Biology Unit 5 evolution
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
false idea of evolution
Lamarckism
Inheritance drives evolution
acquired traits cause heritable changes in species
Traits are gained and lost by use and disuse
Lamarckism was shifted to natural selection
A paradigm shift occurred when people changed to natural selection
In a population
variation exists and this variation is heritable
overproduction of offspring
is common in many species
this leads to competition for resources meaning not all offspring will survive
density independent factors may also affect survival (like temperature)
adaptations
individuals who are better adapted tend to survive and produce offspring
allow for individuals to be better suited to their environment
must be heritable therefore encoded in the DNA
poorly adapted tend to die and produce less offspring due to selective pressures (biotic and abiotic)
natural selection
increases the frequency of characteristics that make individuals better adapted, leading to changes within a species.
terms of natural selection
can only occur if there is variation among members of the same species
mutation give rise to new traits
meiosis and sexual reproduction increase variation between individuals of the same species
Antibiotic resistence (natural selection and evolution in bacteria)
there are many germs in the body but only some are drug resistant
antibiotics kill the bacteria causing the illness as well as the good bacteria protecting the body from infection
the drug-resistant bacteria are now able to grow and take over
some bacteria can give their drug resistance to others
some bacteria examples are MRS or Tuberculosis
gene pool
consists of all the genes and their different alleles present in an interbreeding population
evolution requires that allele frequencies charge with time in populations
the variation id determined by alleles present at a given time
environmental changes alter the selective pressure
the allele frequency will change in the population
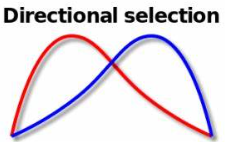
directional selection
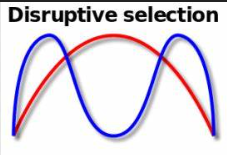
Disruptive selection
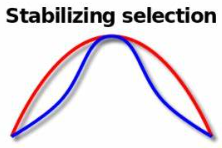
stabilizing selection
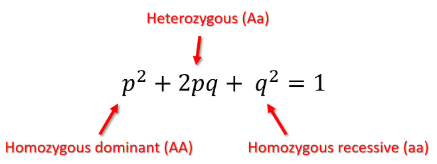
the harty- Weinberg principle
provides a baseline used to predict allele frequency and determine if a population is evolving
what unrealistic assumptions are made for the Harty-Weinburg principle
no mutation in the gene pool
no migration of alleles
no natural selection
mating is random
large population
this helps assume that the alleles don’t change over generations yet if they do then one of these are at work
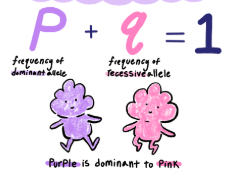
equation number 1
equation number 2
5.2 evolution and speciation
species
can be interbreed and produce fertile offspring
speciation
occurs due to reproductive isolation
allopathic speciation and sympatric
allopatric speciation
is when this isolation is due to a physical barrier
occurs in different geological regions
the population lose the ability to interbreed, forming two distinct species
Sympatric speciation
occurs in the same geographical area
temporal isolation
the time of reproduction between populations is incomplete
behavioral isolation
populations are separated by specific behaviors (like the blue bobied and their mating dance)
polyploidy
having more than two sets of chromosomes
haploid=n diploid=2n triploid=3n
different number cannot pair up properly therefore successfully reproduce
to produce fertile gametes the chromosomes must form homologous pairs
triploid offspring would be infertile at one pair
5.3 diversity and classification
the biological species concept is imperfect but still used to group organisms based on similarities and evolutionary history.
speciation is slow and an endpoint is not always clear
diverging, non-breeding populations might be in the process of speciation
distinguishing between non-breeding population
morphology
group together on a shared physical traits
binomial nomenclature
two names a Genus species
italicized and only the Genus is capitalized
Linnaean taxonomy
a hierarchical classification
based on physical traits
Domain
kingdom
phylum
class
order
family
genus
species
modern classification
relies on physical traits, behaviors (breeding or non-breeding), and genetic similarities
reproductive incompatibility lies in the different chromosomes
whole genome sequencing
determines every base in a genome
used to research differences within and between species
tests hypothetical evolutionary relationship based on physical characteristics
single nucleotide polymorphism
single base substitution (this is the reason humans are .1% genetically different
different species have different genome sizes
plants are (can be) polyploid and have greater genome
genome sequencing
personalized medicine, species identification using a barcode
bacteria are difficult to classify because….
cladogram
terminal branch- most recient species in a lineage
node-hypothetical common ancestor
root- common ancestor of all clades represented on the cladogram
clade- group of organisms that share a common ancestor
molecular evidence is used to construct and or correct cladograms
the molecular evidence that can be used to figure out the cladograms include
rRNA as highly conserved species need it, and there are slight differences between species
Protein analysis fins the similarities in amino acids, yet some proteins are better predictions then others
DNA sequencing can show that some sequences are conserved between species.
5.2 evolutionary change
Convergent evolution
species do not share recent common ancestors
similar selective pressure causes a similarity in morphology
analogous structures and similar function but different evolutionary history.
examples: wings in both birds and bats
Divergent evolution
shared ancestry with changes over time due to differences in selective pressure
evidence of adapted radiation
homologous structures
similar features even if function has changed
examples: pentadactyl limbs within different animals
adaptive radiation
one species becomes into species, a new ecologist’s niche would appear
evolutionary history shows period of little change (stasis) punctuated by periods of adapted radiation
sexual selection as selective pressure
sexually dimorphic= sexual selection
physical and behavioral traits can be interpreted as a sign of overall fitness
this in turn provides a reproductive advantage
lacking these qualities presents a unique type of selective pressure that changes the species over time
behaviors must be heritable
birds of paradise
small islands in Papua Guinea
low predation
adaptive radiation
elaborate courtship rituals
artificial selection
selective breeding changes species
humans choose desirable triats that may or may not increase survival or reproductive advantage
shows how rapid evolution can occur
Examples: Dog breeds and plant varieties
Bacteria resistance
bacteria have evolved resistance to antibiotics due to human activity
resistance is considered natural selection because the bacteria are responding to selective pressure, and humans are not intentionally selecting the trait.