unit 2: planning for management of clinical labs
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:07 AM on 2/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
1
New cards
Clinical Laboratory management planning
process of **assessing an organization's goals** and **creating a realistic, detailed plan of action** for meeting those goals.
2
New cards
road map
The basic steps in the management planning process involve creating a ___ that outlines each task the company must accomplish to meet its overall objectives
3
New cards
__**pre**__**-examination**/pre-analytica
* Patient prep
* Sample collection
* Personnel competency test evaluation
* Sample receipt and accessioning
* Sample transport
* Sample collection
* Personnel competency test evaluation
* Sample receipt and accessioning
* Sample transport
4
New cards
**examination**/analytical or post-exam
* Quality control testing
5
New cards
__**post**__**-analytical**
* Record keeping
* reporting
* reporting
6
New cards
top management
**Planning:**
establishes context, scope, boundaries, and quality policy of QMS
establishes context, scope, boundaries, and quality policy of QMS
7
New cards
quality objectives
**Planning:**
selected with programs established to achieve objectives
selected with programs established to achieve objectives
8
New cards
**core** processes
**Planning:**
QMS & their interactions
QMS & their interactions
9
New cards
performance indicators
**Planning:**
established for the core processes
established for the core processes
10
New cards
control
**Planning:**
established to ensure customer requirements are met
established to ensure customer requirements are met
11
New cards
ISO 9001:2015
requires the organization to **plan, identify, and monitor**
12
New cards
interested parties
ISO 9001:2015:
the ___ that are **relevant** to the organization’s purpose and its strategic direction
the ___ that are **relevant** to the organization’s purpose and its strategic direction
13
New cards
external issues
ISO 9001:2015:
to consider ___ that could **impact their business strategy**, such as new technology and potential market forces
to consider ___ that could **impact their business strategy**, such as new technology and potential market forces
14
New cards
attention
**Importance of Planning in the Clinical Lab:**
1. Planning **focuses** ___ on the __objectives of the clinical laboratory__
1. Planning **focuses** ___ on the __objectives of the clinical laboratory__
15
New cards
risks of uncertainties
**Importance of Planning in the Clinical Lab:**
2. Planning **reduces** ___ on managing clinical labs
2. Planning **reduces** ___ on managing clinical labs
16
New cards
interdepartmental
**Importance of Planning in the Clinical Lab:**
3. Planning helps in **coordinating** ___ **goals and objectives** in the clinical labs
3. Planning helps in **coordinating** ___ **goals and objectives** in the clinical labs
17
New cards
economical operation
**Importance of Planning in the Clinical Lab:**
4. Planning gains ___
4. Planning gains ___
18
New cards
operational costs
**Importance of Planning in the Clinical Lab:**
4. Planning gains economical operation and reduces ___
4. Planning gains economical operation and reduces ___
19
New cards
revenue
**Importance of Planning in the Clinical Lab:**
4. Planning gains economical operation and reduces operational costs and increases ___ in the clinical lab
4. Planning gains economical operation and reduces operational costs and increases ___ in the clinical lab
20
New cards
controlling
**Importance of Planning in the Clinical Lab:**
5. Planning facilitates ___ by allocating resources appropriately, establishing standards of performance, and more effective financial management in the clinical lab
5. Planning facilitates ___ by allocating resources appropriately, establishing standards of performance, and more effective financial management in the clinical lab
21
New cards
good succession planning programs
**Importance of Planning in the Clinical Lab:**
6. Planning helps executive development and ensures ___ for the clinical lab
6. Planning helps executive development and ensures ___ for the clinical lab
22
New cards
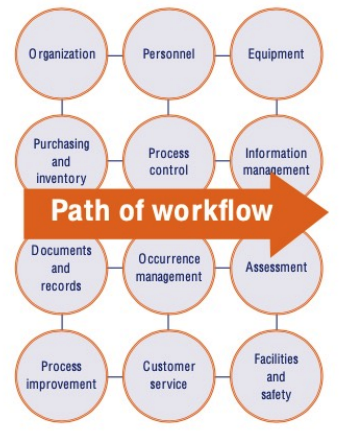
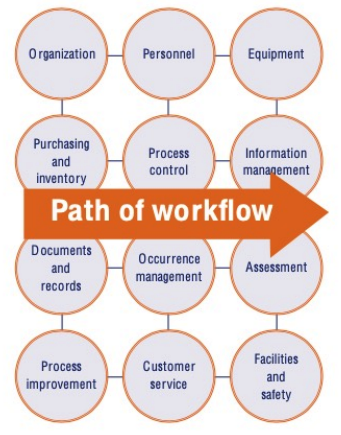
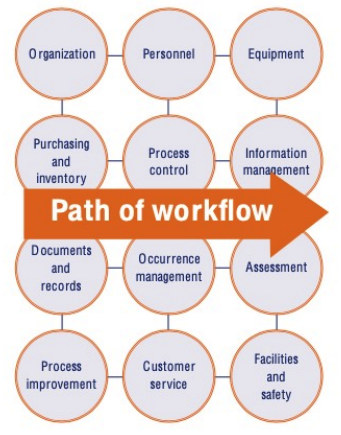
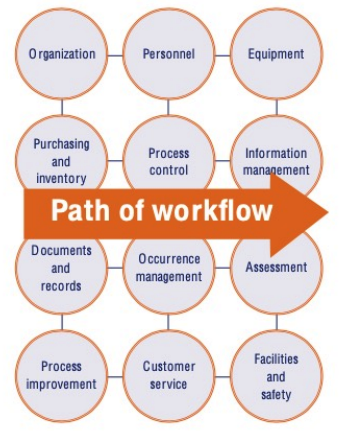
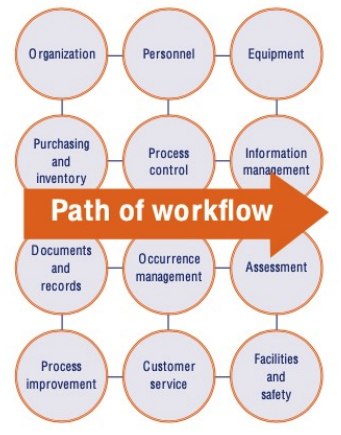
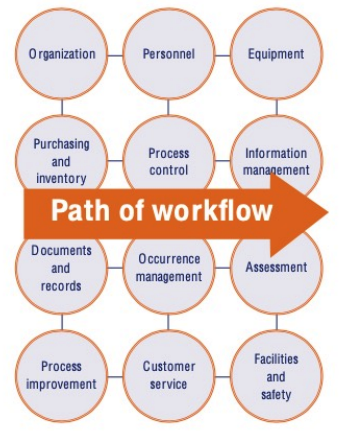
path of workflow
**Planning the Workflow of Clinical Labs:**
* Planning in the clinical laboratory considers the **entire set of operations that occur in testing of patient samples**
* __begins__ with the **patient** and __ends__ in **reporting and results** interpretation.
* Planning in the clinical laboratory considers the **entire set of operations that occur in testing of patient samples**
* __begins__ with the **patient** and __ends__ in **reporting and results** interpretation.
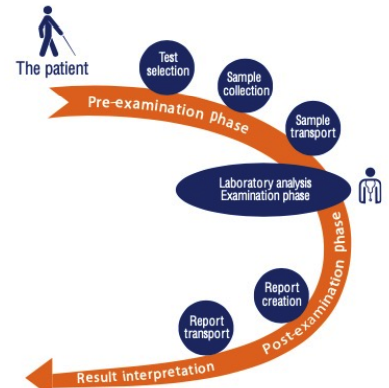
23
New cards
quality
**Planning the Workflow of Clinical Labs:**
* **Planning in the context of Quality Management System** ensures ___ in the many __processes and procedures__ performed in the clinical laboratory
* the laboratory environment
* quality control procedures
* communications
* record keeping
* competent and knowledgeable staff
* good-quality reagents and equipment.
* **Planning in the context of Quality Management System** ensures ___ in the many __processes and procedures__ performed in the clinical laboratory
* the laboratory environment
* quality control procedures
* communications
* record keeping
* competent and knowledgeable staff
* good-quality reagents and equipment.
24
New cards
**WHO Quality Management Handbook**: Planning for the development of quality practices in a clinical laboratory in twelve areas
**Planning the Workflow of Clinical Labs:**
**transcends the Path of Workflow** from pre-analytical, analytical, to post-analytical flow processes in a clinical laboratory
**transcends the Path of Workflow** from pre-analytical, analytical, to post-analytical flow processes in a clinical laboratory
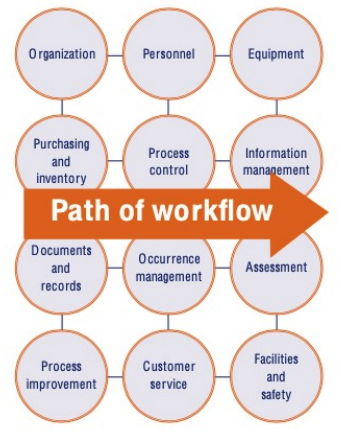
25
New cards
Organization
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:**
* **Planning the structure and management** of the laboratory that implements the quality policies ensures **quality performance**
* **Planning the structure and management** of the laboratory that implements the quality policies ensures **quality performance**
26
New cards
Personnel
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:**
* Diligently planning the most **important laboratory resource**, ensures **competent and motivated teams** in implementing quality management systems
* Diligently planning the most **important laboratory resource**, ensures **competent and motivated teams** in implementing quality management systems
27
New cards
Equipment
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:**
* planning the **acquisition and validation** of ___ by carefully and properly choosing, and ensuring maintained systems through **preventive maintenance programs** helps an __effective path of workflow__
* planning the **acquisition and validation** of ___ by carefully and properly choosing, and ensuring maintained systems through **preventive maintenance programs** helps an __effective path of workflow__
28
New cards
Purchasing and Inventory
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:**
* Planning reagents and supplies management in the laboratory can produce **cost savings** ensures **supplies and reagent availability.**
* Planning reagents and supplies management in the laboratory can produce **cost savings** ensures **supplies and reagent availability.**
29
New cards
Process controls
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:**
* Planning the ___ ensures **quality control** for testing, appropriate management of the sample, collection and handling, and method verification and validation.
* Planning the ___ ensures **quality control** for testing, appropriate management of the sample, collection and handling, and method verification and validation.
30
New cards
Information Management
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:**
* Planning the **production of the main output** of the clinical laboratory (*information in the form of test reports*) **ensures accuracy, confidentiality, and accessibility** of the information which are managed through either __paper systems or computers__
* Planning the **production of the main output** of the clinical laboratory (*information in the form of test reports*) **ensures accuracy, confidentiality, and accessibility** of the information which are managed through either __paper systems or computers__
31
New cards
Documents and Records
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:**
* planning the **creation and storage of documents** needed in the laboratory that informs how to do things ensures that documents are accurate, up to date, and accessible.
* planning the **creation and storage of documents** needed in the laboratory that informs how to do things ensures that documents are accurate, up to date, and accessible.
32
New cards
Occurrence Management
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:**
* Planning for detecting and managing detect these **problems**, handling them properly, learning from mistakes and acting so that __they do not happen again__
* Planning for detecting and managing detect these **problems**, handling them properly, learning from mistakes and acting so that __they do not happen again__
33
New cards
Occurrence
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:** *Occurrence Management*
* is an error or an event that **should not have happened**
* is an error or an event that **should not have happened**
34
New cards
Assessment
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:**
* a **tool** for examining laboratory performance and comparing it to standards, benchmarks or the performance of other laboratories.
* a **tool** for examining laboratory performance and comparing it to standards, benchmarks or the performance of other laboratories.
35
New cards
internal
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:** *Assessment*
* performed **within** the laboratory using its own staff
* performed **within** the laboratory using its own staff
36
New cards
external
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:** *Assessment*
* conducted by a group or agency **outside** the laboratory
* conducted by a group or agency **outside** the laboratory
37
New cards
Process Improvement
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:**
* Planning for **continuous improvement** of the clinical laboratory processes is a **primary goal** and must be __done in a systematic manner__ to ensure **alignment, effectiveness, and efficiency**
* Planning for **continuous improvement** of the clinical laboratory processes is a **primary goal** and must be __done in a systematic manner__ to ensure **alignment, effectiveness, and efficiency**
38
New cards
Customer Services
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:**
* Planning and benchmarking ___ ensures that that the laboratory understand and assess who their customers are and use **feedback for making improvements** to align with external changes
* Planning and benchmarking ___ ensures that that the laboratory understand and assess who their customers are and use **feedback for making improvements** to align with external changes
39
New cards
Security
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:** *Facilities and Safety*
* process of **preventing unwanted risks and hazards** from entering the laboratory space
* process of **preventing unwanted risks and hazards** from entering the laboratory space
40
New cards
Containment
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:** *Facilities and Safety*
* seeks to **minimize risks and prevent hazards** from leaving the laboratory space and causing harm to the community
* seeks to **minimize risks and prevent hazards** from leaving the laboratory space and causing harm to the community
41
New cards
Safety
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:** *Facilities and Safety*
* policies and procedures to **prevent harm** to workers, visitors and the community
* policies and procedures to **prevent harm** to workers, visitors and the community
42
New cards
Ergonomics
**Focus of Planning in Critical Areas of Clinical Lab Management:** *Facilities and Safety*
* addresses **facility and equipment adaptation** to allow **safe and healthy working conditions** at the laboratory
* addresses **facility and equipment adaptation** to allow **safe and healthy working conditions** at the laboratory
43
New cards
**determination** of objectives
**Qualities of a Good Planner:**
* Proficiency in the ___
* Proficiency in the ___
44
New cards
imagination
**Qualities of a Good Planner:**
* Good judgment, ___, foresight and experience
* Good judgment, ___, foresight and experience
45
New cards
accept changes
**Qualities of a Good Planner:**
* Ability to ___
* Ability to ___
46
New cards
opportunities and hazards
**Qualities of a Good Planner:**
* Ability to evaluate laboratory ___
* Ability to evaluate laboratory ___
47
New cards
**achievement** of the objectives
**Values Derived from Planning for Clinical Laboratory Management:**
1. The ___ of the clinical laboratories in the most **efficient and economical** manner.
1. The ___ of the clinical laboratories in the most **efficient and economical** manner.
48
New cards
accurate control
**Values Derived from Planning for Clinical Laboratory Management:**
2. The use of **efficient methods and the development of standards** necessary for ___ within the clinical lab
2. The use of **efficient methods and the development of standards** necessary for ___ within the clinical lab
49
New cards
goal-directed actions
**Values Derived from Planning for Clinical Laboratory Management:**
3. **Integration of activities** of the different units in the clinical laboratory toward ___
3. **Integration of activities** of the different units in the clinical laboratory toward ___
50
New cards
reduction
**Values Derived from Planning for Clinical Laboratory Management:**
4. The ___ of emergency, unexpected problems, and management of risks in the clinical laboratory
4. The ___ of emergency, unexpected problems, and management of risks in the clinical laboratory
51
New cards
**Indicators of Poor Planning**
1. Delivery **dates** **not met**
2. **Idle** machines
3. Materials **wasted**
4. Some machines doing jobs that **should be done
by **__**smaller**__ **machines**
5. Some laboratory **personnel** **overworked**, others are **underworked**
6. Skilled workers doing **unskilled work**
7. Laboratory Personne**l fumbling on jobs** for which they have not been trained
8. Quarreling, bickering, buck-passing and **confusion**
52
New cards
**Benefits of Good Planning**
1. Jobs turn out **on time**
2. **Good relationship** with other
departments
3. People using their **highest skills**
4. Workers know how their jobs **fit**
into the total pattern
5. **Machines doing their proper jobs**
6. Equipment in good shape
7. Materials available
8. Waste kept to a minimum
53
New cards
MBO Process
1. Define Organization **Goals**
2. Define **Employees Objectives**
3. Continuous **Monitoring** Performance & Progress
4. Performance **Evaluation**
5. Providing **Feedback**
6. Perfomance **Appraisal**
54
New cards
* Discussion
* Interaction
* Truly committed managers and involved employees in the decision-making process
* Interaction
* Truly committed managers and involved employees in the decision-making process
MBO encourages ___
55
New cards
mission
**Hierarchy of Plans:**
organization’s **purpose and philosophy**
organization’s **purpose and philosophy**
56
New cards
Objectives
**Hierarchy of Plans:**
**ultimate goal** towards which the activities of the organization are directed
**ultimate goal** towards which the activities of the organization are directed
57
New cards
Strategies
**Hierarchy of Plans:**
general **program of action** and deployment of resources
general **program of action** and deployment of resources
58
New cards
Policies
**Hierarchy of Plans:**
general **statement** or understanding which guide or **channel thinking in decision making**
general **statement** or understanding which guide or **channel thinking in decision making**
59
New cards
Procedures
**Hierarchy of Plans:**
states a **series of related steps or tasks** to be performed in a sequential way
states a **series of related steps or tasks** to be performed in a sequential way
60
New cards
Rules
**Hierarchy of Plans:**
prescribes a **course of action** and explicitly states what is to be done
prescribes a **course of action** and explicitly states what is to be done
61
New cards
Programs
**Hierarchy of Plans:**
**comprehensive plan** that includes future use of different resources
**comprehensive plan** that includes future use of different resources
62
New cards
Budgets
**Hierarchy of Plans:**
statement of **expected results** expressed **in numerical terms**
statement of **expected results** expressed **in numerical terms**
63
New cards
**Strategic** Planning
**Types of Plans:**
* the **identification** of the **mission** and of those **objectives**
* **most efficient** pursuit
* **long-term goals** for the next 5 years
* **top managers** with final authority and responsibility
* the **identification** of the **mission** and of those **objectives**
* **most efficient** pursuit
* **long-term goals** for the next 5 years
* **top managers** with final authority and responsibility
64
New cards
**Tactical** Plans
**Types of Plans:**
* **action** and deals with the **method**(s)
* **Short-range** – strategy implementation (6 months – 2 years)
* **operational or technical** skill
* **middle managers** (__supervisory__ staff)
* **action** and deals with the **method**(s)
* **Short-range** – strategy implementation (6 months – 2 years)
* **operational or technical** skill
* **middle managers** (__supervisory__ staff)
65
New cards
**Operational** Plans
**Types of Plans:**
* **detailed plan** used to provide
* team, section or department
* __**Very**__ **short-term** ( for the next 1 week to 1 year)
* Responsibility of **First-line managers**
* **detailed plan** used to provide
* team, section or department
* __**Very**__ **short-term** ( for the next 1 week to 1 year)
* Responsibility of **First-line managers**
66
New cards
common pathways
**Planning Lab Design:**
1. Ensure that patients and patient samples do not have ___
1. Ensure that patients and patient samples do not have ___
67
New cards
2. circulation paths
**Planning Lab Design:**
2. The design should have different ___ between the __public and biological materials__
2. The design should have different ___ between the __public and biological materials__
68
New cards
Reception area
**Planning Lab Design:**
3. should be located as **close as possible to the entry door**
3. should be located as **close as possible to the entry door**
69
New cards
4. authorized personnel
**Planning Lab Design:**
4. Only ___ should have r**estricted access to rooms** where analyses of samples are done, and hazardous chemicals or other materials are stored
4. Only ___ should have r**estricted access to rooms** where analyses of samples are done, and hazardous chemicals or other materials are stored
70
New cards
Access restriction
**Planning Lab Design:**
5. can be accomplished using signs on door locks and identification badges for staff
5. can be accomplished using signs on door locks and identification badges for staff
71
New cards
Sample **Collection** Areas
**Planning Circulation Pathways in the Clinical Lab:**
Reception area and sample collection room located at the patient’s **entrance**
Reception area and sample collection room located at the patient’s **entrance**

72
New cards
Sample **Processing** areas
**Planning Circulation Pathways in the Clinical Lab:**
**separated** **from other sections** of the laboratory but nearby the testing areas
**separated** **from other sections** of the laboratory but nearby the testing areas

73
New cards
**Circulation** Pathways
**Planning Circulation Pathways in the Clinical Lab:**
* clean and dirty laboratory materials should never cross
* contaminated materials should be isolated
* clean and dirty laboratory materials should never cross
* contaminated materials should be isolated

74
New cards
**Post-examination** Pathways
**Planning Circulation Pathways in the Clinical Lab:**
* communication system
* efficient & reliable
* transferring of messages
* communication system
* efficient & reliable
* transferring of messages
75
New cards
highly automated and manual processes
**Planning Spatial Consideration sin Designing the Lab:**
Laboratory sections (*e.g. Clinical Chemistry, Hematology, Coagulation*) which have ___
Laboratory sections (*e.g. Clinical Chemistry, Hematology, Coagulation*) which have ___
76
New cards
turn-around-time (TAT)
**Planning Spatial Consideration sin Designing the Lab:**
Laboratories with **greater** ___ and/or less volume, as well as those requiring special safety features (*e.g. Clinical Microbiology and radio-assay laboratories*) may be **removed from the central area.**
Laboratories with **greater** ___ and/or less volume, as well as those requiring special safety features (*e.g. Clinical Microbiology and radio-assay laboratories*) may be **removed from the central area.**
77
New cards
two rooms
**Planning Spatial Consideration sin Designing the Lab:**
**Location of room** with specific requirement such as:
* Molecular biology that needs ___
* Fluorescence Microscopy
* Ultraviolet illumination systems for DNA gel photography
**Location of room** with specific requirement such as:
* Molecular biology that needs ___
* Fluorescence Microscopy
* Ultraviolet illumination systems for DNA gel photography
78
New cards
blood bank and the critical care laboratory procedures
**Planning Spatial Consideration sin Designing the Lab:**
should be **readily accessible** to the emergency room, operating room, and ICU.
should be **readily accessible** to the emergency room, operating room, and ICU.
79
New cards
in-patient population
**Planning Spatial Consideration sin Designing the Lab:**
If the laboratory is serving an ___, **accessibility to corridors and elevators** providing access to the main patient care unit is **essential**
If the laboratory is serving an ___, **accessibility to corridors and elevators** providing access to the main patient care unit is **essential**
80
New cards
intra-laboratory traffic flow
**Planning Spatial Consideration sin Designing the Lab:**
must be **separated from the outside**. Provisions should be made for ambulatory patients and blood bank donors coming into the laboratory
must be **separated from the outside**. Provisions should be made for ambulatory patients and blood bank donors coming into the laboratory