World Politics EXAM 3
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Tarriff
tax on specific kinds of imports or exports.
Quota
amount of a certain good that can be imported by a country.
GATTs
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade
the foundational agreement reached between many countries after World War II to reduce tariffs, quotas, and other barriers to trade - restrictions on trade between countries.
What did GATTs do for trade?
more global trade as time went on.
more countries signing onto international trade agreements.
most agreements reduced or cut tariffs.
global tariffs rates (especially in the US) greatly decreased
several country’s GDP greatly increased—almost 2-5 times more.
Uruguay Round
A series of multilateral trade negotiations that took place within GATT from 1986 to 1994.
What did the Uruguay Round do?
trade expansion
lowered tariffs again
included goods and services:
textiles
intellectual property
more agricultural products
more countries signed on
enforcement
created the World Trade Org (WTO)
WTO included dispute resolution process so countries could sue each other for trades violating GATT.
621+ disputes and 350 rulings at this point.
US has brought 150 and defended against 150 disputes.
150
How many disputes as the US defended against and brought to the WTO?
621+, 350
Since the WTO’s inception, ____ disputes and ___ rulings have been brought.
Doha Round
Most recent GATT round under the WTO beginning in Nov 2001, and still considered a failure.
Failures of the Doha round?
failure to:
expand on Intellectual property
make free-er trades, less subsidies on agriculture
include environmental goods: solar panels, turbines, etc.
give better market access to services.
make fewer, non-tariffs barriers
France
US top cosmetic IMPORTER
China, Taiwan, and Germany.
Top 3 Bike EXPORTERS
East Asia: Taiwan, China, Cambodia, etc.
Where does the US IMPORT their bikes from?
United States
Who IMPORTS the most bikes?
Others bought the Russia oil, mostly India and China because it was cheaper now.
When the US stopped buying Russian oil, why didn’t it hurt the Russian economy?
Components of Economic Development
Capital
Labor
Infrastructure
Government
Trade
Resources
Agrarian
agriculture based
Capital Developement
moving from agrarian economy → manufacturing economy → high tech info economy
new products and better production
needs investments and efficient equipment
business - upward or downward spiral
Where do developing countries get their capital?
IGOs (intergovernmental)
World Bank (International Devel. Asso. - IDA)
IMF
regional funds
NGOs (non-governmental)
microloans/aid
direct aid from other countries
multinational corps
investors (big and small)
remittances
exporting
What does the World Bank do?
gives loans at good terms with delayed payback to developing countries.
allows them to leverage resources
mainly gives money for projects
What does the IMF do?
loans money to countries with economic instability
stabilizes currencies and provide foreign currency
debt and economic shocks
guidance: standards, transparency
STRINGS ATTACHED: ex. debt, market liberalization, tax raises, and wage cuts (IMF is not well liked because of these strings)
Who gets World bank loans?
relatively poor countries
Gross national income per Capita must be below and established threshold that changes each year.
ex. in 20221 it was $1,185.
countries with low creditworthiness
they can’t borrow on market terms and therefore have need for concessional resources to finance the country’s Development program.
Labor Development
# of people in workforce
skills of people in workforce relies on:
education level
skill proficiency
health & welfare: increased health = increased productivity
brain drain: good workers move away to make more money = labor force decreases
Infrastructure Development
for good business operation
transport: roads, ports, airports, rails.
energy & energy grids
water & waste removal
communications: phone, mail, internet, delivery.
Government Development
political & economic security
political stability
lack of unrest
lack of social issues
thievery
violence
lack of corruption
trust in gov. (transparency)
bureaucratic efficiency (system of administration that is the most efficient way to organize human activity)
economic stability
stable monetary policy
stable currency
Trade Development
access to trade → max efficiency
access to other markets
access to resources for value added
access to products for inputs
Resource Development
access to:
water
food
land
clean air
minerals (oil, metal, coal, etc)
good geography & climate
ex. landlocked, mountainous, 7—its hard to import/export under these conditions.
Levels of Economic Intergration
Free Trade Area
Customs Union
Common Marker
Internal Market
Monetary Union
Free Trade Area
characteristics:
no tariffs
no quotas
only specific goods/services
ex.
CAFTA (US + Central America)
US + SA
US + Mid-East (Israel, Bahrain, Jordan, ect.)
US + Asia (Australia, Korea, Singapore)
US + Africa (+Morocco)
European Union
ASEAN
little sovereignty given up
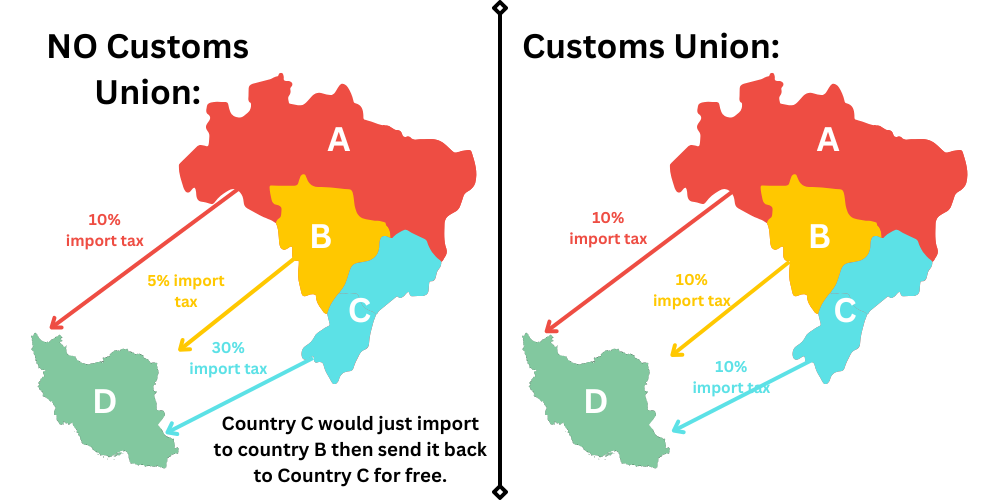
Customs Union
characteristics:
all characteristics of free trade plus-
common external trade policy
negotiates as one entity
all have same trade policy w/ other countries
little more sovereignty given up
Common Market
characteristics:
4 freedoms—these elements can move freely across borders without significant restrictions between member countries.
Goods
Services
People (Labor)
Capital (business, land, etc.)
moderate sovereignty given up
Internal Market
characteristics:
common market characteristics, plus -
common policies
business regulations
workplace safety
labor laws
standards
environmental
agricultural, etc.
gets rid of NTBs (non-tariff barriers)
majority of sovereignty given up
Monetary Union
characteristics:
same currency
one central bank—decides interest rates
same monetary policy
almost all sovereignty given up
Quota
fixed amount of a good that a country can import or exports in a specific time frame.
Less sovereignty.
More economic integration equals ____.
more economic prosperity
Arguably, more economic integration leads to ____.
Different areas of globalization?
trade and service
Economic investment, capital, and tech.
People: labor and tourism
environmental
security
health
information
Trade and Service globalization pros and cons
Pros:
more efficient specialization
product variety
more competition = more advancement
get more for cheaper and/or better quality at same price.
Cons:
cost adjustments
prisoners dilemma (labor /social policy is not as organized
keeping up is stressful.
Economic investment, capital, and tech globalization
Pros:
max efficiency + wealth
help devolpe countries economically
innovation
Cons:
investment instability
corporate influence
money being moved in and out of the country
People: labor and tourism globalization
Pros:
econ boost
more jobs
joy of travel
cultural appreciation and education
Cons:
brain drain
congestion
price inflation
loss of culture and identity
environmental globalization
Pros:
international agreements
tech to solve issues
pressure changes bad behavior
Cons:
hard to address issues bc no global gov
more production = worse environmental health
security globalization
Pros:
less likely conflicts
global pressure for peace
global cooperation easier
Cons:
international terrorism
arms trade
international crime
vulnerabilities