Fixation Part 1
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
defined as the killing, penetration, and hardening of tissues.
FIXATION
First and most critical step in tissue processing
FIXATION
Preserve the morphologic and chemical integrity of the cell in a life-like manner as possible
FIXATION
EFFECTS OF FIXATIVES
● Hardens soft tissues in preparation for further tissue processing
● Render cells resistant to damage caused by chemicals used in further processing
● Inhibit decomposition caused by bacteria and fungi
● Minimize the risk of occupational infection
● Act as mordant for certain stains, thus promoting or hastening staining, or inhibit certain dyes
● Reduce the risk of infections during handling and actual processing of tissues
CHARACTERISTICS OF A GOOD FIXATIVE
● Cheap
● Stable
● Safe
● Quick
● Inhibits bacterial decomposition
● Produce minimum shrinkage
● Rapid and even penetration
● Hardens the tissue
● Makes cellular contents resistant to further processing
● Permit staining
True or False?
No single fixative has all the good characteristics. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages.
True.
FACTORS AFFECTING FIXATION
Fixative of Choice
Time
Tissue-to-Fixative Ratio
Penetration Rate
Thickness of Specimen
Tissue Components
pH
Temperature
Osmolality
Agitation, Vacuum
What is the Fixative of Choice?
10% Neutral Buffered Formalin
■ Morphologic criteria for dx have been established based on Formalin-Fixed Paraffin Embedded Specimen (FFPES)
This means that it must be performed as soon as possible; 20-30 mins after blood supply is cut off
Time
Ideal Tissue-to-Fixative Ratio
1:10 or 1:20 (tissue to fixative ratio)
Penetration Rate of Formalin?
Formalin: 1mm/hr (but slows down as it goes deeper into the tissue)
The Larger the specimen → ?
Longer fixation time, more fixative
Ideal thickness of spx for Light Microscopy
Microscopy: 2cm2 x 0.4cm
Ideal thickness of spx for Electron Microscopy
1-2mm2
Tissue Components that have longer fixation time
■ Fibrous Tissue
■ Mucus → wash with NSS
■ Fat → cut into thin slices → fixed longer
■ Blood → flushed out with saline
Tissue Components that have shorter Fixation time
■ Small of loosely textured tissues
Optimal pH for fixation?
6 to 8 pH (Use buffers)
True or False?
For Electron Microscopy: pH should match physiologic pH
True.
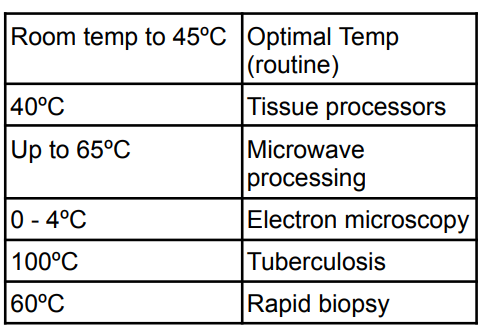
Higher temp in fixation → ?
faster fixation rate and autolysis
True or False?
○ Hypertonicity → cell swelling
○ Isotonicity and Hypotonicity → cell shrinkage
False.
○ Hypertonicity → cell shrinkage
○ Isotonicity and Hypotonicity → cell swelling
in Osmolality, one must maintain tissues at slightly hypertonic solution which is how many Milliosmoles?
400-450 mOsm
This factor Hastens fixation
Agitation, Vacuum
2 General Types of Fixatives
Based on Composition
Based on Action
2 Types of Fixatives based on Composition
Simple
Compound
3 Types of Fixatives based on Action
Microanatomical
Cytological
Histochemical
Types of Cytological Fixatives
Nuclear
Cytoplasmic
Fixative made of only one component
Simple Fixatives
Fixative consists of two or more components of fixatives
Compound Fixatives
General study of tissues w/o structure alteration
Microanatomical Fixatives
● pH ≤ 4-6
● Glacial acetic acid has affinity to nuclear chromatin
Nuclear Fixatives
● pH > 4-6
● HAc destroys mitochondria and Golgi bodies
Cytoplasmic Fixatives
Preserves chemical constituents of cells and tissues
Histochemical Fixatives