BCR TBL 9: Disorders of Red Blood Cells, Platelets and Clotting
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
What globin subunits is HbA1 made of
2 Alpha 2 Beta
What Globin subunits are HbA2 made of
2 Alpha 2 Delta
What are some common symptoms of anaemia
Breathlessness Fatigue Headaches Palpitations Dizziness
Clinical Signs of Anaemia (Not presentation
)
Pallor Tachycardia Systolic Murmur Cardiac Failure
Rare signs of Anaemia
Koilonychia Jaundice Bone Deformities Leg Ulcers
What is Koilonychia
Spoon-shaped Nails
What kind of anaemia is jaundice found in
Haemolytic anaemia
if you have low Mean corpuscular volume what kind of anaemia might you have
Hypochromic
if you have normal MCV what kind of anaemia might you have
Normochromic
if you have highh MCV what kind of anaemia might you have
Hyperchromic
What are the 4 main causes of anaemia
Inherited Haematinic Deficiency EPO Deficiency Bone Marrow issues
What are Haematinic Deficiencies
Iron B12 Folic Acid
What are the 3 main inherited issues
Red cell membrane Haemoglobin Metabolic
What are 2 examples of red cell membrane defect anaemia
Spherocytosis Elliptocytosis
What are some haemoglobin abnormality anaemia
Thalassaemia Sickle Cell
What are the 6 main acquired anaemia categories
Immune Drug induced Acquired membrane Mechanical Infection Secondary to systemic disease
What are some autoimmune anaemia reasons (Antibody)
Warm Cold Biphasic
What are some Alloimmune reasons for anaemia
Transfusion
What is an example of an acquired membrane defect anaemia
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Haemoglobinuria
If you have iron deficiency what happens to your red blood cell produce in terms of size
Smaller
If you have B12 or Folic Acid deficiency what happens to your red blood cell produce in terms of size
Bigger
What is a RBC lifespan
3 Months
How long does it take to produce a red cell
3 Weeksq
What are the stages of red cell maturation after stem cell
BFU erythroid CFU erythroid Pro Erythroblast Erythroblast Reticulocyte Erythrocyte
How long is EPO dependence in red cell maturation
10-13 days
How long is iron Dependence in red cell development
10 days
Where is iron mainly stored
Liver
What transmembrane channel is iron taken in by
DTM-1 HCP-1
How much iron can we absorb when its in haem form
20-25%
What is the protein that stores iron
Ferritin
What is the transporter that puts iron into blood
Ferroportin
Why dont you want free iron in blood
Toxic
What converts ferrous iron to ferric iron
Hephaestin
What is free iron binded to to make it non toxic
Transferrin
what regulates iron absorption
Hepcidin
What allows iron to be released from transporter in vesicles in consumer cell
Lowered pH
Where is iron stored in Liver
Parenchymal cells kupffer cells
What is the main function of Kupffer Cells
Phagocytosis Breakdown of old RBC
Where is iron stored in Kupffer cells
Haemosiderin
What detects low or high iron
Iron responsive elements
What regulates production of iron transporters
Iron Regulatory Protein
What does hepcidin do
Inhibit Absorption of Iron
What is stomatitis
sore tongue and mouth
What is angular Cheilitis
Inflammation of corner of mouth
How to diagnose iron defeciency
Ferritin and transferrin saturation
If someone has iron deficiency what will their Transferrin Saturation and Ferritin be
Less that 20% Low
What is the risk of intravenous iron
Anaphylaxis
What does intracellular folate act as in dna synthesis
Coenzyme
Where do you find folate
Raw Green Veg Liver
What can Methotrexate(a chemotherapy) cause
Pancytopenia
3 main presentation of folate deficiency
Pancytopenia Macrocytic anaemia Glossitis
What is glossitis
Burning sensation on tongue
What can hyperlobulated nucleus in neutrophils show in regards to folate
Folate deficiency`
how do you deal with methotrexate folate issues
Intravenous Folate
how is B12 isolated in body (Before intestine)
Separated from protein by stomach acid
What binds to B12 to protect it from degradation
Haptocorrin
What do gastric cells secrete thats needed for B12 absorption
Intrinsic Factor
Where is B12 Stored
Liver
What is Achlorhydria
Stomach isnt acidic enough
Presentation of B12 deficiency
Macrocytic Anaemia Pancytopenia Glossitis Neuropathy
What kind of bone marrow in Aplastic anaemia
Hypocellular with no infiltrate or fibrosis
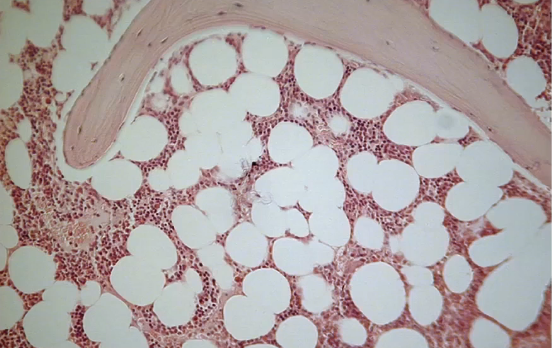
What kind of bone marrow is this
Normal
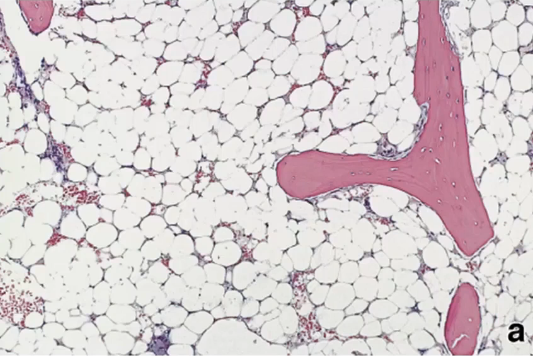
What kind of bone marrow is this
Aplastic
Blood Results for Aplastic Anaemia for severe and Very Severe
Neutrophils < 0.2 Platelets <20 Reticulocytes < 60
Bone Marrow Cellularity for Aplastic Anaemia for severe and Very Severe
<25%
How to treat Aplastic Anaemi
Immunosuppression Transfusion Stem cell transplant
What is the Immunosuppressant in aplastic anaemia
ATG
How does Aplastic Anaemia present
Normocytic with reticulocytopenia thrombocytopenia neutropenia
How does pure red cell aplasia present
Normocytic with reticulocytopenia
What binds to haemoglobin so it can be metabolised by liver
haptoglobin
if there isnt enouigh haptoglobin what happens to haemoglobin`
oxidised into methaemoglobin
What binds to heme groups so it can be metabolised in liver by macrophages
Hemopexin
What does heme bind to when Hemopexin is saturated and what does it form
Albumin Met-Haemalbumin
Methaemoglobin is metabolised in kidney. What does it become
Haemosiderin
What kind of antibody is IgG (Warm , Cold, Biphasic)
Warm Biphasic
What kind of antibody is IgM (Warm , Cold, Biphasic)
Cold
blood tests for Haemolysis
FBC Reticulocytes Increased Bilirubin and LDH DAT
What is Warm Autoimmune Haemolytic Anaemia (wAIHA) due to (Antibodies)
IgG
What is the usual presentation of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
Acute with severe anaemia and jaundice
How to confirm wAIHA
DAT positive IgG C3D complement
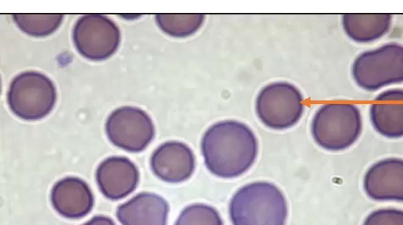
Spherocyte
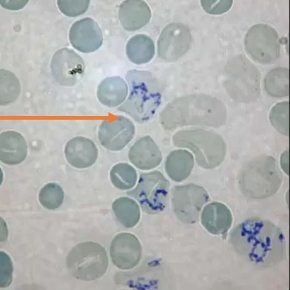
Reticulocyte
What is the first line treatment for wAIHA
steroids folic acid transfusion
What is the second line treatment for Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
Splenectomy Intravenous Immunoglobulins Immunosuppressants
What is Cold Haemagglutinin Disease (CHAD) due to (Antibodies)
IgM
How to confirm Cold Haemagglutinin Disease
DAT positive for C3d
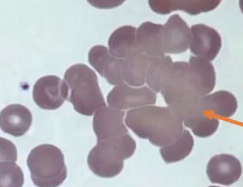
Red Cell Agglutination
How to treat Cold Haemagglutinin Disease
Keep Warm Steroids Transfusion Folic acid Immunosuppressants Complement Targeted Treatment
What is Paroxysmal Cold Haemoglobinuria (PCH) due to (Antibodies)
IgG
How to confirm PCH
Donath Landsteiner Stest
What is the Donath Landsteiner Test
Incubate Blood at 4 degrees Warming causes Haemolysis
Presentation of Spherocytosis
Jaundice at birth Chronic Haemolysis Gallbladder Stones Hyperbilirunemia
What is Cholelithiasis
Gallbladder Stone
How to treat Spherocytosis
Folic Acid Splenectomy Cholecystectomy
What is Elliptocytosis
Defect of Protein 4.1 Which is autosomal recessive
What doe sG6PD do
Protect Red Cells from damage
What happens if you have G6PD deficiency
Acute Intravascular Haemolytic Crisis
What is Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency due to
Autosomal Recessive PKLR gene
What kind of disorder is Pyrimidine 5’ Nucleotidase Deficiency
Autosomal Recessive
What is Paroxysmal Nocturnal Haemoglobinuria caused by
Acquired Membrane defect Phosphatidylinositol Glycan Class A (PIGA)