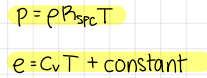1.4. Fundamental equations
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Definition of material volume v(t)
it’s a control volume evolving in time in such a way to be made up by the same fluid particles moving with the fluid (v(t))
Physical property of fluid particle
continuously deformable and of arbitrary size
Mathematical properties of fluid particles
the evolution of each fluid particle within the material volume can be described by a continuous bi-injective function (so that the volume v(t) at any time t can be tracked back to the volume v*=v(t=0))
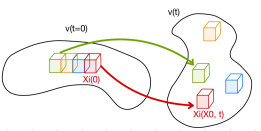
what is x_i equal to? (material volume)
x_i=f_i(xi(0),t)
what is f_i? (material volume)
bi-injective and continuous
the material volume v(t) is made out of…
the same moving particles moving with the fluid, it will always contain the same fluid particles
What is the Reynolds transport theorem useful for?
to calculate the time variation of an integral quantity within a material volume
The two terms on the right hand side of the following identify… (Reynolds transport theorem)
two contributions to the total variation:
the variation in time due to an intrinsic non stationarety of G
the variation due to the changes of the integration volume
Because of the bi-injectivity of the function describing the time-evolution of the material volume… (Reynolds transport theorem)
the balance can be expressed in terms of the initial volume v*, the results can be generalized to any type of fixed volume
Developing of right hand side (Reynolds transport theorem)
formulas

Conservation laws applicable to a material volume
Conservation of mass
Conservation of momentum (general and specialized for Newtonian fluid)
Conservation of energy (total, kinetic, internal)
Statement of conservation of mass
the mass of any arbitrary material volume remains constant in time
Developing of equation of conservation of mass
formulas

(conservation of mass) if v(t) is an arbitrary material volume, and the system is continuous:
Localization lemma
formulas
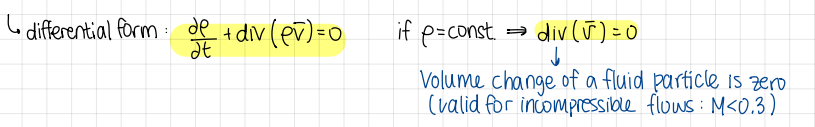
Statement of conservation of momentum (or Newton’s 2nd law)
the rate of change of momentum of any arbitrary material volume is equal to the sum of the external forces applied on the volume
Formula for rigid bodies (conservation of momentum)
formula
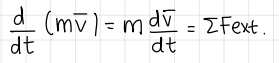
Formula for fluid bodies (conservation of momentum)
formula
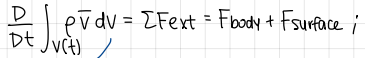
Left hand side of conservation of momentum
formulas

Right hand side of conservation of momentum
formulas
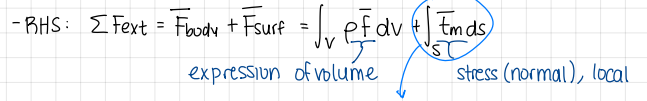
The goal of the stress term in the RHS of conservation of momentum
the goal is to transform the surface volume into a volume integral and represent t_n with the minimum number of uknowns independent of n (Cauchy theorem)
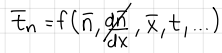
The stress tensor: cauchy theorems: formulas
formulas
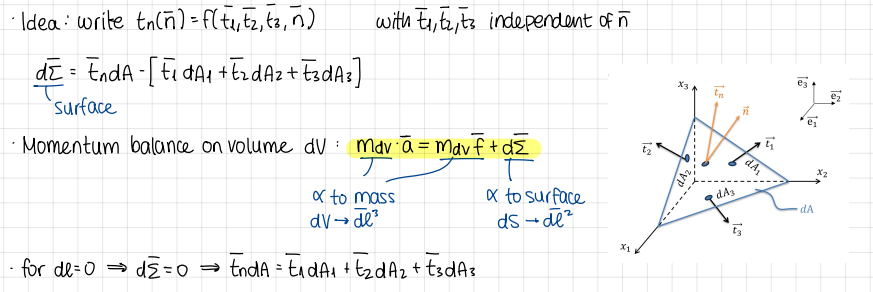
(stress tensor: cauchy theorem) If the limit of I (size of thetraedron) goes to zero…
the terms that depend on mass vanish more rapidly than the terms depending on the surface
so the only way to respect the balance of momentum is for the surface forces to be identically zero
The stress tensor: cauchy theorems: more formulas
formulas

Stress tensor
tensor
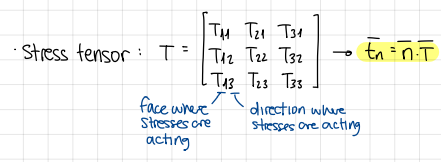
What do the components of the stress tensor T represent?
the components of the stresses acting on three orthogonal planes intersecting with surface dA (ex. the ones defined by the system of reference)
The components of the stress tensor T are…
independent on n, but only on the choice of the reference surfaces
for example, T11 is the component of t1 acting normal to the surface A1, while
T12 is the component tangent to A1 in the direction 2, etc.
2nd Cauchy theorem (stress tensor)
Tij=Tji
By similar reasoning (to 2nd Cauchy theorem) applied to the conservation of angular momentum it can be shown that…
the stress tensor is symmetric
Mechanical pressure formula
formula
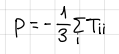
Formula for stress tensor for a fluid at rest (mechanical pressure)
formula
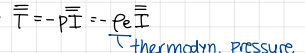
Formula for stress tensor in general (mechanical pressure)
formula

More development of right hand side of conservation of momentum, formulas
formulas
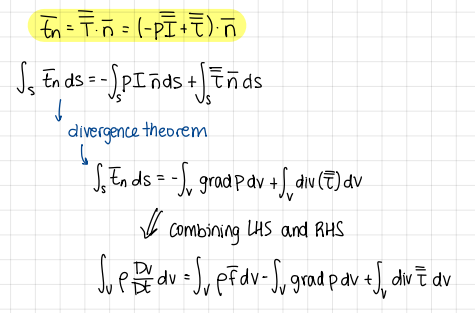
Expanded Localization lemma, formula
formula
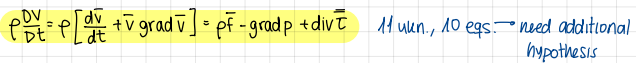
Why need closure hypothesis?
Problem: 4 equations and 11 uknowns → need to introduce some hypotheses
Characteristics of closure hypothesis
The derived equation is valid for any continuously deformable medium
To reduce the number of uknowns we need to make some hypothesis on the type of medium, and in particular on the relationship between the stresses and the deformation rates
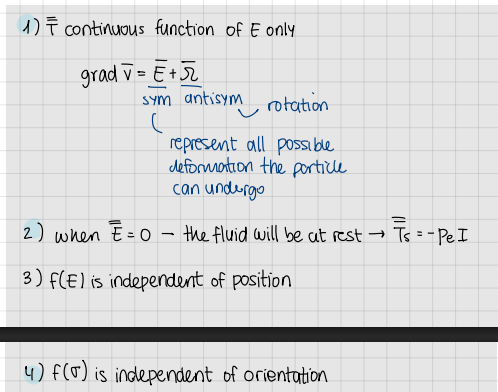
Assumptions of closue hypothesis
T is a continuous function of E only
gradv=E+omega
when E=0 → the fluid will be at rest → Ts=-p_e*I
f(E) is independent of position
f(sigma) is independent of orientation
Viscosity in closue hypothesis: formula
formula
lambda and mu: first and second viscosity coefficents

formulas of i_ij in closure hypothesis
formulas
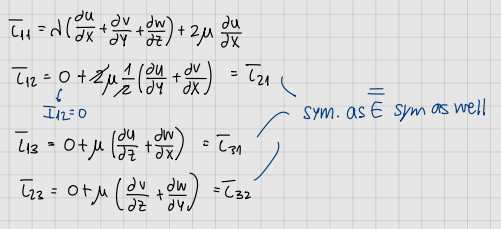
formula of E (closure hypothesis)
formula
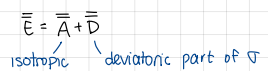
formula of A (closure hypothesis)
formula
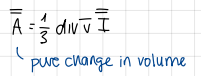
formula of viscosity (closure hypothesis)
formula
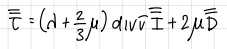
formula of stress tensor T (closure hypothesis)
formula
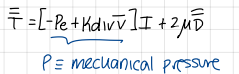
formula of kappa (closure hypothesis)
formula

(closure hypothesis) P=P_e if:
v=0 → P=(-Pe+kappa*div v)
div v=0 (incompressible flow)
kappa=0 → lambda=-2/3*mu (Stokes hypothesis)
kappa*div v « Pe
Developmend and general equation for momentum balance
formulas

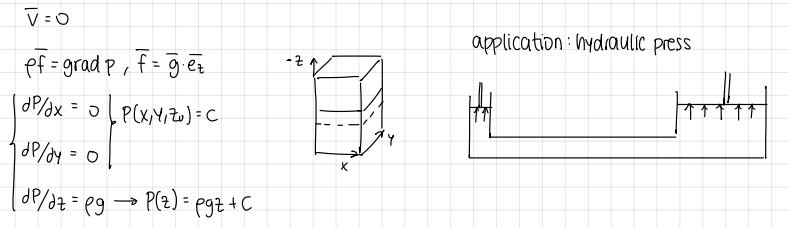
Pascal principle definition
in an incompressible fluid, any change of pressure is instantaneously transmitted to any other point of the fluid
formulas of hydrostatics
formulas
Archimedes principle
a body wholly or partially immersed in a fluid experiences an upward buoyant force equal in magnitucde to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body
how can the Archimedes principle be derived?
from the momentum quation in integral form by noting that a fluid volume at rest is subjected to the following condition:
formula
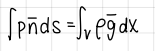
physical explanation of Archimedes principle
for a fluid at rest , the resultant of the hydrostatic pressure acting on any surfaces is equal to the weight of the volume of fluid that it encloses·Therefore, if we replace the mass of fluid with another element it will be subjected to the same pressure forces , whose resultant is a net force in the direction opposite ofthe body force (i .e. upward for gravity!) equal in magnitude to the weight of the displaced volume!
formula
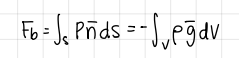
application of Archimedes principle
ships, balloons, etc.
statement of conservation of energy
the variation in time ofthe total energy (i .e.internal and kinetics) of any arbitrary material volume is equal to the sum of work per unit time (power) done by the external forces and the neat heatflux transmitted to the volume
principle of conservation of energy (formulas)
formulas
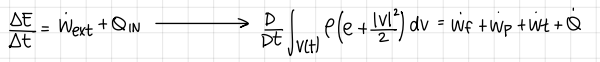
formula and units of work per unit time done by the body forces (conservation of energy)
formula and units
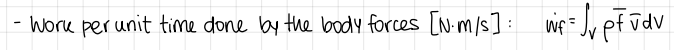
formula and units of work per unit time done by pressure (conservation of energy)
formula and units
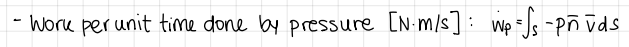
formula and units of work per unit time done by viscous stresses (conservation of energy)
formula and units
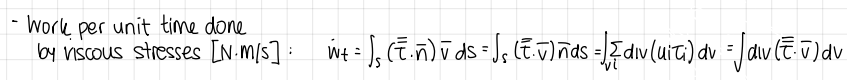
formula and units of heat transferred per unit time through the volume surface
formula and units
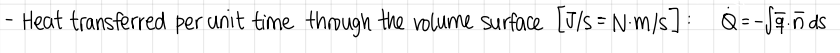
how do you get the differential form of the total energy balance?
by applying Reynold's transport theorem to the right hand side, Divergence theorem and localization Lemma
formula of the differential form of total energy balance
formula
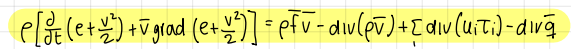
what can we do in order to isolate the contribution of the kinetic and integral energy to the total energy?
we can derive a balance equation for the kinetic energy from the momentum equation
formula of kinetic energy
formula
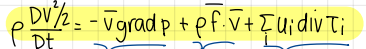

what is this term of the formula of kinetic energy (1/3)
contribution to the kinetic energy of the pressure gradient
positive or negative depending on the sign of the pressure gradient
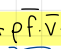
what is this term of the formula of kinetic energy (2/3)
contribution to the kinetic energy due to volume force (ex. buoyancy)
positive or negative in the direction of the body force
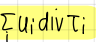
what is this term of the formula of kinetic energy (3/3)
contribution to the kinetic energy due to viscous action
development of internal energy equation
formulas
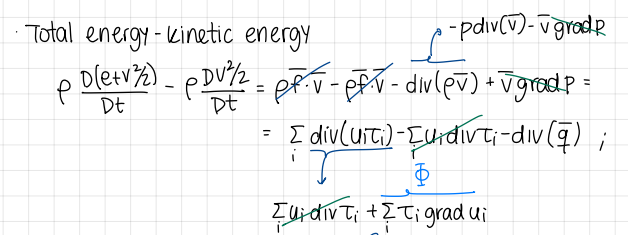
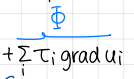
what does this term of the internal energy equation do?
it increases the internal energy
represents the work done per unit time by viscous stresses
write the internal energy equation
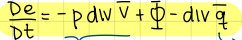
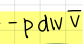
what does this term of the internal energy equation mean? (1/3)
reversible due to compression or expansion
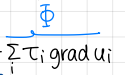
what does this term of the internal energy equation mean? (2/3)
dissipation term
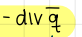
what does this term of the internal energy equation mean? (3/3)
external heat source
write the entropy balance equation and it’s condition
equation
condition → entropy must not decrease for closed systems
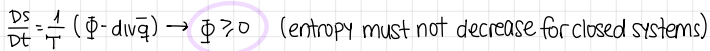
definition of entropy
it’s the measure of the molecular disorder of our system
it can only increase or remain constant
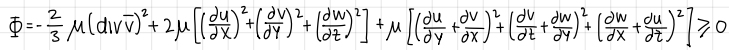
what is this expression?
entropy balance for newtonian fluids
why does dissipation happen?
due to the work done by the viscous stresses to deform a fluid particle
what does dissipation represent?
represents an irreversible form of energy transfer towards the internal energy (ex. increase fluid temperature)
more constitutive equations?
state law for thermodynamic pressure
heat conduction (radiation to be included if present)
state law for pressure
state laws for ideal gas (2)
state law for thermodynamic pressure (formula)
formula
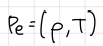
heat conduction (radiation to be included if present) (formula)
formula
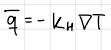
state law for pressure (formula)
formula
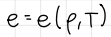
state laws for ideal gas (2 formulas)
formulas