chemistry - states of matter & mixtures: states of matter (2.1 - 2.4)
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
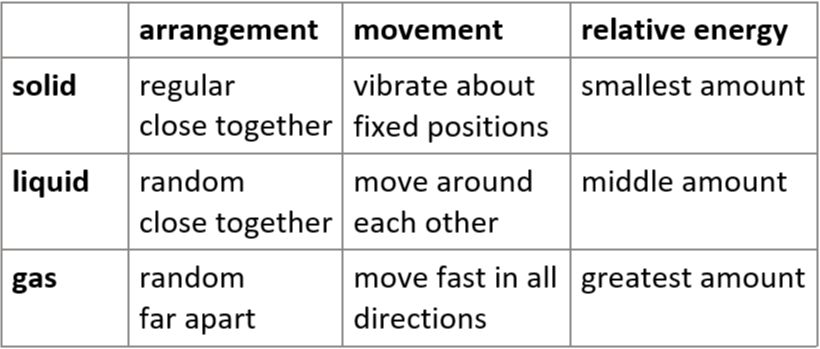
2.1 solid, liquid & gas - arrangement, movement & relative energy of particles
2.2 names of state changes
solid → liquid = melting
liquid → solid = freezing
solid → gas = sublimation
gas → solid = deposition
liquid → gas = evaporation/boiling
gas → liquid = condensing
2.2 physical vs chemical changes
physical/chemical:
can be reversed/can’t be reversed
chemical properties of substance don’t change/do change
particles don’t change/do change
only arrangement, movement & amount of stored energy of particles changes
attraction between particles
weak forces of attraction
2.3 changes in arrangement, movement & energy of particles - melting
particles gain energy & vibrate more
energy transferred from surroundings → particles
overcome attractive forces - particles move around each other, randomly arranged
2.3 changes in arrangement, movement & energy of particles - freezing
particles lose energy & slow down
energy transferred from particles → surroundings
attractive forces form - particles only vibrate, regularly arranged
2.3 changes in arrangement, movement & energy of particles - boiling
particles gain energy & move faster
energy transferred from surroundings → particles
overcome attractive forces - particles move fast in all directions, far apart
2.3 changes in arrangement, movement & energy of particles - condensing
particles lose energy & slow down
energy transferred from particles → surroundings
attractive forces form - particles move slower, close together
2.4 predicting physical state of substance
below meting point = solid
between melting & boiling point = liquid
above boiling point = gas