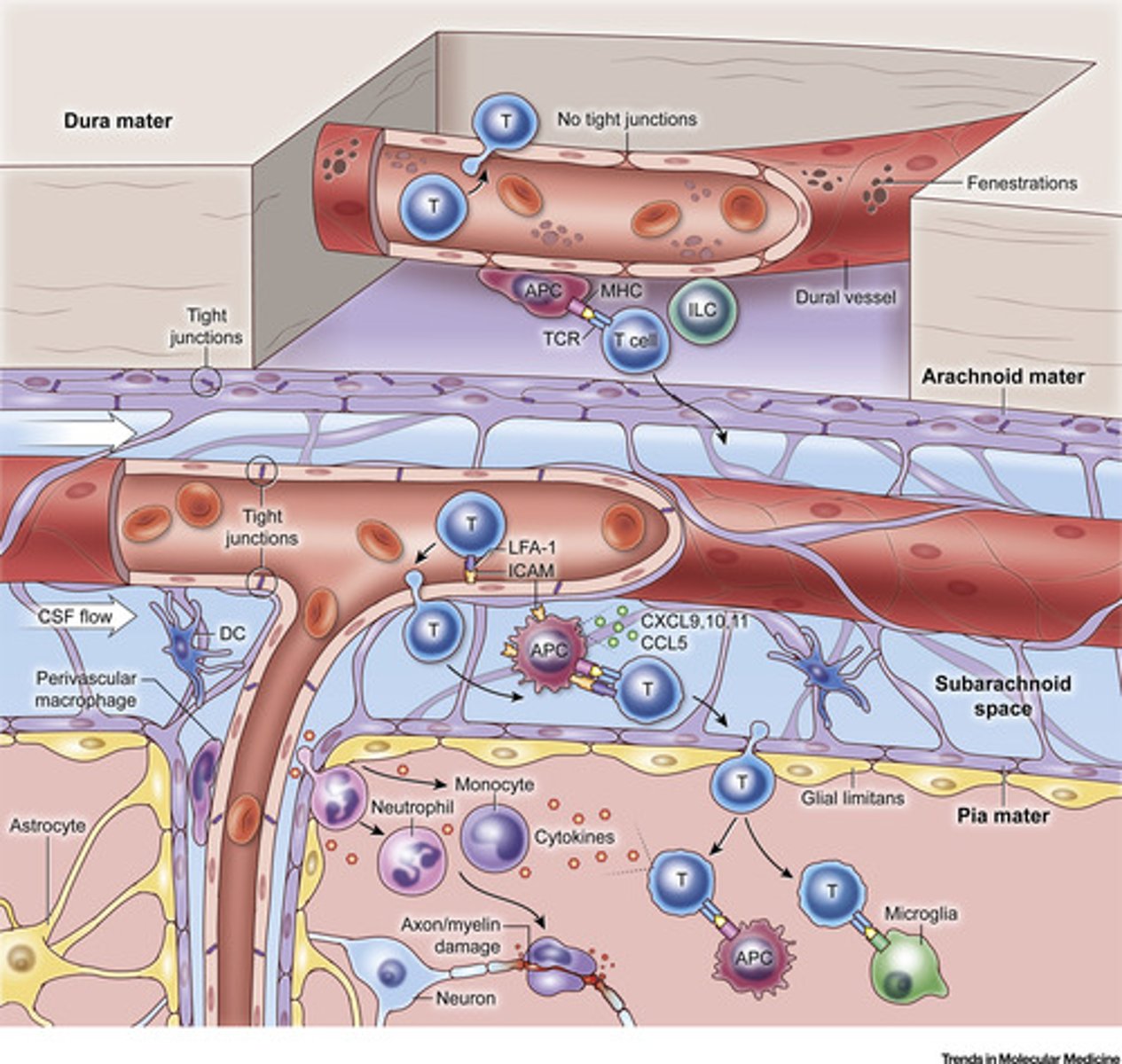
meninges layers
1. dura mater
2. arachnoid
2.5. subarachnoid space
3. pia mater
4. cranium
5. periosteum
6. skin
where does the spinal chord end
L1-L2 or at the conus medullaris
what does the central canal and subarachnoid space contain
CSF
are tracts located in white or gray matter
white
difference between nerve and axon
nerve a group neuron an individual cell
fascicle
bundle of axons surrounded by perineurium
endoneurium
surrounds an axon
epineurium
surrounds the entire nerve
difference between cranial and spinal nerves
cranial originate through foramen at base of the skull and spinal originate through the foramen of the spinal column
paires of spinal nerves
31
spinal nerves type
mixed
number of cervical
8
number of thoracic
12
number of lumbar
5
number of sacral
1
number of coccygeal
1
C1-4
cervical
C5-T1
brachial
T2-12
remain segmented
L1-S4
lumbosacral
dorsal ramus
innervates the skin of the back and spinal muscles
C5
shoulder abduction
C6
elbow flexion, wrist extension, thumb
C7
elbow extension, wrist flexion
C8
finger flexion
T1
medial forearm
T2
medial side of upper arm to medial elbow, pectoral and midscapular areas
L2-L4
Quadriceps
S1
achillies
tricepts reflex
C7 radial nerve
bicepts reflex
C5, musculocutaneous
Brachioradialis reflec
C6 radial
Patellar reflex
L2-L4 femoral
achillies reflex
tibial S1
plantar reflex
Position the thigh in a slight external rotation.
With the reflex hammer, draw a light stroke up the lateral side of the sole of the food AND inward across the ball of the foot like in an upside down J shape.
Normal Response: Plantar flexion of the toes (toes curl) and inversion and flexion of the forefoot.
abdominal reflex
causes lateral movement of umbilicus as abdominal muscles on one side contract
neuropraxia
Neuropraxia is the mildest form of traumatic peripheral nerve injury. It is characterized by focal segmental demyelination at the site of injury without disruption of axon continuity and its surrounding connective tissues. This condition results in blockage of nerve conduction and transient weakness or paresthesia.