LMCC 2025-Rhumato
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Monoarthrite ddx
-Arthrite septique
-Goutte
-Arthrite inflammatoire
-Trauma
Spondylite ankylosante examen physique
H 20-30 A
-Schober + (aug. distance entre 2 points < 5 cm)
-Distance occipu-mur > 2cm
-Diminution expansion thoracique
SA tests
-HLA B27 + (souvent)
-RX lombaire (bamboo, dagger sign)
-RX pelvis (sacro-ilite)
SA treatment
AINS
DMARDS
agents bio comme anti-TNF
si attente périphérique: dmards synthéthiques (SSZ ou MTX)
Syndrome anti-phospholipide
Autoimmune disease causing thrombosis of veins, arteries and small vessels.
Sx: miscarrages, AVC, EP, retinal thrombosis.
SAP criteria

Tx SAP
-Warfarine à vie (viser INR 2-3)
-Femmes enceinte: aspirine 75-150mg à partir de la 12e semaine + HBPM
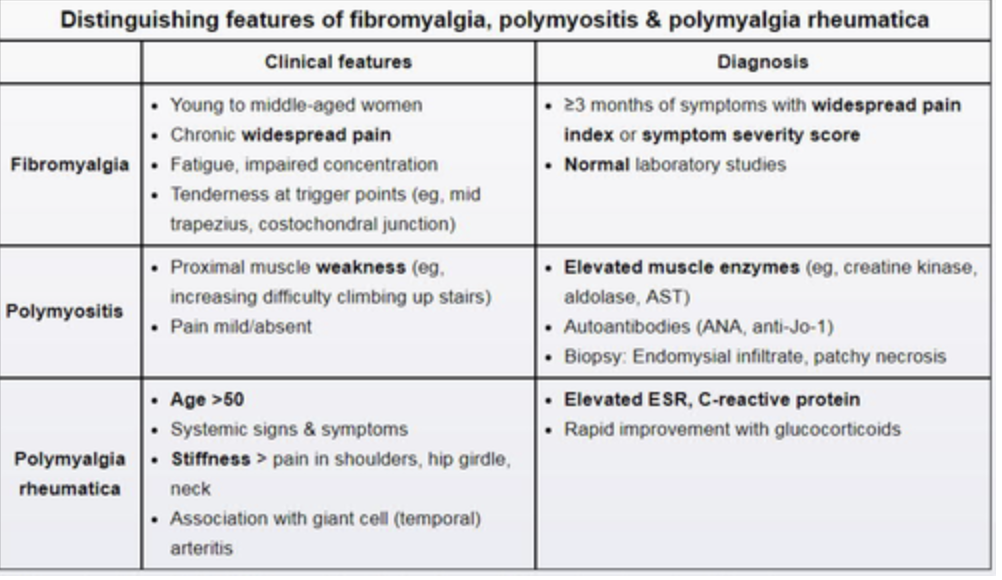
Fibromyalgie
Dx d’exclusion.
Chronic, widespread body pain. This should be in at least 4/5 body regions (left and right upper body, left and right lower body and axial regions).
Giant cell arthritis (artérite temporale) tests
Echo: halo sign
Bx (inflammation granulomateux): gold standard
GCA tx
CS IV si sx visuels
CS PO haute dose 40-60mg DIE puis sevrer
Référence urgente en ophtalmo et rhumato
Goutte
Atteint + souvent 1ere MTP, mais peut aussi atteindre knees, ankles, midtarsal joints, wrists, elbows and small joints of the hands.
Goutte test dx
-Aspiration de l’articulation (GS): monosodium urate crystals with negative birefringence.
-Acide urique sérique
Goutte tx
AINS ad 1-2 jours post résolution (+ IPP) + Colchicine ad résolution de la dlr
CS PO si CI aux 1-2.
Allopurinol en chronique si >2 crises par an, Tophi, Érosions osseux
Apparences des aspirations en goutte vs pseudogoutte etc.
Goutte: aiguille, négativement biréfringeants
Pseudogoutte: rhomboid, positivement biréfringeants.
Pseudogoutte tx
Aigu: CS inj., cool packs, aspiration jointures.
Chronique: AINS + IPP, colchincine
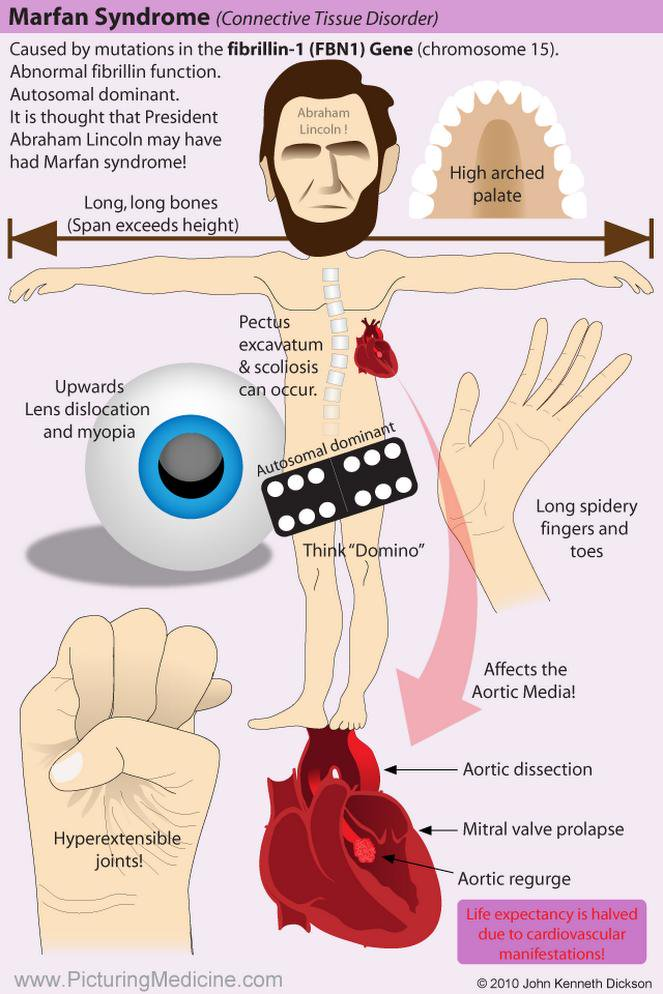
Marfan sx
Autosomal dominant connective tissue disorder caused by mutations in the fibrillin 1 gene.
Osteoarthrite sx
-Crepitus
-Joint swelling
-Reduced motion
-Nodules d’Herberden et Bouchard
OA RX

Osteoporosis
GS: ODM
T < -2.5
Osteopénie si entre < -1 et -2.5
Calcium + vit. D sérique
Indications ODM
> 65 A
F ménopausée et H 50-64 A avec FDR
Fx de fragilité
Fx de hanche chez parent
Tabagisme actif
Forte conso ROH
Usage CS
H, F < 50 ans avec FDR:
Fx de fragilité
Usage CS
Hypert4
Maladie de Cushing
PAR
PMR sx
-Pain and stiffness of the neck, shoulders (bilateral) and pelvis.
-Systemic: weight loss, low-grade fevers, fatigue and anorexia.
-GCA can be associated
PMR vs. polymyositis vs fibromyalgia
PMR tx
CS PO
Polymyosite
Bilateral proximal muscle weakness (anterior neck flexors, ceinture pelvienne, épaules).
Systemic: Weight loss, Fevers, Anorexia, Fatigue, Arthralgia
Dermatomyositis sx
sx myosite + sx cutanés:
Shawl sign
V sign
Papules de gottron
Rash heliotrope
Holster sign (erythema of the buttocks, hips and lateral thighs)
Myosite tests
CK
Antibodies to Jo-1 (polymyosite), Mi-2 (dermatomyosite) and ANA
EMG
Muscle biopsy
Myosite tx
CS PO haute dose
DMARDS
Arthrite psoriasique sx
Pain, stiffness and swelling of peripheral and/or axial joints, enthesitis (inflammation of tendons), dactylitis (painful swelling of a whole digit) and nail changes.
Arthrite psoriasique tests
-RX mains et pieds: pencil in a cup, deformation, etc.
-RX lombo-sacrée (trouvailles similaires à SA)
-PAS D’ANTICORPS
Arthrite psoriasique tx
AINS, DMARDS, CS inj.
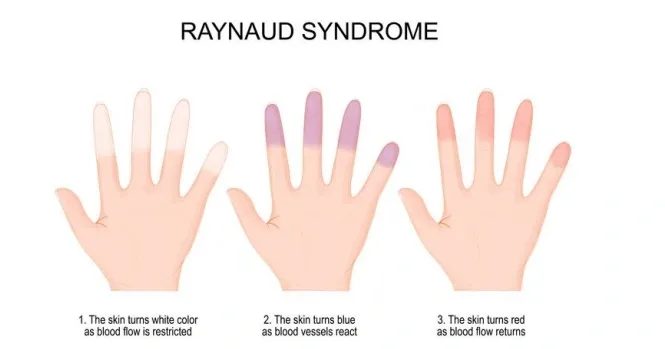
Raynaud’s phenomenon
triggers: triggered by cold exposure, with other triggers including emotional stress, vibration injury, smoking and medications (e.g. beta-blockers).
tx: conservateur, nifedipine peut être considérer.
Arthrite réactive
-Within 4 weeks of an infection (ITSS or GI infx).
-Triad: can’t pee (urethrite), can’t see (uveite), can’t climb a tree (arthrite asymétrique).
Arthrite réactive tests
-Chlam/gono, culture des selles (c. diff), PCR viral
-Analyse liquide synovial (r/o septique, mais présence de leucocytose)
-RX des articulations
Arthrite rhumatoide
-Symmetrical synovitis affecting primarily the small joints of the hands (NOT IPD) and feet (MTP).
Swan-neck deformity
Boutonnière deformity
Ulnar deviatioon
-Sx inflammatoire
-Peut atteindre plusieurs systèmes (pneumo, neuro, ophtalmo, cardio, etc.)
AR tests
FR +, anti-ccp +
AR tx
DMARDS
Sarcoidose
Granuloma formation in various organs, with the most commonly affected being the lungs.
Sx: fever, polyarthralgia, erythema nodosum, dry cough, dyspnoea, fatigue and weight loss.
sarcoidose tests
Calcium and ACE serum (↑), RXP, bx granulome.
Sarcoidosis tx
AINS, CS haute dose, immunosuppresseurs.
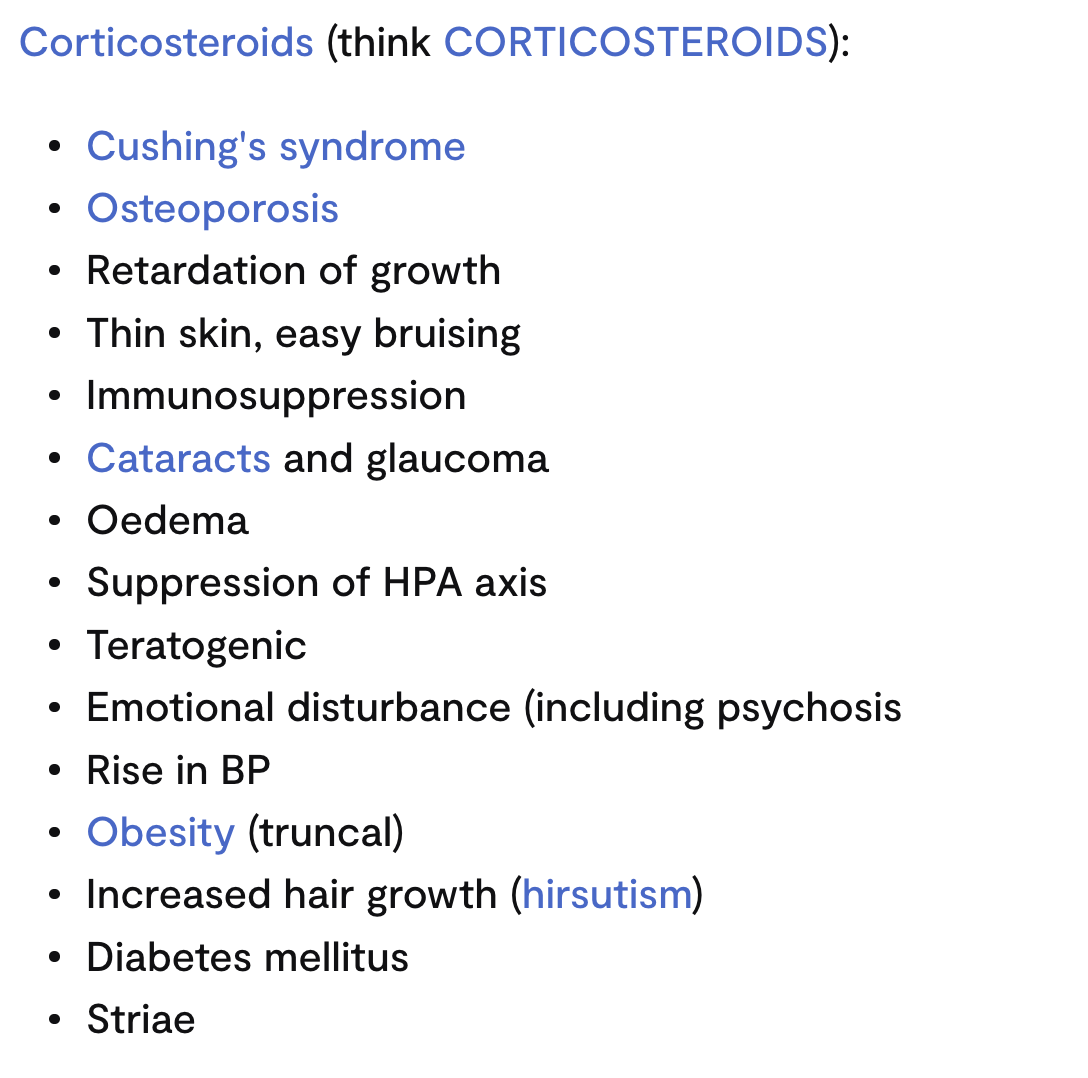
ES CS
Syndrome de sjogren
Autoimmune disorder characterised by destruction of the lacrimal and salivary glands causing drying of the eyes and mouth (+ Raynaud).
-Can be 2aire à SLE or RA
Sjogren tests
-Anti-Ro (SSA) and anti-La (SSB) antibodies
-Schirmer's test (which measures tear production): if less than 5 mm is wet after 5 minutes this is positive
-Echo and biopsy of the salivary glands
SLE
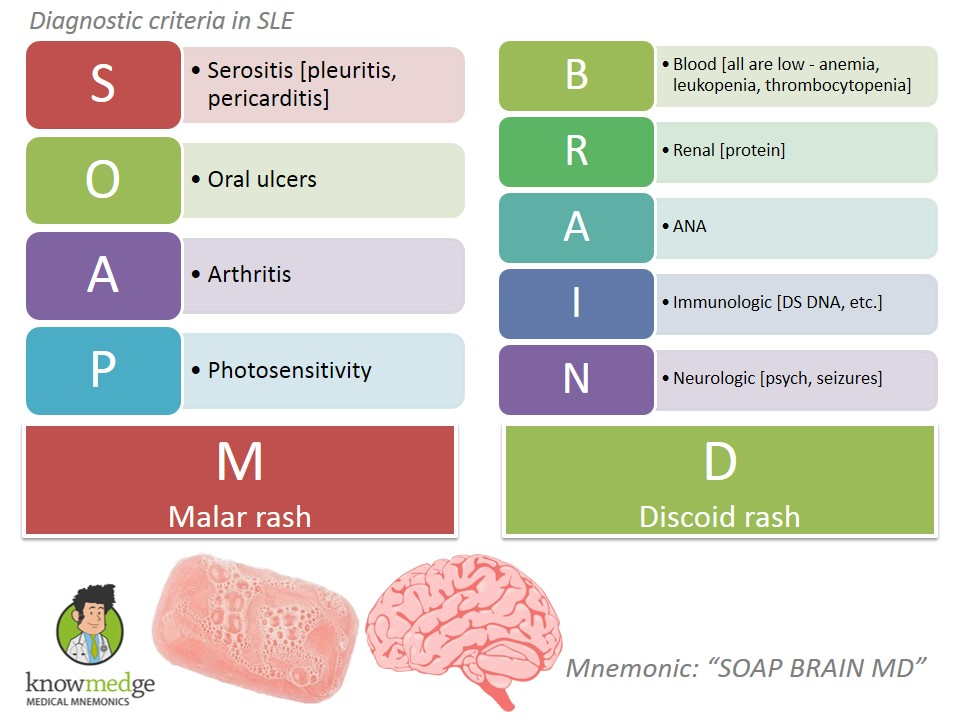
SLE tests
ANA, anti-dsDNA , antiphospholipid Ab, and anti-Smith antibodies.
SLE tx
Hydroxychloroquine (DMARD)
CS, DMARDS, agents bio
Sclerodermie
Difference between limited vs. disseminated:
LcSSc (CREST syndrome) is more common and only peripheral skin is affected with slower progression of disease and later involvement of internal organs.
DcSSc affects truncal as well as peripheral skin and progresses more rapidly.
**Important complication: pulmonary hypertension
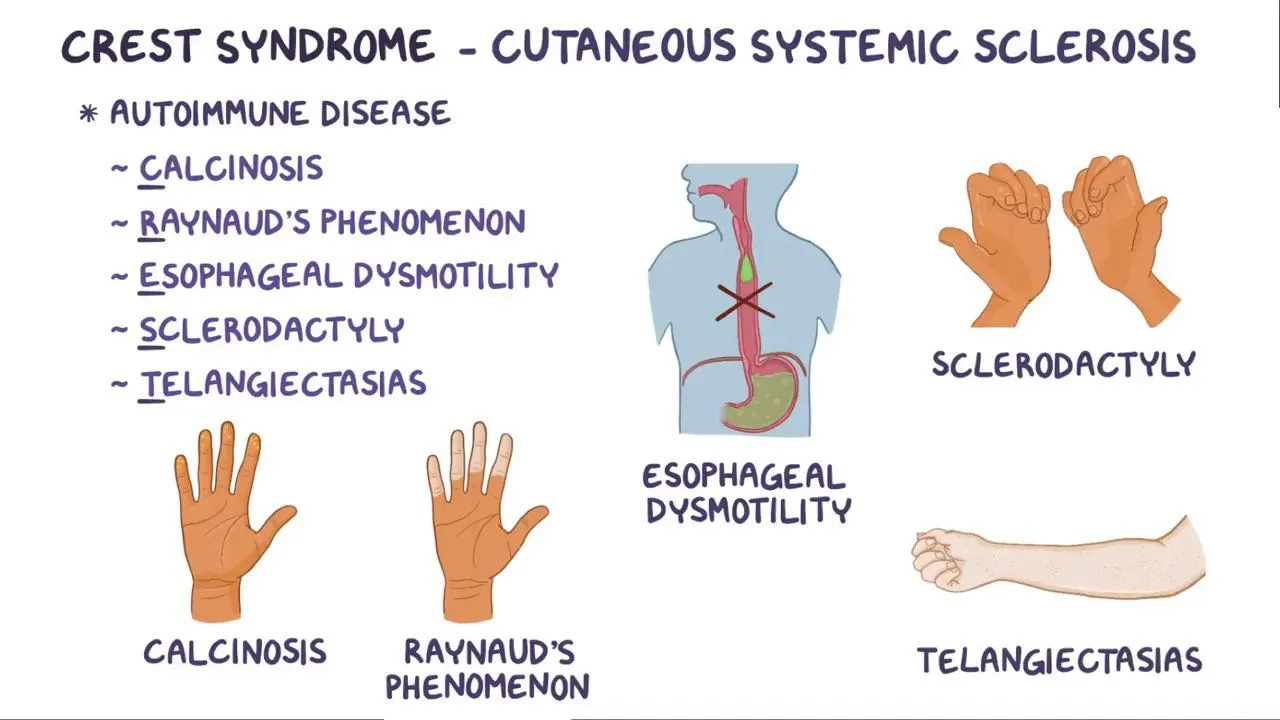
Sclerodermie tests
anti-Scl 70 (disseminated), anti-centromere (limited sclerodermie) and anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies
Sclerodermie tx
Regular monitoring for complications, physiotherapy to aid mobility and muscle strength, immunosuppressive treatment for dcSSc.