Behavioural Ecology: Understanding Animal Interactions
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Behaviour
Animal's response to environmental cues.
Behavioural Ecology
Study of interactions within populations and ecosystems.
Fixed Action Patterns (FAPs)
Unchangeable action sequences triggered by stimuli.
Innate Behaviour
Behaviour under genetic control, consistent across species.
Phenotype
Observable physical properties of an organism.
Foraging
Searching for and exploiting food resources.
Fighting
Aggressive interactions between individuals.
Communicating
Exchanging information through signals or cues.
Mating
Reproductive behaviors to attract partners.
Environmental Cues
External factors influencing animal behaviour.
Abiotic Factors
Non-living components affecting ecosystems, like temperature.
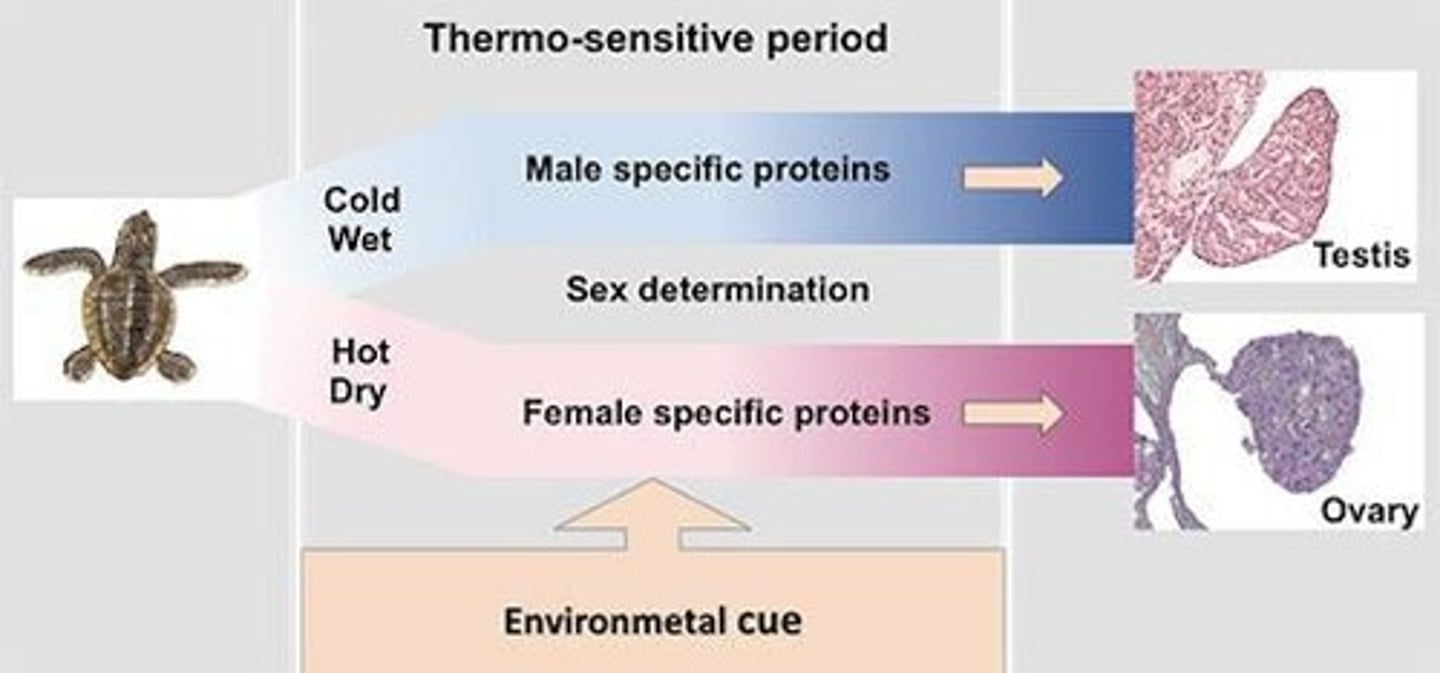
Sex Determination
Process influenced by environmental factors like temperature.
Yawning
Fixed action pattern seen in many species.
Soil Horizon of Leaching
Layer with poor soil due to nutrient loss.
Tropical Rain Forests
Biomes characterized by high humidity and biodiversity.
Terrestrial Biomes
Major land ecosystems defined by climate and vegetation.
Learning Characteristics
Ways animals acquire new behaviours through experience.
Population Implications
Effects of individual behaviours on group dynamics.
Community Implications
Influence of behaviours on species interactions.
Key Life Processes
Essential behaviours for survival and reproduction.
Stimulus
Any event or object that elicits a response.
Experience
Past interactions that shape future behaviours.
Nature
Genetics and abiotic environmental factors influencing behavior.
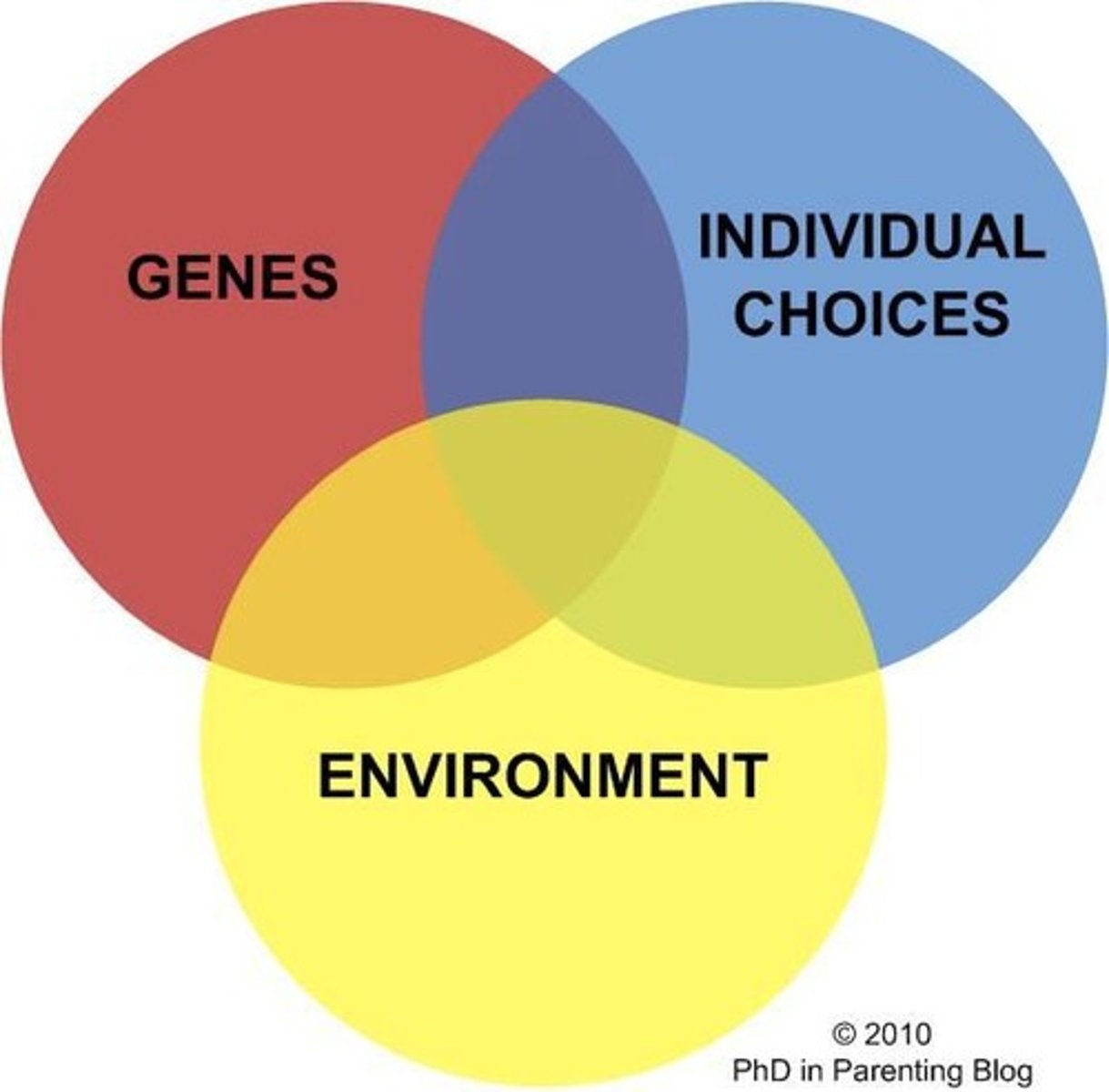
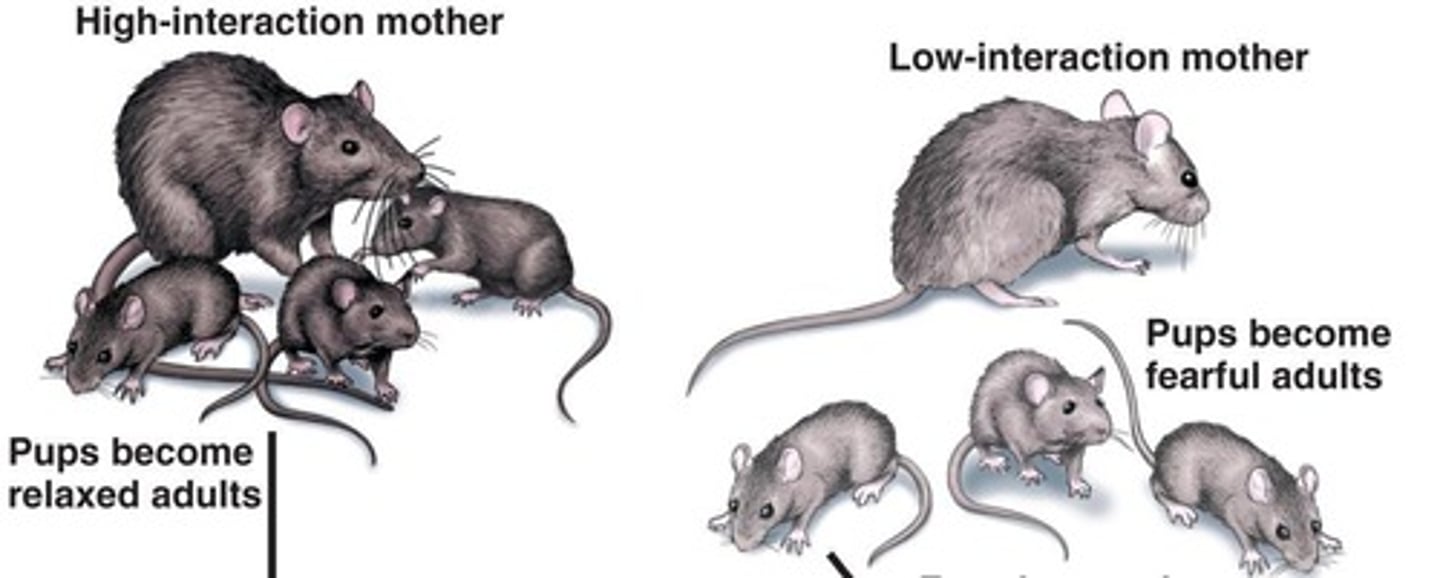
Nurture
Experiences from parents and individuals shaping behavior.
Learning
Modification of behavior due to specific experiences.
Habituation
Decline in response to repeated stimulus exposure.
Imprinting
Learning during a sensitive period, usually irreversible.
Kinesis
Random movement in response to environmental stimuli.
Taxis
Directed movement toward or away from a stimulus.
Spatial Learning
Establishing landmarks for navigation and resource location.
Associative Learning
Linking a stimulus or behavior with a specific response.
Classical Conditioning
Associating an arbitrary stimulus with an outcome.
Social Learning
Learning by observing and imitating others' behaviors.
Cognition
Processing and using information gathered through senses.
Problem Solving
Using past experiences to navigate new challenges.
Behavior
Result of genetic and environmental interactions.
Foraging
Searching, recognizing, capturing, and consuming food.
Generalists
Organisms that consume a wide variety of foods.
Specialists
Organisms that feed on specific food types only.
Optimal Foraging Theory
Balancing energy intake with expenditure during foraging.
Animal Movement
Behavioral responses to environmental stimuli.
Conservation Programs
Initiatives aimed at protecting species and habitats.
Essential Life Processes
Key activities like foraging, fighting, communicating, mating.
Signal
Stimulus transmitted between animals.
Communication
Sending, receiving, and responding to signals.
Agonistic behavior
Confrontational interactions, rarely harmful.
Hierarchy establishment
Dominance determined through posturing.
Kermode bear
Spirit bear subspecies of American black bear.
Harmonic chorus
Wolves harmonize to create illusion of numbers.
Olfactory communication
Use of scent for signaling among wolves.
Infrasound
Sound waves below human hearing range.
Post-copulatory sequence
Grunts signaling female condition after mating.
Fixed Action Patterns (FAPs)
Innate behaviors triggered by specific stimuli.
Mating systems
Patterns of reproductive behavior among species.
Promiscuous mating
No strong pair bond or lasting relationship.
Monogamous mating
One male and one female share parental care.
Polygyny
One male mates with multiple females.
Polyandry
One female mates with multiple males.
Courtship rituals
Behaviors confirming species and mating readiness.
Sneaker males
Males that use stealth to mate.
Environmental influences
Factors affecting animal behavior and interactions.
Genetic influences
Inherited traits impacting behavior.
Social Learning
Learning through observation of others.
Problem Solving
Cognitive ability to find solutions.
Foraging behavior
Strategies animals use to find food.
Fighting behavior
Aggressive interactions for dominance or mating.