BSC1010L-6 Final Exam Review: Key Concepts and Labs
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Enzyme
An enzyme is a catalyst that helps speed up chemical reactions in an organism.
Active Site
The region on an enzyme where the substrate binds.
Specific Substrate
Each enzyme has a specific substrate and therefore active site.
Optimal Environmental Conditions
Each enzyme has specific environmental conditions at which it functions optimally (ex: temperature, pH, presence of inhibitors, etc.).
Rate of Reaction
The rate of reaction is influenced by concentrations of enzyme and/or substrate available.
Catecholase
Catecholase is an enzyme found in potatoes and aids in the reaction between catechol (substrate) and oxygen.
Benzoquinone
When O2 is present, catechol is oxidized and converted to benzoquinone, causing darkening in the potato.
Optimum Temperature
There is an optimum temperature at which the enzyme functions.
Denaturation
When temperature is too high, the enzyme is denatured (the structure of the enzyme breaks down).
Effect of pH on Enzyme Activity
The active site shape can change shape depending on the pH.
Optimum pH
There is an optimum pH at which the enzyme functions.
Enzyme/Substrate Complex
An enzyme/substrate complex is formed when substrate is bound to its enzyme.
Reaction Rate and Enzyme Concentration
Reaction rate will increase as enzyme concentration increases up until the reaction is limited by substrate availability.
Substrate Concentration
If the amount of enzyme is kept constant but the substrate concentration increases, the velocity will increase until it reaches its maximum.
Saturation of Enzymes
Substrate increases no longer speed up the rate of reaction because all enzymes become saturated.
Pectinase
Used applesauce to test the effect of pectinase on juice making. Pectinase creates more juice
Cell Respiration Equation
C6H12O6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + ATP + Heat.
Glycolysis
Formation of pyruvate (in cytoplasm).
Citric Acid Cycle
Occurs in mitochondria.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
Occurs in mitochondria.
Anaerobic Respiration
Cell respiration in absence of O2.
Fermentation
Formation of CO2 and ethanol (plants, some microbes (yeast)) or formation of lactic acid (some microbes, animals).
ATP Production in Anaerobic Respiration
Produces 18 fold less ATP per glucose than aerobic respiration.
Magnesium Sulfate
Activator of glycolysis.
Sodium Fluoride
Inhibitor of glycolysis.
Glucose
Energy source for respiration.
Measuring CO2 Production
Height of bubbles of CO2 after incubation.
Photosynthesis Equation
CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + H2O + O2
Photosynthesis Dependence
Photosynthesis is light dependent and chlorophyll dependent.
Role of Pigments
Pigments are responsible for absorption of light.
Primary Pigments
Primary pigments in photosynthesis are chlorophyll a and b.
Accessory Pigments
Other accessory pigments (carotenoids and xanthophylls) also absorb light.
Chlorophyll Production in Fall
In fall, chlorophyll production stops and accessory pigments are responsible for most of light absorption.
Paper Chromatography
Paper chromatography separates the pigments in plants.
Pigment Movement in Chromatography
Some pigments move faster up the paper than others, depending on solubility and other factors.
Pigment Adsorption
Pigments adsorbed strongly are more polar and move slower; those adsorbed weaker move faster up the paper, less polar.
Xanthophylls
Yellow band in chromatography represents xanthophylls.
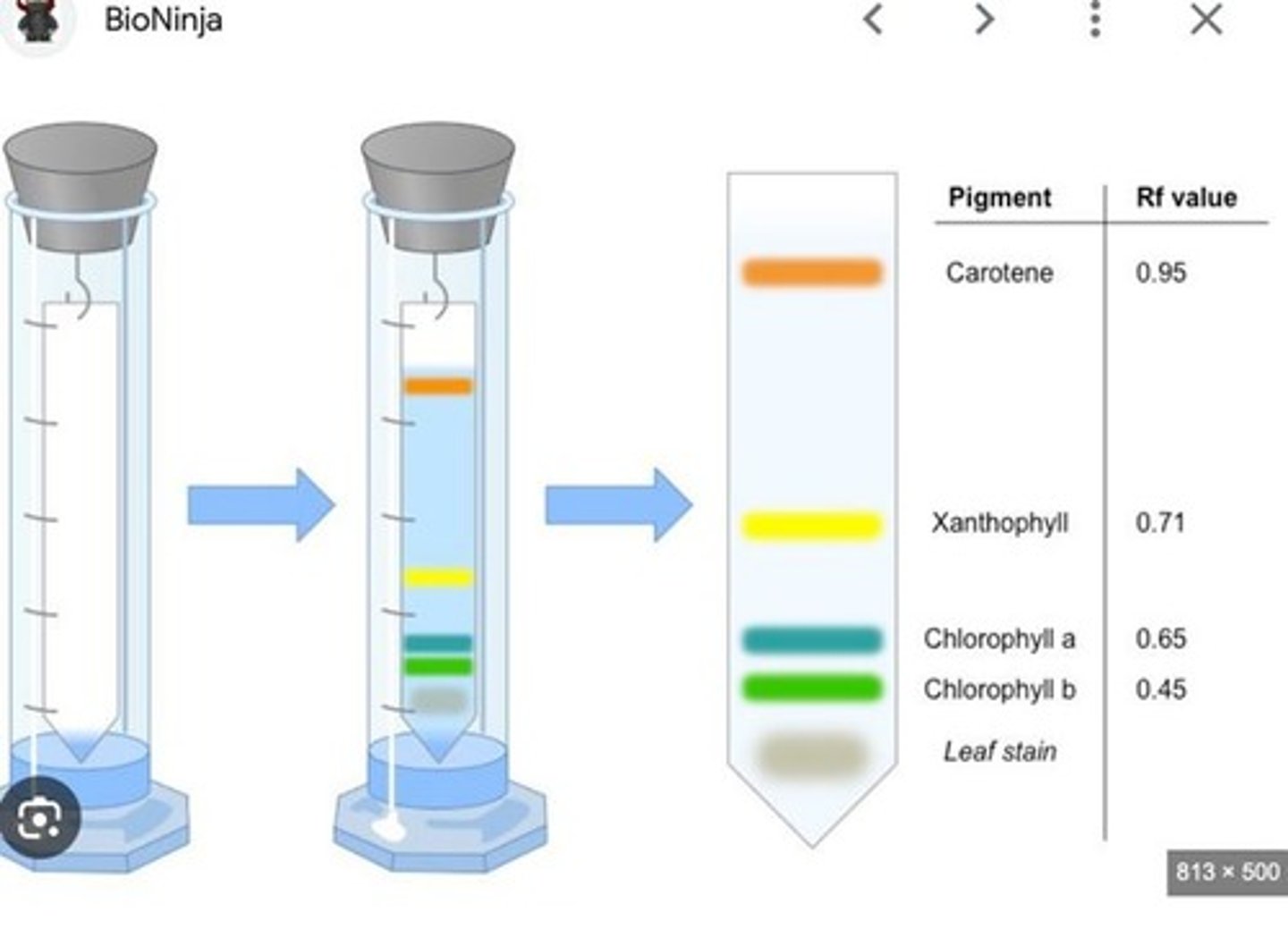
Carotenes
Yellow-orange band in chromatography represents carotenes.
Chlorophyll a
Blue-green band in chromatography represents chlorophyll a.
Chlorophyll b
Yellow-green band in chromatography represents chlorophyll b.
Rf Value
Rf = distance moved by pigment/distance from pigment origin to solvent front.
Spectroscope Function
Spectroscope separates white light into its component colors (appear as a spectrum).
Light Absorption by Chlorophyll
Light not visible through the extract has been absorbed. Blue light is the best light for photosynthesis
Wavelength
The shorter the wavelength, the higher the energy value.
Phenol red
pH indicator that turns yellow in acidic solutions and red in basic solutions.
Uptake of CO2 during Photosynthesis
Phenol red is used to observe uptake of CO2 during photosynthesis by Elodea.
Mitosis
Replication and division of the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. Diploid cells. Cell production and growth.
Cell cycle
Includes Interphase (G1, S, G2), mitosis (less than 10% of cell cycle), cytokinesis.
G1 phase
Preparation of proteins for mitosis.
S phase
Replication of DNA, chromosomes consist of pair of sister chromatids, attached at the centromere.
G2 phase
Molecules and structures necessary for mitosis are synthesized.
Prophase
Nuclear membrane breaks down, chromosomes become visible, spindle starts to form.

Metaphase
Sister chromatids are attached to spindle and align along the metaphase plate.
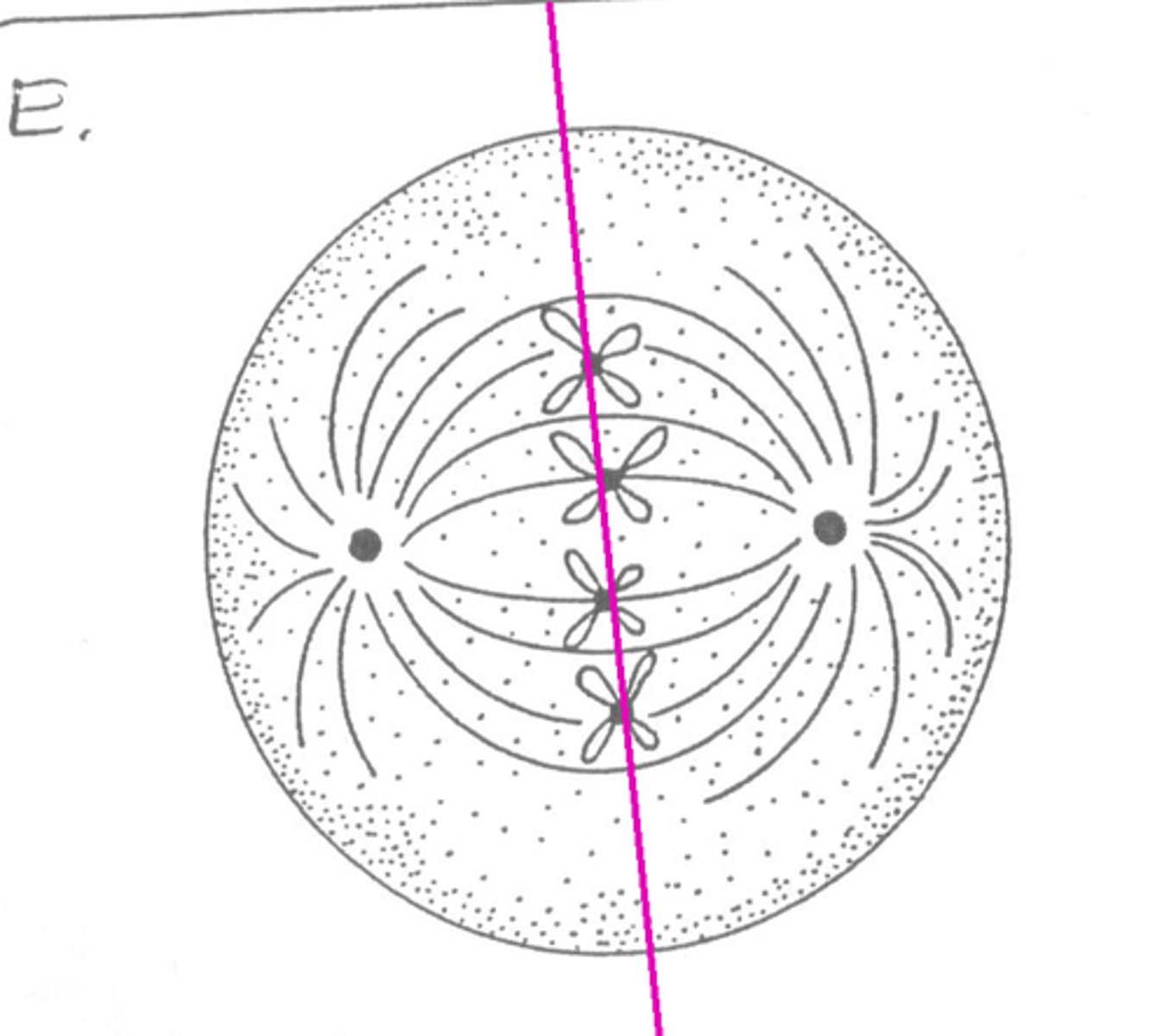
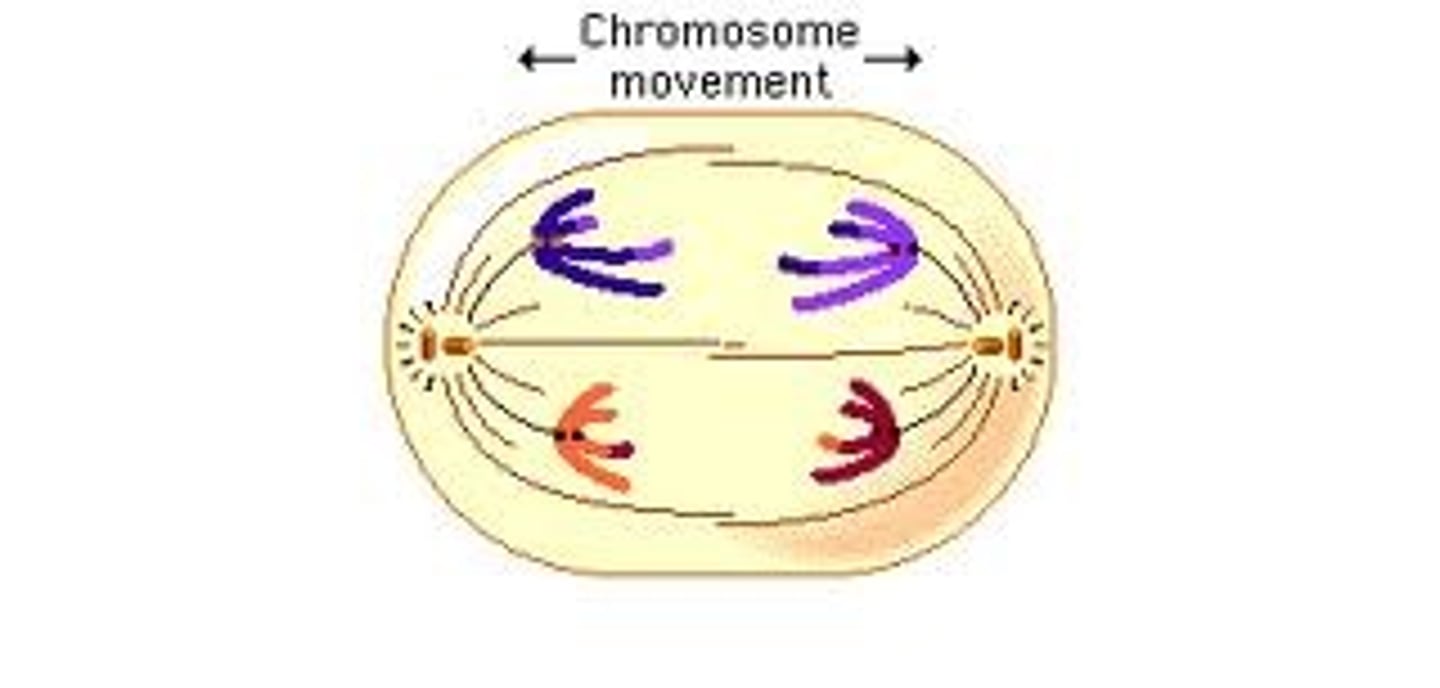
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate and become individual chromosomes, move towards the poles.
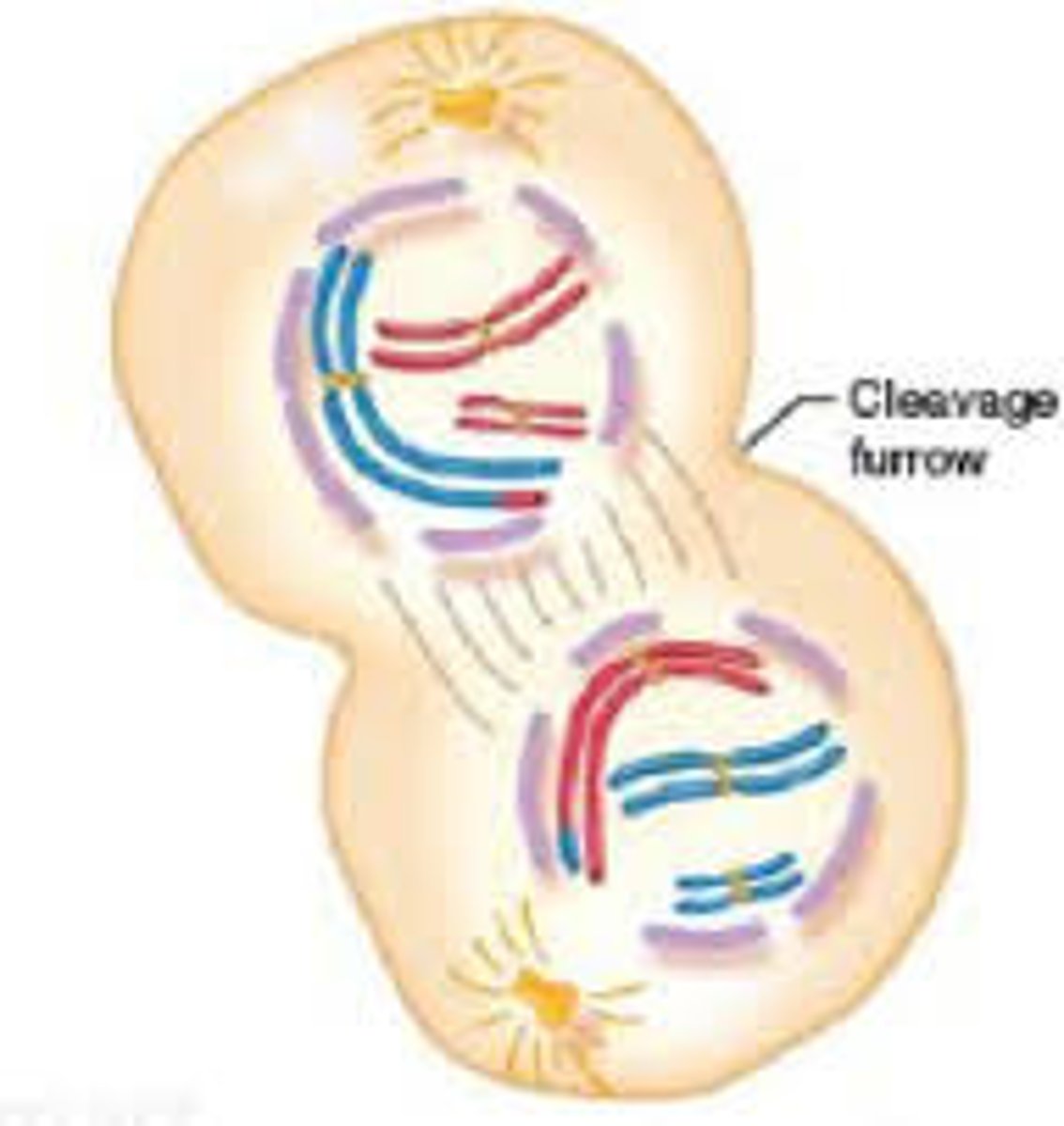
Telophase
Chromosomes decondense and nuclear envelopes reform, cleavage furrow separates the 2 cells (animals) or cell plate (plants).
Diploid
Nucleus with 2 of each type of chromosome.
Meiosis
Recombination of parent's genes and production of gametes (sex cells), produces haploid daughter cells (reduction division).
Diploid cells (2n)
All cells in the body except gametes.
Homologous chromosomes
The 2 chromosomes of a pair, each homologue has same loci for the same genes.
Haploid cells (n)
Gametes. during sexual reproduction, 2 gametes fuse to restore original diploid nuclei
each gamete contains 23 chromosomes
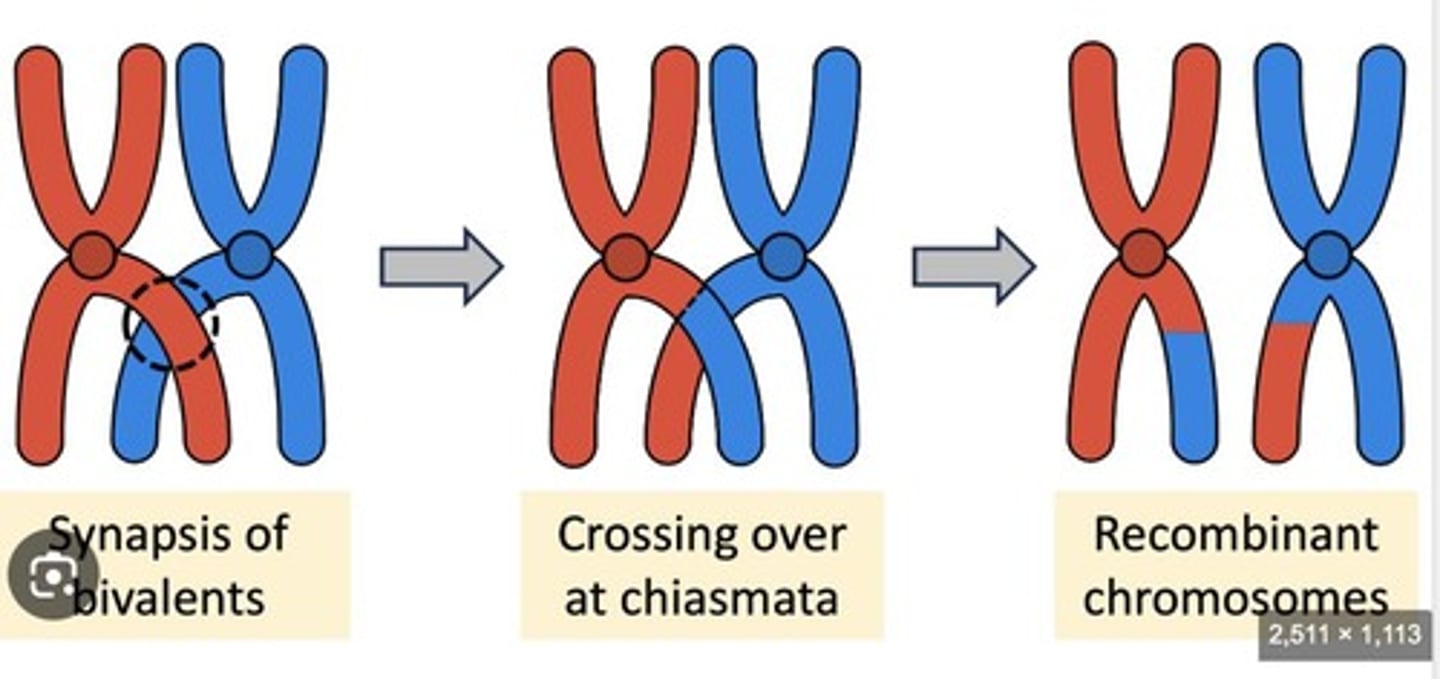
Crossing over
Pairing of homologous chromosomes to form a synapse, followed by exchange of genetic information at chiasma. Only in meiosis
Meiosis I
Includes interphase, prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I and cytokinesis.
Meiosis II
Includes prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II and cytokinesis.
Mitosis vs Meiosis
Mitosis produces 2 genetically identical diploid daughter cells; Meiosis produces 4 genetically different haploid daughter cells.
Detergent
Breaks down the cell membrane.
Meat tenderizer
Breaks down proteins (histones) to unravel DNA.
Alcohol
Precipitates the DNA. Found this in the pea juice when mixed with ethanol
Mendelian Genetics
Genes occur in pairs (alleles).
Law of Segregation
Each gamete has an equal chance of possessing either of the pair of homologous chromosomes.
Law of Independent Assortment
Genes on nonhomologous chromosomes will be distributed randomly into gametes.
Genotype
All alleles present in the cell, e.g., Pp.
Phenotype
Physical appearance, e.g., Purple.
Homozygous
Paired alleles are identical, e.g., PP or pp.
Heterozygous
Paired alleles are different, e.g., Pp.
Monohybrid Cross
Involves only 1 trait.
Dihybrid Cross
Involves 2 traits, with a phenotypic ratio of offspring 9:3:3:1.
Incomplete Dominance
Heterozygous genotype results in intermediate characteristics.
Codominance
Both alleles contribute to the phenotype of a heterozygote.
Sex-linked Inheritance
Involves alleles on sex chromosomes and are thus linked to gender.
F1 generation
first generation of offspring
Blood type
determined by antigens on surface of red blood cells. If antigen A or B is present, no antibodies against this antigen are produce
Person with type A blood has antigen A on surface and produces antibodies against antigen B
sex-linked inheritance
All traits previously discussed are produced by alleles on autosomes
Sex-linked inheritance involves alleles on sex chromosomes and are thus linked to gender
XX: female
XY: male
Both male and females can have X-linked traits present
If a male has an X chromosome that carries the recessive allele, the allele is expressed (no chance for masking by a dominant allele on another X chromosome)
widow's peak
Dominant trait for hairline shape.
pigmented iris
dominant
Hitchhiker's Thumb
recessive
dimpled chin
dominant