Biology Week 3: Enzymes and Energy Harvest
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
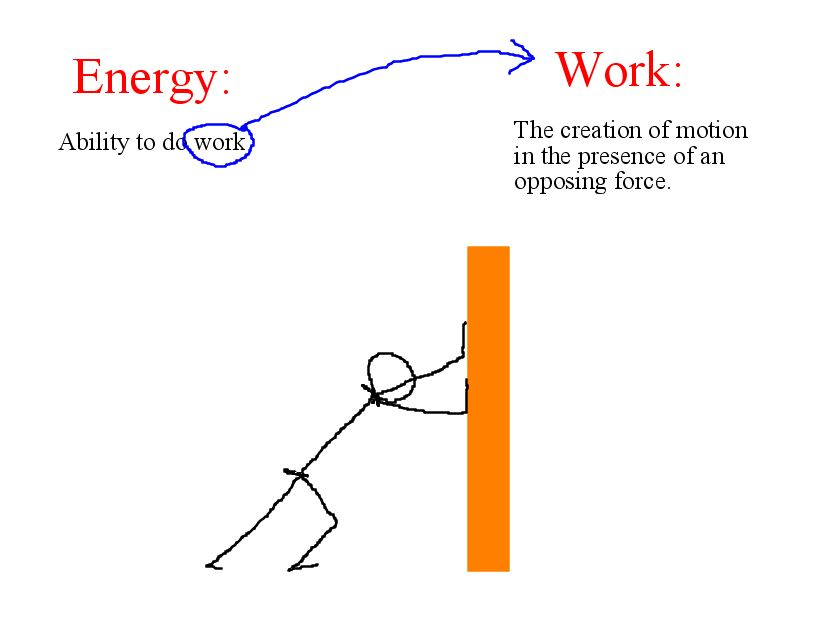
What is energy?
The capacity to do work (cause change)
What kind of energy is stored in chemical bonds?
Potential energy
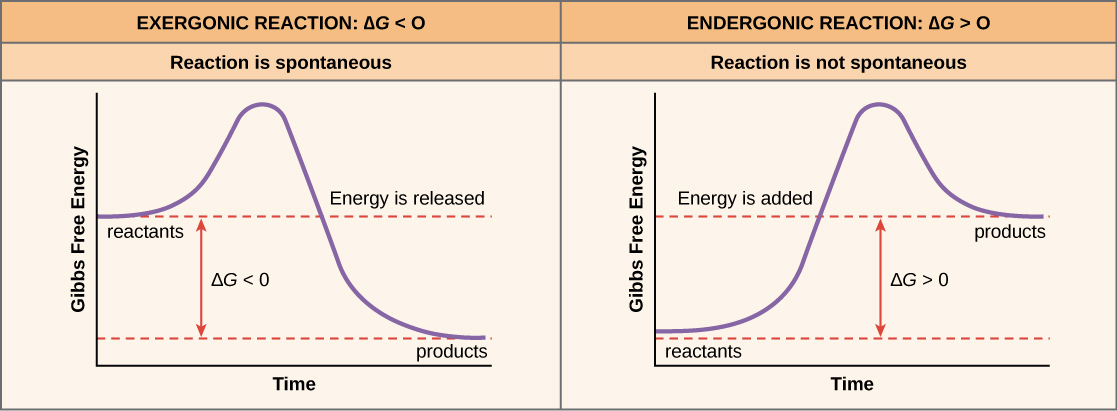
What is an exergonic reaction?
When the reactant(s) have more energy than the product(s). Energy releasing.
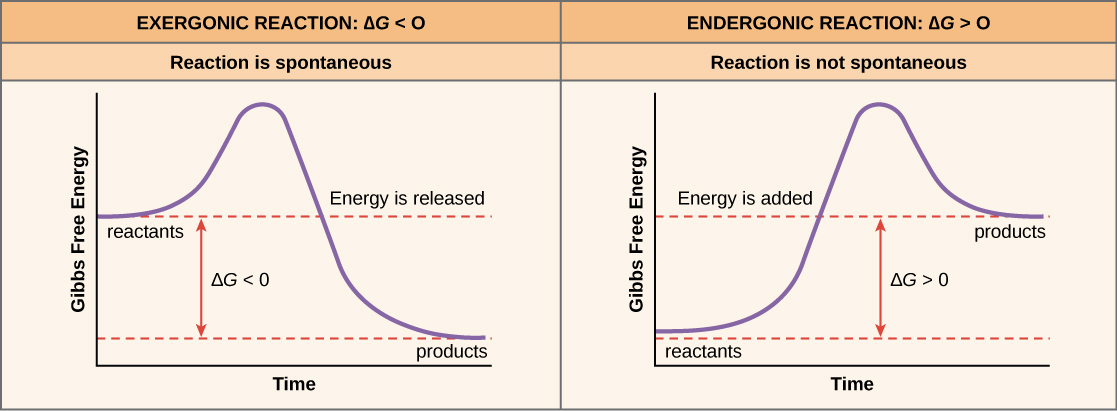
What is an endergonic reaction?
When the product(s) have more energy than the reactant(s). Energy absorbing.
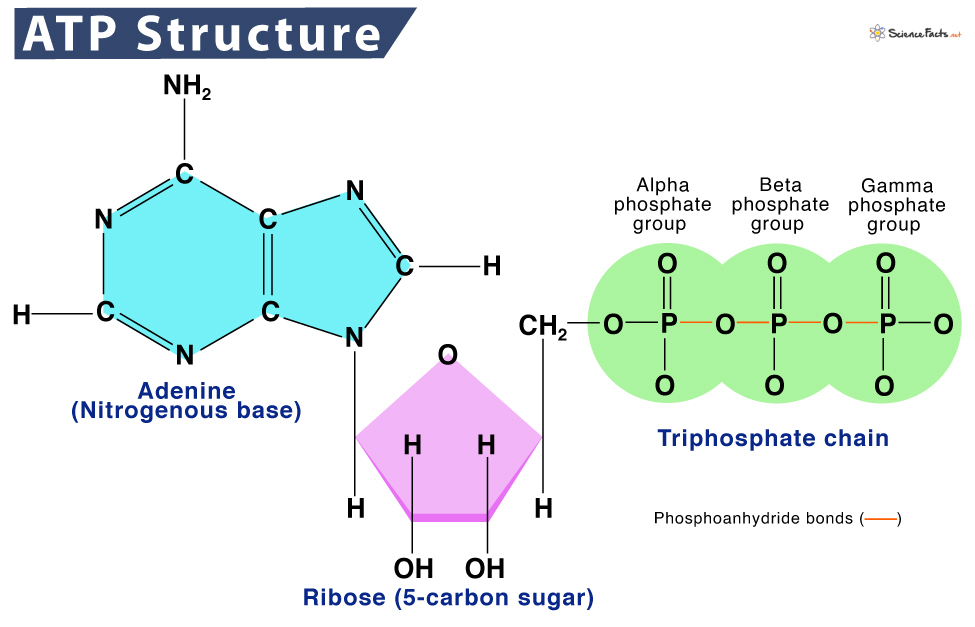
What is ATP made of?
A nitrogenous base (adenine), a five-carbon sugar (ribose), and three phosphate groups linked together.
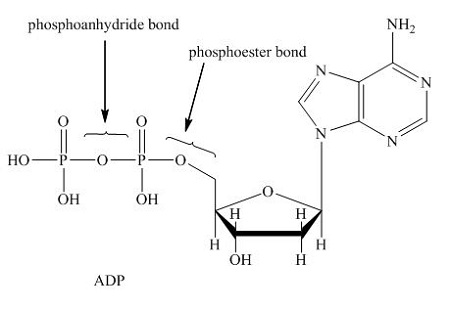
The high-energy bonds that link together the phosphate groups in ATP are called _______________ bonds.
phosphoanhydride
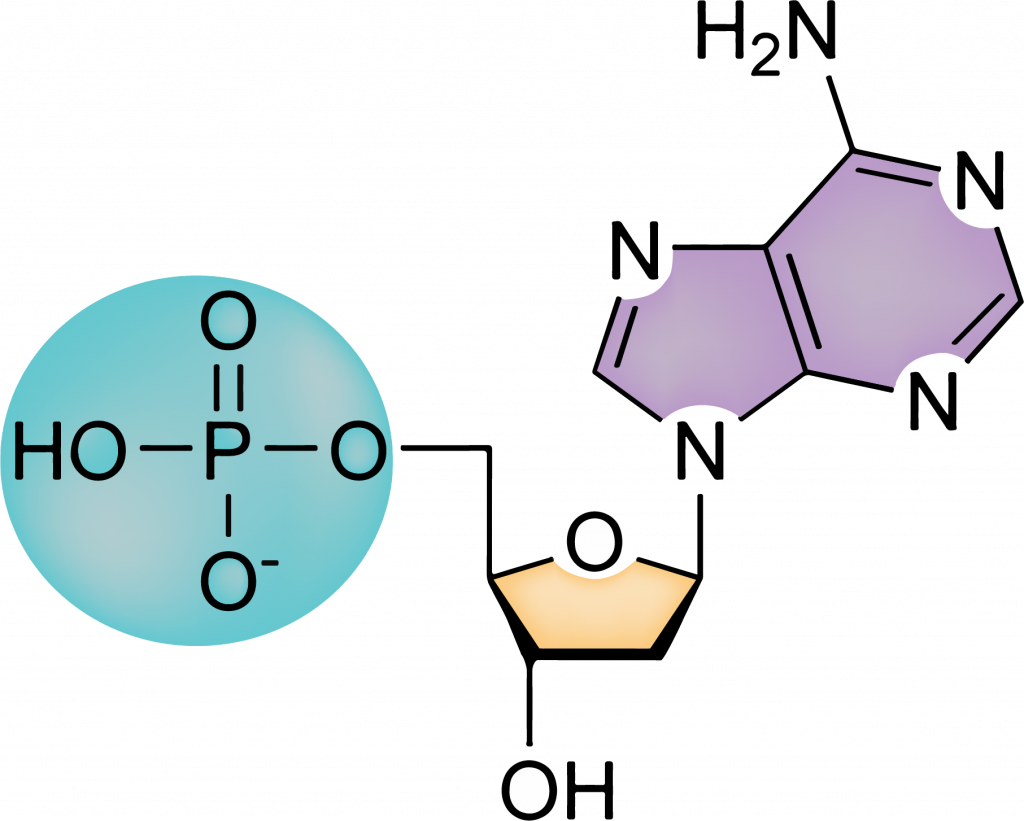
ATP is what kind of macromolecule?
Nucleic Acid
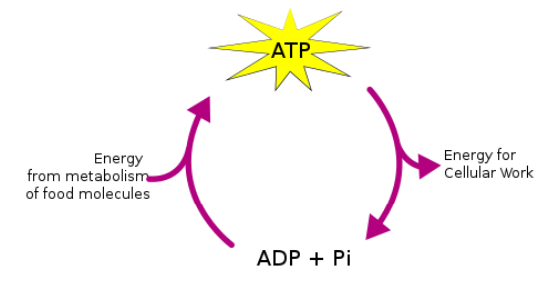
Hydrolysis of ATP
ATP + water → ADP + Pi (organic phosphate) + energy
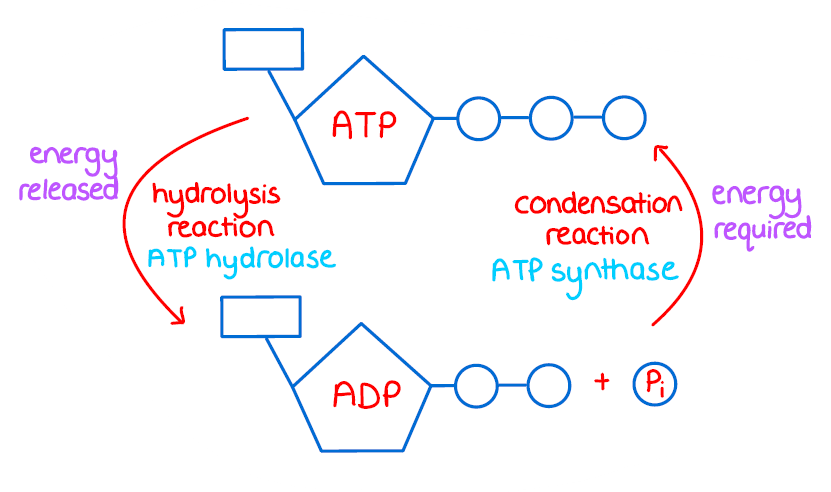
Is ATP a stable molecule?
NO! It' is very high energy and unstable.
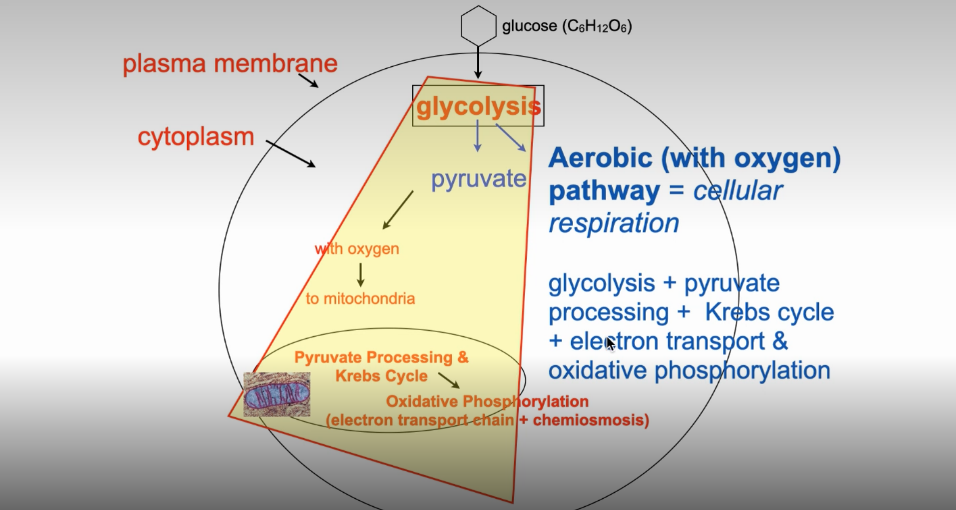
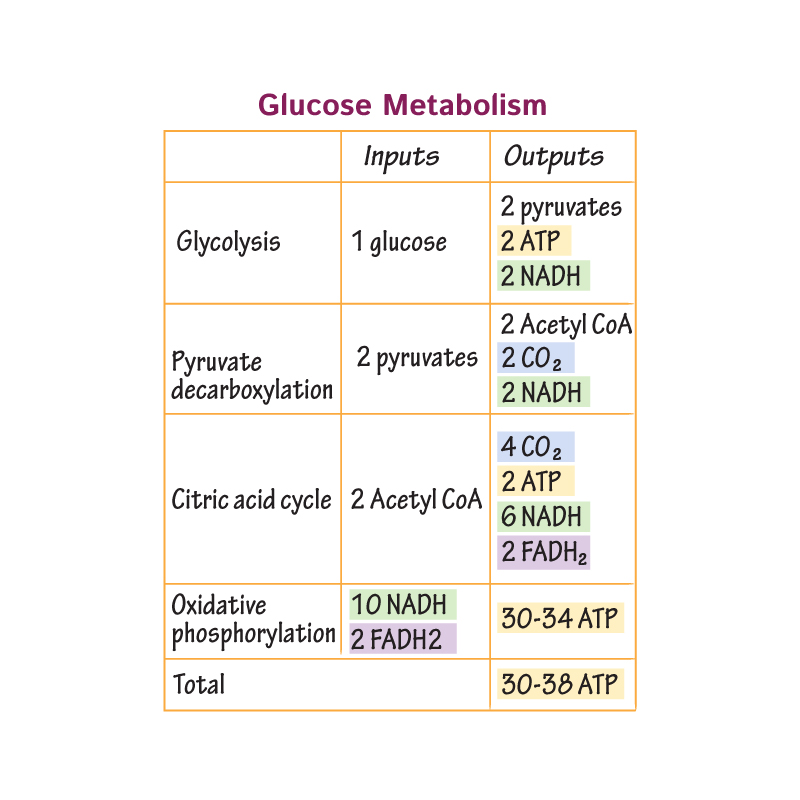
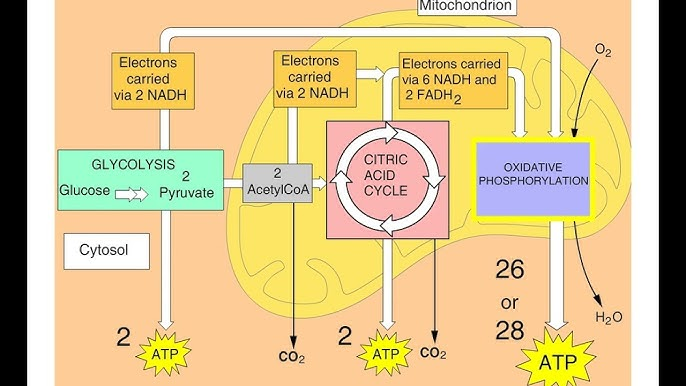
Aerobic Pathway (Cellular Respiration)
Glycolysis (cytosome)
Pyruvate Processing (mitochondrial matrix)
Citric Acid Cycle/Krebs Cycle (mitochondrial matrix)
Electron Transport Chain AKA Oxidative Phosphorylation & Chemiosis (inner mitochondrial membrane)
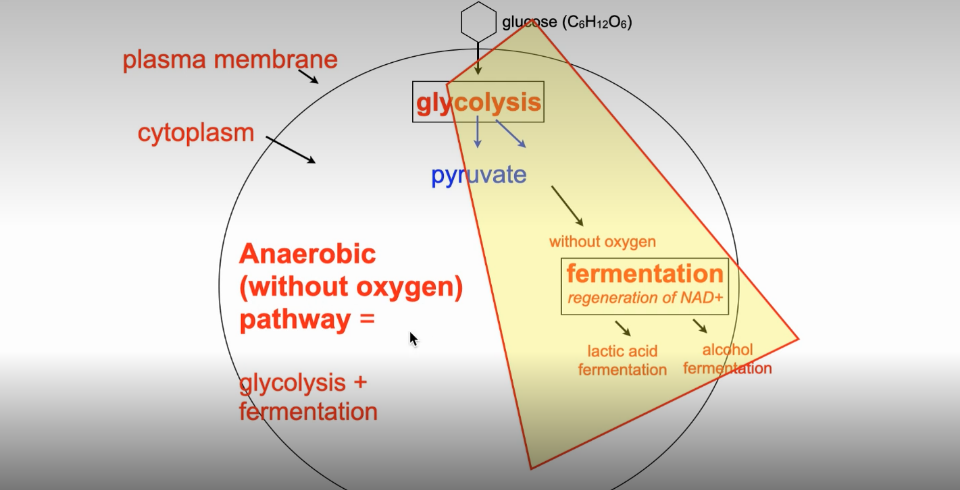
Anaerobic Pathway
Glycolysis (cytosome)
Fermentation/regeneration of NAD+ (cytoplasm)
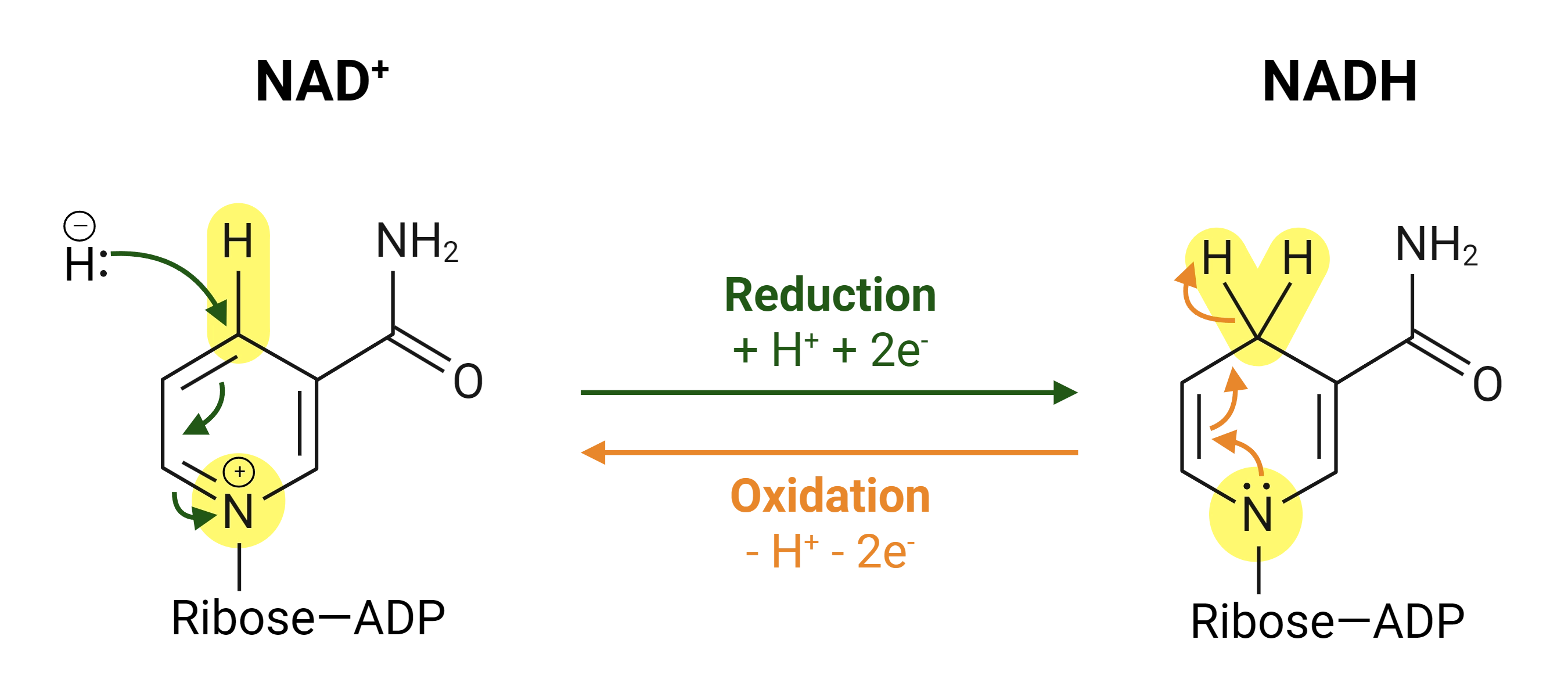
Oxidation = ____ of e-
loss
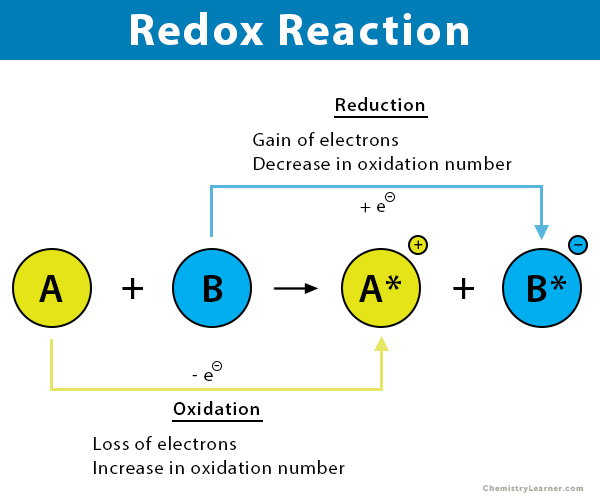
Reduction = ____ of e-
gain
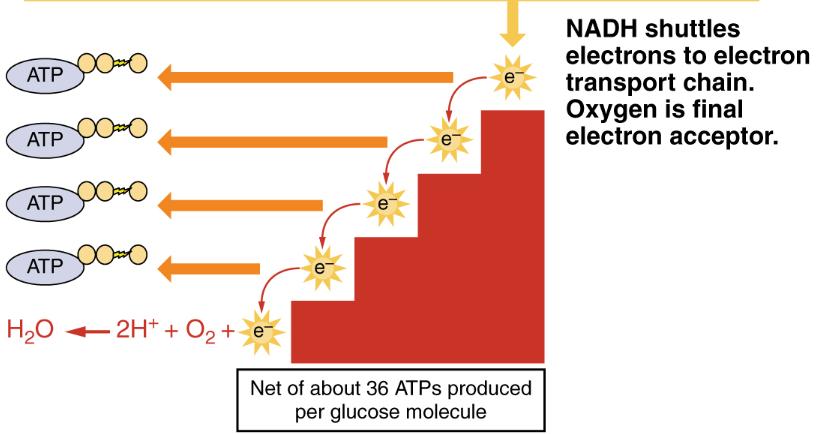
What are electron shuttles?
NAD+, NADH, FAD, and FADH2
Is NAD+ or NADH the reduced form?
NADH
Is FAD or FADH2 the reduced form?
FADH2
What is the difference between Acetyl CoA and CoA?
Acetyl CoA has an additional 2-carbon acetyl group.
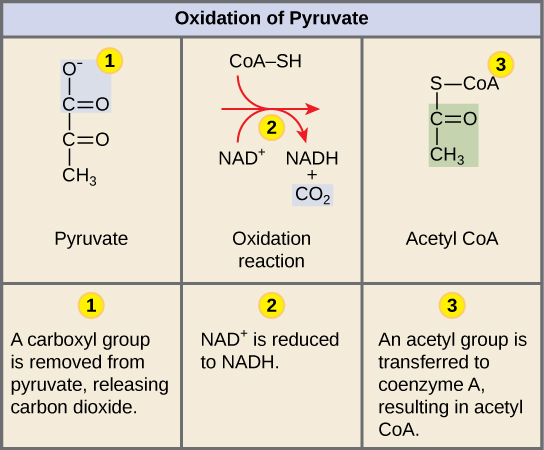
What are the products and reactants of cellular respiration?
Reactants: oxygen and glucose
Products: CO2, water, and ATP
What is the first step for both the aerobic and anaerobic energy harvest pathways?
Glycolysis
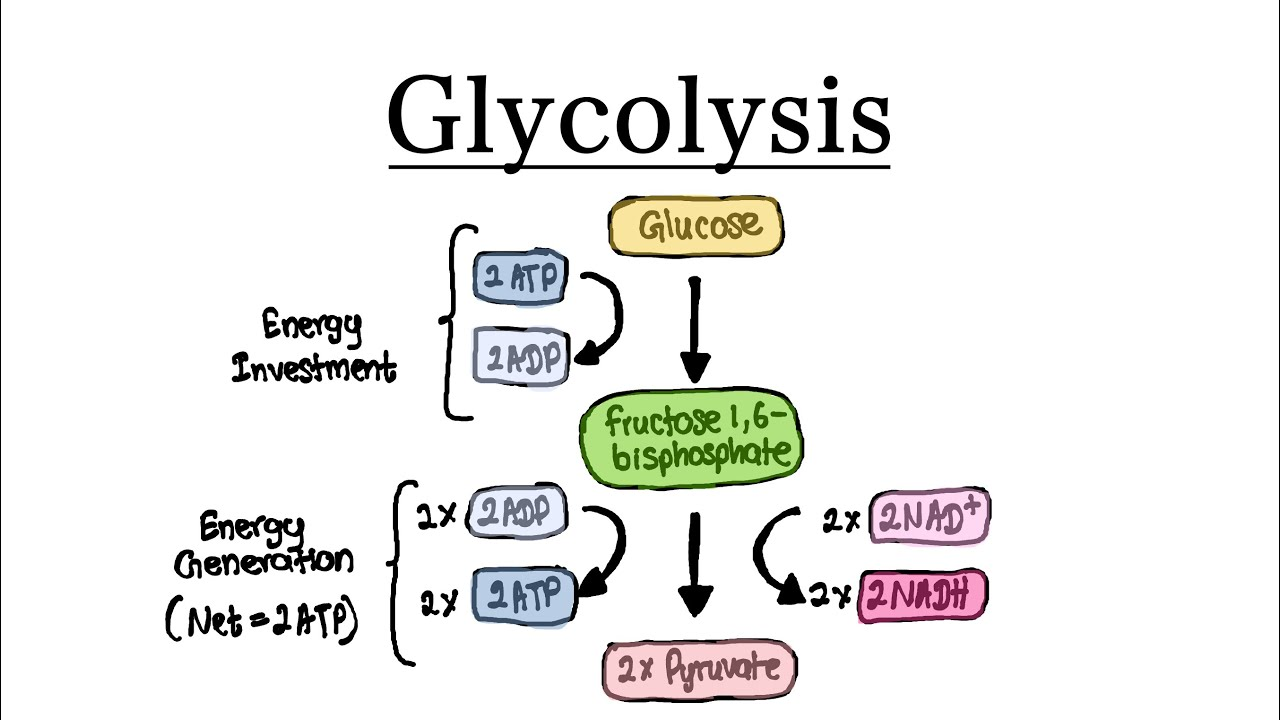
Where does glycolysis occur?
In the cytoplasm
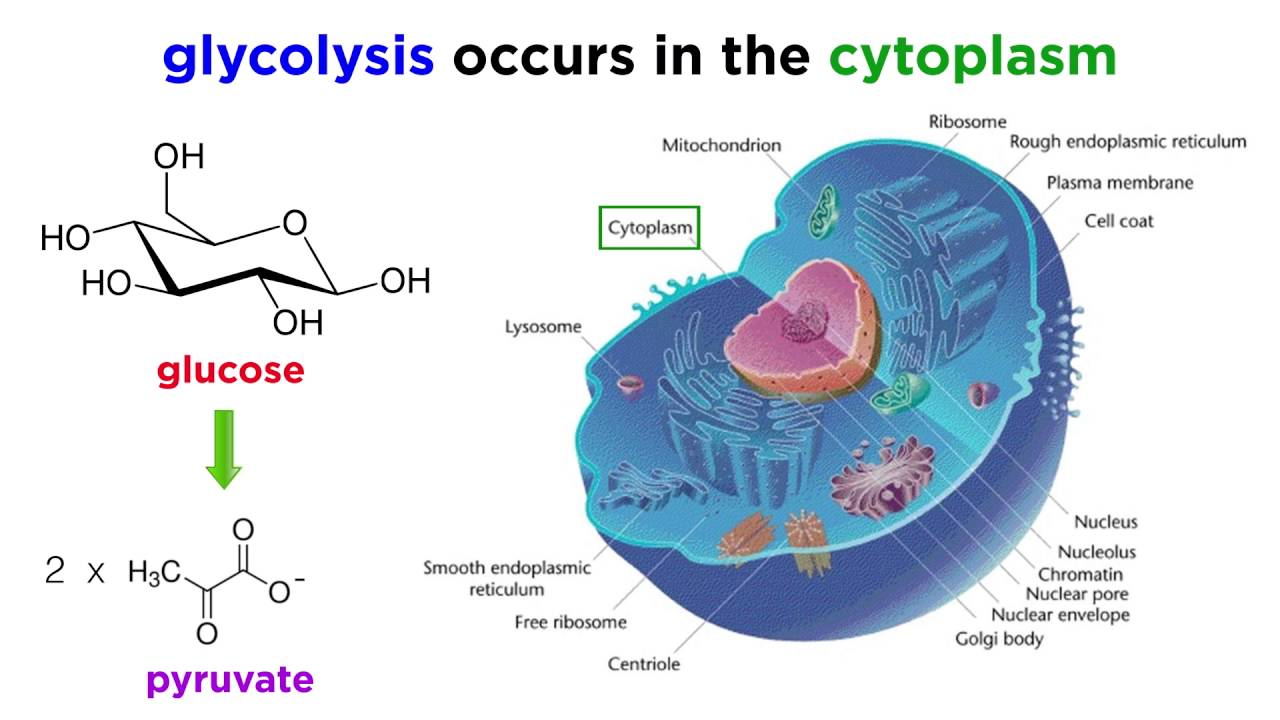
During the energy investment phase of glycolysis, how many ATP molecules are invested?
2
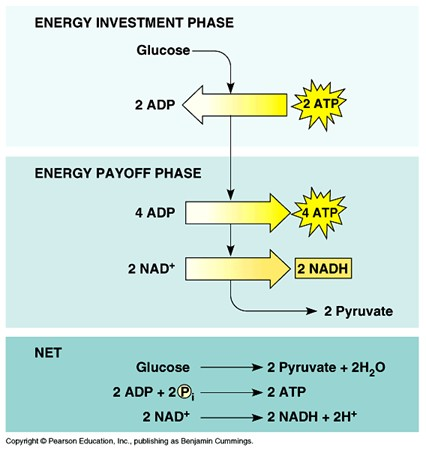
During the energy pay-off phase of glycolysis, what happens?
NAH+ is reduced to NADH (2 molecules per glucose) and ATP is produced (4 molecules per glucose).
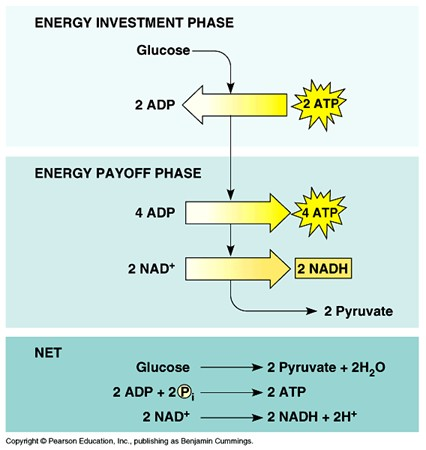
Why is glycolysis described as having an "energy-requiring" phase and an "energy-releasing" phase?
Because it uses stored ATP and then yields a net increase in ATP.
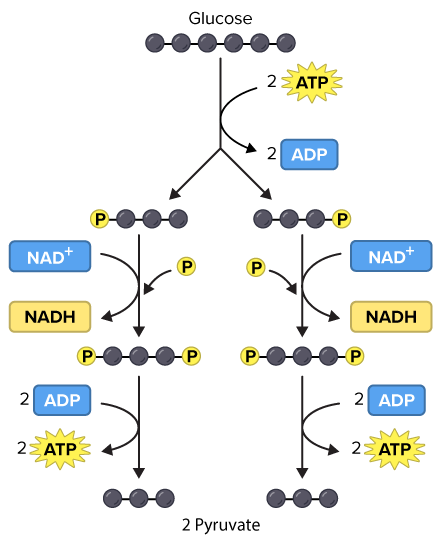
What are the products of glycolysis?
NADH (2)
ATP (4)
Pyruvate (2)
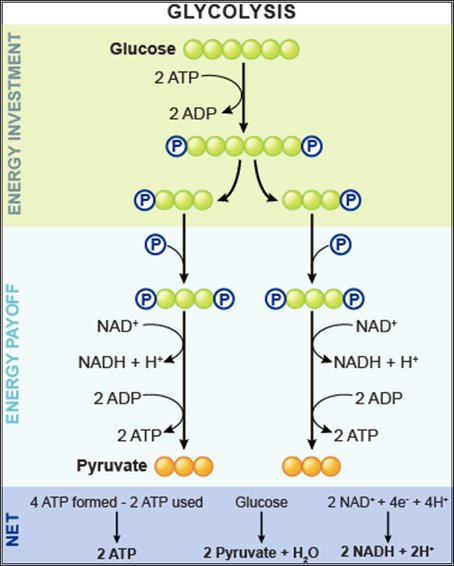
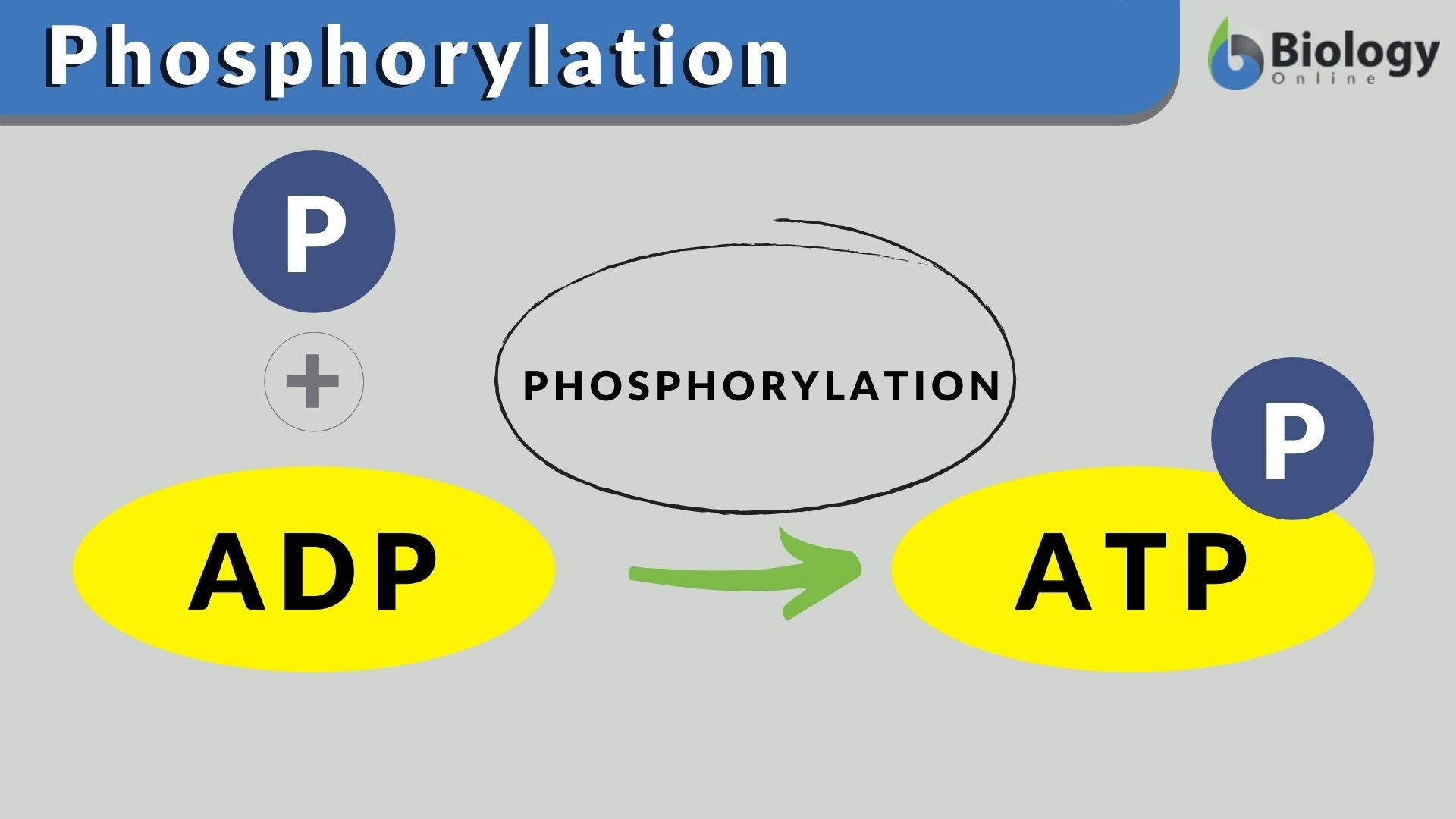
ADP is _____________ to reform as ATP.
phosphorylated (gains a phosphate group)
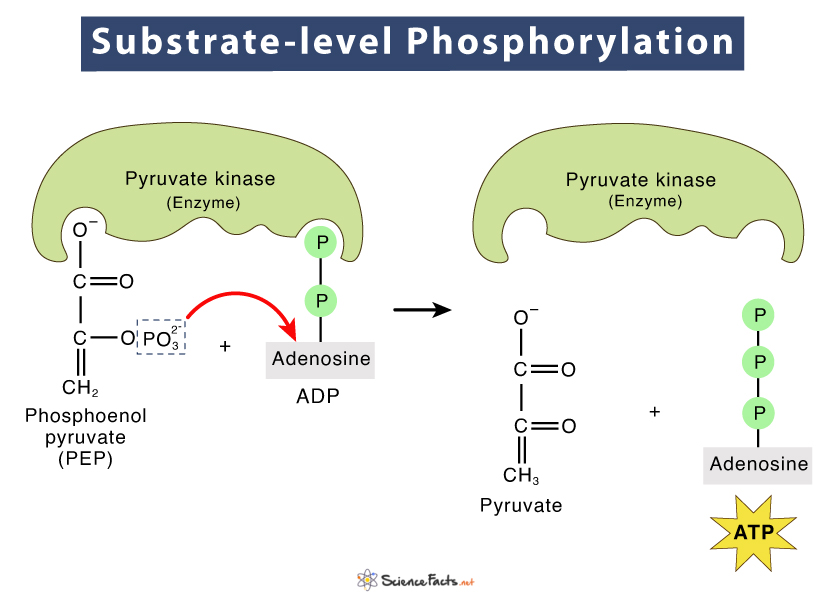
What is substrate-level phosphorylation?
An enzyme catalyzed reaction that transfers a phosphate group from a substrate to ADP.
Which molecule is the key junction at the points where the aerobic and anaerobic pathways diverge?
Pyruvate
After glycolysis, if an electron acceptor like oxygen is not present, then __________ will occur.
fermentation
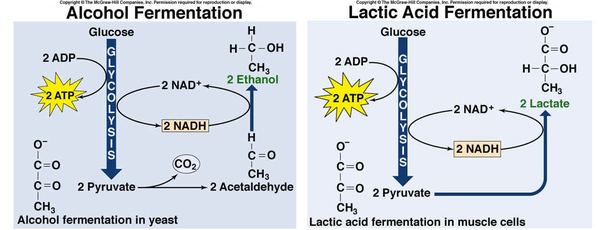
Fermentation is the regeneration of what?
NAD+ (a nucleic acid containing sugar subunits though that may or may not be important)
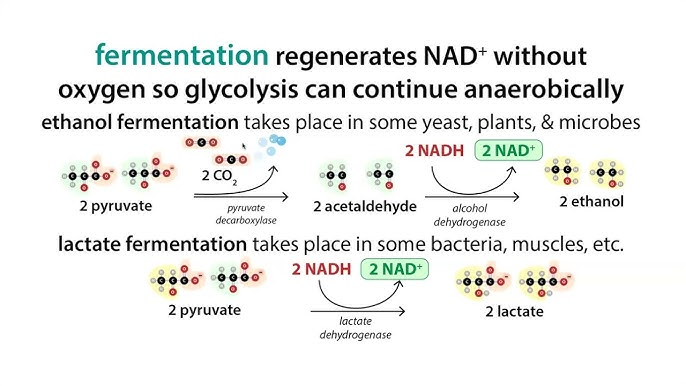
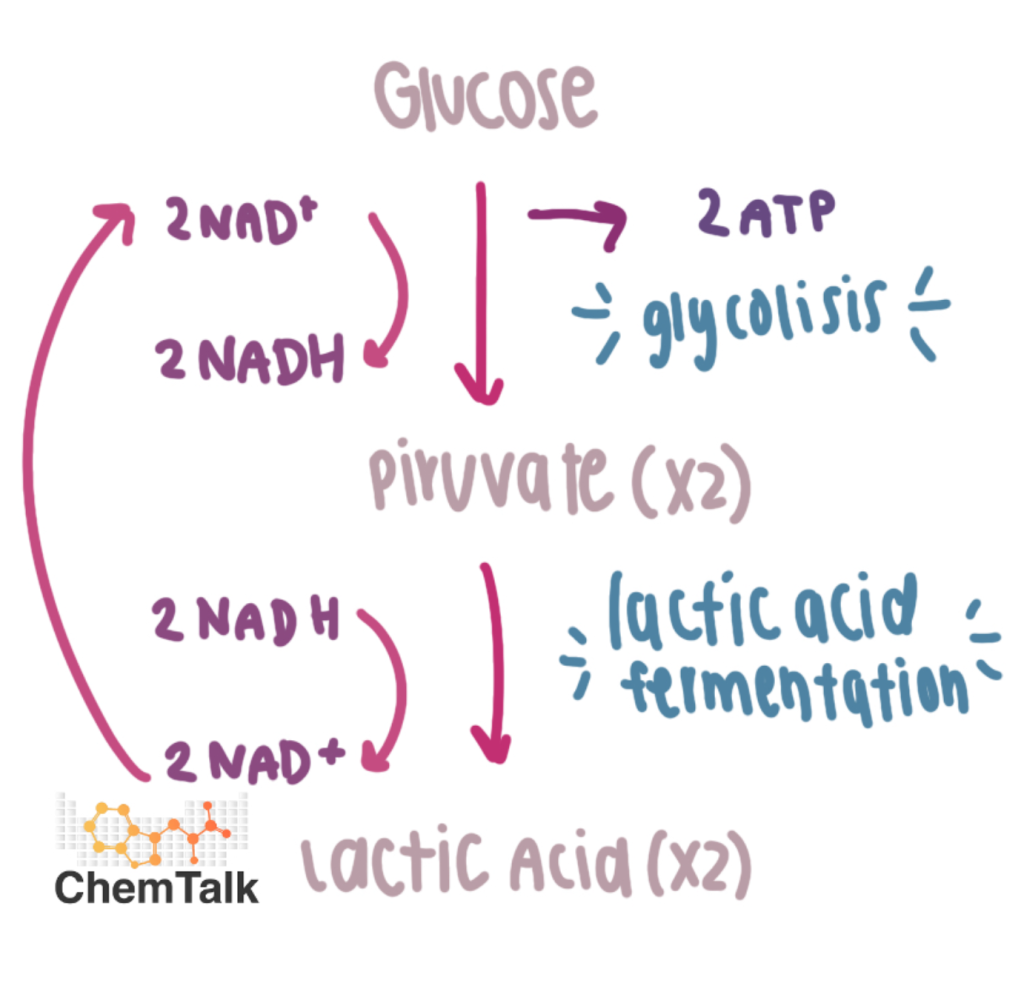
Lactic Acid Fermentaion
Human muscle cells, bacteria that produce yogurt, other food products
No intermediate
Outputs: 2 lactate, 2 NAD+, 2 ATP (from glycolysis)
NAD+ is regenerated/recycled over and over
Alcohol Fermentation
Yeast, some bacteria, some plant tissues, some protists
2 Acetylaldehyde acts as an intermediate
Outputs: 2 CO2, 2 ethanol, 2 NAD+, 2 ATP (from glycolysis)
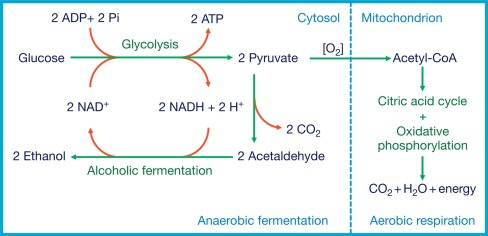
After glycolysis, if an electron acceptor like oxygen is present, then ________ __________ will occur.
pyruvate processing
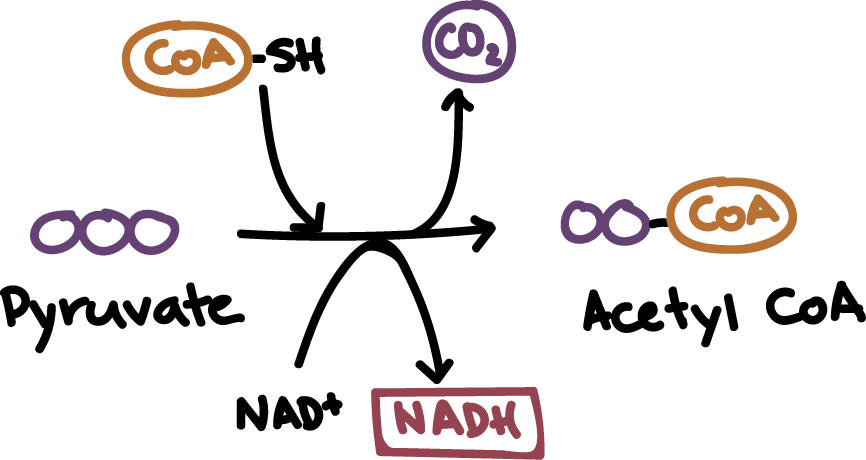
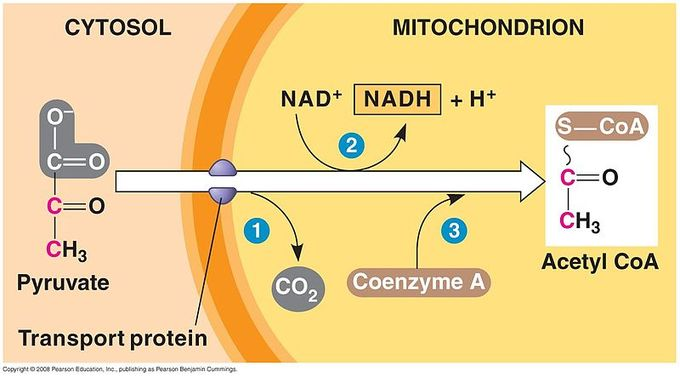
Where does pyruvate processing occur?
In the mitochondrial matrix
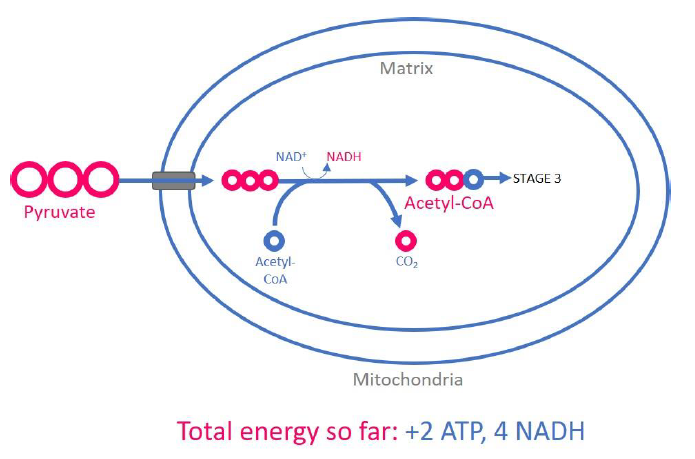
Pyruvate processing outputs per glucose molecule
2 molecules CO2
2 molecules NADH
2 molecules acetyl CoA
After pyruvate processing comes the ______ _____ _____.
Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle)
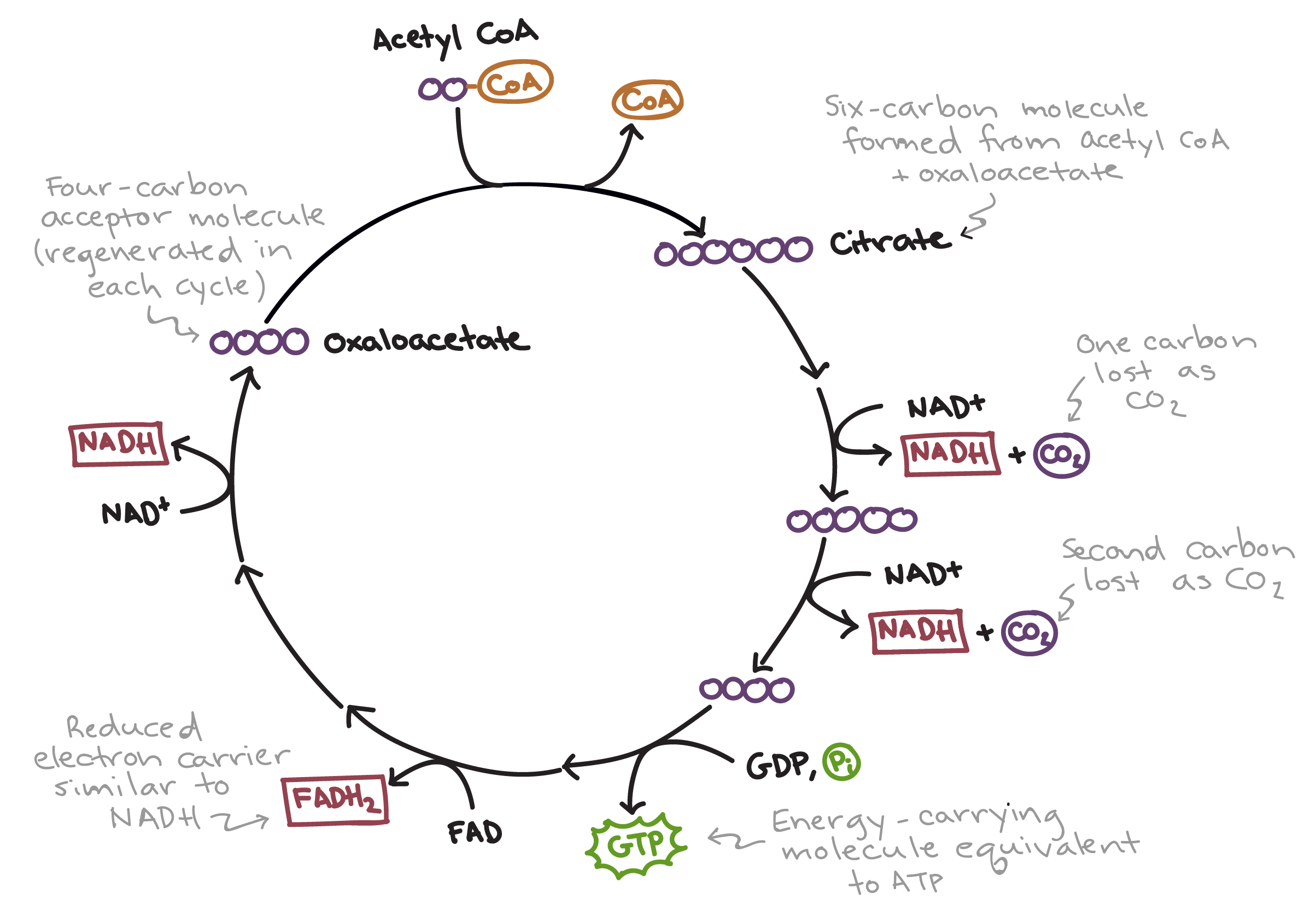
Citric acid cycle outputs per glucose molecule
4 molecules CO2
6 molecules NADH
2 molecules FADH2
2 molecules ATP (or GTP)
After the citric acid cycle comes the ___
ETC (Electron Transport Chain)
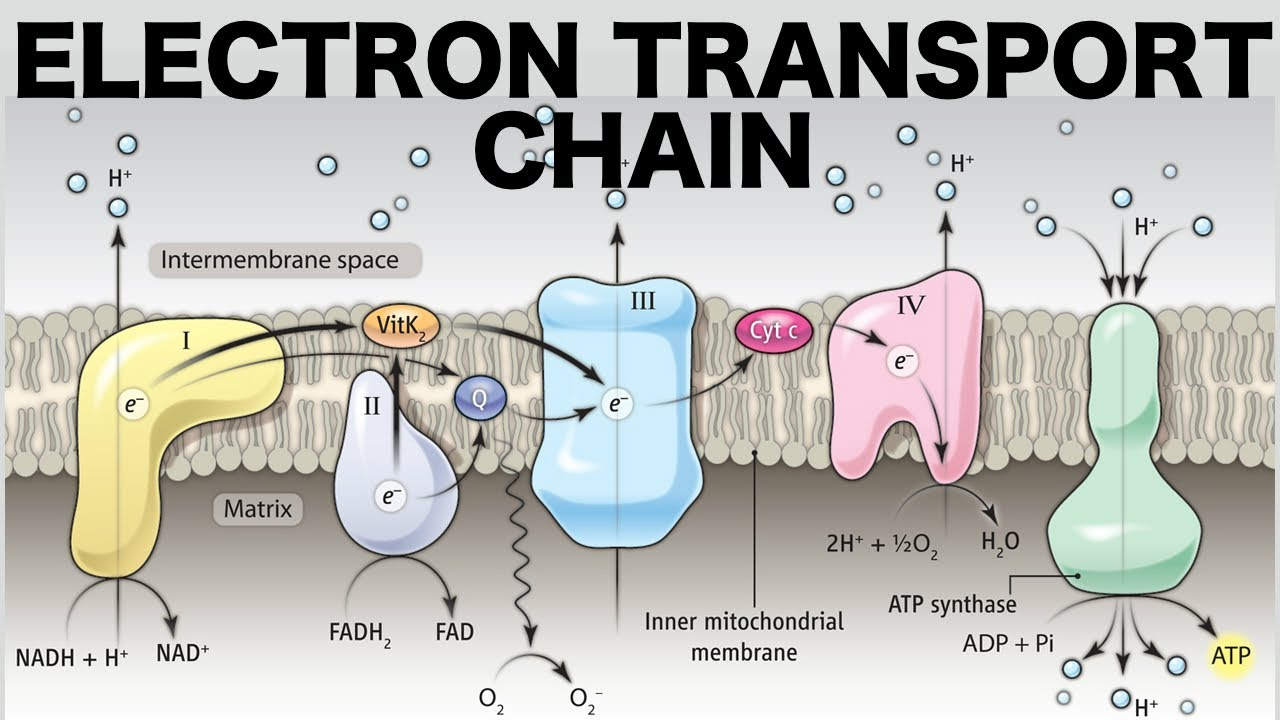
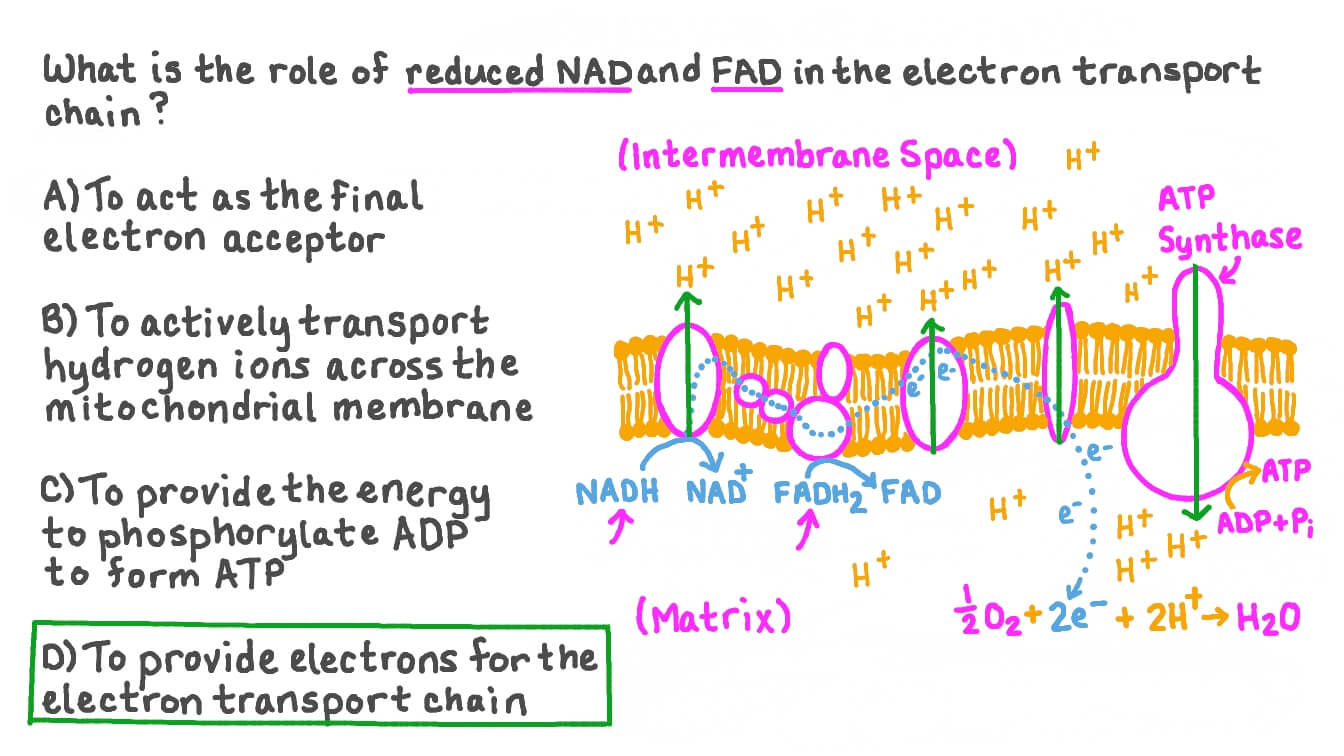
What happens in the electron transport chain?
NADH delivers electrons to complex I and is oxidized, NAD+ comes out
FADH2 delivers electrons to complex II and is oxidized, FAD comes out
O2 accepts these electrons becomes H2O.
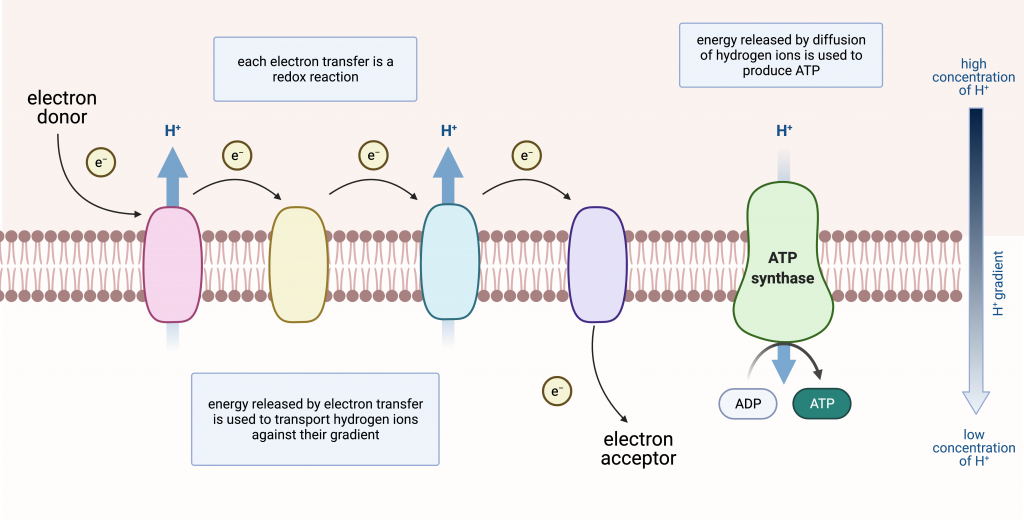
What happens to the energy from electrons flowing through the ETC?
It is stored as potential energy in the proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
If complex I of the ETC is inhibited, what would be the effect on the mitochondria?
Complex I would be in a reduced state because there would be an accumulation of e-
Complex IV would be in an oxidized state because it is waiting for electrons to flow through but “lost” them.
The concentration of NAD+ in the cell would decrease because NADH can’t be reduced.
The concentration of ATP in the cell would decrease because there are less H+ ions.
The concentration of lactic acid in the cell would increase the anaerobic pathway would kick in as a backup, performing fermentation.
The rate of glycolysis in the cell would increase because the anaerobic pathway would kick in as a backup.
The concentration of molecular oxygen in the cell would increase because it wouldn’t be made into H2O anymore.
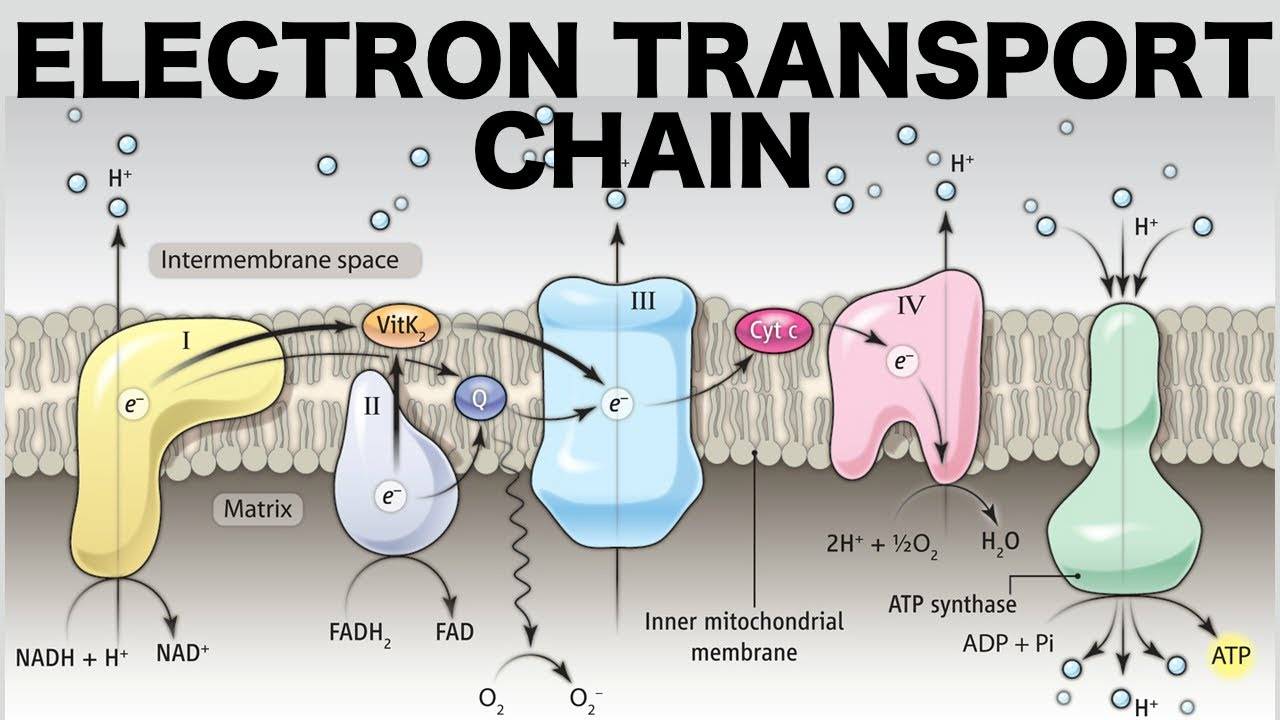
After the ETC comes ___________.
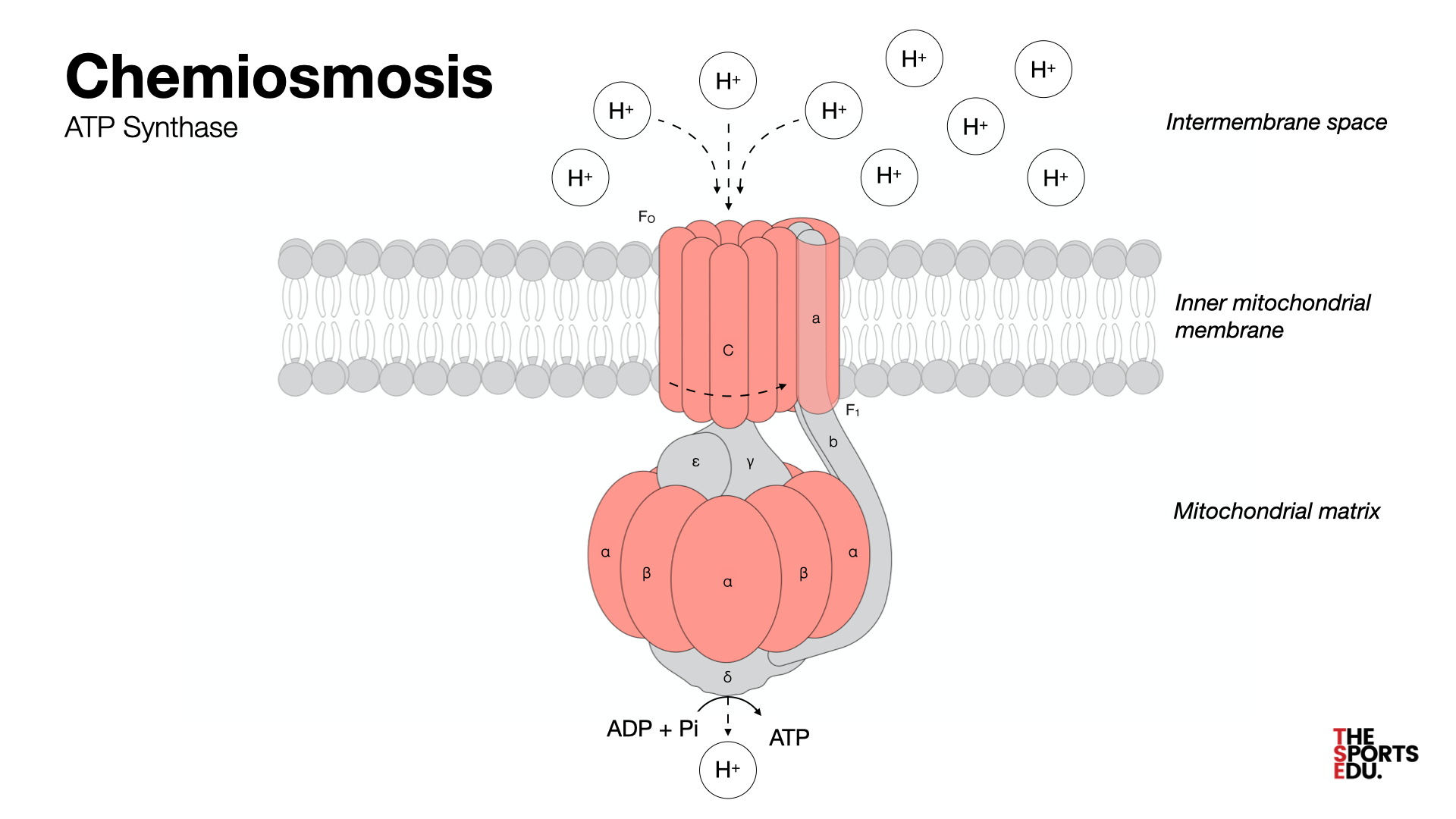
Chemiosmosis
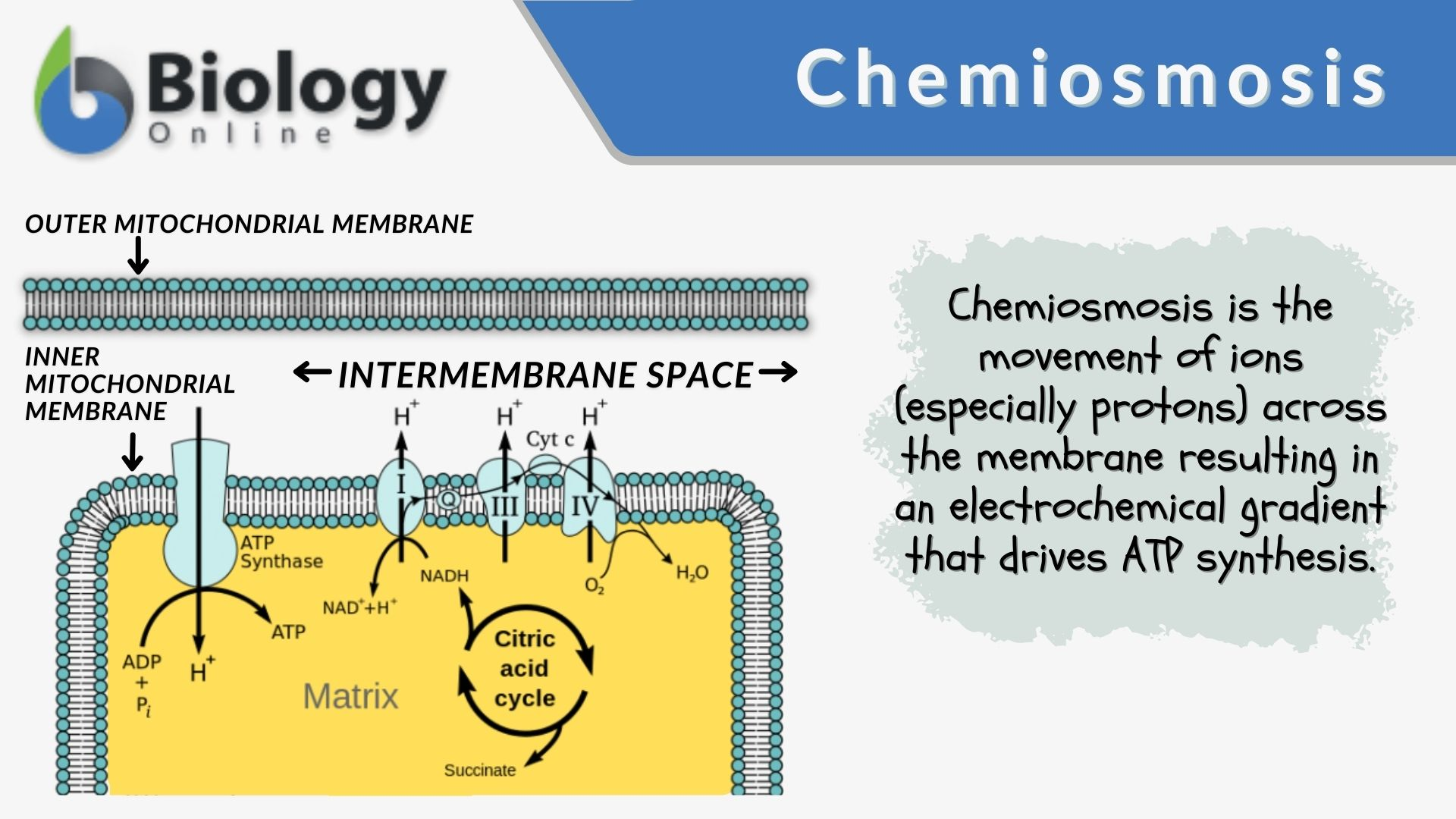
During chemiosis, there is a ______-______ ______ and an H+ gradient forms in the inter membrane space.
proton-motive force
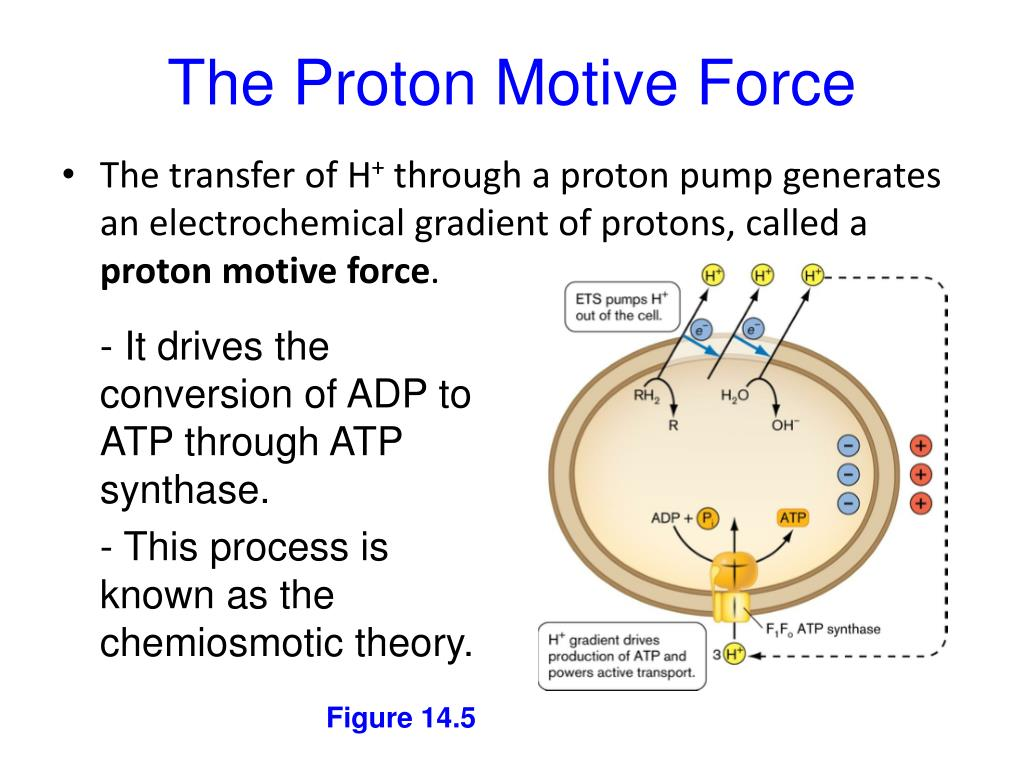
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
The production of ATP using the process of chemiosmosis in the presence of oxygen (the electron acceptor).
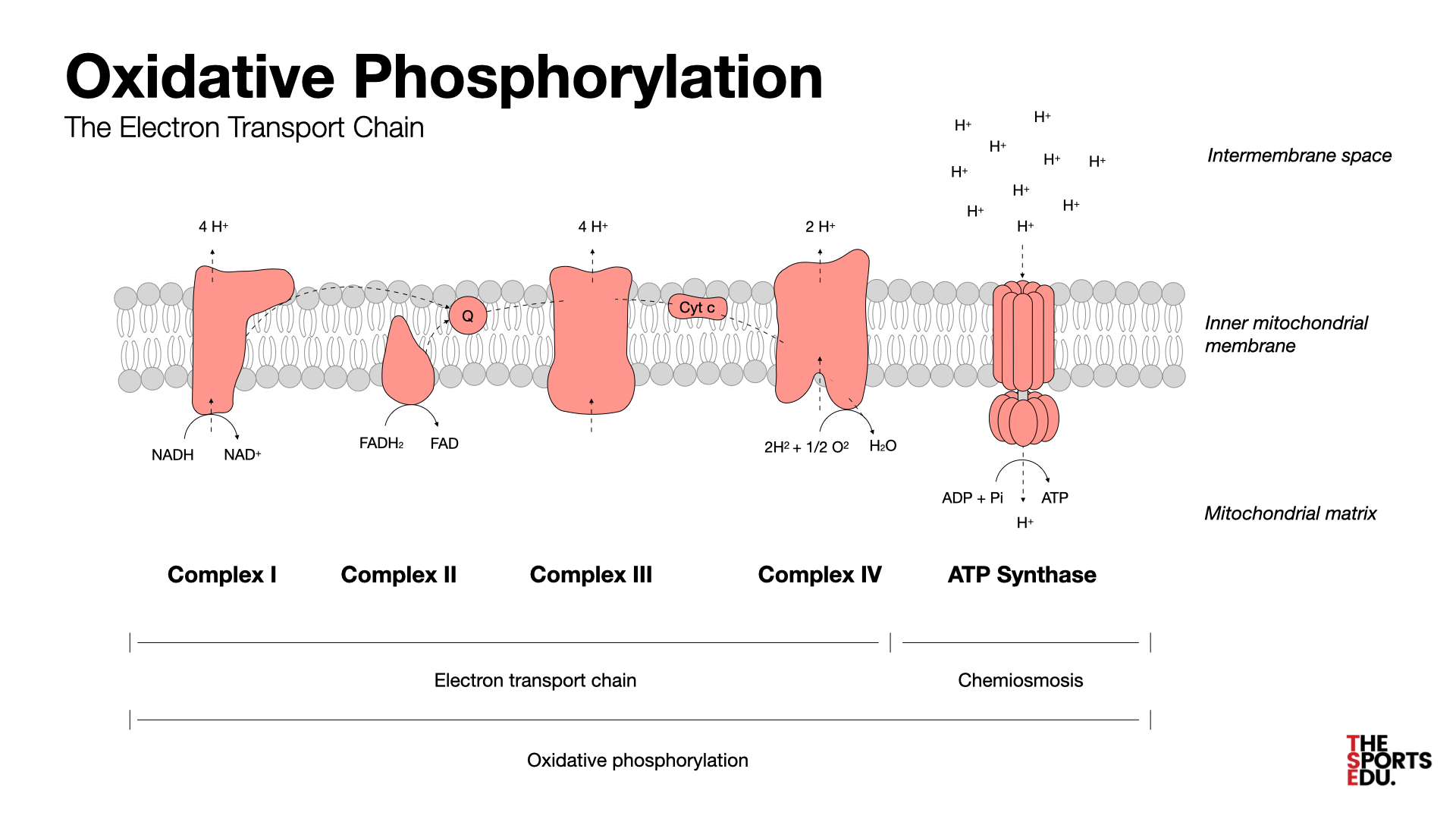
What role do NADH and FADH2 play in oxidative phosphorylation?
They reduce complexes of the ETC by providing electrons.
Where does chemiosmosis take place?
In the mitochondrial matrix in the ATP synthase.
After chemiosmosis, approximately how many ATP molecules were produced in total?
Approximately 29
What are enzymes?
Proteins (mostly) that catalyze chemical reactions.
Are enzymes used up during reactions?
No!
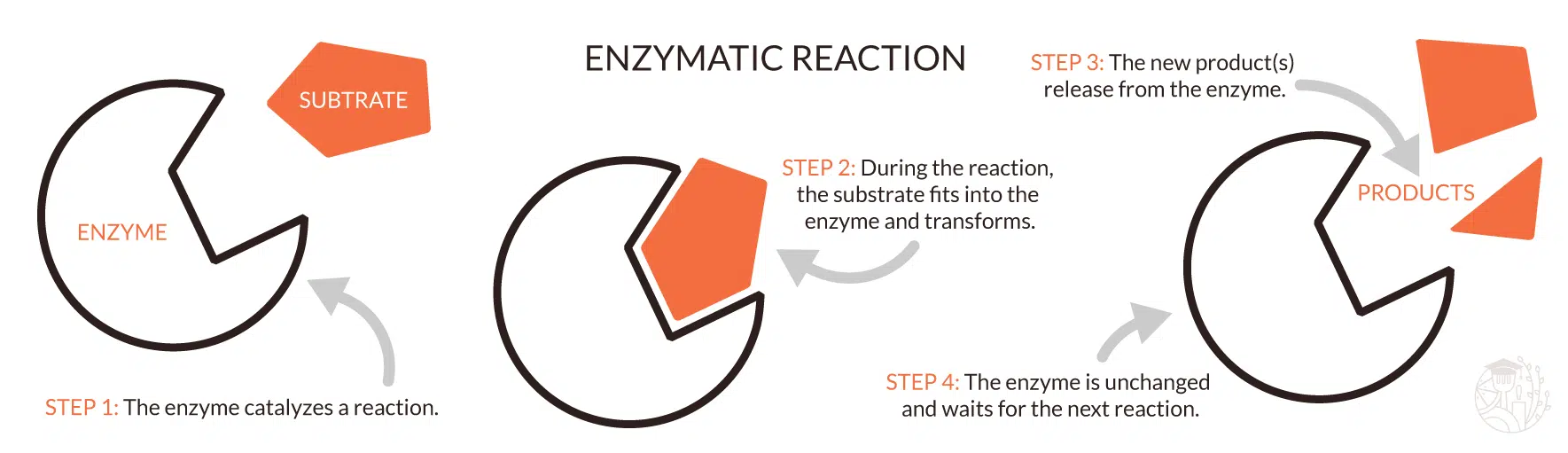
True or False: Enzymes can only break apart molecules.
False. They can also bind them together.
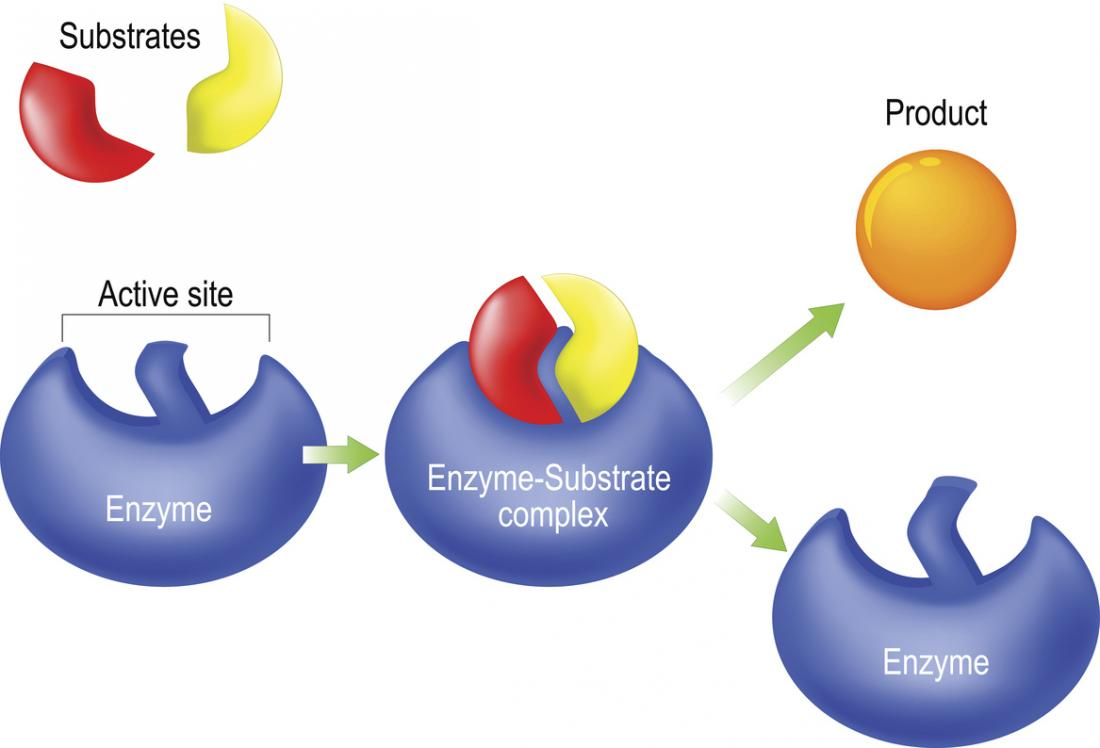
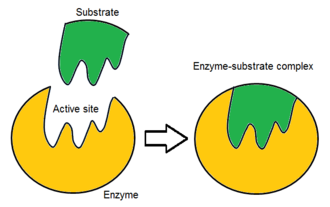
What is a substrate?
A molecule that is acted upon by an enzyme
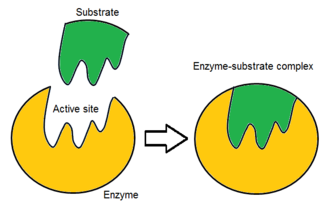
What is an active site?
Where the substrate(s) bind and react.
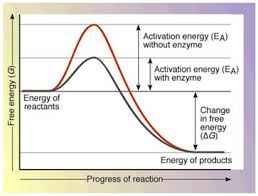
Do enzymes lower or raise the activation energy required for a reaction?
lower
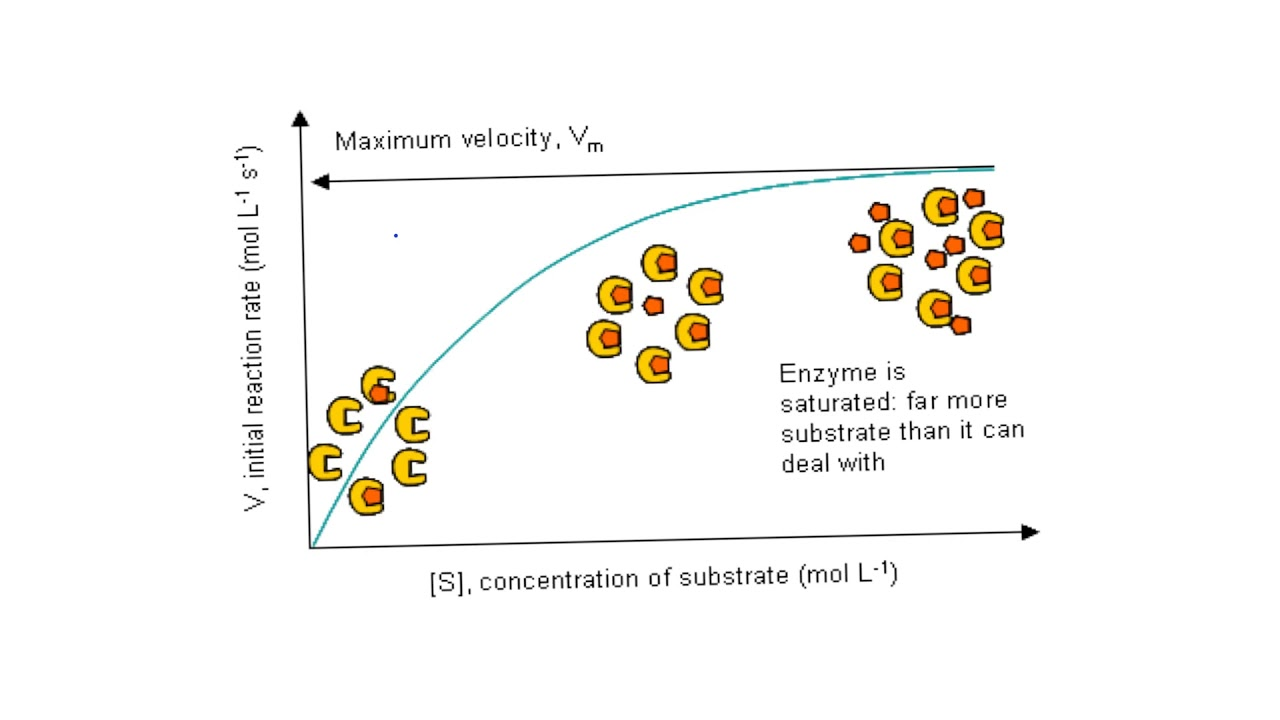
What does it mean when an enzyme is saturated?
The active sites on the enzymes are all filled.
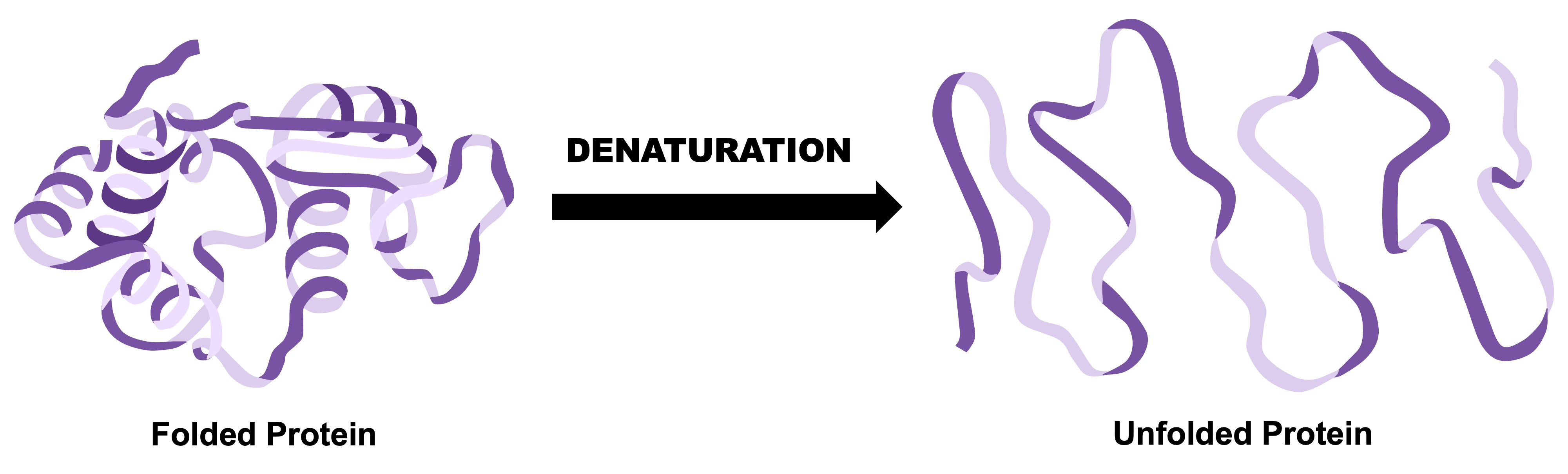
Typically, what happens to an enzyme at high temperatures or acidity?
It denaturates (unfolds).
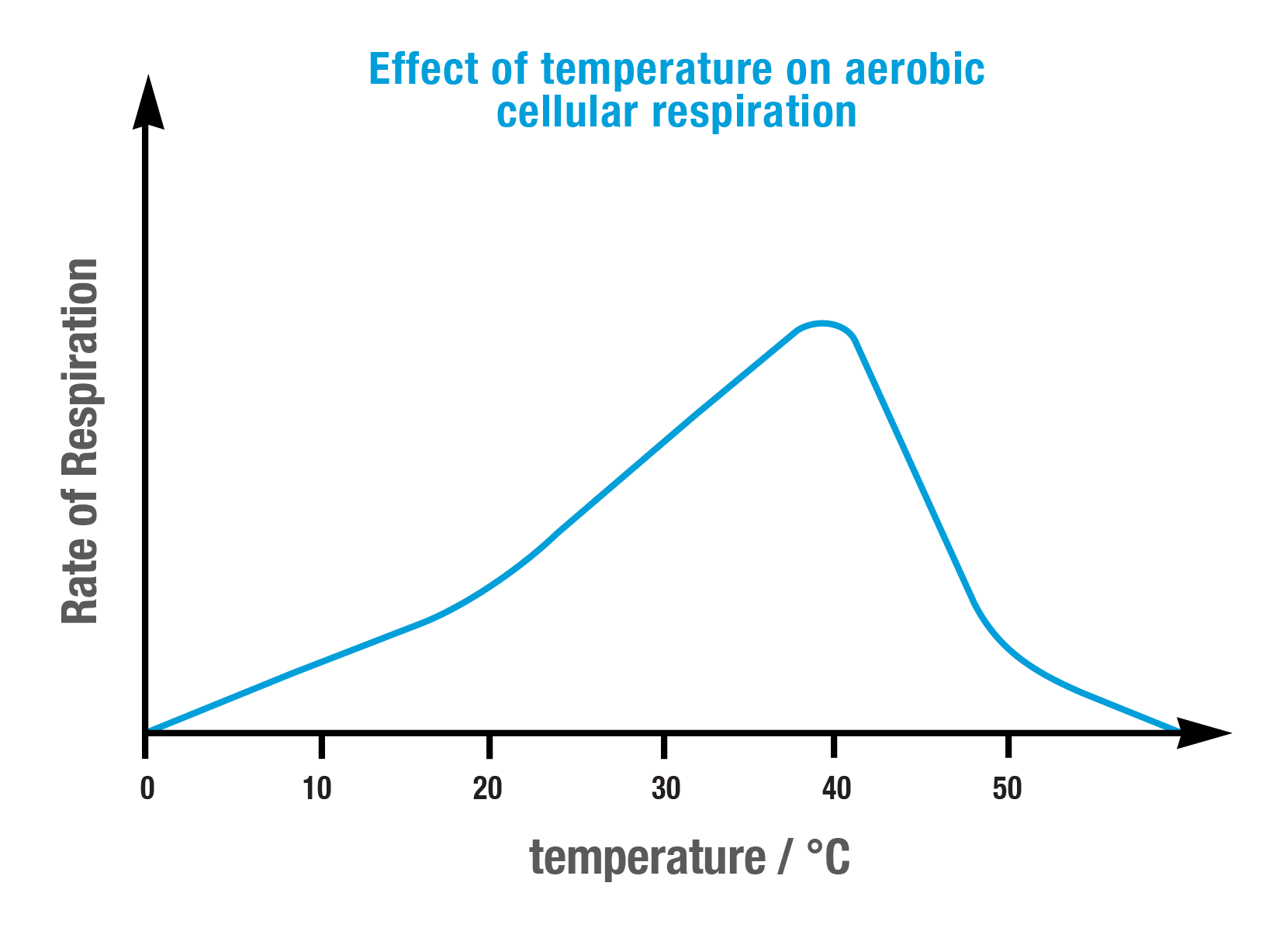
What is the ideal temperature for cellular respiration to occur?
37 degrees Celsius
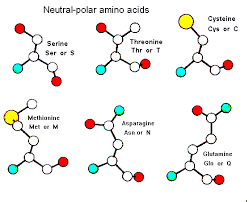
The R group on serine contains a carbon and a hydroxyl group (CH2-OH). Serine belongs to which class of amino acids?
Polar