(CIE A2 Biology) ABA + stomatal closures
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
ABA (abscisic acid)
plant-produced to stimulate stomatal closures during periods of water stress induced by high temperatures/reduced water supplies
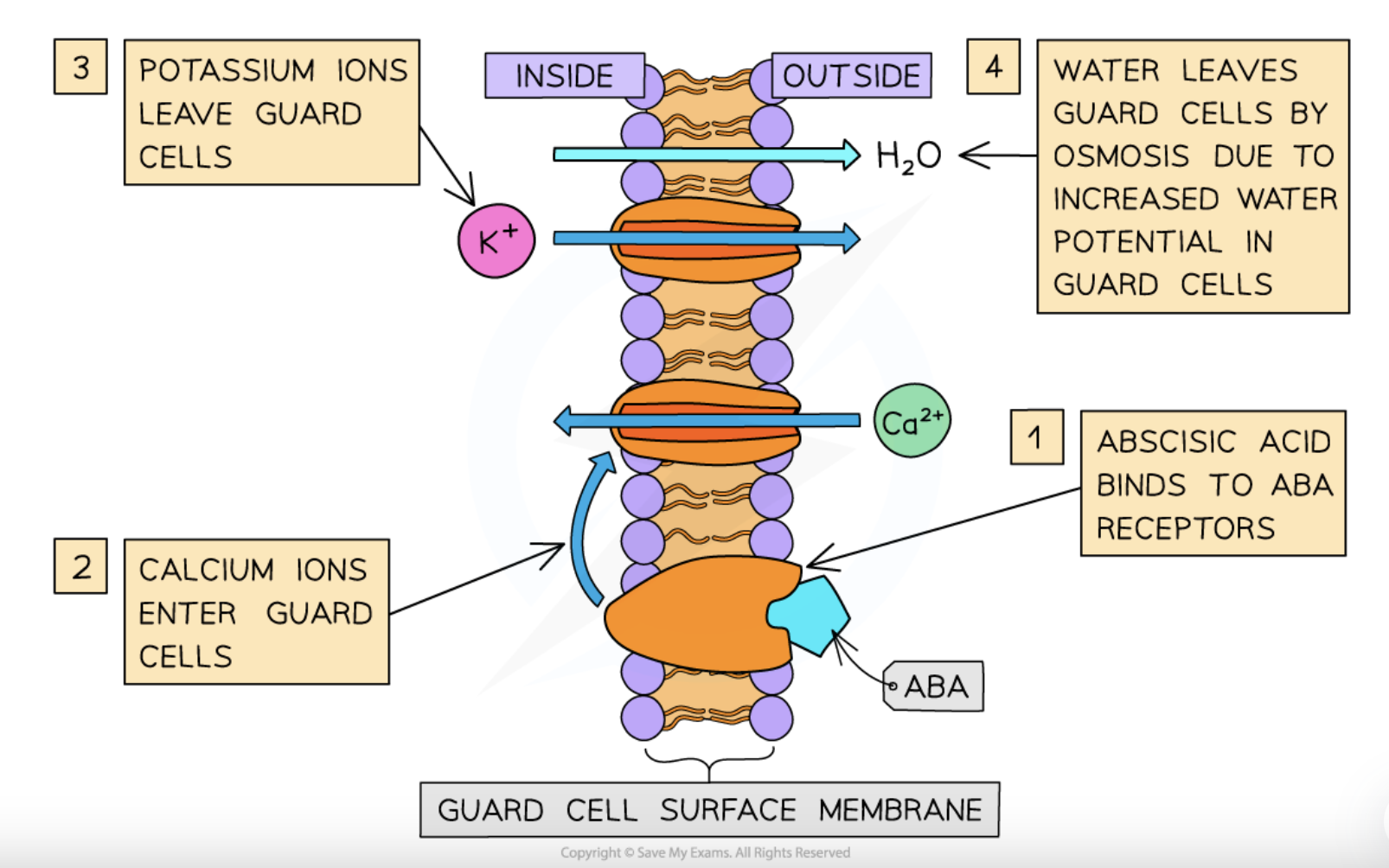
what happens when ABA binds to receptors on guard cells
the proton pumps get inhibited to stop active H+ ion transport out of these cells while calcium ions also move into the cytoplasm to act as second messengers
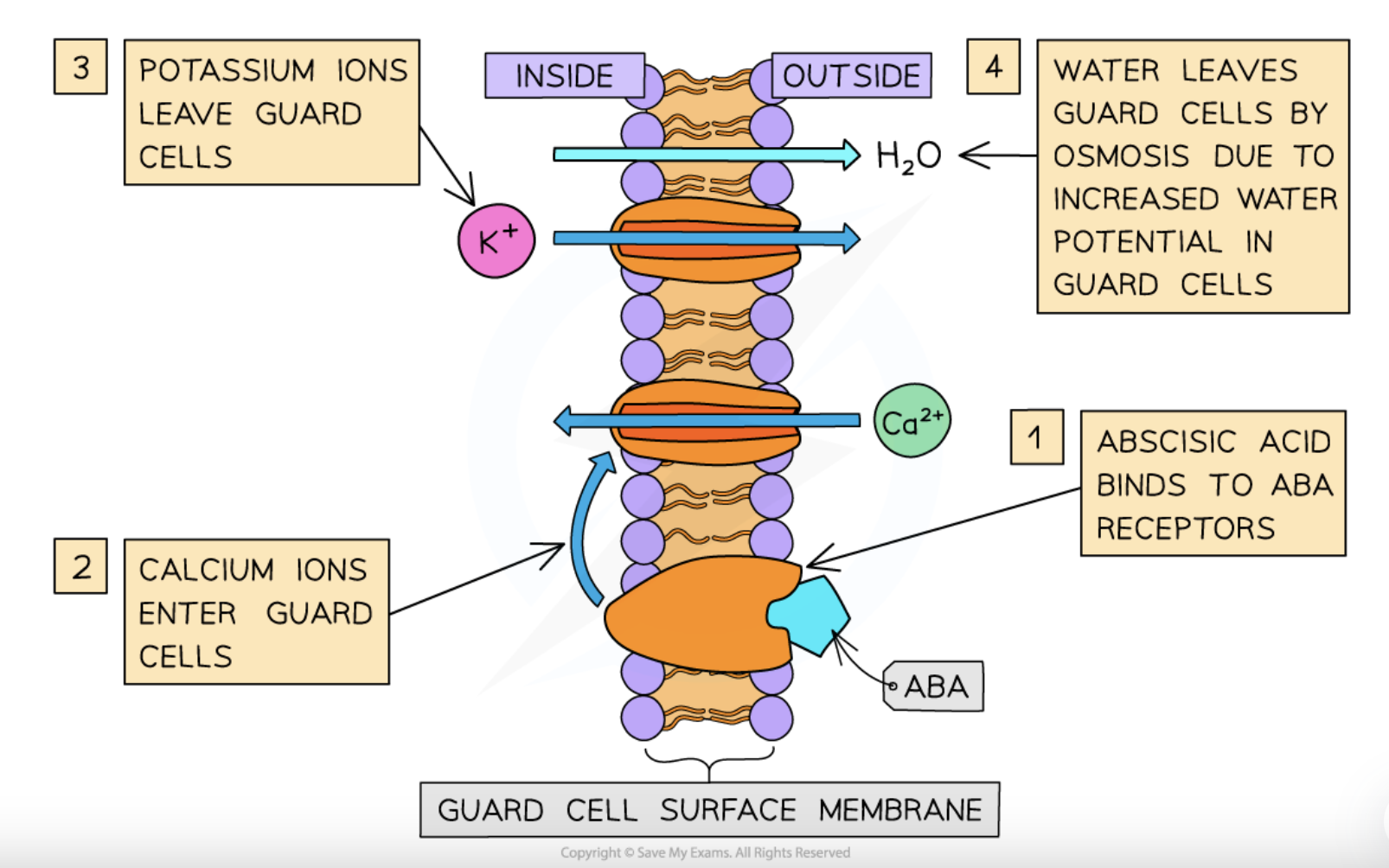
how the calcium ions moving into the cytoplasm act as second messengers
by opening channel proteins for negatively-charged ion/K+ ion departures + closing the channel proteins that allow for K+ ion entries to increase guard cell water potential
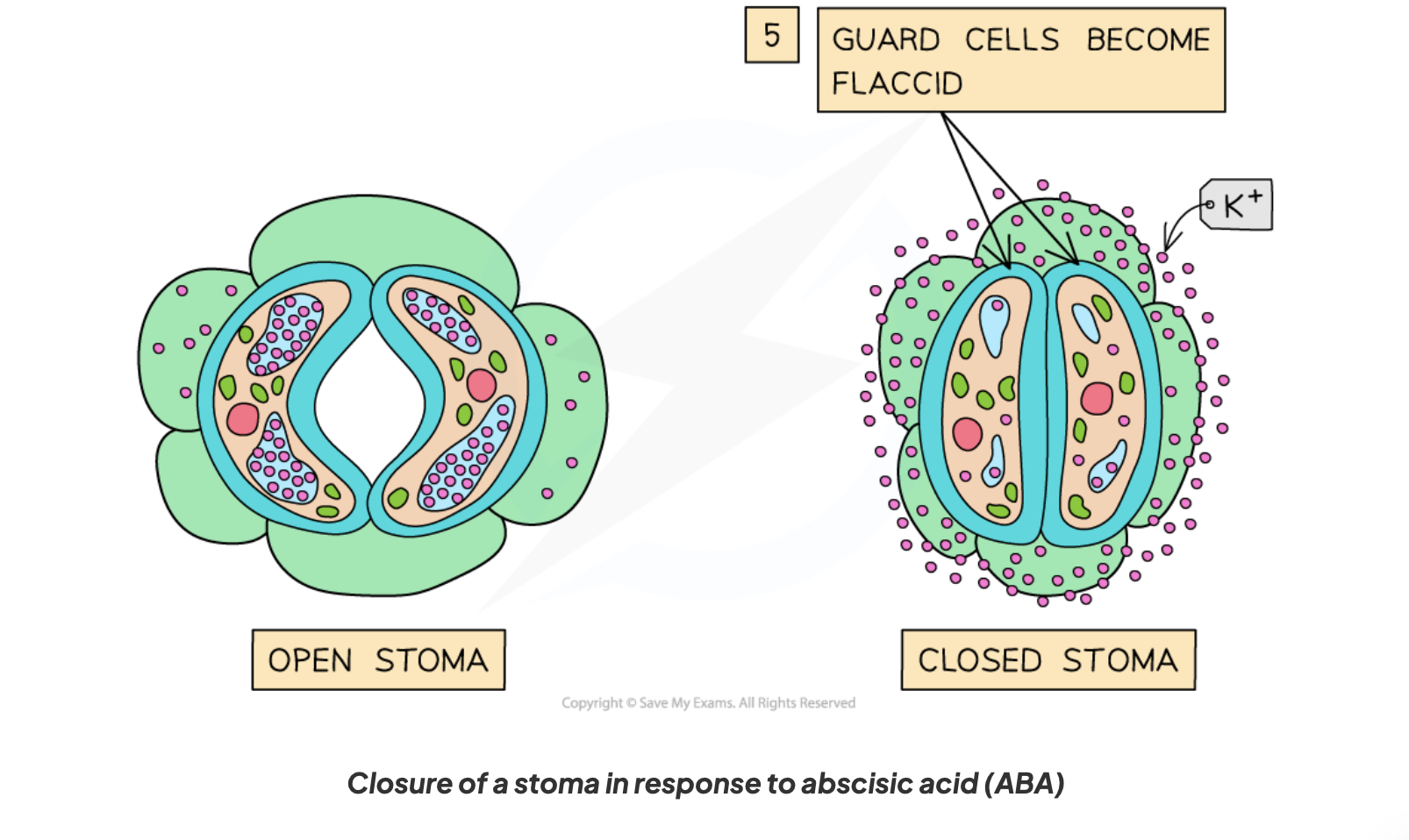
what happens after the guard cells gain more water potential during water stress periods
they become flaccid due to water leaving them by osmosis thus shutting the stomata up