IB Chemistry HL Topic 14 (Chemical Bonding and Structure)单词卡 | Quizlet
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
sigma bond
This type of bond is formed by head-on overlap of atomic orbitals, resulting in electron density concentrated between the nuclei of the bonding atoms.
pi bond
This type of bond is formed by the sideways overlap of atomic orbitals, resulting in electron density above and below the plane of the nuclei of the bonding atoms.
formal charge
a hypothetical charge worked out with the following equation: (number of valence electrons) - [(1/2)(number of bonding electrons)] - (number of nonbonding electrons)
single covalent bond
consists of two electrons shared between two atoms A and B; this bond is a sigma bond
double covalent bond
consists of four electrons (two pairs) shared between two atoms A and B; this bond is 1 sigma bond plus 1 pi bond
triple covalent bond
consists of six electrons (three pairs) shared between two atoms A and B; this bond is 1 sigma bond plus 2 pi bonds
incomplete octet
an element with fewer than 8 valence electrons (example: boron)
expanded octet
more than 8 valence electrons surrounding the central atom
Formal charge equation
FC=(# of valence electrons) - 1/2(number of bonding electrons) - (number of non-bonding electrons)
hybridization
a concept used in Valence Bond Theory to explain the number of bonds that an atom can form and the spatial orientation of these bonds; the mixing of atomic orbitals to generate hybrid orbitals that are equivalent
delocalization
electrons that are shared by/between all atoms in a molecule or ion as opposed to being localized between a pair of atoms
resonance
involves using two or more Lewis structures to represent a particular molecule or ion; structure is one of two or more alternative Lewis structures for a molecule or ion that cannot be described fully with one Lewis structure alone
sp3
4 electron domains (single bond)
sp2
3 electron domains (double bond)
sp
2 electron domains (triple bond)
possible overlap combinations: sigma bonding
s + s
s + px
px + px
possible overlap combinations: pi bonding
py + py
pz + pz
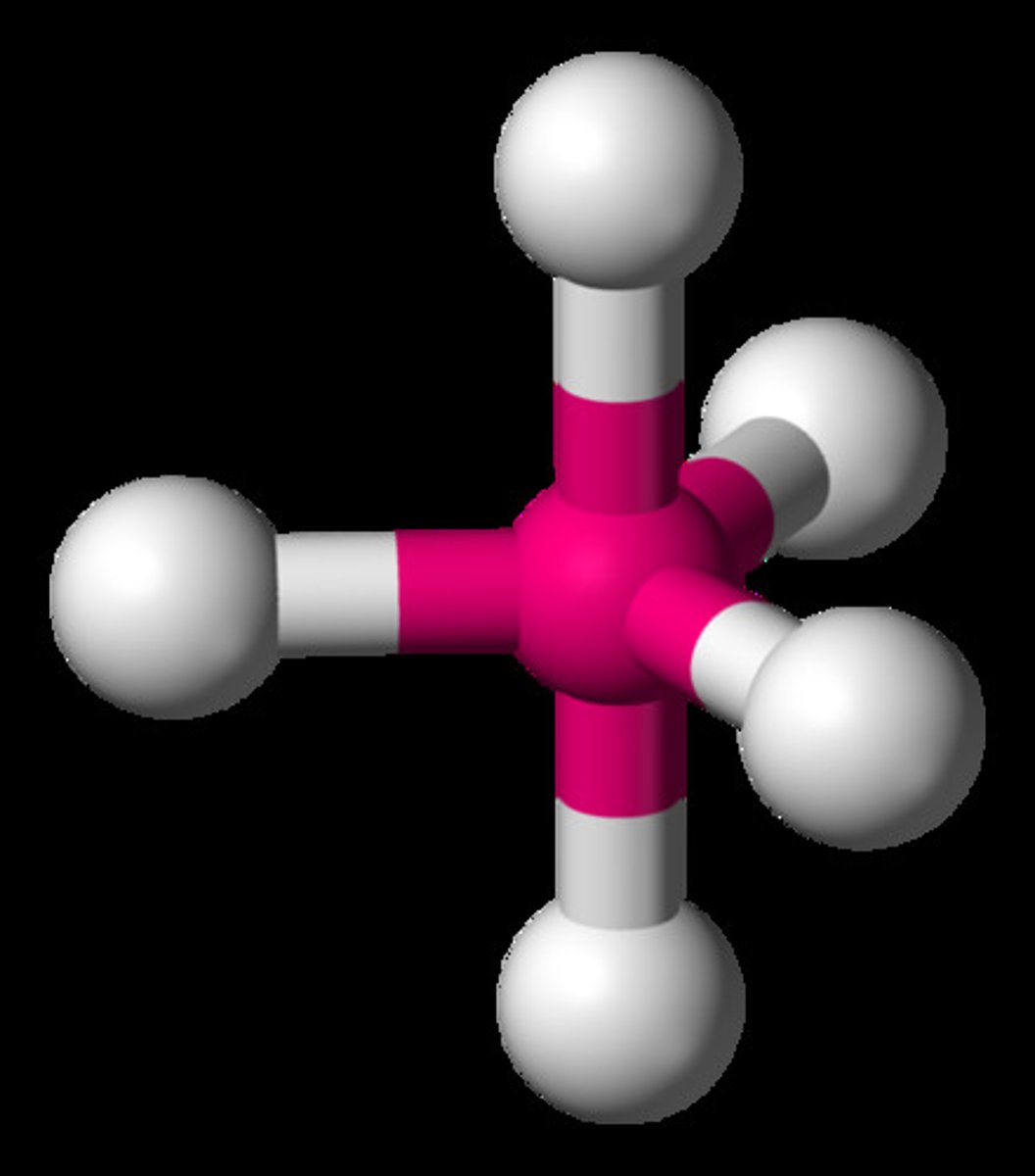
trigonal bipyramidal
5 electron domains
axial 90 degrees
equatorial 120 degrees
no lone pairs
5 BPs
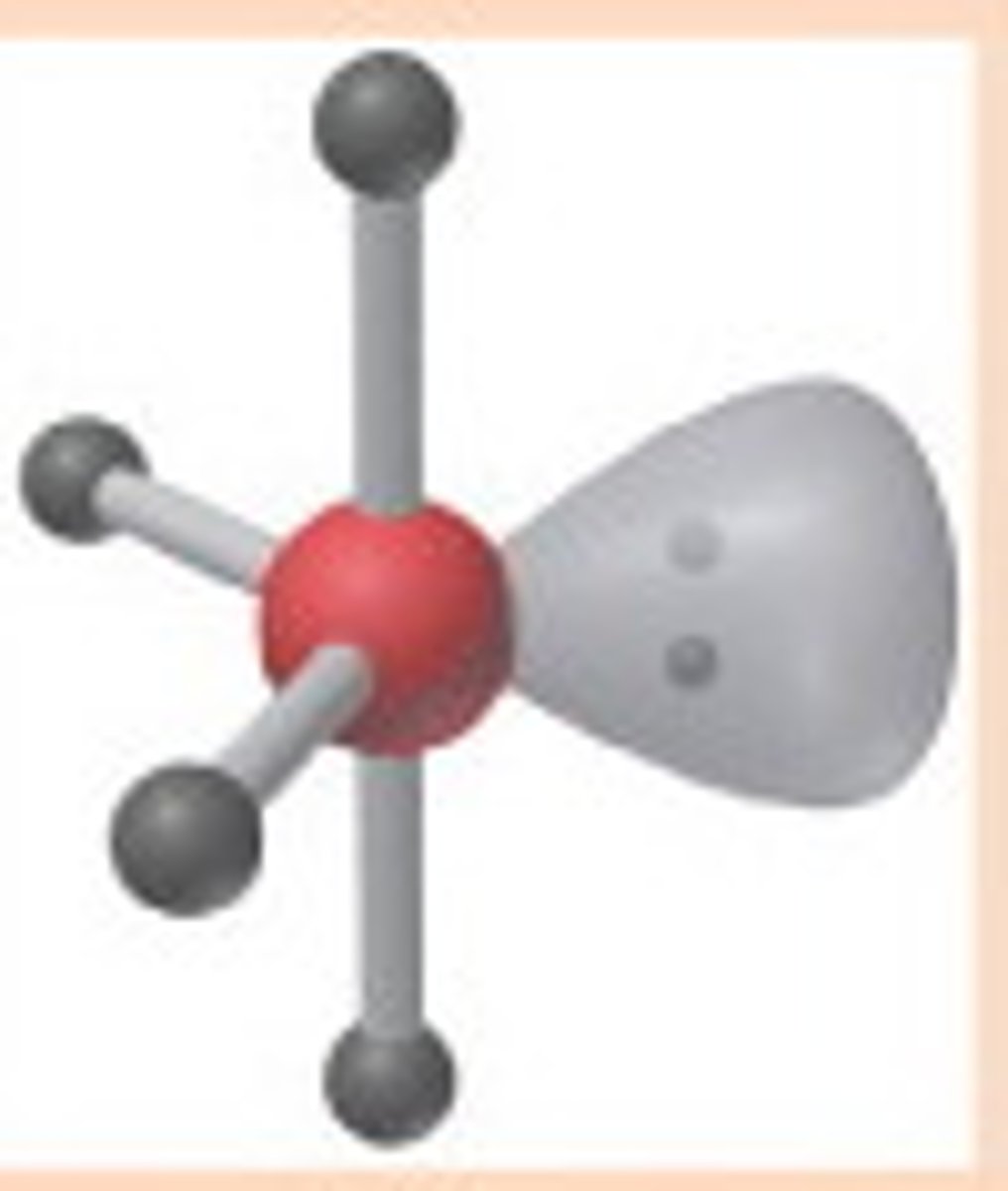
seesaw
5 electron domains
axial >90 degrees
equatorial >120 degrees
1 lone pair
4 BPs
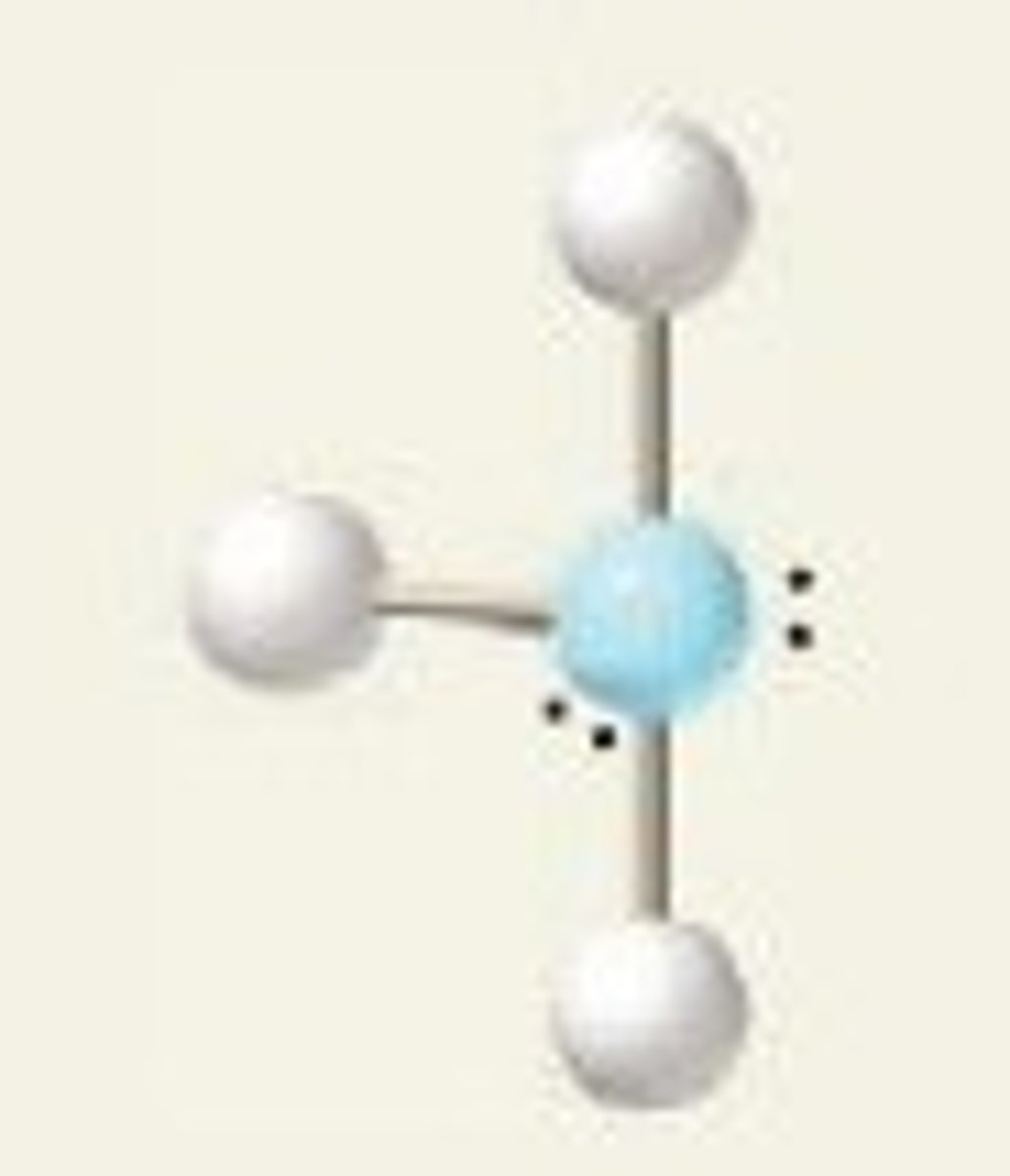
T-shaped
5 electron domains
90 degrees
2 lone pairs
3 BPs
linear (5 electron domains)
5 electron domains
180 degrees
3 lone pairs
3 BPs
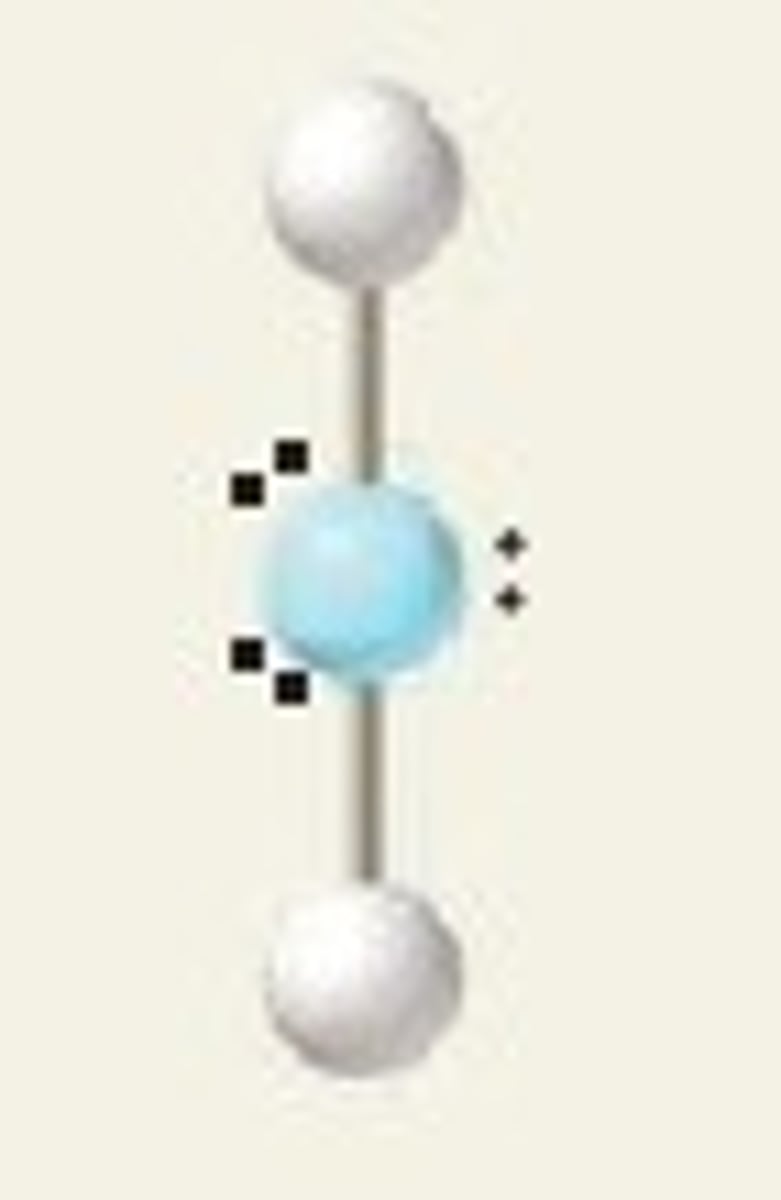
octahedral
6 electron domains
90 degrees
0 lone pairs
6 BPs
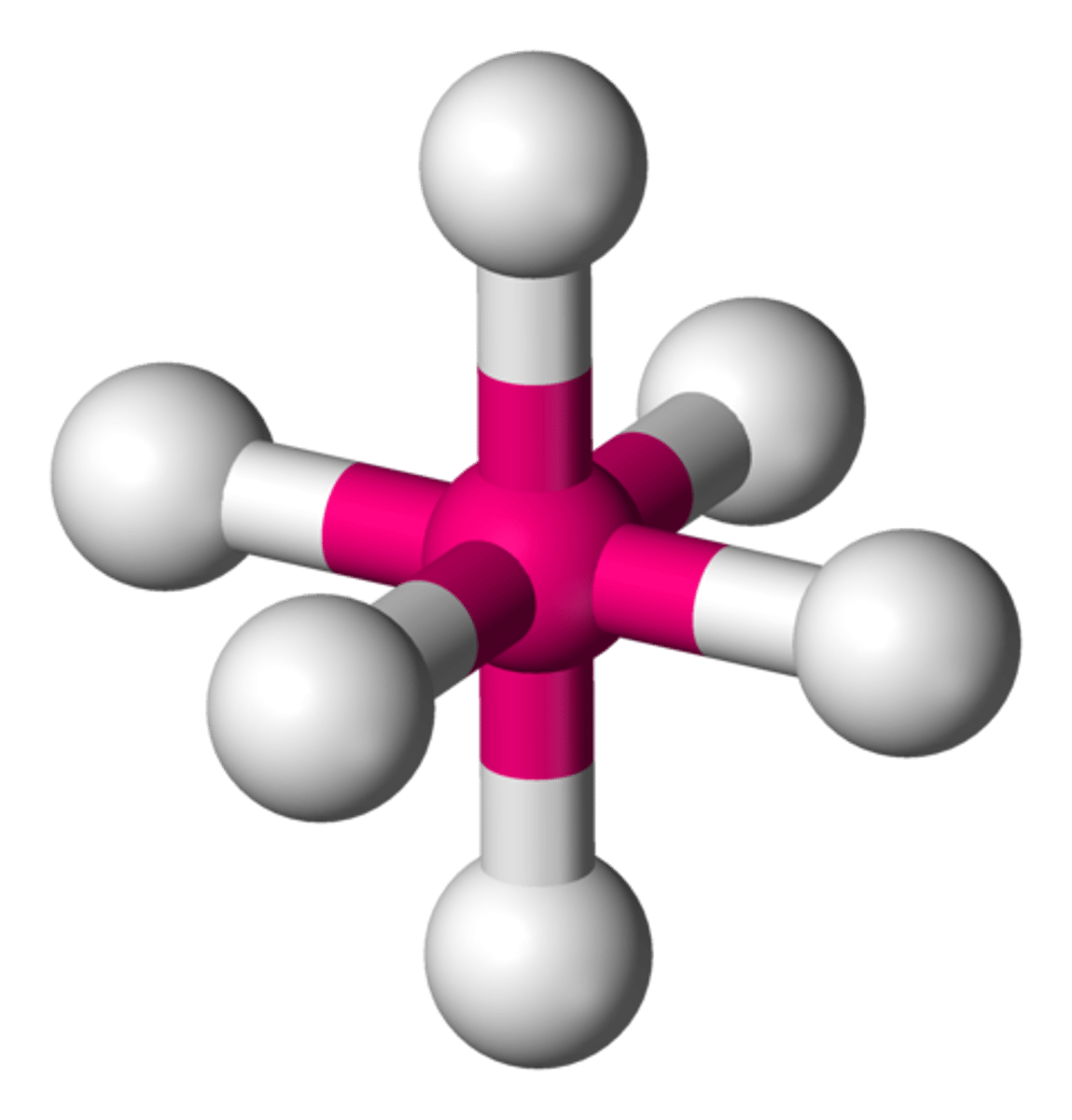
square-based pyramidal
6 electron domains
90 degrees
1 lone pair
5 BPs
square planar
6 electron domains
90 degrees
2 lone pairs
4 BPs
s orbital shape
spherical
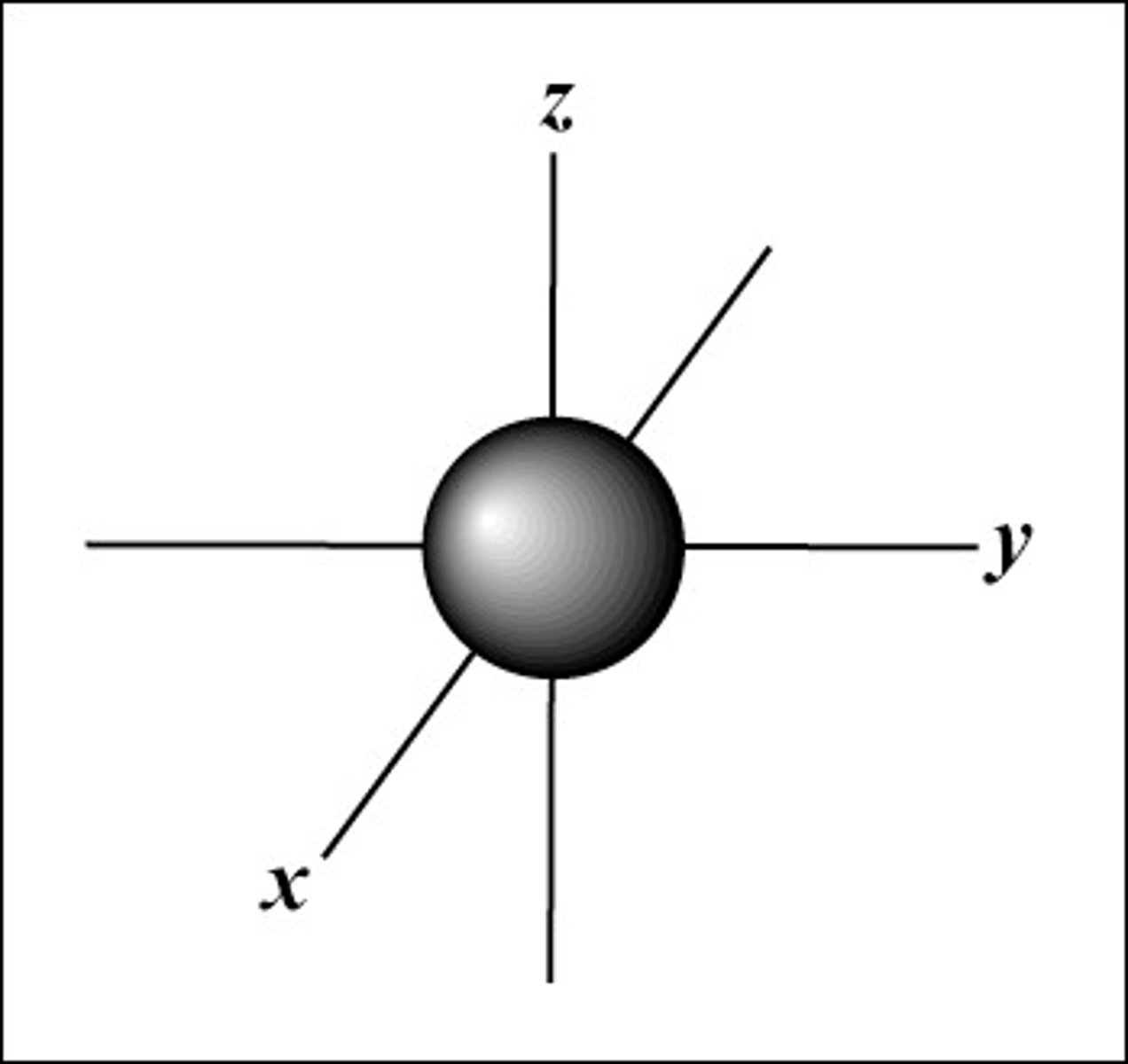
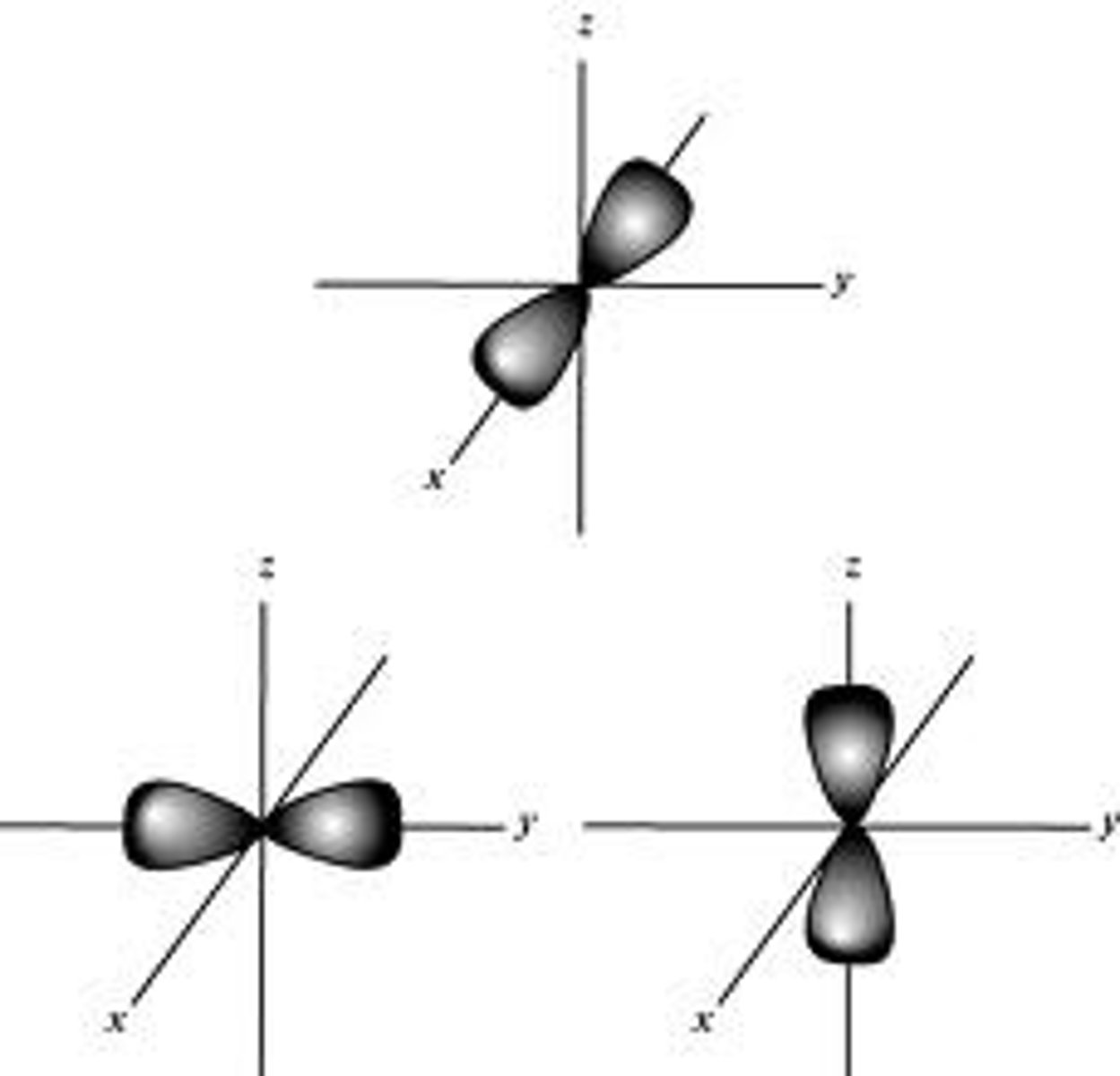
p orbital shape
dumbbell