Alkenes
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What are alkenes
Unsaturated hydrocarbons (contain double bond)
There is a high electron density in the double bond
What are polymers?
Large molecules formed from small identical molecules called monomers

What are addition polymers?
Addition polymers are formed from alkenes
(The monomers are alkenes)
Process called addition polymeriasation
Naming addition polymers
Poly (Name of alkene monomer)
e.g. Polyethene
Why are addition polymers unreactive?
Addition polymers are alkanes, despite being formed from alkenes (double bonds of the alkenes open up, connecting all the monomers to make the addition polymer)
Contain a large number of c-h and c-c bonds
These bonds are non-polar and strong, making them difficult to break
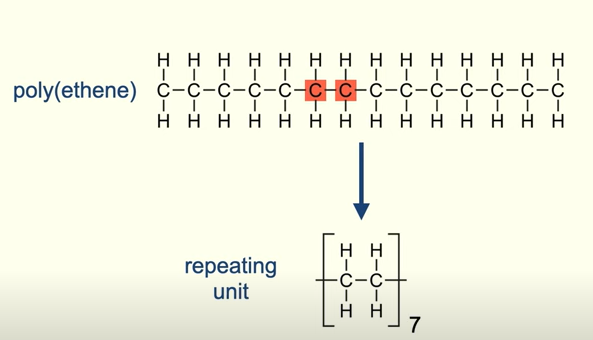
What is the repeating unit?
It show the arrangement of atoms, that are repeated in the polymer chain
For most repeating units there is a n outside the brackets to show that the unit repeats many times in the polymer
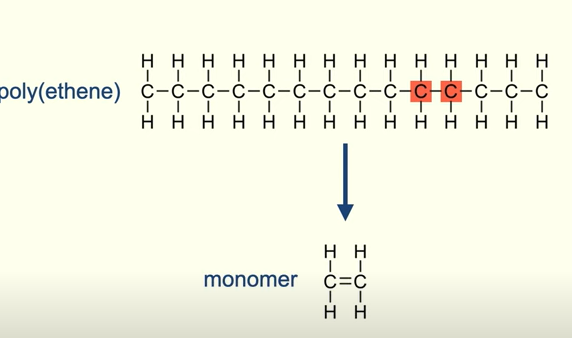
structure of a monomer from the polymer chain
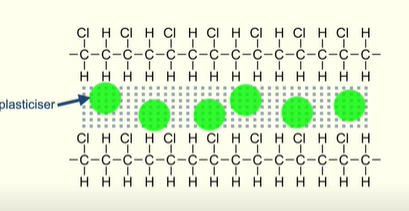
What is poly(chloroethene) or PVC used for?
Its a rigid polymer used to make plastic pipes
What can flexible PVC be used for?
soft and is used to make flooring
Insulation on electrical cables
(Made flexible by using plasticisers)
What is a plasticiser?
A small molecule that fits between polymer chains
Causing the chains to move further apart
Weakening the intermolecular forces between the chains
This allows the polymer chains to move over each other making the polymer flexible
Why are addition polymers bad for the environment?
They are unreactive
So they are non-biodegradable, meaning they are not broken down by microorganisms
As a result addition polymers can pollute the environment for a long time
What can we do rather than sending polymers to landfill?
Can be combusted to create energy
(But combusting polymers can release harmful chemicals)
Another method to dispose of polymers
Polymer waste can be sorted into the different polymers
And recycled to create different products
This reduces the amount of wate in landfills and limits usage of crude oil
(As there is less of a need to produce new plastic from monomers derived from the crude oil)
What is feedstock recycling
Feedstock is the raw materials used by the chemical industry
In feedstock recycling, waste polymers are converted back into simpler hydrocarbons
Which are then cracked and converted into different polymers
Adv=no need to sort out the different waste polymer
General formula for alkenes
CnH2n
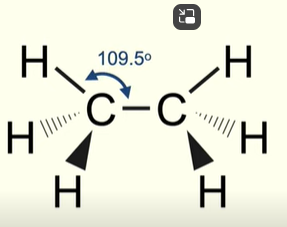
Structure and bonds in alkanes
All covalent bonds in alkanes are sigma
Sigma bonds form when electron orbitals directly overlap
Sigma bonds are fully rotational
Alkanes have a tetrahedral structure
Structure and bonding of alkenes
The double bond in alkenes consists of both pi and sigma bonds
Sigma bonds between c-h bonds
When double bond forms, one sigma bond is formed between c-c
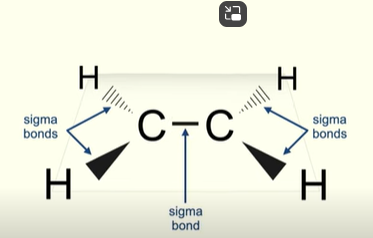
Structure and bonding of alkenes 2
P orbitals overlap
Pi bonds (unlike sigma) cannot rotate
only 1 pi bond between c-c

Why cant the pi bond rotate?
Any rotation of the pi bond would reduce the overlap of the p orbitals
Why are alkenes highly reactive
Due to the double bond
The bond contains 2 pairs of electrons
1 pair in sigma bond and 1 pair in pi
The bond enthalpy of pi bond is lower than sigma
so less energy is required to break pi bond
making the electrons in the pi bond more likely to take part in a reaction
Why do Pi bonds have a lower bond enthalpy than sigma bonds?
In a pi bond the orbitals overlap sideways so the bond is easier to break
In a sigma bond the orbitals directly overlap
Define electrophilic addition
Refers to a process where an alkene reacts with an electrophile
Define an electrophile
Any positive ion or molecule that is attracted to a region of high electron density
How does a hydrogen halide react with an alkene
Hydrogen halide consists of a polar bond
The halogen is always more electronegative than the H
The positive hydrogen will act as an electrophile and be attracted to the high electron density in the double bond
The positive charge of the hydrogen atom will attract the pair of electrons in the pi bond of the alkene
Pair of electrons move towards the H atom

The hydrogen atom can only form 1 covalent bond. What happens next?
The pair of electrons in the covalent bond between H and Br, move onto the bromine atom
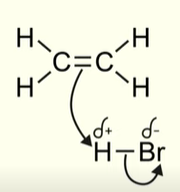
The products after the first stage of electrophilic addition

What does the bromide ion do now?
The electron pair on the bromide ion are attracted to the positive carbon in the carbocation
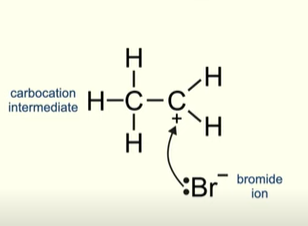
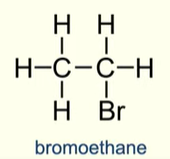
What is the final product of Hydrogen bromide reacting with ethene
Bromoethane
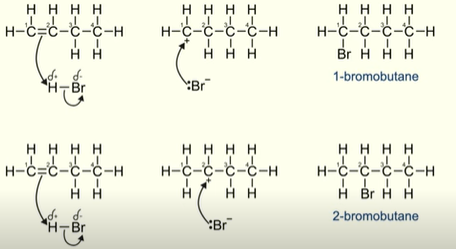
What happens when an asymmetric alkene reacts with a hydrogen halide?
You will form a 2 different products depending on where the positive carbon is in the carbocation
It will be a major product or a minor product
What does the stability of a carbocation depend on?
How many alkyl groups are bonded to the positive carbon
What is a primary carbocation ?
Positive carbon is bonded to 1 alkyl group
What is a secondary carbocation?
Positive carbon is bonded to 2 alkyl groups
Why is the secondary carbocation more stable?
The alkyl groups are electron donating
This electron donation from the alkyl groups reduce the positive charge of the carbon
Making it less likely to react. Therefore the secondary carbocation is more stable
What forms the major product?
The more stable carbocation
Why is the mechanism for a halogen molecule reacting with an alkene different to the mechanism of a hydrogen halide reacting with an alkene?
Halogen molecule (e.g. Br-Br) does not contain a permanent dipole
What happens in the first stage of the mechanism of a halogen molecule reacting with an alkene?
Halogen molecule (Br2) has no permanent dipole
But the region of high electron density in the double bond of the alkene repels the electron pair of the covalent bond in the Br molecule
Br2 now has an induced dipole
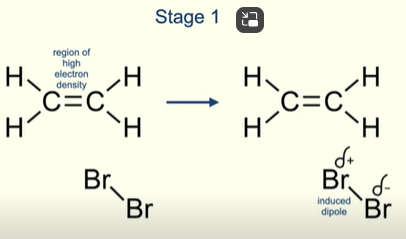
What happens after the induced dipole is formed?
Pair of electrons in the pi bond of the alkene are attracted to the positive bromine (electrophile)
The pair of electrons in the the Br molecule move to the other bromine and covalent bond breaks

What the final product formed after the halogen molecule reacts with the alkene
Electron pair on the bromide ion is attracted to the positive carbon in the carbocation
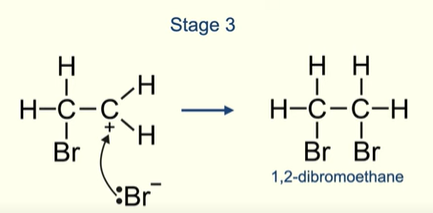
What happens when you add a halogen to an asymmetric alkene?
You only get one product
How do you test for an unsaturated molecule (alkene) using a halogen?
Use bromine water which is orange/brown
Add drops of bromine water into the substance being tested
Shake the test tube
If the substance is unsaturated the bromine will add across the double bond resulting in a colourless product
If the substance is saturated the bromine will not react
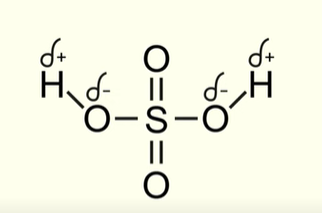
What is the structure of sulfuric acid in terms of electronegativity
Oxygen is highly electronegative
So the hydrogen atoms have a partial positive charge
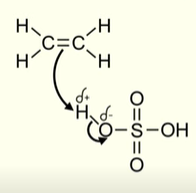
What happens in the first stage of the reaction between an alkene and concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
Electron pair in the pi bond of the alkene is attracted to the positive hydrogen atom (which acts as an electrophile)
What are the products formed after stage 1 of an alkene reacting with H2SO4
Carbocation intermediate
Hydrogensulfate ion
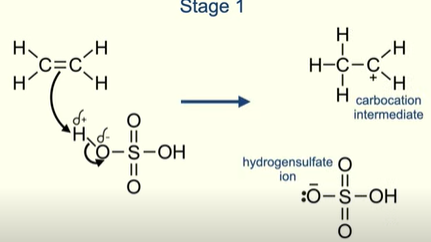
What happens with the Hydrogensulfate ion and the carbocation
Lone pair of electrons on the Hydrogensulfate ion are attracted to the positive carbon atom

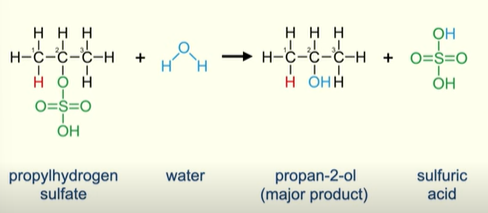
What happens if you add water to the product (e.g. ethylhydrogensulfate)of an alkene reacting with H2SO4
You make an alcohol (in this case ethanol)
The alcohol takes the place of the hydrogen sulfate
And reform sulfuric acid

What happens when an asymmetrical alkene reacts with H2SO4
Hydrogensulfate ion will bond to the more stable carbocation
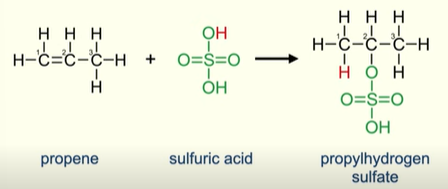
What happens if you add water to the product of an asymmetrical alkene reacting with H2S04
OH of the water replaces the Hydrogensulfate
Making a major product and sulfuric acid
In the example the major product is Propan-2-ol and minor product is Propan-1-ol (only produced in a small quantity)