Psych Exam 2 CNS Depressants (Sartor)
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
what arethe 3 classes of CNS depressants
sedatives, hypnotics, and tranquilizers/anxiolytics
sedative CNS depressants
o reduces activity and excitement, calms the recipient
§ For hyper-excited/manic
hypnotic CNS depressants
o produce drowsiness and facilitates the onset and maintenance of sleep
tranquilizer/anxiolytic CNS depressants
o reduce anxiety without drowsiness
indications of CNS depressants
o Anxiety-related disorders
o Insomnia
o OCD
o Seizures/convulsions
o Alcohol withdrawal
GABA function
-inhibitory (breaks)
-causes hyperpolarization of neurons
glutamate function
-excitatory (gas)
- cuases depolarization of neurons
sedative hypnotic subclasses
-benzos
-barbiturates
- misc (busprione, chloral hydrate, z drugs, ramelteon)
barbiturates original uses
· as sedatives, hypnotics, anesthetics, and anticonvulsants
which barbiturate is still used as an anesthetic
phenobarbital
ultra-short barbiturates (onset + duration)
§ Onset <1 min; duration a few mins
which barbiturates are ultra-short acting
methohexital and thiopental
methohexital brand name
brevital
thiopental brand name
pentothal
short barbiturate duration
~2 hours
intermediate barbiturate duration
~3-6 hours
which barbiturates are intermediate-acting?
amobarbital and pentobarbital
amobarbital brand name
amytal
pentobarbital brand name
newbutal
long-acting barbiturate duration
~6 hours
which barbiturates are long-acting
phenobarbital (luminal)
phenobarbital brand name
luminal
effects of barbiturates on sleep
o Shorten sleep latency (fall asleep quicker)
o Increase in total sleep
o Often decrease in waking time during the night
o REM suppression
o Reduce neurogenic respiratory drive
barbiturate overdose
· : highly toxic in acute overdose
o Ten times the therapeutic dose may lead to fatal respiratory or CV depression
o Effect increased when combined with alcohol or other CNS depressants
o Coma and death from respiratory depression
o More common in elderly
misuse of barbiturates
o Relaxed contentment and euphoria- short/intermediate group generally preferred
o Can induce tolerance- need more drug to get effects the more you use it
o Physiological dependence
barbiturate withdrawal symptoms
insomnia, agitation, irritability, hyperthermia, risk of seizures
steps of lethal injection and what they do
o Barbital (thiopental or pentobarbital) causes sedation
o Followed by muscle relaxant (pancuronium bromide) which causes muscle paralysis and respiratory arrest
o Followed by KCl which stops the heart
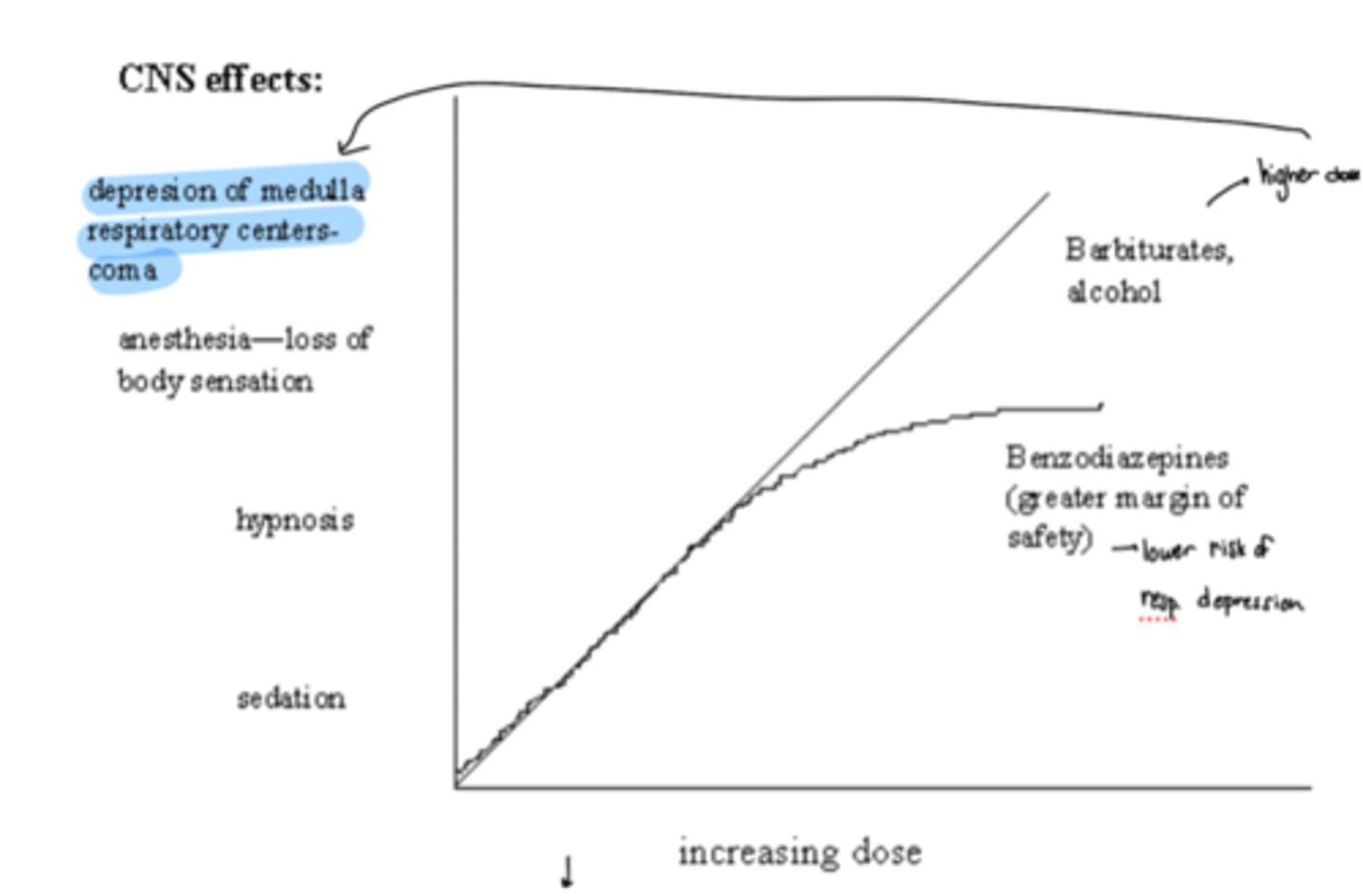
barbiturates vs benzodiazepines
· At increasing doses, both can cause sedation, hypnosis
· At higher doses benzos peak in effect until they reach very very high doses
· On the other hand, higher doses of barbiturates can cause anesthesia and depression of medulla respiratory centers/coma
effect of barbirturates on GABA
· Enhance GABA receptor activity acting as a positive allosteric modulator (bind to BABA-A receptor which decreases the rate of dissociation of GABA and increases the duration of GABA Cl channel opening)
· The longer it’s open, the more hyperpolarizing occurs/ inhibition
· Can be GABA receptor agonist at high doses
what areas do barbiturates affect other than GABA?
o Potentiate glycine (inhibitory NT)
o Inhibit glutamate receptor (excitatory NT)
· May also have non-specific membrane effects
net result of barbiturates
reduction in neuronal activity
structure of GABA-A receptor
-5 subunits (2 alpha, 2 beta, 1 gamma)
-Cl- channel pore in the middle
-multiple allosteric binding sites
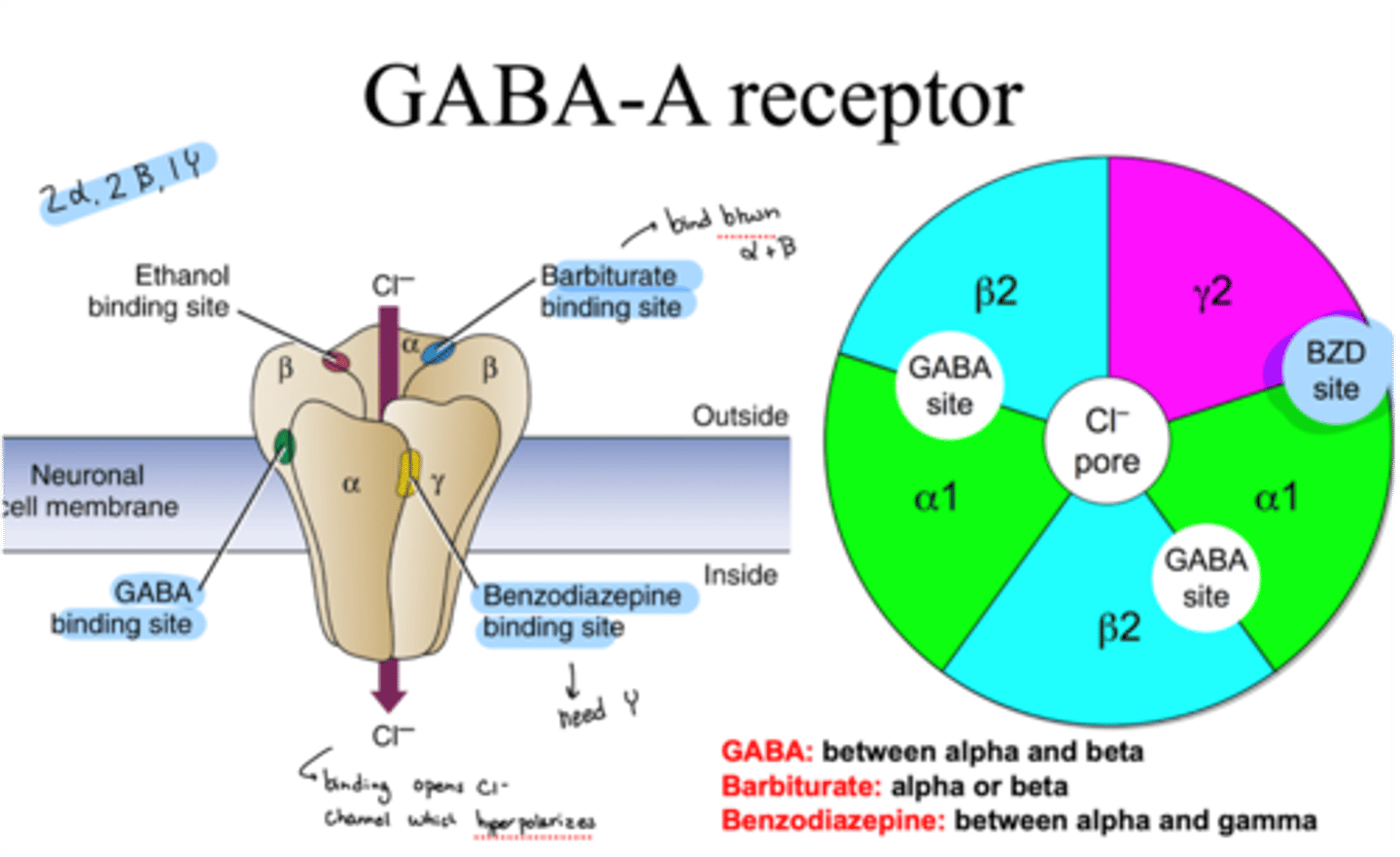
where does GABA bind on GABA-A receptor
binds between alpha and beta
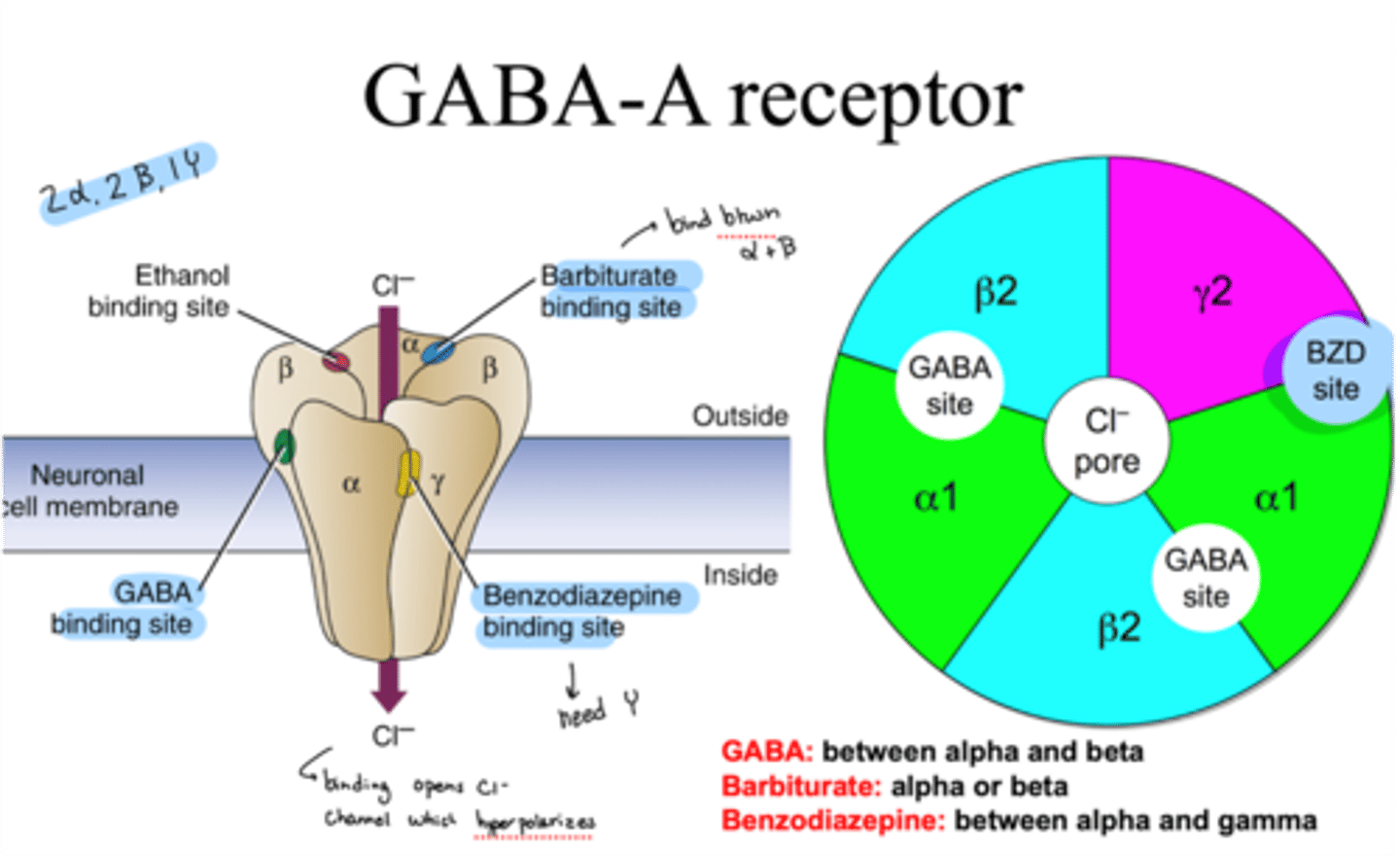
where do barbiturates bind on GABA-A receptor
binds on alpha or beta
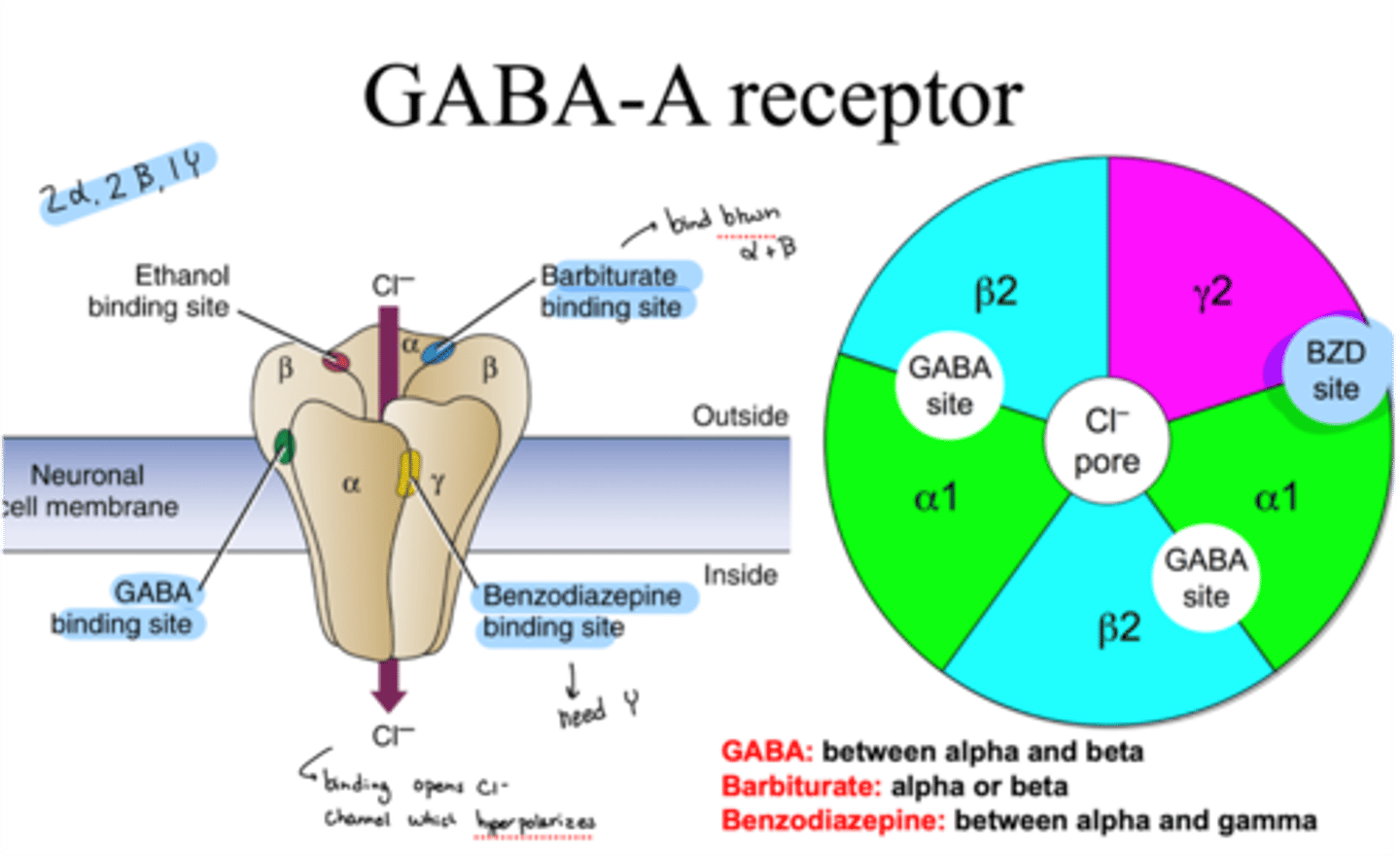
where do benzodiazepines bind on GABA-A receptor
bind between alpha and gamma
GABA receptor subunit subtypes
· Different assemblies of 16 subunits although there may be 1 million possible
· Alpha, beta, gamma, sigma, epsilon, pi, theta
role of GABA receptor's alpha subunit
critical for affinity of GABA and for benzodiazepine effects
role of alpha 1 subunit on GABA-R
important for hypnotic effects
may cause anticonvulsant effects
Z drug affinity on GABA-R
have higher affinity for alpha 1 subunit
role of alpha 2 subunit on GABA-R
highly expressed in the limbic system
important for anti-anxiety effects
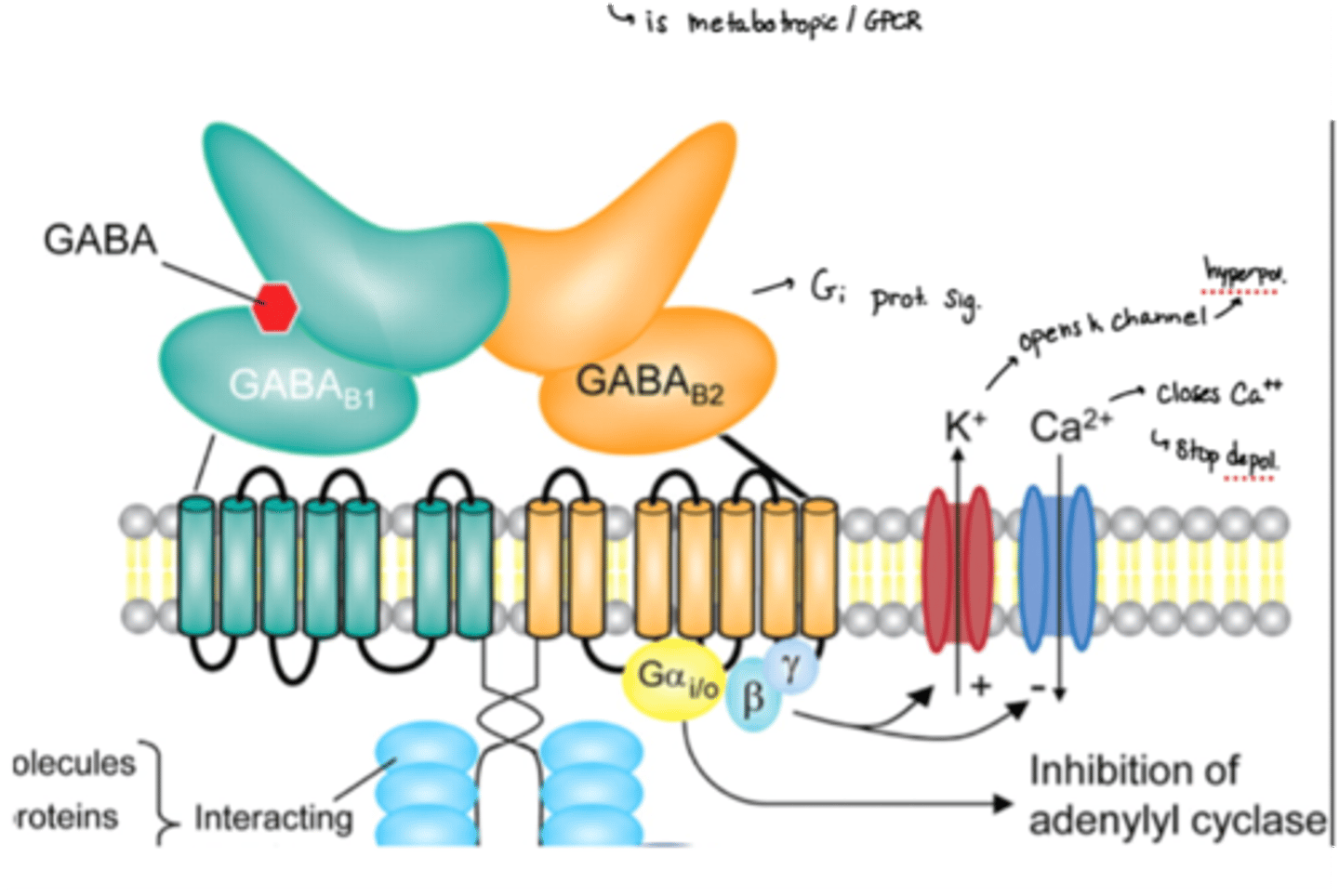
what type of receptor is the GABA-B receptor?
is a Gi GPCR
2 subunits of GABA-B receptor
beta 1 and 2
MOA of GABA on GABA-B receptors
· GABA binds to B1 and the B2 binds to the subunit proteins
· Inhibits activity by opening K channels (more hyperpol) and closing Ca channels (stop depol)
chloral hydrate
o Sedative and hypnotic
o 1st CNS depressant develop for inducing sleep
o Not FDA approved
o Replaced by Z drugs
paraaldehyde
o Relatively safe hypnotic
o Used in psych wards and people with AUD until the 60's
o 30% of dose is excreted through the lungs which causes halitosis (bad breath)
o Anticonvulsant (doesn't suppress breathing at therapeutic doses)
bromides
o older sedative-hypnotic
o NaBr, KBr
o KBr still used in veterinary practice as anticonvulsant
o NaBr no longer used due to toxicity
o Bromides mimic the activity of Cl- but larger so hyperpolarizes for longer
methaqualone (Qualude)
o GABA receptor agonist
o Marketed as a safe, non addicting barbiturate substitute
o Became schedule I in 1984
o OD symptoms: delirium, coma, restlessness, hyperreflexia, convulsions, tachycardia, cardiac and respiratory depression
Z drug indication
for insomnia
Z drug vs BZDs
Z drugs aren't benzodiazepines and tend to have fewer side effects in comparison
which CNS depressants are antihistamines
diphenhydramine, doxylamine, pyrilamine
what type of drug are antihistamines (what do they do at which receptors?)
H1 receptor antagonist
antichoolinergic side effects of antihistamines
§ Cant see, pee, spit, or poop
§ Long-term associated with dementia
herbal/natural products that are CNS depressants
o Valerian
§ May decrease GABA metabolism and binds to GABA
o Passion flower
§ Tea may contain GABA
o Lemon balm/hops
o Tryptophan
propofol indication
injection for anesthesia
onset (IV) if propofol
~30 secs
-short half life of 3 mins so must be used as an infusion for longer sedative periods
what does propofol do at which receptor
GABA-A receptor enhancement
xyalazine (what does it do at which receptor?)
NE alpha-2 agonist ( decrease in NE releases)
xylazine use
o Not approved for humans
o Used to cut drugs of abuse which can cause many side effects
o "Tranq" is its nickname
gamma-hydroxy butyrate (GHB), what is it and what does it do at whcih receptor
o Endogenous NT, precursor to GABA, glutamate and glycine
o GHB receptor agonist, weak GABA-B agonist
effects of GHB on a patient
o Produces dreamy/euphoric effect, relaxation
§ Onset ~15 min, duration 3-4 hours
§ Rapidly metabolized (depleted in 12- 24 hours)
§ Can produce coma, respiratory failure
§ Also dance club drug, date rape drug, abuse by body builders (can acutely elevate GH)
sodium oxybate brand name
xyrem
sodium oxybate (Xyrem) indication
treat narcolepsy and excessive daytime sleepiness
what receptor does Xyrem interact with
GABA-B and GHB receptor action
functions of the limbic system
· controls emotion and emotional responses
o Fear + rage
o Mood
o Motivation
o Pain + pleasure
o Memory (especially with strong emotional component)
o Fight or flight (autonomic regulation)
hippocampus function
long-term memory, spatial navigation, contextual information
cingulate gyrus function
· autonomic functions as well as cognitive and attentional processing
amygdala function
· involved in aggression, fear, reward
o “salience” – significant information that stands out
fornix function
· white matter connection between hippocampus and hypothalamus
hypothalamus function
· homeostasis, link CNS to endocrine system, feeding, sleep, motivation
thalamus function
· relaying sensory info, consciousness, sleep, and alertness
fear
an emotional reaction to a specific, real danger
stress
caused by an external trigger, short-term
anxiety
persistent, excessive worries that don't go away even in the absence of a stressor
what is the main brain region for anxiety and fear
the amygdala
amygdala and anxiety
o Lesion of amygdala produces docile animals
o Coordinates autonomic threat response
o Integrates sensory info and prior learning (association of a queue with a stressor)
o May regulate hormonal response to threat
o Fast response but not necessarily accurate
cortex and anxiety
· recognition and cognitive appraisal of threat
Slow and thought out
amygdala other functions
· supports skills necessary for a complex social life
o Involved in interpersonal functions like interpreting facial expressions, reacting to visual threats and trusting strangers
o The larger social network a person has the larger their amygdala
general adaptation syndrome, what is it?
· Hans Selye proposed a paradox that physiologic symptoms activated by stress can not only protect and restore but also damage the body
stages of general adaptation syndrome
o Alarm: your body reacts to a stress, activates the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis (HPA)
o Resistance: parasympathetic branch of the ANS counteracts the changes that the stressful stimulus has produced, and attempts to restore a state of homeostasis
o Exhaustion: the body’s resources have been depleted
§ Chronic stress
· HTN
· MI
· Depression
· Sleep disturbances
· Decreased metabolism
· Migraines
· Decrease serotonin
steps of the stress response system
1. Hypothalamus releases CRH (corticotropin-releasing hormone)
2. CRH interacts with the pituitary gland which then releases ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
3. ACTH interacts with the adrenal gland to produce cortisol
4. The hypothalamus responds to the cortisol
working model of anxiety
· Prefrontal cortex uses reason and thought to process incoming info
· Limbic system (amygdala especially) registers threats and dangers and induces reflexive fear responses
· In anxiety, inhibitory inputs from cortex may be disrupted resulting in unchecked amygdala activity
anti-anxiety drugs
· Alcohol
· Barbiturates
· Benzos
· Buspirone
· SSRIs/SNRIs
· Antihistamines
· Beta-blockers
what action do BZDs have?
GABA-A receptor modulation
effects of low to moderate does of BZDs
· relaxation, relief from anxiety and tension, promote sleep, muscle relaxation, epilepsy
effects of high doses of BZDs
can cause respiratory depression
binding of benzos vs barbiturates
· Barbiturates at low concs- augment the affinity of the GABAA receptor for GABA and increase the mean channel opening time induced by GABA (similar to benzos)
· At high barb doses- barbiturates directly increase channel openings, even in the absence of GABA
· benzos have no direct effect on channel opening but only increase the affinity of the receptor for GABA and frequency of channel openings
· gamma subunit is not needed for barbiturate activity
neurosteroids, what action do they have for anxiety?
· endogenous positive allosteric modulators of GABA-A receptor
· changes in neurosteroid levels are associated with conditions like stress, depression, pregnancy, neural development , aging
· different GABA R subtypes have different sensitivity
natural products for anxiety
picamillon
diet
L-theanine
picamillon and anxiety
GABA bonded to niacin so it can travel across the BBB
diet and anxiety
complex carbs increase glutamine
L-theanine and anxiety
found in some herbal teas, may increase GABA synthesis
MOA of pregabalin
o MOA: selective inhibitor of voltage dependent Ca channel (VDCC)
§ Blocks Cl from coming through to lower depolarization
pregabalin is a GABA analog BUT...
o doesn’t act on GABA-A receptors or alter the uptake/metabolism of GABA
MOA of buspirone
o 5HT1A receptor agonist
o Also D2 antagonist
o NOT GABA- no anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant, or psychomotor impairment
o Less sedation, little interaction with alc
o Slow response
does busprione act on GABA?
no, it doesn't
serotonin and anxiety
· May have anxiolytic and anxiogenic effects depending on the rain region involved, receptor subtype and location on neuron
· Anxiogenic effects are mediated by HT2A stimulation
· Anxiolytic effects are from stimulation of HT1A receptors
5HT1A MOA in anxiety
· somatodendritic auto receptors, coupled to the Gi protein
o Mediate inhibitory neurotransmission
o Partial agonists are anxiolytic
o Is stimulatory
5HT2 MOA in anxiety
o Is inhibitory
o Pts ith anxiety have more sensitive 5HT2R’s
o SSRIs increase 5HT to desensitize 5HT2R
5HT2A and 5HT2C antagonists in anxiety
are anxiolytic
5HT2 agonists in anxiety
trigger panick attack and PTSD flashbacks